
































TLW's Cityscope™ (World City Historyscope) |
By T.L. Winslow (TLW), the Historyscoper™ |
© Copyright by T.L. Winslow. All Rights Reserved. |
Original Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2017. Last Update: Mar. 19, 2023. |









Westerners are not only known as history ignoramuses, but double dumbass history ignoramuses when it comes to the history of World Cities. Since I'm the one-and-only Historyscoper (tm), let me quickly bring you up to speed before you dive into my Master Historyscope.
Studying world cities is a sneaky back door way to study world history. Don't try it :)


About 7,500 B.C.E. the city of Catal Huyuk (Çatal Hüyük) (Çatalhöyük), the first known city (Neolithic farming village where babes don't wear tops?) is founded in SC Turkey 80 mi. SW of the ancient Konya Lake on the Konya Plain (N of the Taurus Mts.) (until -5700); discovered in 1961 by James "Jimmie" Mellaart (1925-2012) of the U. of London; the houses adjoin each other, rooms have built-in benches, white clay plaster is used, and people live on the roofs; the Seated Woman of Catal Huyuk Sculpture depicts a goddess cradling newborn leopard cubs; the dead are beheaded and set out to be eaten by vultures (excarnated), then the bones stored under beds?; the original city (Catal East) is abandoned in the early Neolithic age after a mini-Ice Age begins (-6200), then after several hundred years in the later Neolithic and Copper age a new one (Catal West) is built to the west, which lasts 1.5K years?
About 6,300 B.C.E. the city of Damascus on the E foothills of the Anti-Lebanon Mts. is settled (modern-day pop. 1.7M); in 661-750 C.E. it becomes the capital of the Sunni Muslim Umayyad Caliphate.
About 4,400 B.C.E. the city of Susa is founded in the lower Zagros Mts. of Persia between the Karkheh and Dez Rivers about 160 mi. E of the Tigris River, named after the god Inshushinak, ruled by the Proto-Elamite, Elamite, First Persian, Seleucid, and Parthian Empires; it is abandoned in 1218 C.E.; the modern-day town of Shush has a pop. of 65K.




About 3,600 B.C.E. (-5000 to -4000?) the Ubaidian people found the civilization of Sumer (Ki-engir) (Shumerum) in Mesopotamia along the Lower Euphrates River in modern-day S Iraq (ends -1900), becoming the first civilization in the region, complete with writing ca. -3200; the chief cities are Eridu (Eridug) ("Sum. "mighty place) (home of Enki) (oldest city on Earth?), Adab (modern-day Bismya), Isin, Kish Island (in the Persian Gulf), Kullab, Lagash, Larsa, Nippur (on the Euphrates River), and Ur (at the mouth of the Euphrates River), which becomes a city-state ca. -2600; they worship the triad of Baal (Bel) (Sum. "lord") (AKA Beelzebub), Anu (An) ((Sum. "sky", "heaven") (king of the gods, spirits, demons, and constellations), and Enki (Ea) (Sum. "lord of the Earth") (lord of water and intellect, associated with the Square of Pegasus S band of constellations), depicted with the head of a man on the body of a fish, dwelling in the nether sea of Apsu; also the Moon good Sin (Nanna) (son of Enlil and Ninlil), his son Shamash (Utu), god of the Sun and justice, and Anu's descendants the Anunnaki (Anunaki) (Ananaki) (Anunna) (they are really aliens from outer space who created humans and domestic animals via genetic engineering?); the four elements of heaven, earth, air, and water were created by the utterance of the divine word, and man was fashioned of clay, and created to serve the gods with food, drink, and shelter so that they can live in leisure; they leave hundreds of thousands of cuneiform script clay tablets incl. "The Epic of Gilgamesh", some with cylinder seals (signatures).

About 3,150 B.C.E. King Narmer (Catfish) (AKA Menes) of the Thinite Confederacy becomes the first king to unite Upper and Lower Egypt, becoming the first to use the title of pharaoh ("great house"), founding the Egyptian First Dynasty (ends -2909), and the Early Dynastic Period (ends -2686), with capital at Thinis (This) (Tjenu) (near Abydos?); he goes on to build the city of Memphis at the apex of the Nile Delta in Lower Egypt, and improves and enlarges the site by constructing a dam to divert the Nile River, beginning the basin system of agriculture in the Nile Valley; Memphis becomes the center of worship of Ptah, the god of creation; the city of Sais on the upper W side of the Nile Delta is an important cult center; all the pharaohs of this dynasty have retainers sacrified and buried near their tombs, along with animals in Abydos (Abdju); in succeeding dynasties the humans are replaced by ushabtis (figurines); the earliest depiction of a sailboat (made of bundled papyrus reeds) dates to this dynasty - catfish beats scorpion?
About 3,000 B.C.E. the Phoenician-Canaanite city of Beirut ("be'erot" = wells) (named after Beroe, daughter of Adonis and Aphrodite?)
W of the Beirut River in modern-day Lebanon is settled (modern-day pop. 361K/2.2M), going on to be controlled by Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Arabs, Crusaders, and Ottomans.
About 3,000 B.C.E. the city of Konya is first settled, going on to be controlled by the Hittites around 1,500 B.CE.., followed by the Sea Peoples around 1,200 B.C.E., and the Phrygians around 800 B.C.E., who call it Iconium, "the last city of Phrygia" (Xenophon); in 690 B.C.E. it is taken by the Cimmerians, and is absorbed into the Persian Empire until Macedonian king Alexander the Great captures it in 333 B.C.E., after which Seleucus I Nicator and the kings of Pergamon rule it until its last king Attalus III gives it to the Romans, who incorporate it into the Roman Empire under Emperor Claudius, who renames it Claudiconium; in 1084 C.E. the Seljuks conquer it, making it the capital of the Seljuk sultanate of Rum in 1097-1243.
About 3,000 B.C.E. the licentious Baal, Ashtoreth, and Car (Moon godess) worshiping Semitic Phoenicians (Phenicians) (Kena'ani or Canaanites = "merchants") (Gr. "phoinix" = red-purple) settle the E Mediterranean coast, a long narrow (5 to 15. mi.) strip of land from the Orontes River or Eleutherus River in the N to Mt. Carmel in the S, bounded on the E by the Lebanon Mts.; they worship the Moon because it rules the tides, and they want to rule the seas?; the city-states of Arvad (Arwad) (Rouade), Gubal (Djebeil) (Byblos), Marathus, Ecdippa, Acco (Akko) (Acre), Simyra (Sumra) (Tell Kazel), Dor (Dora) (southernmost), Zarephath (Sarafind) (Sarepta), Tripolis (Tripoli), Berytus (Beirut) and Sidon (Saida) (25 mi. S of Beirut) (first mentioned in the 15th cent. B.C.E. Tell el Amarna Letters), and Tyre (Sur) (Zor) ("rock") (from a double rock off the coast) ("daughter of Sidon") (50 mi. S of Beirut) are founded - white sidewall tire below the root?
About 3,000 B.C.E. the city of Rhagae (Rhages) (Rages) (Rai) (called Europus by the Greeks) is founded by the Medes 5 mi. SE of modern-day Tehran in N Iran, becoming the capital of the Median Empire and going on to become one of the great cities of antiquity along with Nineveh and Ecbatana.
About 2,800 B.C.E. the Uruk (Erech) Dynasty way S of Kish based in the city of Ur ("Aur" = light) is founded by Meskiaggasher after Etana dies, ruling from the Mediterranean to the Zagros Mts., and becoming the rival of Kish; Meskiaggasher's son Enmerkar attacks neighboring Aratta (NE of Mesopotamia) to capture its art treasures, taking along his eight sons; youngest son Lugalbanda is left behind in the remote mountains and falls ill, and receives help from the Anzu bird, who helps him reuinite with his father, going on to become king; the army of Aratta keeps them at bay for more than a year because their god is punishing them; the whole Epic Cycle of Enmerkar and Lugalbanda is described in cuneiform tablets.
About 2,600 B.C.E. the pop. in the Indus Valley and Sarasvati River regions begins to mushroom due to farming (ends -2000), building two large cities by -2500 at Harappa on the Indus River S of Lahore in W Punjab, Pakistan, and Mohenjo-Daro near Larkana in S Sindh, Pakistan, with public bldgs. and sanitation, leaving the sculptures Dancing Girl and Priest-King; discovered in the 1920s.
About 2,600 B.C.E. the Canaanite city of Jericho ("reah" = fragrant) ("Yareah" = Moon) is founded on the W bank of the Jordan River (modern-day pop. 20K), becoming known for its extensive walls with rectangular towers, and extensive cemetery with vertical shaft-tombs and underground burial chambers, with the nickname "City of Palms"; about 1550 B.C.E. it is abandoned; according to the Bible (Joshua Ch. 6), the Battle of Jericho sees the Israelite army of Gen. Joshua blow down the walls with trumpets; it is excavated in 1868, 1907-9, 1930-6, 1952-8, 1997-2000, and 2009, revealing eyeliner and scarabs from Egypt - no evidence of any trumpets?


About 2,500 B.C.E. the Ebla ("white rock") civilization (built over limestone bedrock to take advantage of natural springs) flourishes in N Syria, with a pop. of 200K, incl. 20K in the town of Ebla, with a library of 1.8K+ clay cuneiform Ebla Tablets, discovered in 1974-5 C.E. by Italian archeologist Paolo Matthiae (1940-); the tablets refer to the town of Ha-lam, identified with Aleppo (Halab) (modern-day pop. 1.8M), known for it white marble.
About 2,400 B.C.E. the city of Carchemish (Karkemish) in N Syria is first mentioned, going on to be ruled by the Mitanni, Hittite, and Neo-Assyrian Empires, and become the location of an important battle in 605 B.C.E. between the Babylonians and Egyptians (Jer. 46:2).
About 2,400 B.C.E. the city of Kirkuk in modern-day Iraq near the Khasa River 150 mi. N of Baghdad (modern-day pop. 850K) is mentioned in cuneiform records, becoming part of the Akkadian Empire of Sargon of Akkad in 2335 B.C.E.; about 2150 B.C.E. it becomes Arraphka, capital of the kingdom of Gutium, which is destroyed by the Neo-Sumerian Empire about 2090 B.C.E., going on to become part of the Old Assyrian Empire in 2025 B.C.E. to 1750 B.C.E., and Assyria in 1725 B.C.E.
About 2,300 B.C.E. the city of Babylon on the Euphrates River in Mesopotamia is founded, becoming a major city under Amorite king Hammurabi in the 18th cent. B.C.E., becoming the largest city on Earth from -1770 to -1670 and from -612 to -320, becoming the first city to reach 200K pop.; it is abandoned about 1000 C.E.


About 2,300 B.C.E. (2,800 B.C.E.?) the Millennium Fever mother city of Jerusalem (Salem) ("peace") (Arabic "al-Quds" = the holy) (Yiddish "Yerushalayem" = teaching of peace) (modern-day pop. 883K/1.25M) 35 mi. from the E shore of the Mediterranean Sea is founded by the Canaanite (Hittite?) (Hurrian?) (Amorite?) Jebusites (Shem and Eber, ancestors of Abraham?) on the ridge of the Judean Mts. between the N edge of the Dead Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, on the hard limestone Ophel (Heb. "fortified hill") above the Gihon (Heb. "to gush forth") Spring, which emerges from the Kidron (Heb. "dark, mourn") Valley to the E; the city was originally surrounded by thick green forests of almond, olive, and pine trees.

About 2,140 B.C.E. Intef the Elder (the Great), son of Iku becomes king #1 of the Egyptian Eleventh (11th) Dynasty (ends -1991), which eventually refunifies Egypt; its capital is in the city of Thebes on the bend of the Nile in Upper Egypt; it consists of the cities of Karnak in the N half (right or E bank), and Luxor in the S half (right or E bank); the last pyramid tombs are built in this period; the Valley of the Kings is later situated on the left or W bank.
Shut up old ladies, I'm coming for you at 3 o'clock? About 2,000 B.C.E. the Hittites are pushed (by the Hurrians?) W through Cappadocia ("beautiful horses") in the Anti-Taurus Mts. in SE Anatolia (Asia Minor), where they build underground cities (later enlarged by Christians), becoming integrated into the Land of Hatti and absorbing the Hattians into their kingdom, based in Hattusa(s) (Pteria?) near modern-day Boghazkoy (Boghaz Keui) 200 km. W of Ankara, and worshiping the Sun goddess Arinna along with every other god they can get their hands on?; ethnicity doesn't matter as long as you learn to speak Hittite and dump the berries in?; women warriors are welcome; they join the new Old Assyrian Trade Network (ends -1750); the Bible mentions the Hittim, descended from Canaan's son Heth (Gen. 10:15), which are really the Khatti in Syria, kin to the Phoenicians and Amorites?


About 2,000 B.C.E. the first Palace of Knossos (Cnossus) is built by the Minoans in Knossos, Crete, becoming the oldest city in Europe, beginning the First Palace Period (ends -1700), which also produces the palaces of Malia (on the N coast) and Phaistos (Phaestus) in SC Crete; the Labyrinth of Knossos is allegedly built by Daedalus for King Minos of Crete; discovered in 1878 by Minos Kalokairinos, and excavated in 1900-35 by Sir Arthur John Evans (1851-1941).

About 2,000 B.C.E. the city of Troy in Asia Minor where the Aegean Sea meets the Hellespont is founded by Greeks, who go on to create nine levels of habitation (Early Bronze Age to Roman times) for later archeologists to dig through; excavated in 1871-2 by German archeologist Heinrich Schliemann (1822-90).
The wild blonde dangly Greeks set up shop in the Me-Scene? About 1,900 B.C.E. the city of Mycenae on the plain of Argolis in Greece (in NE Peloponnesus S of the Isthmus of Corinth, 55 mi. SW of Athens) is founded, going on to develop the Mycenaean Civlization (ends -1125), which strongly borrows from the Minoan civilization of nearby Crete by -1600, and by -1400 becomes supreme in the Aegean area, incl. the cities of Tiryns near Mycenae, Orchomenos, and Thebes in Boeotia (birthplace of Hercules), Athens in Attica (modern-day pop. 660K/3M), home of the Acropolis (Gr. "top of the city"), and Pylos in Messenia in SW Greece; the king is called the wanax, and the army cmdr. is called the lawagetas; the basileus and a priest class bring up the rear; Mycenaean supremacy continues until the fall of Troy (-1200), after which the Dorians (Gr. "conquerors") from the N destroy it and the survivors flee; the Gla Fortress protects the region; the architecture is based on huge rough-hewn "Cyclopean" stones, thought to be made by the Cyclops; the strongly-fortified palaces contain megara (large rectangular halls), and the warlike Mycenaeans are the first to use the safety pin; Homer later preserves the age in his "Iliad" and "Odyssey", and claims that Mycenae is the home of King Agamemnon; Heinrich Schliemann (1822-90) excavates Mycenae in 1868 C.E.
About 1,800 B.C.E. the Assyrian city of Nineveh ("exceedingly great city") (founded -3000?) on the E bank of the Tigris River in Upper Mesopotamia near modern-day Mosul, Iraq is first mentioned as an important center for worship of the Mesopotamian goddess Ishtar; too bad, it lies on a fault line and suffers a number of earthquakes; in 612 B.C.E. after becoming the largest city in the world 50 years earlier, it is abandoned after a civil war and sacked by a coalition of former subject peoples incl. the Babylonians, Medes, Chaldeans, Persians, Scythians, and Cimmerians.
About 1,500 B.C.E. the town of Miletus is founded by Mycenaeans from Crete as a stronghold on the W coast of Asia Minor near the mouth of the Maeander River (until -1100), becoming the first of 10 Greek colonies on the Sea of Marmara or Black Sea, and the first city with a modern grid plan (by Hippodmos), which is copied by the Romans; the Temple of Didyma, devoted to Apollo the Didymaion (twin) is built, becoming the 2nd most famous oracle in the Hellenistic world after Delphi.
In 1,400 B.C.E. after the Hittite raids against Egypt give the Phoenician city-states the chance to revolt, the Phoenician city of Tyre becomes a flourishing center of maritime trade; Phoenician traders reach as far W as West Africa and Britain?





On June 11, 1184 B.C.E. the impregnable walled city of Troy (Ilium) in Asia Minor near the Hellespont (Dardanelles) is destroyed by fire in the last year of the 10-year Trojan War after the first special ops commando raid in history, made possible by the original 1-trick pony Trojan Horse (the original Kobayashi Maru Maneuver?), which Trojan priest Laocoon (Laocoön) tries in vain to expose by tapping with a spear, causing the goddess Athena to send sea serpents to strangle him and his sons Agesander, Athenodoros, and Polyclitus, which the Trojans interpret as proof that the horse is sacred; the doings in the 10th year are later celebrated by Homer's Iliad; the U.S. 10th Special Forces Group (Green Berets) later features a silver Trojan Horse on their badge; a band of survivors led by Aeneas (son of Aphrodite or Venus and Anchises, a cousin of King Priam) escape and search for a new home, ending up in Rome (Latium), where King Latinus (son of Inachus, son of Dardanus, son of Saturn) allows them to stay, and reneges on a promise to King Turnus of the Rutuli, marrying his daughter Lavinia to Aeneas instead, causing Turnus to turn-turn-turn declare war on Aeneas, which he loses, getting killed, after which Aeneas' Troy-born son (via 1st wife Creusa, who dies before reaching Latium) Ascanius founds Alba Longa SE of Rome on Lake Albanus in the Alban Hills (ends 7th cent. B.C.E.), and becomes its first king, establishing the line that leads to Romulus and Remus; Homer's Odyssey contains one of the earliest historical references to Crete, claiming that it's populated by Achaeans, Cydonians, Pelasgians, Dorians, and Eteocretans (pre-Hellenic natives), and has 90 independent cities, with #1 being Cnossos; shortly after the Trojan War ends, the city of Tenea is founded 15 km SE of Corinth and 20 km NE of Mycenae by Trojan POWs with the permission of Agamemnon.

In 1,122 B.C.E. Zhou Wu Wang (d. -1119) (-1046 to -1043?) and his father Wen revolt against Chou-hsin, ending the Shang Dynasty and founding the Xi (Northern) Zhou (Chou) Dynasty (China's 3rd dynasty) (ends -256), awarding Korea to Chinese prince-scholar Qi Zi (Ji-zi) (Ki Tse), who founds the independent Kingdom of Choson (Chosen) (Joseon) (ends -194/-108). about this time the city of Peiping (later Peking and Beijing) ("northern capital") (modern-day pop. 18.6M/24.9M) in NE China 90 mi. NE of the Gulf of Pohai and 12 mi. W of the Pei River is founded as a frontier outpost; it is walled about 1045 B.C.E.
In 1,104 B.C.E. the island city of Cadiz (Cádiz) in SW Spain (modern-day pop. 123K) is founded as Gadir (Agadir) ("wall", "compound") by the Phoenicians, becoming the oldest W Euro city to survive to modern times, trading with the city-state of Tartessos near the mouth of the Guadalquivir River until it is flooded out; a temple to the Phoenician god Melqart is built on the S end, later conflated by the Greeks and Romans with Hercules as Hercules Gaditanus and the Tyrian Hercules, becoming known for its oracle and wealth; later the Greeks claim that the city was founded by Hercules after his Tenth Labor, the slaying of 3-headed Geryon; the Herculeum (Temple of Melqart) is still standing in the 1st cent. C.E., giving rise to the myth of the Pillars of Hercules?; same as the Biblical city of Tarshish?
In the early 11th cent. B.C.E. (-1028 to -1043) the city of Rangoon ("end of strife") (Yangon) in Lower Burma (modern-day pop. 5.3M/7.6M) is founded as Dagon by the Mon as a small fishing village centered around the Shwedagon Pagoda; in 1755 King Alaungpaya conquers it and renames it Yangon; in 1852 the British conquer Lower Burma and move the capital there from Moulmein, renaming it Rangoon and going on to capture Upper Burma in 1885, turning Rangoon into "the garden city of the East"; in 1948 Burma wins independence from Britain, and in 1989 the name is changed to Yangon; on Mar. 27, 2006 the capital is moved to the new city of Naypyidaw (Naypyitaw) (Nay Pyi Taw) ("abode of kings") in C Myanmar (modern-day pop. 925K).
About 1000 B.C.E. the city of Pavlopetri (Gr. "Paul's Stone", "Paul's and Peter's") S of the Peloponnese, first inhabited about 2,800 B.C.E. is consumed by the sea after the first of three earthquakes.
About 1000 B.C.E. the Semitic seafaring Phoenicians invent the Phoenician (Proto-Canaanite) Alphabet, attributing it to the legendary figure Cadmus (Kadmos) ("from the east") from Tyre, who founds the acropolis-citadel of Cadmea AKA Thebes (modern-day pop. 22K), known for the story of the Spartoi ("sown men"), and the Seven-Gated Wall built by Amphion, along with the story of Laius, who butt-fucks Chrysippus, making Thebes famous for pederasty, and the story of Oedipus and the Seven Against Thebes, along with the exploits of Heracles (Hercules) (son of Zeus and Alcmene), the immolation of Semele, and the advent of Dionysus.
In the 10th cent. B.C.E. a Greek colony in Smyrna in SW Asia Minor *modern-day Izmir, pop. 2.8M/4.1M) is founded, later claiming to be the birthplace of Homer; it is located at the terminus of the inland trade routes from the Hermus (Gediz) and Meander valleys from the east.
In the 9th cent. B.C.E. the city of Samarkand ("samar" + "kand" = rock + fort) in modern-day Uzbekistan (modern-day pop. 500K) is founded.
In the 9th cent. B.C.E. Lanuvium (Lanivium) 20 mi. SE of Rome is founded by Diomedes of Troy; in this cent. Rome is really founded?
In 814 B.C.E. the Phoenician settlement in Kition (Latarkia) moves out and founds the new independent town of Qart Hadasht (New City), later called Carchedon by the Greeks, and Carthage (Carthago) by the Latins; it eventually has a 20-mi.-circumference wall built around it; according to myth it was founded (in -814?) by Queen Dido (Elissa) (Alissar), daughter of King Belus of Tyre, whose brother and co-monarch Pygmalion murdered her hubby-uncle Sychaeus (Acerbas), high priest of Melqart in the temple, hiding it from her for a long time and causing her to flee there; after being offered as much land by native chief Iarbas as a bull's hide can cover, she cuts one into thin strips and pastes them together to maximize the area; after committing suicide to avoid marrying him, a nig, er, African prince, and/or hooking up with lily-white Troy survivor Aeneas and doing it because he jilted her, she is visited by Aeneas in the underworld, who sees her reunited with Sychaeus, and won't look at him; Carthage is destroyed by the Romans in 146 B.C.E.; they engaged in child sacrifice?
By the 8th cent. B.C.E. the Greek city-state (polis) system emerges, with the main cities being Athens (in Attica) (modern-day pop. 664K/3.0M) (which imports grain from the Black Sea region), Chalcis (Chalkis) (in Euboea) (known for its metalwork), Eretria (in Euboea) (known for its coinage), Miletus (on the W coast of Asia Minor) and Samos (an island in the E Aegean Sea) (both known for furniture and textiles), Ancient Corinth (in Corinthus 48 mi. W of Athens), and landlocked Sicyon (Sikyon) (Sekyon) in Argolis W of Corinth, between the Nemean and Sythas Rivers, and home of Lake Lerna and the multi-headed hydra?); commerce is mainly by sea; the Delphic Oracle is rededicated, becoming the #1 site for the worship of Apollo; the Greek Archaic Period in Art begins (ends -510) (-750 to -480?), switching from abstract geometric patterns to a more naturalistic style; the men marry at age 30 and women at 15-16, becoming breed mares and slaves, living in seclusion, except for Spartan women, who receive physical training with men (you can have it if you kick my ass first?); Mt. Pentelicus and Mt. Paros produce marble, Mt. Laurium and Mt. Pangaeus produce silver, Mt. Pangaeus and Thasos produce gold; Laconia produces iron, and Cyprus produces copper, causing the Romans to name copper after it (cyprium) - you own it, we tote it?
By the 8th cent. B.C.E. Soccaly, er, Sicily (shaped like a deflated soccer ball and placed at the toe of the boot of Italy for easy kicking?) is inhabited by Sicans, Sicels (Sikels), Elymi (Elymians), as well as Phoenician colonists; S Italy is inhabited by Sicels, Messapii (SE heel) and the Dacian Apuli (Salentini) (Sallentini) (Calabri), who found the fortress city of Apulon (Apulum) near modern-day Alba Iulia, Romania - it's theirs to lose?
In the 8th cent. B.C.E. the city of Sparta (originally Lacedaemon, after King Lacedamon of Laconia, son of Zeus and nymph Taygete, husband of Sparta, daughter of Eurotas, and father of Amyclas, Eurydice, and Asine), capital city of Laconia in the SE Peloponnesus (Land of Pelops) (Gr. "dark face") (Morea) ("mulberry") in the Eurotas River Valley is founded by Dorians via the merger of 4-5 Laconian villages; the Spartan Dyarchy allegedly begins when King Aristodemus dies, leaving twin sons Eurysthenes and Procles, who found the two jointly-reigning royal dynasties of the Agiads (ends -215) and the Eurypontids (ends -192?); the original inhabitants are enslaved, becoming the Helots.
In the 8th cent. B.C.E. the Greek kingdom of Lydia (ends -547) in W Asia Minor between the Ionian cities of the W coast and Phrygia, with capital at Sardis (Sardes) on the N base of Mt. Timolus on the gold-bearing Pactolus River 2.5 mi. S of the Hermus River (5 mi. NE of Smyrna) is founded by Lydus (son of Atys), worshiping the gods Santas, Baki (Bacchus) et al.
In the 8th cent. B.C.E. the colony of Sexi (Sexi Firmum Iulium) is founded by the Phoenicians in the Costa Tropical of SE Spain (in the Malaca district near modern-day Almunecar) in a colonization race with the Greeks; during the age of the Roman Empire it incl. the suburbs of Villa Fatuus Maximus, Socordia, and er, Paenis- I'm too sexi for my toga?
In the 8th cent. B.C.E. the city of Todi (Tutere) (Tuder) ("border") in C Italy on a tall double-crested hill overlooking the E bank of the Tiber River is founded by the Umbri at the Etruscan frontier.
In 784 B.C.E. Menua dies, and his son Argishti (Argishtis) I (-827 to -764) becomes king #6 of Urartu (until -764), building the Fortress of Erebuni (Arin Berd) ("Fortress of Blood") on the N border on the W Ararat plain as his capital (finished -782), growing into modern-day Yerevan, Armenia (modern-day pop. 1M).
In 757 B.C.E. the coastal town of Cumae in Campagnia in S Italy (NW of Neapolis or Naples) is founded in Oscan territory by Greek colonists from Pithecusae, Chalcis and Eretria, and Cyme, becoming the first colony in Magna Graecia (Greater Greece); Lake Avernus nearby is the fabled entrance to the underworld, and near the shore are caves which become the seat of an acropolis which is the seat of the ageless Cumaean Sibyl (Gr. "prophetess"), who gives out golden boughs to those wishing to go to the underworld; "The Sibyl, with frenzied mouth uttering things not to be laughed at, unadorned and unperfumed, yet reaches to a thousand years with her voice by aid of the god" (Heraclitus).
In 756 B.C.E. the city of Trabezon (originally Trapezous) (Gr. "trapeza" = table") (modern-day Trabzon, pop. 768K) on the SE shore of the Black Sea is founded by Milesian traders as a trading colony along with Sinope (modern-day Sinop, pop. 36K) on the C shore, Cyzicus on the SW shore, and Abydos in the Hellespont, trading with the Greek Mossynoeci (Gr. "Mossynoikoi" = dwellers in wooden towers); in 258 C.E. the Goths sack and rebuild Trabezon.


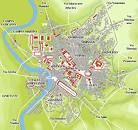

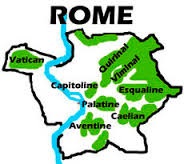
Every people has a founding myth, a frame for their identity, which lets them restart the calendar with year one, and contains within itself the seeds of their ultimate destruction? The Romans claim to come from Long and White, and must be bragging? On Apr. 21, 753 B.C.E. the city of Rome (Roma) (modern-day pop. 2.9M/4.36M), is traditionally founded by twins (fraternal or identical?) Romulus (-771 to -717) and Remus (-771 to -753), born in nearby Alba Longa (12 mi. to the SE in the Alban Hills on the W crater rim of Lake Albano) of the god Mars and mother Rhea (Rea) Silvia (Ilia), a vestal virgin who is the daughter of King Numitor of Alba Longa, and a descendant of Aeneas (Gr. "he who is praised") (the very title later adopted by Muhammad?), leader of the Trojans and son of Anchises and Venus, who escapes from Troy and wanders for years before coming to Latium, and whose son Ascanius or Iulus is the founder and 1st king of Alba Longa, keeper of the Palladium or image of Pallas Athena stolen from Troy by Ulysses and Diomedes, which ends up in the Roman temple of Vesta; at birth they are kidnapped by order of the jealous Numitor, then deposited on the banks of the Tiber (in a basket like Moses?) to die, but rescued and raised by she-wolf Lupa (sucking wolf tit and drinking wolf milk, to make them into predators?), who suckles them in the Lupercal(e) (Lat. "she-wolf"), a cave on the SW foot of the Palatine Hill (uncovered in 2007 C.E.); they are later raised by shepherd Faustulus and his wife Acca Larentia (Larentina), until they grow up and return to kill the king, then recruit Latin colonists from Alba Longa for their new digs, originally called Saturnia after Saturn, "father of the gods", then Rome, City of the Seven Hills, home of the united cities of Latium (named after the god Lateinos (Chaldean "to lie hidden"), their version of Saturn, offspring of the Sun, represented with a ring or halo around his head, and known as the Hidden God, the God of Mystery, with both Saturn and Lateinos having the Number of the Beast 666, hence the pope also?), on the left (E) bank of the Tiber River 17 mi. inland from the Tyrrhenian Sea near malarial swamps where the river makes two sharp bends in a reverse S-shape; the Seven Hills of Rome (Poor Queer, er, Queen Vicky Eats Crow At Christmas?) are: Palatine Hill (C) (centermost) (140 ft. above the Tiber E of the S bend) (home of the aristocrats) (first to be settled); Quirinal Hill (NE) (named after Sabine war god Quirinus); Viminal Hill (NE) (finger-shaped land pointing toward C Rome between the Quirinal Hill to the NE and Esquiline Hall to the SE); (located between the Forum and the Campus Martius); Esquiline Hill (E) (N part of the Oppian Hill); Capitoline Hill (named after the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus) (original name: Mons Saturnius) (W) (; Aventine Hill (SW) (home of the plebs or plebeians, consisting of two small peaks and a gully); Caelian Hill (SE); later the Pincian Hill (NE) (N of the Quirinal) and the Janiculum Hill (W) (on the right bank of the Tiber opposite the N bend) are inhabited with overflow pop.; the area between the Capitoline and Palatine Hills is a marshy valley, which is drained by -500 and turned into a marketplace (the Forum); actually, the legendary founding is moose hockey, and communities existed on the Palatine, Capitoline and Esquiline Hills by -1000, and the city was really formed by the Etruscans after they conquered Latium around -600 and forced the independent communities under their yoke?; the Circus Maximus is later built between the Palatine and Aventine Hills (with the cheap seats on the Aventine side?); the Tarpeian Rock is on the S side of the Capitoline Hill, and used for executing traitors by throwing them off the top; the Campus Martius (Lat. "Mars Field") parade ground W of the Quirinal and Capitoline Hills, E of the N bend of the Tiber River is the first expansion area for overflow pop. before bridges are built across the Tiber and a fort built on the Janiculum Hill for future expansion; the city is open for 1K years until the Aurelian Wall is built c. 270 C.E., encircling all the hills and connecting with the Tiber to the N and S; Romans begin counting time up from this date, or rather, counting down from this date, after Romulus and Remus attempt to conjure a vision from the gods, and Romulus conjures twelve fowls circling over the hills, while Remus is short-changed, only conjures six and fouls out, and the augur Vettius proclaims that Romulus will be king, after which Romulus marks the square sacred boundary of Rome on the Palatine Hill above the E shore of the River Tiber, known as the Roma Quadrata with the sacred bronze plow on the feast day (Parilia or Palilia) (Apr. 21) of the herd-flock god Pales (the hermaphrodite ass-god of ancient Caanan, for whom Palestine is named, as well as the Palatine Hill), then orders a ditch dug and sacred wall (pomerium) built around it, which jealous Remus jumps over, causing Romulus to kill him for sacrilege, becoming Rome's first king (which is why it's called Rome instead of Reme?); Vettius claims that the vision means that the fowls are eagles, indicating that Rome will kick everybody's butt and the city will thrive for twelve cents., but then the eagles will turn into vultures, indicating that Rome will fall and the inhabitants will become bird food (proof that paganism is true, or just a self-fulfilling prophecy, or a deep psychological meaning about killing one's good side so the bad side can run riot, becoming fatal in the end?) (if only he'd said twelve millennia?); when Jesus Christ is later portrayed as entering Jerusalem triumphantly on an ass, you figure it out?; speaking of bad side, Romulus rules for 37 years, waging war with the Sabines under Titus Tatius (d. -748) of Cures (on the left bank of the Tiber River 26 mi. from Rome), starting it by arranging for the mass-kidnapping and Rape of the Sabine Women in C Italy, which causes Tatius to capture Rome with help from Tarpeia, daughter of the cmdr. of the Roman citadel, who opens the gates on the promise that she will receive what the Sabines have on their left arms, whch gurns out to be their shields, after which they throw her from the Tarpeian Rock (which becomes the mode of execution of all capital punishment), after which the Sabine women (led by Romulus' wife Hersilia, daughter of Tatius) convince Tatius and Romulus to reconcile and rule Rome jointly, with the combined community called the Quirites; in modern times the historicity of Romulus is questioned, with German historian Theodor Mommsen uttering the soundbyte in 1854: "The founding of a city in the strict sense, such as the legend assumes, is of course to be reckoned altogether out of the question: Rome was not built in a day"; in 1900 Giacomo Boni (1859-1925) claims to find the tomb of Romulus; in 2007 U. of Rome prof. Count Andrea Carandini (1937-) uncovers evidence of the sacred wall plus Romulus' palace?; the next six kings are Numa Pompilius (-715 to -676), Tullus Hostilius (-673 to -641), Ancus Marcius (-640 to -617), Lucius Tarquinius Priscus (-616 to -578), Servius Tullius (-578 to -534), and Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (-534 to -510), the last three being Etruscans; the govt. is based on three tribes, the Ramnes, Tities and Luceres (Latins, Sabines and Etruscans?), with the pop. split into the patricians (large landowners) and the plebs (plebeians) (clines) (Lat. "fillers") (small landowners); only the patricians constitute the populus (citizens), and have political rights and can serve in the army; the govt. is run by elective king and a small royal council of elders (senate), plus a 100-man assembly of elders (patres) composed of 10 curiae (assemblies) for each tribe, each elder serving for for life and having to be a patrician; the rex leads the army in person, and is preceded by lictors (officers), who bear the fasces, the symbols of power and punishment, and is the supreme judge in all civil and criminal suits; Roman citizenship requires membership in a gens (Lat. "to beget"), i.e., a clan traceable through the male line to a common free ancestor without any slaves in the middle; at first only patricians can use the "gentile" name as the middle of their three names, but later the plebes are permitted; Romulus later worships in the small temple of Jupiter Feretrius ("Jupiter who carries away the spoils of war") on the Capitoline Hill; the crude round hut called the House of Romulus on the central Palatine Hill stands for the next eight cents. - when do they install the mechanical bulls?
The beginnings of the Sicilian Mafia as a gaggle of pirates? In 750 B.C.E. the city of Zancle ("sickle-city"), (modern-day Messina) on the NE end of Sicily on the W shore of the Strait of Messina (Mamertinum Fretum) (Fretum Siculum) is founded by pirates from Cumae.
In 734 B.C.E. the city-state of Syracuse in SE Sicily is founded by the Bacchiadae clan oligarchy of the Corinthian (Anatolian) Greeks led by Archias, going on to become the #1 city in Sicily; they found another colony on the island of Korkyra (Corcyra) (modern-day Corfu) in NW Greece.
In 729 B.C.E. Leontini (Lentini) (Leontinoi) in SE Sicily is founded as a Naxian colony by Thucles; other Naxians under Evarchus found Catana.
In 728 B.C.E. the Megarians give up trying to colonize Trotilon and Thapsos in Sicily, and instead colonize Megara Hyblaea, 14 mi. N of Syracuse.
In 717 B.C.E. Sargon II begins his royal residence of Dur-Sharrukin (modern-day Khorsabad), a planned city in modern-day N Iraq (9 mi. NE of Mosul) (finished in -704), which becomes capital #4 of Assyria; excavated in 1843 by Paul-Emile (Paul-Émile) Botta (1802-70) of France; the entrance to Sargon II's palace throne room features a pair of reliefs of a 16-ft.-high Winged Bull that combines features of a man (head), eagle (wings) and lion (tail); it ends up in the Oriental Inst. of the U. of Chicago.
In 710 B.C.E. the capital city of Ecbatana (Hamadan) is founded by Deioces, first king of the Medes in the mountainous E fringes of Babylonia between the Elburz and Zagros Mts.
In 710 B.C.E. Chalcis colonizes Torone in the Chalcidice in NE Greece, and goes on to found 30 small colonies on the peninsula.
In 708 B.C.E. the city of Croton (Crotona) in S Italy in the sole of Italy's boot on the E coast of Bruttium (Calabria) on the Gulf of Taranto is founded as a Greek colony, becoming the leading city of Magna Graecia, known for its healthy climate and great athletes, later building the Temple of Hera Lacinia, which becomes the main religious shrine of Magna Graecia; by modern times it is reduced to a single column.
In 706 B.C.E. the city of Tarentum (Taras) (modern-day Taranto in S Italy) is founded by Parthenian (children of Greek women and Spartan men) colonists led by Phalanthus, becoming Sparta's only colony?

In 705 B.C.E. Sargon II is KIA in battle, and his son Sennacherib (Sin-Ahhe-Eriba) (d. -681) (Akkadian "the Moon god") becomes king of Assyria, dissociating himself from what he thinks of as his loser father, and abandoning his father's newly-built capital in order to move to Nineveh, which he turns into a magnificent city, with a royal palace of 80 rooms built on a foundation of 160M bricks, and featuring bas-relief stone panels of winged lions or bulls with a man's head, along with grisly scenes of cruel treatments of POWs incl. impalings.
In 689 B.C.E. the city of Gela (Gr. "laugh") (named after the Gela River) in S Sicily is founded by Greek colonists from Rhodes and Crete, becoming the home of Greek tragedian Aeschylus.
In 688 B.C.E. the city of Hyperesia in Achaea defends itself from an army from Sicyon by tying burning torches to the horns of goats, spooking them into retreating, causing the town to be renamed Aigeira ("goat town").
In 685 B.C.E. Greeks from Megara colonize Chalcedon on the Asiatic side of the Hellespont, and it becomes known as "the city of the blind" because the settlers missed the better site of Byzantium on the European shore.
In 680 B.C.E. Argishti II dies, and his son Rusa II (d. -645) becomes king #10 of Urartu, building the new capital of Rusahinili (Toprakkale), along with a great water canal from the Hrazdan River (Ildaruni) to Quarlini.
In 677 B.C.E. vassal king Abdi-Milkuti ('Abdmilkot) revolts from Sennacherib, who captures Sidon, beheads him, and razes the city to the ground, then deports its pop., turning it into an Assyrian province; a new city is built opposite it called Ir-Asaraddon (Kar-Esarhaddon); the island city of Tyre becomes the main city of what's left of Phoenicia, with Baal I as king, stripped of his mainland territories and forced to pay tribute.

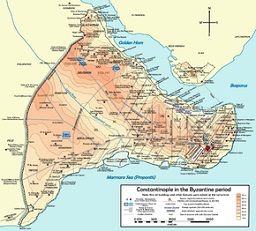
In 657 B.C.E. Greeks from Megara found a colony at Byzantium (Byzantion) (modern-day pop. 14.1M/14.7M) on the site of the 11th-13th cent. B.C.E. Thracian fishing village of Lygos between the Golden Horn (an arm of the Bosphorus) and Sea of Marmara (Propontis) on the European side of the Bosphorus across from Chalcedon on the Asiatic side, and name it after Megarian leader Byzas (Byzantas) of Thrace, who was told by the oracle of Apollo at Delphi to settle there, marrying Lygos gov. Barbysios' daughter Phidalia; located on the Silk Road, and the only sea route between the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, it dominates trade; on May 11, 330 C.E. Roman emperor Constantine dedicates it as his new capital, becoming the largest and wealthiest city in Europe from about 450-1204, when it is captured by the Latin Crusaders, then reconquered by the Greek Byzantines in 1261, holding on against yearly Ottoman Muslim attacks until it falls on May 29, 1453, becoming Istanbul ("to the city"), after which the Ottoman Empire rules it until its dissolution on Oct. 29, 1923, when it becomes part of the Turkish Repub.
In 651 B.C.E. the Sicilian Greek colony of Selinus is founded by Dorian Greek colonists from Megara Hyblaea; being the closest one to the Phoenician cities it sometimes switches sides in Greek-Phoenician disputes?
In the latter half of the 7th cent. B.C.E. the Greek city-colony of Paestum (Posidonia), 25 mi. SE of modern-day Salerno (50 mi. ESE of Naples) on the Gulf of Salerno is founded by colonists from Sybaris, and devoted to Poseidon, to whom they build a colossal Doric Temple of Poseidon, (Hera?) which survives to modern times as one of the most well-preserved ancient Greek temples.
Between 650 B.C.E. and 323 B.C., Greece has 1.2K separate city-states.
About 630 B.C.E. the town of Histria (Istros) (Gr. "By the Danube") on the Dobrudja Black Sea Coast at the mouth of the Danube River is founded, becoming the first Greek town in modern-day Romania, opening up trade with the interior.
In 627 B.C.E. the city of Epidamnos (Epidamnus) (Epidamnos) (modern-day Durazzo or Durres, pop. 201K) in Illyria on the Albanian coast opposite Bari and Brindisi across the Adriatic Sea is founded by Greek colonists from Corinth and Corcyra, becoming known for its natural rocky harbor surrounded by swamps and cliffs, making it very durable and secure from attack; the Romans seize it in the 4th cent. B.C.E. and change its name to Dyrrachium.
In 620 B.C.E. Greek colonies housing Greek soldiers are founded in Egypt around the trade center of Naucratis (Naukratis) (Gr. "the city that wields power") at the mouth of the Nile River, encouraged by Psamtik; the different Greek tribes who live there create the first nat. Greek identity? - ancient multiculturalism?
About 600 B.C.E. the Celtic Gauls, experiencing overpop. problems invade N Italy under their king Bellovesus with six excess tribes, the Bituriges, Arverner, Senonen, Haeduer, Ambarrer, Carnutes, and Aulerci, receiving help from the Greeks in Massilia (Marseille) to cross the Alps in the Tauriner area, then defeat the Etruscans under king Tarquinius Priscus at the Tessin River, and settle Insubria, founding the city of Mediolanum (modern-day Milan) (Lat. "middle of the plain") ("central town or sanctuary"?) ("half-wool", after a boar sow is lifted from the excavation of the city walls?) (modern-day pop. 1.3M), and becoming known as the Insubres, and the region as Insubria.
About 600 B.C. the city of Vercelli on the Sesia River between modern-day Milan and Turin in modern-day Piedmont, Italy (modern-day pop. 46K) is founded, becoming known for rice paddies; in 1228 the world's first publicly-funded univ. is founded there (closed in 1372).
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. the city of Delhi (modern-day pop. 16.8M/26.5M) in N India is founded, going on to become the capital of several kingdoms and empires and get captured, sacked, and rebuilt several times.
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. the 15th cent. B.C.E. city of Kabul (Kubha) on the Kabul River in modern-day Afghanistan (modern-day pop. 4.6M) is conquered by the Achaemenid Empire, becoming a center of learning of Zoroastrianism, followed by Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam (870 C.E.).
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. the city of Massalia (Massilia) (Marseille) on the Gulf of Lion on the Mediterranean (modern-day pop. 855K/1.5M) is founded by Ionian (Phocaean) Greek and Phoenician colonists, despite Carthage trying to prevent it; the first historic mention of the Celtic Gauls (Gaels) ("love people?") and their country of Galatia (Gael. "Gaeltachd" = "land of the Gaels") ("milk-giving"?), who get introduced to olives and grape wine, and take a litle too well to wine, not drinking it diluted like civilized people?; the Anatolia (Greeks) find it hard to colonize Italy, being confined to the W; they are discouraged by the Phoenicians from settling in S Spain and Corsica, but establish colonies in Egypt.
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. the city of Neapolis (New City) (modern-day Naples, pop. 975K/3.1M) is settled by Ionian Greeks from Cumae.
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. the city of Theline (modern-day Arles) in S France on the Rhone River is founded by the Greeks.
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. the seaport of Pozzuoli on the Bay of Naples is founded by Greek colonists.
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. the town of Constanta (Tomis) in Romania on the Black Sea Coast is founded, becoming the oldest to survive to modern times.
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. Corinth founds the colony of Potidaea in the N Aegean in order to trade with Macedonia.
In the 6th cent. B.C.E. the Mediterranean port city of Marmaris (originally Physkos or Lyscus) in a part of Caria belonging to Rhodes (modern-day Mugla Province, W Turkey on the Turkish Riviera), with a magnificent harbor and sacred grove to Leto; Herodotus claims that a castle existed there since 3,000 B.C.E.
In 582 B.C.E. Acragas (Akragas) (Agrigentum) (modern-day Girgenti) on Mt. Camicus in S Sicily is founded by Greeks from Gela, becoming the #2 city after Syracuse, building great temples in the Valley of the Temples.
In 515 B.C.E. the city of Benghazi (Bengasi) is founded on the N African coast (modern-day Libya) by citizens of Cyrenaica (modern-day pop. 650K).
About 500 B.C.E. the city of Khujand (Khodjent) in Tajikistan on the Syr Darya (Jaxartes) River at the mouth of the Fergana Valley near the borders of Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan (modern-day pop. 181K/931K) is founded, becoming the 2nd largest city in Tajikistan; in 1936-91 C.E. it is renamed Leninabad.
In the 5th cent. B.C.E. the city of Mtskheta 12 mi. N of modern-day Tbilisi at the confluence of the Aragvi and Mtkvari Rivers is founded, going on to become the capital of the Kingdom of Iberia (Kartli) in the 3rd cent. B.C.E., and the birthplace of Christianity in Georgia in 337 C.E., and HQ of the Georgian Orthodox Church.
In the 5th cent. B.C.E. after finding salt veins, the Celts settle the city of Salzburg (Ger. "Salt city") (modern-day pop. 150K) in Austria near the N foothills of the Alps, and found the city of Vienna (Vianiomina) (Vindobona) (Gael. "fair/bright settlement/bottomland") (named after the Celtic god Vindos?) on the Danube River (modern-day pop. 1.8M/2.6M); the earliest Celtic chariot burials in Britain begin about this time - Ahnuld's ancestors?
In 490 B.C.E. the city of Patna (Pataliputra) on the Ganges River in NE India (modern-day pop. 1.69M/2.0M) is founded by the king of Magadha, becoming the capital of the Magadh Empire under the Haryanka, Nanda, Mauryan, Shunga, Gupta, and Patna Empires, known as a center of learning, fine arts, and astronomers incl. Aryabhata, Vatsyayana, and Chanakya, reaching 400K pop. by 300 B.C.E.; it goes on to become a pilgrimage center for Buddhists, Hindus, Jains, and Sikhs; after the fall of the Gupta Empire, it declines until it is revived in the 17th cent. by the British as a center of internat. trade; after the partition of the Bengal presidency in 1912, it becomes the capital of Bihar and Orissa Province.
In 409 B.C.E. the city of Rhodes on the island of Rhodes, designed by Greek urban planner ("the Father of European Urban Planning") Hippodamus of Miletus (-498 to -408) is built, based on the Hippodamian (Grid) Plan, becoming its 4th major town after Camirus (Kamiros), Lindus (Lindos), and Ialysus (Isalyssos).
About 400 B.C.E. measles enters the human pop. that lives in big cities?
About 400 B.C.E. the Celtic (Alerci) Cenomani tribe of Gaul (modern-day Maine) under Elitovius crosses into the Po River Valley of Italy and drives out the Etruscans, founding a town on the later site of Cremona (ends -218), going on to part ways with other Celtic tribes in being friendly with the Romans; meanwhile the Celtic Boii tribe from Bohemia crosses the Great St. Bernard Pass and conquers the Etruscan town of Felsina, renaming it Bononia (modern-day Bologna, pop. 389K/1M), going on to intermarry with the Etruscans but stay Celtic.
About 400 B.C.E. the Celtic kingdom of Noricum is founded in modern-day Austria and Slovenia, bordered on the N by the Danube River, on the W by Raetia and Vindelicia, on the E and SE by Pannonia, and on the S by Italy, with capital at Virunum at the foot of Mt. Magdalensberg, becoming the S outpost of the Celts and launching point for attacks on Italy, becoming known for cattle breeding rather than agriculture because of their poor soil, and for supplying iron for Noric Steel, as well as Celtic nard (saliunca) for perfume.
In the 4th cent. B.C.E. Jews begin migrating to Rome and various Mediterranean towns, forming separate communities; by the next cent. large numbers live in Greece, esp. Rhodes and Thessaloniki (Salonica) (founded in -315 by Cassander of Macedon) (modern-day pop. 325K/1M) which becomes known as "the Mother of Israel".
About 340 B.C.E. the city of Tianjin (Tientsin) (Chin. "ford of Heaven") on the Bohai Gulf of the Yellow Sea on the N coast of China (modern-day pop. 12.7M/15.4M) is settled, becoming China's largest coastal city.

In Jan. 332 B.C.E. blonde-blue Macedonian king (since -336) Alexander III the Great (-356 to -323) sieges the well-protected island city of Tyre under its last king Azemilkos, and captures it in Aug. after a 7-mo. siege by building an enormous mole connecting it permanently with the mainland, during which time he goes underwater in a diving bell to observe divers removing underwater obstacles, and has his vessels equipped with chain cables so that they couldn't be cut adrift at night; he crucifies 2K POWs and sells 30K more into slavery; the Persian navy disintegrates, and Phoenician trade slackens as the Phoenicians lose their identity and are Grecianized; Alexander then obtains the submission of the provinces of Galilee, Samaria and Judah, and invades Egypt, and Persian satrap Mazaces surrenders without a fight, ending the 31st Egyptian Dynasty (begun -343); Alexander stay in Egypt for a year, visiting the Egyptian coast and ordering the Temple of Luxor restored to its ancient glory, then having an overwhelming desire to found a new city (according to Roman author Arrian), which becomes Alexandria (modern-day pop. 5M), then visits the Oracle of Amon-Ra at the Siwah Oasis in the Western Desert (barely making it and almost dying of thirst), where is proclaimed the son of god; there were settlements in the Alexandria area for several hundred years? On Apr. 7, 331 B.C.E. the city of Alexandria on the Cape Lochias peninsula, protected by the island of Pharos is founded by Alexander III the Great, with Cleomenes of Naucratis (d. -322) as gov. #1; a number of Jews settle there immediately - and begin churning out the New Testament?
Early in 329 B.C.E. Bessus tries to prevent Alexander the Great from crossing the Oxus (Amu Darya) River into Bactria, but fails, and his own men hand him over to Alexander, who mutilates him by cutting off his ears and nose, then has him brought back to the place where he killed his master and tried by a Persian court and crucified; Alexander then invades soggy Persian-held Sogdiana in C Asia SE of the super-salty (10%) Aral Sea between its filler-uppers the Oxus (Amu Darya) (S) and Jaxartes (Syr Darya) (N) Rivers, and conquers the Persians under Spitamenes (Spitamaneh) (-370 to -328) with difficulty, conquering the capital Samarkand (Maracanda) in modern-day Uzbekistan (modern-day pop. 500K) before invading Afghanistan and capturing Gandara (Kabul) 125 mi. E of the Khyber Pass (modern-day pop. 4.6M), causing the Afghanis to resist with guerrilla fighting, which Alexander meets with scorch-and-burn tactics; he then detours NE through the Hindu Kush ("Hindu killer"?) in the spring, and captures Arachosia in Mar.; meanwhile the pagan Kafirs in Kafiristan are formed by Greeks staying in the country, becoming an unconquerable region that is later used as the setting of Rudyard Kipling's 1888 story The Man Who Would Be King.
In the late 4th cent. B.C.E., (-150) the city of Trier (Triers) (Treves) (modern-day pop. 110K) in the lower Moselle River Valley in the W of the modern-state of Rhine-Palatinate near the modern-day Luxembourg border is founded by the Celtic Treveri tribe; it goes on to become one of the four capitals of the Roman Empire in the late 3rd and early 4th cents. C.E.
In 310 B.C.E. Agathocles of Syracuse lands at Cape Born and attacks Carthage, causing the siege of Syracuse to be lifted; Agathocles stays in Africa until -307, capturing the Berber town of Tunis (named after Phoenician goddess Tanith or Tanut) (modern-day pop. 1M/2.6M).
In 303 B.C.E. Seleucus I Nicator cedes NW India to Chandragupta (Sandrocottus), rebuilds the city of Osroe (Chosroes), and founds the city of Edessa (named after the ancient capital of Macedonia) in SE Turkey (NW Mesopotamia) near the Syrian border (modern-day Urfa, pop. 560K); in the 2nd cent. B.C.E. it is known as Antiochia on the Calirrhoe, becoming the capital of the Kingdom of Osroene from -132 to 242; in 639 it falls to the Muslims; in 1098-1144 it becomes the capital of the Crusader County of Odessa before falling to the Turkic Zengid Dynasty and being absorbed by the Ottoman Empire in 1517.
In 302 B.C.E. the Spartans under Cleonymus (Cleonimos) sail up the Po River, but are repelled by the Patavians (Veneti) from modern-day Padua (Patavium) on the Brenta River (modern-day pop. 214K) (oldest city in N Italy to survive to modern times) (which according to Virgil and Livy was founded in 1183 B.C.E. by Trojan prince Antenor); the Spartans try to take Tarentum, fail, then make an alliance with Tarentum against the Lucanians, causing Tarentum to lose faith with other Greek colonies.
About 300 B.C.E. the city of Ankara (Ancyra) ("anchor") (modern-day pop. 5.2M) is settled by Greeks from Pontus, becoming a trading center between ports on the Black Sea, Crimea, Assyria, Cyprus, Lebanon, Georgia, Armenia, and Persia; in 278 B.C.E. C Anatolia is occupied by the Celtic Galatians, who make Ankara the HQ of the Tectosages tribe, Pessinos (modern-day Balhisar) the HQ of the Trocmi tribe, and Tavium E of Ancyra as the HQ of the Tolstibogii tribe.
About 300 B.C.E. the city of Nicosia in N Cyprus (modern-day pop. 116K/323K) is rebuilt on the site of Ledra by Leucus, son of Ptolemy I Soter, and named Leucoton or Lefkotheon; in the 4th cent. C.E. Lefkosia (Kallenikesis) becomes the seat of bishop St. Tryphilius (Trifilios), a student of St. Spyridon; in 647 Salamis is destroyed by the Arabs, and in 965 Nicosia becomes the new capital of Cyprus; on Sept. 9, 1570 the Ottomans capture and sack it, causing Turks to immigrate to the N and Greeks to hide-out in the S; on July 5, 1878 Nicosia comes under British rule; in 1955-64 a Greek revolt attempts to oust the Turkish pop., causing Turkey to invade in 1974, causing Nicosia to become the only world capital shared by two powers.
About 300 B.C.E. the city of Toulouse (Tolosa) (modern-day pop. 479K/1.3M) on the Garonne River in S France 93 mi. from the Mediterranean Sea and 420 mi. from Paris is founded by the Celtic tribe of Tolosates or Volques (Volcae) Tectosages (Tectosagi); origin of the name Welsh?
In the 3rd cent. B.C.E. the city of Scupi (modern-day Skopje) (Gr. "skopein" = lookout") on the Vardar River in Macedonia on the N-S route between the Balkans and Athens (modern-day pop. 506K) is founded by the Celtic Dardanians (Dardani) ("oak people") of Paionia (Macedonia), who make it the capital of Dardania in the next cent.
In the 3rd cent. B.C.E. the Romans establish a settlement called Matrice on the banks of the Manzanares River in Spain, which later becomes Madrid (modern-day pop. 3.1M/6.5M).
About the 3rd cent. B.C.E. the principality of Chach (Chachkand) on the Chirchik River near the foothills of the West Tian Shan Mts. builds a square citadel 5 mi. S of the Syr Darya River, which grows into the city of Tashkent (City of Stone) (Turk. "tash" = stone) (modern-day pop. 2.3M) by the 17th cent. C.E. after Genghis Khan destroys it in 1219 and it is rebuilt, becoming a strategic center on the Silk Road, reaching 100K pop. in 1809; in May 1865 it is conquered by Russia, becoming the capital of Russian Turkistan.

About 280 B.C.E. after Ptolemy I Soter ordered its construction shortly after announcing himself king in -305, the 394 ft.-449 ft. (120m-137m) 800-talent limestone (Pharos) Lighthouse of Alexandria is finished by his son Ptolemy II Philadelphus on the small island of Pharos on the W edge of the Nile Delta, served by the port of Eunostos and its inner basin Kibotsos, connected with the Great Harbor of Alexandria to the E by the 1.2Km (7 x 180m) Heptastadium mole, becoming the world's first important lighthouse, guiding ships into the harbor for 1.6K years before being toppled by an earthquake in 1323 C.E.; the light is created by a furnace at the top; it is allegedly designed by Greek architect-engineer Sostratus of Cnidus; it is badly damaged by an earthquake in 956 C.E.; the last of its stones are used in 1480 C.E. to build the Citadel of Qaitbay; in 1994 C.E. French archeologists discover some of its remains; the mole is gradually filled-in, becoming the modern Ras el-Tin quarter of Alexandria.
In 279 B.C.E. Singidunum ("round fort") (modern day-Belgrade, pop. 1.2M/1.6M) in Serbia at the confluence of the Sava and Danube Rivers is mentioned for the first time, populated by the Celtic (Gallic) Scordisci tribe, which conquers the regions of modern-day Serbia, Croatia, Bulgaria, and Romania before being absorbed as the Roman provinces of Pannonia, Moesia, and Dacia in the 1st cent. C.E.; the "dun" part is Celtic for fortress; the previous inhabitants were the Thracian tribe of Sings.

In 273 B.C.E. Bindusara Maurya dies, and in 269 after killing 99 of 100 brothers, his son Ashoka (Asoka) (Sansk. "without grief") Maurya (the Great) (-304 to -232) of Magada, grandson of Chandragupta becomes king #3 of the Maurya Dynasty in Magadha, India (until -232), going on to become "the greatest ruler the world has seen" (H.G. Wells), and a patron of Buddhism, producing the earliest known writings in the sacred language of Pali (Sans. "row", "line", "series") ("language of mankind's philosophy"); the Seven Islands of Bombay (Mumbai) (named after the goddess Mumbadevi) on the W coast of India (modern-day pop. 12.4M/20.7M) are incorporated into the Maurya Empire (ends -180).
About 250 B.C.E. the port of Shanghai ("upon the sea") (modern-day pop. 24M/34M) in the Yangtze River Delta in C China on the East China coast is greatly improved by the excavation of the Huangpu (Chunshen) River on the orders of Lord Chunshen (d. -238), PM of the Kingdom of Chu during the Warring States Period of China, causing Shanghai to be nicknamed Shencheng ("City of Shen").
In 226 B.C.E. Carthaginian gen. Hamilcar Barca (b. -275) is KIA after allegedly founding the port of Barcelona (originally Barcino) in Spain in 218 B.C.E. (modern-day pop. 1.6M/5.3M).
In 214 B.C.E. the city of Guangzhou (Canton) (originally Panyu) (modern-day pop. 14M/25M) is founded on the E bank of the Pearl River 75 mi. NNW of Hong Kong and 90 mi. N of Macau by the Qin as a military base for their first unsuccessful invasion of the Baiyue lands of S China; in 226 C.E. after being incorporated into the Han Empire, it becomes the seat of Guang Prefecture, becoming known as the Rice City, City of the Immortals, City of the Five Rams, and City of Flowers.
In 206 B.C.E. Hannibal is bottled by the Romans into Calabria in Italy's heel; meanwhile Roman gen. Scipio the Elder wrests Spain from Hamilcar Barca of Carthage at the Battle of Ilipa (Silpia) 10 mi N of modern-day Seville in S Spain, using the new Reverse Cannae formation to outwit them, and conquers Cordoba (Kart-Juba = "city of Juba") (modern-day pop. 326K); Spain now becomes a cash and slave cow for the Barca family of Rome; Scipio founds the city of Italica (5 mi. N of modern-day Seville) nearby for his wounded Roman soldiers, later becoming the birthplace of Roman emperors Trajan and Hadrian; the 8th cent. B.C.E. city Seville on the Guadalquivir River (modern-day pop. 703K/1.5M) is conquered and renamed Hispalis, becoming a market-industrial city, while Italica goes residential; the ancient city of Granada in Bastetania (modern-day pop. 237K) is conquered and renamed Municipium Florentinum Libertanum; in 711 C.E the Muslim Umayyads of N Africa conquer S Spain from the Visigoths, and aren't expelled until Jan. 2, 1492 by Catholic kings Ferdinand V and Isabella I.
In 197 B.C.E. the seaport of Salernum (modern-day Salerno) (modern-day pop. 133K) in SW Italy on the Gulf of Salerno (29 mi. ESE of Naples) is founded by the Romans.

In 123 B.C.E. the Romans under gen. Gaius Sextius Calvinus conquer the Celtic Salluvii (Salyes) tribe in S Gaul, causing their king Tutomotulus (Teutomalius) to flee to the protection of the Allobroges tribe, which controls the territory between the Rhone River and Lake Geneva N of Massalia, causing Rome to declare war on them too; the Romans destroy the chief town of the Salluvii and found the Roman colony of Aquae Sextiae (hot springs of Sextius) (modern-day Aix-en-Provence) (modern-day pop. 142K) giving some of the captured territory to Massilia; the Romans also capture Arles in S Gaul from the Salluvii and attempt to build into a commercial city, although it never escapes from the shadow of Massalia.
In 121 B.C.E. the Allobrogian border town of Geneva (Gaelic "genawa" = bend, knee) at the Rhone River exit from Lake Geneva (modern-day pop. 199K) is conquered by the Romans.
In the 1st cent. B.C.E. the town of Budapest (modern-day pop. 1.8M) is built on the Gellert Hill in Pannonia (Hungary); they call it Ak Ink ("spring rich in water").
In the 1st cent. B.C.E. Ephesus becomes the world capital of the slave trade (till 100 C.E.).
In 50 C.E. Roman soldiers found the city of Londinium (London) (Celtic llyn-din, "stronghold on the lake") (The City) (originally 677 acres) (modern-day pop. 8.8M/14M) on the N bank of the Thames River 30 mi. from the estuary on the North Sea) on the site of a Celtic wooden bridge (where they built a Roman fort in 43?), beginning England's "liquid history"; four systems of Roman roads begin construction centering on London, with a 5th built later not centered there; the Roman road later called Stane (Stone) Street runs 50 mi. from London SW to Noviomagus (Gael. "new plain") Reginorum (Regnentium), former home of the Regini subtribe of the Atrebates, which the Saxons later call Chichester; the city of Bath in SW England emerges as a great place to, er, take a bath, use your Bath chair, and as a center of Roman fashion, show off your bod; a legend that mythical king Bath Dude, er, Bladud (father of King Lear) built Bath and dedicated the medicinal springs to the Roman goddess Minerva causes the Temple of Aquae Sulis to be conflated with her, and a large gilded bronze head of the babe survives to modern times; Romans occupy Cornwall until 250 C.E.?
In 80 B.C.E. Roman gen. Quintus Sertorius begins the Sertorian War (ends -72) against dictator Sulla, and (in -57?) captures Ebora (Evora) (Évora) (Gael. "of the yew trees") (AKA Liberalitas Julia) (modern-day pop. 56K) in Portugal 68 mi. SE of Lisbon, where a Roman aqueduct and temple of Diana are later built, organizing the tribes of Hispania and Lusitania to form an independent province and launch guerrilla war; Julius Caesar later renames the 8th cent. B.C.E. settlement of Olissipo (Lisbon) (Phoenician "Alis-Ubo" = safe harbor) in the Tagus River estuary (modern-day pop. 545K/2.8M) (allegedly founded by Odysseus on his way home from Troy) to Felicitas Julia.
About 80 B.C.E. the town of Durocorteron (Durocortorum) ("round fortress") 80 mi. ENE of Paris is founded as the capital of the Gallic Remi tribe, who go on to ally with Julius Caesar in his conquest of Gaul in -58 to -51, receiving special favors, reaching a pop. of 30K-100K; it later becomes the city of Reims (Rheims) (modern-day pop. 187K).
In 59 B.C.E. the city of Florentia (Firenze) (modern-day Florence) in N Italy on the Arno River 143 mi. NW of Rome (modern-day pop. 383K) is founded at the foot of the hill on which Faesulae (modern-day Fiesole) was founded as a retirement community for veterans of Julius Caesar's army, and since it's on the Via Cassia between Rome and the north it rapidly becomes a commercial center.

In Sept. 52 B.C.E. the Pan-Gallic Rebellion of 52 B.C.E. sees Arvernian leader Vercingetorix (b. -82) and 70K (200K?) Celts from 28 tribes hole-up in an impregnable wooden hill fort in Alesia (Alisia) near modern-day Dijon in C France, but after the young inexperienced Vercingetorix makes the mistake of sending his cavalry off to get reinforcements, Caesar fixes his wagon by building two concentric 11+-mi. rings of earthworks in five weeks, allowing him to siege the fort while keeping neighboring Celts from aiding him; when Vercingetorix releases the aged, women, and children, Caesar refuses to let them pass and instead waits for the gates to open so he can take the fort, causing them to be trapped outside until they all starve; despite 250K Celtic troops arriving, they can't get through the Roman defenses, and after the fort is taken, Vercingetorix is kept in a pit for five years, then used in a triumph before being strangled, with the Romans making a copy of the -241 Greek statue called "The Dying Gaul"; a Roman legion under future traitor Gen. Quintus Labienus (d. -39) conquers Ile de la Cite (modern-day Paris) after the Parisii settlers burn their houses; the Romans found a colony on the site of modern-day Orleans in NC France 69 mi. SW of Paris (modern-day pop. 114K); over the next decades a new town named Lutetia Parisii (modern-day Paris, pop. 2.2M/12.4M) is built on the left bank of the Rhine, which grows to a pop. of 12K-20K mainly on the left bank of the Seine River, while the Romans wipe out all traces of Celtic presence in Gaul; in Mar.-Apr. 2006 C.E. remains of a road and several houses, one with under-floor thermal heating are discovered on the Sainte-Genevieve Hill (Montagne Sainte-Geneviève) on the left bank.
About 50 B.C.E. the Roman Legio XV Apollinaris builds a fort on Castle Hill near the Ljubljanica River that becomes the colony of Iulia Aemona (Emona); bout 1200 market rights are granted to Old Square in Ljubljana (modern-day pop. 280K/538K), and in 1220-43 it acquires town privileges; in 1270 it is conquered by King Ottokar II of Bohemia, becoming property of Rudolph of Habsburg in 1278, who gives the admin. to the Counts of Goriza in 1279 until 1335, when it becomes the capital of Slovenian Carniola and is renamed Laibach, enjoying being situated in the middle of the trade route between the Danube River Valley and the Adriatic Sea; the Habsburgs own it until 1797.

In July 43 B.C.E. after demanding a consulship and being refused, Octavian marches S to Rome without opposition, neutralizes Cicero's clique and forces a special election, which he wins on Aug. 19, being formally recognized as Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus, Julius Caesar's adoptive son, rendering Cicero and his senators kaput and in the denial stage; too bad for them, Octavian abandons his fair weather friends and gets laws passed calling for the prosecution of Caesar's assassins, adopting his uncle, er, father Caesar's old tactic of inviting his rivals to help him defeat his enemies, and on Nov. 26 meets with Antony and Lepidus in Bononia, entering an official autocratic Lex Titia creating the Second Triumvirate, with a 5-year commission to reform the state, after which they proceed to work together to punish their enemies, executing 300 senators (incl. Cicero on Dec. 7) and 2K equestrians; you're-so-good Antony gets the Senate to officially recognize the revamped Roman city of Colonia Copia Claudia Augusta Lugdunum (Colonia Copia Felix Munatia) (AKA Lugudunum from Gael. "desired mountain) (modern-day Lyons, France, pop. 506K/2.2M) in Cisalpine Gaul at the confluence of the Rhone and Saone Rivers (58 mi. NW of Grenoble) for settlement of Roman refugees of the the war with the Allobroges, who had been expelled from Vienne and were encamped nearby, while Octavian attempts to best Caesar by beginning the construction of a new, larger Roman Forum, featuring the ultimate Temple of Mars Ultor, as well as the Tabularium for public archives - extra, extra, read all about it?
In 38 B.C.E. the city of Cologne (Köln) (modern-day pop. 1M/3.5M) on both sides of the Rhine River in modern-day North Rhine-Westphalia near the German borders with Belgium and Netherlands 28 mi. SW of Dusseldorf and 16 mi. NW of Bonn is founded by the Cisrhenian Germania Ubii tribe as Oppidum Ubiorum; in 50 C.E. it is renamed Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium; in 85 C.E. it becomes the capital of the Roman province of Germania Inferior, located on an important trade route between E Europe and W Europe.

The original Awesome Blossom? In Jan. 27 B.C.E. Octavian declares the republican govt. restored to the "Senate and people", and offers to resign his position as consul, but the Senate, wisely noting how he retains exclusive control of the army by apparently dividing the provinces between him and them, with the ones with the fewest troops going to them, gives him the position of princeps (first citizen), then, after he graciously refuses the title of Romulus, on Jan. 16 gives him the title Imperator Caesar Divi Filius Augustus (Emperor Caesar Exalted or Revered One Son of God), with the title augustus heretofore reserved for gods, beginning the emperor worship cult, magnanimously mounting the pantheon of month-gods by renaming the 6th month Sixtilis after himself (August), and shortening February so that he can make it as long as July, while juggling other months to their modern-day lengths; "Behold the man — the promised one, of whom you know - / Caesar Augustus, son of a god, predestined to rule/ And to restore the Golden Age to Latium,/ Where Saturn used to rule. His empire will extend/ Beyond the Garamants and Indians, over lands/ In the far north and south of the stars of the zodiac/ And the yearly path of the Sun" (Virgil); Augustus fixes the number of senators at 600; he receives an enormous proconsular province incl. Spain, Gaul, Syria, and Egypt (the grain supply of Rome), governed by loyal salaried "legati Augusti pro praetore" with long terms of office, and bypasses senators by appointing equestrians into prefect positions, incl. prefectus annonae (grain supply), prefectus vigulum (fire dept.), prefectus Aegypti (governing Egypt as Octavian's private possession), and prefectus praetorio for his new Praetorian Guard (ends 312), consisting of nine cohorts (one less than a normal legion) of 500 men scattered through Italy, each with 12 (later 16) year terms and special pay privileges, incl. the right to station in Rome, which spooks the citizens until they get used to it, after which he increases each cohort to 1K men; he puts his vast private wealth into an imperial treasury (fiscus), kept distinct from the Senate's aerarium; Augustus divides Gaul into four admin. regions, Gallia Narbonensis (from the Alps to the Cevennes Mts.), Aquitania (bounded on the N by the the Loire River, and containing 14 more tribes than in Caesar's days), Gallia Lugdunensis (between the Loire, Seine, and Saone Rivers, with capital at Lugdunum or Lyons), which incl. the Belgic tribe of the Veliocasses (Velocasses) and their capital Rotomagus (modern-day Rouen, pop. 111K/655K) on the Seine River in Normandy, and Gallica Belgica (between the Seine and Rhine Rivers, to the North Sea); rank and file soldiers are prohibited from marrying for the next two cents., although the order is widely ignored?; the org. lasts until the 4th cent. C.E.; Achaia (Greece excluding Macedonia) becomes a Roman senatorial province, with Corinth as capital; Ephesus becomes the capital of the proconsular province of Asia (until a little after 297 C.E.); "If we compute the number and duration of the reigns, it will be found that a period of six hundred years is filled by sixty emperors, incl. in the Augustan list some female sovereigns, and deducting some usurpers who were never acknowledged in the capital, and some princes who did not live to possess their inheritance. The average proportion will allow ten years for each emperor - far below the chronological rule of Sir Isaac Newton, who, from the experience of more recent and regular monarchies, has defined about eighteen or twenty years as the term of an ordinary reign." - Gibbon, Ch. 48.

In 16 B.C.E. the Romans begin expanding their territory W along the Danube River, creating the Celtic provinces of Noricum, bounded by the Danube River on the N, Rhaetia and Vindelicia on the W, and Pannonia on the E and SE, and Rhaetia (Raetia) (Etruscan?), W of Pannonia and N of Italy; too bad, Roman gen. Marcus Lollius (Paulinus?) (-55 to 2) (gov. of Gallia Comata) is defeated by the Germanic Sugambri at the Battle of Vindobona (modern-day Vienna, pop. 1.9M/2.6M) on the Danube River with his V Alaudae legion losing its eagle standard, causing emperor Augustus to become determined to end the pesky German problem once and for all, but ending up making Vindobona a frontier town, fortifying it next year.
In 16 B.C.E. after defeating the Belgic Treveri (Treviri), the town of Augusta Treverorum ("city of Augstus in the land of the Treveri") (modern-day Trier or Treves, pop. 115K) in a valley between low vine-covered red sandstone hills in modern-day Rhineland-Palatinate near the German-Luxembourg border (modern-day pop. 115K) at the foot of Mt. Petrisberg on the 315 mi. Moselle River (which starts in the French Vosges and flows into the the Rhine River) is founded as the capital of the Roman province of Galla Belgica.
In 15 B.C.E. the city of Augsburg at the convergence of the Lech and Wertach Rivers in Swabia, S Bavaria is founded as the garrison camp Augusta Vindelicorum by Claudius Drusus and Tiberius on orders of their stepfather Emperor Augustus, becoming capital of the Roman province of Raetia in 120 C.E.; on Mar. 9, 1276 it is granted the status of free imperial city, going on to produce the Fugger and Welser banking families and the Augsburg Confession of 1530.
In 15 B.C.E. the Romans merge several Celtic settlements on the Salzach River in the province of Noricum (Austria) into the town of Juvavum (modern-day Salzburg, "Salt Fortress") (modern-day pop. 151K) which receives municipium status in 45 C.E., attracting Jewish settlers.
In 15 B.C. the Roman camp Castra Vetera is founded on the Furstenberg River near modern-day Birten, Germany as a base for campaigns into Germania, housing 8K-10K legionaries; it is destroyed in 70 C.E.
In 15 B.C.E. Bauzanum (modern-day Bolzano) (modern-day pop. 106K) in Tyrol (Tirol) 35 mi. N of Trent and 58 mi. S of the Brenner Pass at the junction of the Talavera and Isarco Rivers (near the Adige River) (later the crossroads of the Brenner Route to Germany and the Adige Valley Route to Switzerland) is settled by the Romans under Nero Claudius Drusus.
In 15 B.C.E. the town of Zurich (Zürich) in NC Switzerland (modern-day pop. 403K) at the NW tip of Lake Zurich is founded by the Romans as the customs station of Turicum around the Lindenhof Hill.
In 14 B.C.E. Roman gen. Druses builds a fort in modern-day Wurms (Worms) (modern-day pop. 82K) (originally Celt. "Borbetomagus" = settlement in a water area, which is transformed into Lat. Wormatia, after Ger. "wurm" = dragon) on the left bank of the Upper Rhine River on the Wonnegau Plain (40 mi. SSW of Mainz) in modern-day Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, which started out as a Celtic town then became the capital of the German Vangiones.

In 12 B.C.E. Roman armies led by Augustus' stepson Nero Claudius Drusus I (Major) (the Elder) (-38 to -9) cross the Rhine River, conquering Vindelicia, Raetia, and Noricum, and extending Roman territory; by -10 they found Bonn (modern-day pop. 319K/11M) on the Rhine River in modern-day North Rhine-Westphalia 15 mi. SSE of Cologne (halfway between modern-day Paris and Berlin) (where the Romans settled members of the Germanic Ubii tribe), named after the Eburoni tribal coalition of Gaul; in 1597-1794 is becomes the capital of the Electorate of Cologne, and the 1770 birthplace of super-composer Ludwig van Beethoven; in 1949-90 it becomes the provisional capital of West Germany.
In the 1st cent. C.E. the spa town of Baden-Baden (Ger. "to bathe") in SW Germany (modern-day pop. 54K) is founded by the Romans (enjoying 29 natural springs flowing from artesian wells under Florentine Hill), along with the city of Frankfurt (Ger. "ford of the Franks") on the Main River (modern-day pop. 732K/5.6M) - looks lived in?
In 50 C.E. Roman soldiers found the town of Londinium (London) (Celtic llyn-din, "stronghold on the lake") (The City) (originally 677 acres) (modern-day pop. 8.8M/14M) on the N bank of the Thames River, 30 mi. from the estuary on the North Sea) on the site of a Celtic wooden bridge (where they built a Roman fort in 43?), beginning England's "liquid history"; four systems of Roman roads begin construction centering on London, with a 5th built later not centered there; the city of Bath in SW England (modern-day pp. 89K) emerges as a great place to, er, take a bath, use your Bath chair, and as a center of Roman fashion, show off your bod; a legend that mythical king Bath Dude, er, Bladud (father of King Lear) built Bath and dedicated the medicinal springs to the Roman goddess Minerva causes the Temple of Aquae Sulis to be conflated with her, and a large gilded bronze head of the babe survives to modern times; Romans occupy Cornwall until 250 C.E.?
In 70 C.E. the Romans build the small Duroliponte Fort on Castle Hill near modern-day Cambridge, England on the Cam River 50 mi. N of London (modern-day pop. 131K/280K), which becomes a town in about 120; after the Romans leave Britain in 410, the Anglo-Saxons begin occupying it, founding Grantebrycge (Granta-bridge) on the border between East Anglia and Middle Anglia; in 875 the Vikings occupy it, causing the pop. to grow, shifting from Castle Hill on the left bank to Quayside on the right bank; in the 10th cent. the Saxons return to power, striking coins calling the town "Grant"; in 1068 William I the Conqueror builds a castle on Castle Hill; the first town charter is granted by Henry I in 1120-31, giving it a monopoly on waterborne traffic and tolls; in 1209 Cambridge U. is founded by students running from hostile townsfolk in Oxford; the Romans build their first vineyard irrigation system in Britain around Duroliponte.
In 79 C.E. the Roman legions under three of their best generals conquer Wales and partially subdue the Celtic Brigantes in Yorkshire; Gnaeus Julius Agricola, Roman gov. of Britain founds the fort of Mamucium (Lat. "breast-like town") (Mancunium) near the confluence of the Medlock and Irwell Rivers between the Pennine Mts. on the N and E, and the Cheshire Plain on the S to protect against the remaining Brigantes; the fort is abandoned in the late 4th cent. C.E.; sometime after the 1066 Norman Conquest lays the area waste, the town of Manchester (modern-day pop. 540K/2.8M) grows up around the ruins; in this cent. the Roman towns of Lincoln (Lindon) (Lindum) (ca. 48) (modern-day pop. 130K/190K), Bath (Aquae Sulis) (ca. 60) (modern-day pop. 89K) (known for 120F/49C mineral springs), and Leicester (Ratae) on the Soar River (ca. 50) (modern-day pop 348K/1.39M) are also founded, along with Cardiff (ca. 75) (modern-day pop. 361K/1.1M) in Wales on the N coast of the Bristol Channel at the mouth of the Taff River.
In 84 C.E. the city of Baku (Persian "bad-kube" = wind-pounded city") in the Caucasus region on the Caspian Sea 92 ft. below sea level in modern-day Azerbaijan (modern-pop. 2.3M/4.3M) is first mentioned by the Romans.
In 90 C.E. the Romans build a fort at the site of the Celtic settlement of Radasbona at the confluence of the Danube, Naab, and Regen Rivers at the northernmost point of the Danube River, which becomes the SE German town of Regensburg in E Bavaria (modern-day pop. 148K), going on to become the 4th largest city in Bavaria after Munich, Nuremberg, and Augsburg.

About 100 C.E. Roman emperor (98-117) Trajan (Marcus Ulpius Traianus) (53-117) makes longtime Thracian-Celtic Serdi tribe town Sardica (Ulpia Serdica) (modern-day Sofia, Bulgaria, pop. 1.26M/1.68M) a municipium (center of an admin. region) of Rome, and it is built-up with walls, baths, amphitheater, and all the other good stuff; in the 14th cent. the name Sofia begins to be used after St. Sofia Church.
In 125 C.E. Roman emperor Hadrian rebuilds an old Thracian town on the banks of the Tundzha River at its confluence with the Maritsa (Meric) River in NW Asia Minor 130 mi. NW of Byzantium, and renames it Hadrianopolis (Adrianopolis) (Adrianople) (modern-day Edirne, pop. 165K/400K).
In Oct. 130 C.E. Hadrian's Bythinian-born Greek male lover Atinous (b. 110) drowns in the Nile; Hadrian has him deified, and on Oct. 30 has the city of Antinoopolis built on the spot, which lasts for five cents. - don't talk there with your mouth full?

About 161 C.E. Greek historian Arrian of Nicomedia (b. -86) dies, leaving Indica, a history of Alexander the Great's expedition to India, mentioning Oman and the port city of Muscat (Arab. "moscha" = inflated hide) in the Gulf of Oman (modern-day pop. 1.2M).
In the 2nd cent. C.E. the port city of Sarapion (Serapion) on the Indian Ocean coast in modern-day S Somalia is first mentioned, later becoming Mogadishu (Xamar) (Hamar) ("tamarind") (modern-day pop. 2.4M).
On Sept. 3, 301 C.E. San Marino (modern-day pop. 33K), the oldest repub. to survive to modern times is founded in the Apennines 11 mi. SSW of modern-day Rimini by St. Marinus (-366) from Rab Island in Dalmatia (Croatia), becoming known for its wine and building stone quarried on Mt. Titano - a safe pimple on mighty Rome's increasingly ranged rump?
In 383 C.E. after receiving a warm welcome and making it a Roman city, after Roman emperor Gratian's death the 1st cent. B.C.E. Allobroges town of Cularo on the Isere River in SE Gaul is renamed Gratianopolis in his honor, the name being eventually corrupted to Graignovol then Grenoble (modern-day pop. 158K/687K).
In the 4th cent. C.E. the port city of Antwerp on the Scheldt River linked by the Westerschelde Estuary to the North Sea 25 mi. N of Brussels and 9 mi. from the Dutch border (modern-day pop. 517K) (named after a giant named Antigoon on the Scheldt River, who stopped passing boatmen and severed a hand and threw it into the river if they refused to pay a toll, until hero Silvius Brabo does it to him, causing the city to be named Dutch "hand" + "werpen" = hand + to throw) (named after Dutch "anda" + "werpum" = at + the wharf) is settled by the Germanic Franks, and evangelized about 650 by St. Amand.

In the 4th cent. C.E. the 1st cent. C.E. Roman city (former Gallic city of Turones) of Caesarodunum (Lat. "hill of Caesar") on the Loire River in Gaul becomes known as Tours (Fr. "tower") (modern-day pop. 134K), with a new amphitheatre that becomes one of the five largest in the Roman Empire; about 380 it becomes the capital of the Roman province of Lugdunum, dominating the Loire Valley, Maine, and Brittany. In 336 C.E. Constantine I campaigns on the Danube frontier, and gives the Vandals (relatives of the Goths, who are pushing them) permission to cross the Danube River into Pannonia (Hungary W of the Danube); 20-y.-o. (St.) Martin of Tours (316-97) (whose name comes from Mars, the god of war), who two years ago was an unbaptized Roman soldier, and had a dream about cutting his cloak and sharing it with a naked beggar in Amiens, which caused Jesus to restore his cloak, after which he got baptized quick and refused to fight the Gauls at Worms, saying "I am a soldier of Christ and cannot fight", causing him to be arrested, but luckily the peace with the Goths happened just in time, and he was allowed to leave military service, moves to Tours on the Loire River, becoming a disciple of Trinitarian champion St. Hilary of Poitiers, where he takes on pesky Arian Goths and Gallic Druids - so Mister Hilary, what's hot?
In 402 C.E. Roman emperor Honorius decides to find a safer site than Milan for his royal palace, and chooses the ancient lagoon-filled Etruscan city of Ravenna (modern-day pop. 158K) on the Adriatic coast of E Italy in Umbria, 10 mi. from the southermost of the seven mouths of the Po River, digging a harbor for 250 warships and the naval station of Classis, then building the artificial Via Caesaris causeway connecting the marshy country to an island city made up of a a series of Venice-like canals with houses built on wooden piles in three quarters; too bad, this leaves Rome open to barbarian invasions, forcing the popes to step up as mayors; it becomes the capital of the Western Roman Empire until 476, then capital of the Ostrogothic Kingdom until 540, then the center of the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna until 751, when it becomes the capital of the Kingdom of the Lombards; it eventually becomes one of the most populous cities of Italy.

In 447 C.E. king (since 435) Mihrdat dies, and his son (St.) Vakhtang Gorgasali ("wolf-headed") I Gorgasali (439-522) becomes Chosroid king #32 of Kartli (Iberia) in E Georgia (until 522), making the town of Tbilisi (Tiflis) on the Kura River (founded 479) (modern-day pop. 1.1M/1.4M) the capital while allying with the Byzantines unsuccessfully against his Persian Zoroastrian Sasanian masters and going down fighting.
In 457 C.E. St. Patrick founds his main church in Armagh in Northern Ireland (modern-day pop. 15K), going on to become Ireland's ecclesiastical capital, sea of the archbishops of Armagh, and the primates of all Ireland for the Roman Catholic Church and the Church of Ireland.
I'm not your stepping stone? In 452 C.E. fugitives from Aquileia, Altinum, and Padua (the Veneti, descendants of Stone Age Swiss lake dwellers?) (allegedly led by a priest receiving signs from heaven) take refuge on the 120+ islands of the shallow marshy lagoons between the Piave (Adige and) Po Rivers (N-S), founding the city of Venice (Venetia) (Venezia) (Lat. "city of the Phoenicians") (modern-day pop. 265K), with a govt. of tribunes for each of the 12 principal independent islands, who finally in the 7th cent. elect a common Top Dog, er, Doge as it becomes known as "the Bride of the Adriatic"; in 2009 the buried city of Altinum in N Italy 7 km. N of Venice near the Marco Polo Airport is rediscovered sunk under the lagoon.
In 482 C.E. Kiev (modern-day pop. 2.9M/3.4M), the oldest Slavic city is founded on the right bank of the Dnieper River 600 mi. N of the Black Sea on a steep line of wooded bluffs 300 ft. over the river by Slavic tribe leader Kyi and his brothers Shchek and Khoryv and sister Lybid; in 1917 it becomes the capital of Ukraine.
In 540 C.E. St. Finian founds Movilla Abbey (Gael. "Magh Bhile" = plain of the sacred tree) on a pagan site on a hill overlooking 58 sq. mi. Strangford Lough (ON "strangr fjordr" = strong sea-inlet) on the Ards Peninsula (largest inlet in the British Isles) 1 mi. NE of modern-day Newtownards, Northern Ireland, going on to becoming a main Irish Christian center; in 825 the Vikings sack it, but it survives until the 1542 Dissolution of the Monasteries; in 1606 Hugh Montgomery founds the modern-day town of Newtown, which becomes Newtownards (modern-day pop. 28K).
In 544 C.E. the first mention of bubonic (blefed) plague in Ireland, which causes the disperson of the disciples of St. Mobhi, while St. Columba (Colmcille) returns to Ulster, founding the monastery of Derry (Gael. "Daire"/"Doire" = oak grove) on the W bank of the Foyle River in County Donegal at the S end of Inishowen Peninsula (modern-day pop. 83K/90K); in 1610 it is separated from County Donegal and combined with County Coleraine and parts of County Antrim and County Tyrone to form County Londonderry, with the city resettled by planters sent by London livery cos., who rebuild the town with high walls in 1613-19 and rename it Londonderry, becoming the first planned city in Ireland, its grid pattern later copied by the colonies of British North Am.; after it is sieged 3x in the 17th cent. and its walls never breached, it becomes known "the Maiden City"; in the late 20th cent. the unionists want to keep the name Londonderry, but the nationalists want to call it Derry, causing it to be called "the Stroke City" (Derry/Londonderry) by local broadcaster Gerry Anderson.
In 560 C.E. the city of Glasgow in W Scotland (modern-day pop 615K/1.8M) on the N bank of the Clyde River is founded as a small church built by St. Kentigern (Mungo) (-603), apostle to the Scots, spreading to both banks and eventually connected by 11 bridges, becoming the largest seaport in Britain - pronounce it glass-guh?
In 597 C.E. Pope Gregory the Great's Lateran Great White Hope St. Augustine of Canterbury (-604) lands on the Isle of Thanet then arrives in King Aethelbert's main town of Kent, using his Frankish Catholic wife Bertha to convert (pussy-whip?) him, then within a few mo. of arriving baptizes him and a number of his subjects, and begins the Anglican church tradition, founding Canterbury Church and becoming the first archbishop of the former Roman town of Canterbury in 601, spreading Christianity to neighboring kingdoms where Ethelbert has influence, although he has trouble converting London; Ethelbert creates episcopal sees, and builds Augustine a basilica, which he names Christ's Church; it is destroyed by fire in 1067.
In the 7th cent. C.E. the seaport of Inverness (Gael. "Mouth of the River Ness") in N Scotland on Beauly Firth (largest town in the Scottish Highlands) at the mouth of the Ness River (modern-day pop. 63K) becomes a Pict stronghold.
In the 7th cent. C.E. the once-boss town of Mutina in the Po Valley of Italy is buried by a great flood and abandoned, and the new village of Cittanova ("new city") is built a few mi. to the NW between the Secchia and Panaro Rivers, becoming the city of Modena (modern-day pop. 185K).
In the 7th cent. C.E. the city of Tartu in Estonia (modern-day pop. 93K) is founded as the fortress of Tarbatu, becoming Estonia's 2nd largest city after Tallinn.
In the 7th cent. C.E. the pre-Roman town of Tigguo Cobauc ("place of cave dwellings") between the Leen and Trent Rivers in Mercia, England (known for its network of artificial underground sandstone caves) 128 mi. N of London comes under the rule of Saxton chieftain Snot, causing the name to be changed to Nottingham ("home of Snot's people") (modern-day pop. 321K/1.6M).
In 634 C.E. St. Edwin of Northumbria founds the city of Edinburgh (Edwinesburch) (Edwinburgh) (Gael. "Din Eidyn" = Edwin's fort) (modern=day pop. 470K/1.25M) on the Firth of Forth, centered around Castle Rock on Lookout Hill - say EH-din-BUH-rah?
In 641 C.E. after conquering Egypt in 640, the garrison city of Fustat (Fostat) is founded by Muslim gen. 'Amr ibn al-'As (583-664) (a companion of Muhammad) as the capital of Egypt, housing the Amr Mosque (Mosque of Amr ibn al-As), the first mosque in Africa, built next year.
In 642 C.E. the city of Giza, Egypt (al-Jizzah) ("the valley or plateau") on the Giza Plateau 12 mi. N of ancient Memphis on the W bank of the Nile River 3 mi. SW of Cairo (modern-day pop. 3.6M) is founded by the Muslims, becoming the 3rd largest city in Egypt and world's 2nd largest suburb after Yokohama Japan, tied with Incheon, South Korea and Quezon City, Philippines.
About 650 C.E. the city of Ghent (Gael. "ganda" = confluence) at the confluence of the Scheldt and Leie Rivers in East Flanders, Belgium (modern-day pop 257K) begins as two abbeys founded by St. Amand(us) (584-675), going on to become the biggest city in Europe N of the Alps after Paris by the 13th cent., with a pop. of 65K.
In the 8th cent. C.E. the 700 Dead (Forgotten) Cities in NW Syria between Aleppo and Idlib begin to be abandoned after Arab conquest changes the trade routes (ends 1000 C.E.), leaving well-preserved Byzantine and pagan bldgs. incl. the 5th cent. C.E. Church of St. Simeon Stylites 19 mi. NW of Aleppo.
In the early 700s the town of Ribe in SW Jutland, Denmark (modern-day pop. 8.1K) is founded, becoming the first Viking city and the oldest town in Denmark to survive to modern times; it is first mentioned in 854.
About 700 C.E. St. Rupert founds the bishopric of Salzburg (Ger. "salt castle") (modern-day pop. 153K) on the ruins of the ancient Roman city of Juvavum, known for its salt (salz) mines (which he began?), building the Church of St. Peter at the foot of the Monchberg Mt. at the stop where St. Maximus allegedly was martyred in 476, along with a Benedictine monastery.
In 714 C.E. the Moors capture the Spanish (earlier Roman) town of Arriaca (Caraca) in C Spain on the Henares River 35 mi. ENE of Madrid (until 1081), changing its name to Guadalajara (Arab. Wad-al-hajarah = "valley of the stones"); meanwhile Visigoth king Achila II dies in battle, and Ardo (Ardonus) (Ardabastus) (-720) becomes the definitely last Visigoth king of he-said-she-said Christian Spain (until 720), which has shrunk to the NE corner plus Narbonensis province on the far side of the Pyrenees, and soon, only Narbonensis.
In 753 C.E. the city of Ferrara in Italy 30 mi. NNE of Bologna (modern-day pop. 132K) is first mentioned in a document of Lombard king Desiderius, who captures it from the Exarchate of Ravenna; in 756 the Franks conquer it and present it to the papacy, which in 988 cedes it to the House of Canossa, becoming a free commune after the death of Matilda of Tuscany in 1115, only to become a pawn in the war between the Guelph Adelardi and Ghibelline Salinguerra families until Obizzo II of the imperial House of Este takes it over in 1264 (until 1598).
In 772 C.E. Charlemagne begins a 32-year campaign to convert the Sad Sack pagan Saxons under Widukind to Christianity using the cruel, fierce (Muslim copycat?) Sword and Cross Technique (take the Cross or I'll give you the sword), and begins a system of taxes (tithes) to support the Church, schools, and the poor (ends 804); the confederation of W Slavic (Wend) tribes known as the Obotrites (Obodrites) (Abotrites) (Abodrites) in modern-day Mecklenburg and Holstein in N Germany (known for their busy trade emporium of Reric) ally with Charlemagne against the Germanic Saxons and Slavic Veleti; Charlemagne expels many Saxons and replaces them with friendly Wends (Polabian Slavs) (Elbe Slavs) from the Elbe River area, who found Liubice ("lovely") on the confluence of the Trave and Schwartau Rivers across from Teerhof Island 2.5 mi. N of modern-day Lubeck (Lübeck) in Schleswig-Holstein (modern-day pop. 216K).
In 794 C.E. Japanese Yamato emperor Kammu moves his capital from Buddhist clergy-dominated Nara to the new city of Heian (Jap. "safety and tranquility") (modern-day Kyoto) in S Honshu Island, Japan (modern-day pop. 1.47M) (until 1185); the Early Nara Period of Japanese art (begun 710) ends, and the Heian Period in Japan (ends 1185).
In the 9th cent. C.E. Vikings found the town of Arklow ("meadow of Arnkell") in County Wicklow at the mouth of the Avoca (Avonmore) River under Arklow Hill on the E coast of Ireland near Dublin (modern-day pop. 14K/13k); the Nineteen Arches Bridge linking the S and N parts (Ferrybank) of town becomes the longest handmade stone bridge in Ireland.
About 800 C.E. the town of Wexford ("Veisafjordr" = inlet of the mud flats) on the S side of Wexford Harbor, estuary of the Slaney River near the SE corner of Ireland (modern-day pop. 20K).
In 808 C.E. Charlemagne founds the fortress of Hammaburg (finished 830) in the area of ancient Treva to defend against Slavic incursion, later growing into the town of Hamburg (Old Saxon "ham" = banks) (modern-day pop. 1.8M/5.1M) on the N branch of the Elbe River at its confluence with the Alster River about 75 mi. from the North Sea, and the county of Brandenburg.
In 812 C.E. the Vikings found the city of Limerick (Luimneach) (Loch Luimnigh) (modern-day pop. 94K/162K) in midwest Ireland (Munster) as a walled city on King's Island in the Shannon River.
On June 6, 818 C.E. Arab Shiite imam #8 Ali al-Rida (al-Reza) (b. 765) is martyred in Tus, Persia (poisoned with poison grapes by Al-Ma'mum); he is buried beside the grave of Harun in Mashhad, Persia (Arab. "place of martyrdom", "shrine") in Khorasan in NE Persia (modern-day pop. 3.0M/3.3M) where the Imam al-Reza (al-Rida) Shrine is later built, visited by up to 20M pilgrims a year in modern times.
In 840 C.E. the city of Bruges (Old Dutch "brugga" = bridge) (modern-day pop. 118K) is first mentioned, going on to become the largest city of the province of West Flanders in NW Belgium, with the nickname "the Venice of the North". In 1252 German Hanseatic merchants establish common rights at the Flemish harbor of Bruges, allowing them their own ordinances and officials, causing Bruges and Lubeck to become the twin pillars of the Hanseatic League.
About 845 C.E. the yummy town of Essen is founded in the Ruhr Valley (modern-day pop. 582K).
In 853 C.E. the Vikings found Waterford (Norse "wether" + "fjord" = ram + fjord) in Munster, SE Ireland at the outlet of the Suir (Siur) River (modern-day pop. 53K/83K); in 902 it is vacated along with all other longship ports after the native Irish drive them out; in 914 the Vikings return and build it into Ireland's first city, becoming the oldest city in Ireland to survive to modern times.
In 860 C.E. the city of Leiden (Leithon) (Ger. ""leitha" = canal) in South Holland at the confluence of the Oude Rijn and Nieuwe Rijn (Old and New Rhine) is first mentioned, built on the artificial hill Burcht van Leiden; on Feb. 8 1575 it becomes a univ. city with the founding of Leiden U. (oldest univ. in the Netherlands), becoming known for as a center for science, giving the city the nickname "City of Discoveries", with alumni and faculty incl. Jacobus van't Hoff, Johannes Diderik van der Waals, and Kamerlingh Onnes.

Russia's next top model is? In 862 C.E. Novgorod ("new town") (modern-day pop. 218K) (in modern times one of Russia's oldest towns) is founded on the Volkhov River by the Rus (from Finnish "ruoysi", meaning "those who rowed") Viking Ulrich; Scandinavian Varangian Viking prince Rurik (Riurik) (ON "famous ruler") (830-79) is allegedly invited by the people of Novgorod to rule their city, founding the Russian Tsar (named after Caesar) Dynasty, and reopening the Norse trade to the E that had been cut off by the Huns and Avars in the 5th and 6th cents., beginning trade with Constantinople and the Khazars along the Russian waterways of the Dvina, Dnieper, and Don Rivers; "Our country is large and has an abundance of everything, but there is no order or justice amongst us. Come and take possession of the land and govern us." (Ancient Chronicle of Kiev); Vikings Askold and Dir leave Rurik's Novgorod and sail S down the Dnieper River, founding the town of Kiev (modern-day pop. 2.9M/3.4M) and becoming its rulers; the E Slav town of Polotsk (modern-day pop. 82K) on the Polota and Dvina Rivers is first mentioned, becoming the most heavily fortified city in Kievan Rus.
In 873 C.E. humble Czech ploughman Premysl (Przemysl) the Ploughman (pr. "SHEH-mih-shuhl") of the peasant village of Stadice marries princess Libuse (Libussa) (Lubossa), daughter of Bohemian ruler Krok, becoming a prince and founding the Przemysl (Premysl) Dynasty in Bohemia (ends 1306); Libuse goes on to found the city of Prague (modern-day pop. 1.28M/2.1M) on the Vltava River in NW Bohemia on seven hills like Rome, which goes on to become known as "the Mother of Cities".
In 874 C.E. Norse Vikings under Ingolfur (Ingolfr) Arnarson of Norway discover and settle Iceland (AKA Island or Lydveldid Island) at Reykjavik (Norse "bay of smoke") (named by Arnarson) (modern-day pop. 123K/217K) at the mouth of the Faxafloi River on the S shore of Faxa Bay close to the Arctic Circle (world's northernmost capital), and drive the Irish hermits out, creating a New Norway with a high culture, with the city's volcanic springs giving abundant boiling hot water; the city is not officially founded until 1786 as an official trading town - blonde babes and hot tubs, who needs civilization?
About 900 C.E. the city of Oxford, England (modern-day pop. 170K/244K) is founded as a ford for oxen in the Thames River called Oxenforda, becoming a major military frontier town between the kingdoms of Mercia and Wessex and evolving into a center of learning and center of pop. of the county of Oxfordshire in SE England, with Oxford U. first mentioned in 1096; ; in 1191 it is chartered as a city, going on to become known as "the city of dreaming spires" (Matthew Arnold).
The year 900 C.E. is the traditional date for the founding of the S Kenyan coastal city of Mombasa (modern-day pop. 1.2M/2M) on Mombasa Island by pagan queen Mwana Mkisi; Arab geographer Al Idrisi mentions it in 1151; the first stone mosque is built about 1300 by Shehe Mvita.
In the 10th cent. C.E. the city of Timbuktu (Tombouctou) (Tuareg "Tin Abutut" = lady with the big navel) on the S edge of the Sahara Desert 10 mi. N of the main channel of the Niger River (modern-day pop. 54K) is founded by Tuareg leader Imashagan, along with the Sankore Madrasah Islamic univ. in 989, which becomes a major center of learning during the reign of Mansa Musa in 1307-32, reaching 10K pop. in the 13th cent. and 50K in the 16th cent.; in 1468 it is absorbed by the Songhai Empire; in 1591 it is occupied by a Moroccan army, who move their capital there from Gao; in 1612 the new ruling class called the Army establishes independence from Morocco; the French take over in 1893; in 1960 it becomes part of the Repub. of Mali.
In the 10th cent. the Czechs assert their authority over all Bohemian tribes, and the Bohemian fortress of Wrotizlav (Wroclaw) (Vratislavia) (Wrotizlava) (Breslau) in Silesia, Prussia in SW Poland 185 mi. SW of Warsaw on the Oder River (modern-day pop. 638K/1.1M) is founded as a bishopric.
In 912 C.E. the city of Caen (modern-day pop. 108K) becomes the W capital of Normandy; William the Conqueror is buried there in 1087.
In 915 C.E. the Vikings occupy and expand the 6th cent. monastic settlement (founded by St. Finbarr) of Cork (Gael. "corcach" = marsh) on the Lee River in Munster, SW Ireland (modern-day pop. 125K/208K), turning it into a trading port, with its harbor becoming one of the largest natural harbors on Earth by navigational area; the city is granted a charter by Prince John in 1185.
In 921 C.E. the White City of al-Mahdiyya (modern-day Mahdia) on the coast of Tunisia S of Monastir and SE of Sousse in N Africa is founded as the Fatimid capital of Ifriqiya by Caliph Abdallah al-Mahdi.
In 922 C.E. the city of Dresden in Germany is founded as a Slavonic settlement (modern-day pop. 543K).
In 927 C.E. the city of Perpignan (Perpiniano, Pirpinianum, Perpenya) (modern-day pop. 118K/305K) in Septimania in SE France is first mentioned as part of the County of Roussillon, going on to become the capital; in 1172 Count Girard II bequeaths it to the counts of Barcelona, beoming a partly self-governing commune in 1197, and capital of the new Kingdom of Majorca in 1276, launching a golden age and becoming a center for the manufacture of cloth, leather, gold, and other luxury crafts; in 1344 it again becomes part of the County of Barcelona, only to lose half its pop. a few years later to the Black Death; in 1463 Louis IX of France captures and occupies it, leading to a violent uprising in 1473; in 1493 Charles VIII of France restores it to Ferdinand II of Aragon; in Sept. 1642 the French recapture it; on Nov. 7, 1659 the Treaty of the Pyrenees formally cedes it back to France.

In 944 C.E. the city of Algiers (Arab. "al-Jazair" = the islands) (Arab. "Jazair Bani Mazghana = the islands of the sons of Mazghana) on the W side of a bay on the Mediterranean Sea (modern-day pop. 3.4M/5M) is founded by Berbert-Zind-Sanhaja Dynasty founder Buluggin ibn Ziri (-984), becoming known as El-Behdja or Alger la Blanche (Algiers the White) for its white bldgs.
About 960 C.E. the city of Dunkirk in coastal N France 6.2 mi. from the Belgian border (modern-day pop. 91K) starts as a fishing village in the flooded coastal area of the English Channel S of the Western Scheldt, where Count Baldwin III erects a town wall to protect it from Viking raids; it goes on to become the scene of the May 1940 Dunkirk Evacuation.
In 965 C.E. the city of Cracow (Krakow) ("Krak's Town") (modern-day pop. 767K/1.73M), named after (mythical?) Krakus (Krak) (Grakch), ruler of the Lechitians is first mentioned as a major commercial center captured from Moravia by Bohemian duke Boleslaus I in 955, after which Polish king (960-92) Mieszko I incorporates it into his Piast Dynasty holdings near the end of his reign; in 1038 it becomes the Polish capital; it is granted city rights on June 5, 1257.
In 969 C.E. the Shiite Ismaili Fatimids under gen. Gawhar al-Siqilli (928-93) extend their N African empire by invading and conquering Ikhshidid-controlled Egypt, then set their sights on Syria, taking Jerusalem and burning the Dome of the Holy Sepulchre, founding the Ism'ili Shiite Egyptian Fatimid Dynasty (ends 1171), denying the legitimacy of the Abbasid caliphate and wanting to be numero uno, eventually controlling Egypt, N Africa, the Hijaz, and most of Syria; Janhar el-Kaid founds the new capital of Cairo (al-Qahirah) ("the Conqueror") (modern-day pop. 9.5M/20.4M) 3 mi. N of the old capital of Fustat (founded 641) (which was taken on Aug. 5), although the latter remains the center of pop., commerce, and industry; the Qaramitas take advantage of the fall of the Ikhshidids and seize control of S Syria.
In 979 C.E. the city of Brussels (Old Dutch "home in the marsh") in Belgium on the Senne River (modern-day pop. 1.1M/2.1M), first mentioned in 695 by St. Vindicianus, bishop of Cambrai as the hamlet of Broselia, home of a chapel to St. Gaugericus on an island in the river built ca. 580 is founded when Duke Charles of Lower Lotharingia is given Low-Lorraine by HRE Otto II and builds a fortress on the island in the Senne River, transferring the relics of St. Giudula from Moorsel to the St. Gaugericus Chapel, becoming a major trade route between Bruges, Ghent, and Cologne, growing to 30K pop. by 1225, specializing in the textile trade, going on to become the capital of Belgium and expand to 19 municipalities.
In 988 C.E. the town of Dublin ("dark pool") in Ireland at the confluence of the Poddle and Liffey Rivers (modern-day pop. 550K/1.9M) is first settled on the site of the 841 Viking settlement of Dyflin near the Christian Gaelic settlement of Ath Cliah ("ford of hurdles").
In 993 C.E. the city of Potsdam on the Havel River 15 mi. SW of Berlin (modern-day pop. 175K) is first mentioned as the ancient Slavonic town of Poztupimi ("beneath the oaks"), occupied by the Hevelli tribe of Slavs in the 8th cent., which HRE Otto II gives to the Quedlinburg Abbey run by his aunt Matilda; it is mentioned as a small town in 1317, and is granted a town charter in 1345, reaching 2K pop. in 1573, losing half in the Thirty Years' War of 1618-48; in 1660 it becomes the hunting residence of Elector Frederick William I of Brandenburg, and the HQ of the Prussian barracks; in 1815 it becomes the capital of the Province of Brandenburg, with Berlin alternating in 1827-43 and after 1918.
In 995 C.E. the city of Durham, NE England on the Wear River (modern-day pop. 48K) is founded by divine intervention when a milkmaid tells the congregation carrying the bier of St. Cuthbert (634-87) that she lost her dun cow at Dun Holm, and they take it as a sign to place the body of there.
In 997 C.E. the seaport of Nidaros is founded by King Olav Tryggvason on the S side of the Trondheim Fjord in Norway (250 mi. S of modern-day Oslo) as the capital of Norway (until 1380); it is renamed Trondhjem in 1564, and Trondheim in 1931 (modern-day pop. 190K/274K).
In 997 C.E. the first written reference is made to the port city of Gdansk on the Motlawa branch of the the Gdania River in Poland on the S edge of Gdansky Bay in the Baltic Sea (modern-day pop. 463K/1M).
Early in the 11th cent. C.E. the Saxons settle in Bristol (modern-day pop. 454K/1.0M) on the banks of the Avon River at its confluence with the Frome River, about 120 mi. W of London; they originally call it Bricg Stowe ("settlement by the bridge"); it receives a royal charter in 1155, going on to make it to the top three cities after London in tax receipts by the 13th cent. until it is surpassed by Birmingham, Manchester, and Liverpool during the Industrial Rev., becoming the launch point for exploration of North Am. by John Cabot in 1497, and a center for shipping African slaves to North Am. in 1700-1807, carrying 500K slaves on 2K ships.
In the 11th cent. C.E. Dunwich on the Suffolk coast of England 92 mi. NE of London and 9 mi. S of Southwold flourishes as the capital of the Kingdom of the East Angles, with a large port, naval base, two seats in parliament, and one-sixth the pop. of London; too bad, the fast-eroding coastline causes the pop. to dwindle, reaching a breaking point with a storm surge in 1286 and two great storms in 1287, reducing the pop. to 200 by modern times.
In the 11th cent. C.E. the Kingdom of Goryeo (Koryo) (founded in 918) builds a summer palace in the "Southern Capital", which becomes known as Seoul (modern-day pop. 10.1M/25.6M); in 1392 the new Joseon (Chosun) (Choson) Dynasty moves its capital to Seoul.
In 1002 the city of Erlangen in Bavaria on the Regnitz River 11 mi. NW of Nuremberg (modern-day pop. 110K) is first mentioned under the name Villa Erlangon; in 1361 it is acquired by HRE Charles IV, who makes it part of Czech.; in 1364 a city is built near the village, which in 1374 is granted its own mint, and in 1398 is granted municipal rights by Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia; in 1402 it is acquired by the House of Hohenzollern as part of the Principality of Brandenburg-Kulmbach (Brandenburg-Bayreuth starting in 1603); in 1810 it is acquired by the kingdom of Bavaria; in 1686 the first French Huguenots fleeing persecution arrive, and margrave Christian Ernst of Brandenburg-Bayreuth assigns the land to them and builds Neustadt for them; in 1706 the old town burns down, and is rebuilt, and in 1812 the two towns merge.

In 1010 Later Ly Dynasty founder-ruler (1009-28) Ly Thai To (974-1028) moves the capital of Dai Viet from Hoa-Lu to Dai La Citadel in La-Thanh, claiming to see a dragon ascending the Red River and renaming it Thang Long ("ascending dragon"), and the former "pacified south province" of China is kicking ass, with its own destiny; in 1397 the capital of Dai Viet is moved to Tay Do (Thanh Hoa), which becomes Dong Do ("Eastern Capital"); in 1802 the Nguyen Dynasty moves its capital to Hue, changing the name to Thang Long ("soaring dragon"); in 1831 Nguyen emperor renames it Hanoi (modern-day pop. 7.6M/16.1M).
In 1012 the city of Poznan (Polish "poznac" = recognize) (Posen) between the Warta and Cybina Riers in WC Poland (modern-day pop. 551K/1.1M) is first mentioned by chronicler Thietmar of Merseburg in an entry referring to the bishop of Poznan in 970, and another referring to the city of Poznan in 1005; it goes on to become the home of St. John's Fair (Jarmark Swietojansk), St. Martin's croissants, and Adam Mickiewicz U. (1919).
In 1015 the Slav settlement of Leipzig (Slav "lipsk" = lime/linden/basswood tree) in Saxony at the confluence of the White Eister, Pleisse, and Parthe Rivers at the S end of the North German Plain 99 mi. SW of Berlin (modern-day pop. 582K) (founded before 1000?) is first mentioned as "Urbs Lipzi" in the chronicles of Bishop Thietmar von Mersenburg.
In 1045 the town of Schaffhausen ("scapha" = ford) in N Switzerland on the N (right) bank of the Rhine River W of Lake Constance (northernmost canton) (modern-day pop. 36K) is first mentioned as striking its own coins, founded by the counts of Nellenburg in a finger of land surrounded on three sides by Germany, causing the pop. to be German-speaking; in 1049 the counts of Nellenburg found the Benedictine Monastery of All Saints (Kloster Allerheiligen); about 1200 it becomes an imperial free city; in 1277 HRE Rudolf I grants it a charter of liberties; in 1330 HRE Louis of Bavaria gives it to the Hapsburgs, and it takes until 1418 to regain independence, becoming a full member of the Old Swiss Confederacy in 1501.

In 1048 Norwegian king (since 1046) Harald III Sigurdsson Hardrada (1015-66) makes a trading place (kaupstad) out of the seaport of Oslo ("meadow at the foot of a hill/meadow consecrated to the gods") (founded 1040) (modern-day pop. 673K/1.59M) on the Aker River at the N end of Oslo Fiord 80 mi N. of the Skagerrak, going on to become the capital and most populous city in Norway; in 1624 it burns down during the reign of Christian IV, and is moved closer to Akershus Fortress and renamed Christiania (Kristiania) in his honor; on Jan. 1, 1838 is becomes a municipality; in 1877-97 it is renamed Kristiania; in 1925 it is renamed Oslo.
In 1050 the city of Nuremberg in Bavaria, Germany on the Pegnitz River (modern-day pop. 510K/3.5M) is first mentioned; in 1062 it is given the right by HRE Henry IV to hold a fair and coin money transferred to it from Furth; its patron is St. Sebald.
About 1050 the city of Stuttgart near Bad Cannstatt on the Neckar River in SW Germany (modern-day pop. 623K/5.2M) starts as a stud farm for the war horses of Duke Liudolf of Swabia; it is granted a charter in 1320, becoming capital of the House of Wurttemberg from the 15th cent. to 1918, becoming known for always bouncing back after catastrophes incl. WWII bombing and known as "the cradle of the automobile"; it is spread across several hills, valleys, and parks.

In 1062 the city of Marrakesh (Marrakech) (modern-day pop. 928K) N of the Atlas Mts. in Morocco 360 mi. SW of Tangier, 203 mi. SW of Rabat, 149 mi. S of Casablanca, and 153 mi. NE of Agadir is founded by Berber Almoravid leader Abu Bakr ibn Umar (-1087), cousin of king Yusuf ibn Tashfin as the Almoravid capital (until 1147), going on to introduce the Maliki School of strict Islamic Sharia law to the Maghrib, and import Andalusian art and culture, politically unifying tribal Morocco, becoming known as "the Red (Ochre) City" for its many red sandstone bldgs.; Jemaa el-Fnaa (el Fna) becomes the busiest square in Africa.
In 1067 the earliest written reference to the city of Minsk (Russ. "exchange") in the Principality of Polotsk (modern-day Belarus) on the Svislach and Nyamiha Rivers (modern-day pop. 2.1M); in 1242 it becomes part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, receiving town privileges in 1499.
In 1095 the first recorded mention of the city of Dubai (Dibei) (Arab. "Daba Dubai" = They came with a lot of money [to the souq]) on the SE Persian Gulf coast (modern-day pop. 2.9M), known for its pearls, as mentioned by Venetian pearl merchant Gasparo Balbi in 1580; in 1822 it has a pop. of 700-800 and is ruled by the emirs of Abu Dhabi; in 1833 the Al Bu Falasa tribe led by Ubaid bin Saeed (-1836) and Maktum bin Butti, who become joint rulers of Dubai, with Maktum establishing the Maktoum Dynasty of the Emirate of Dubai, going on to become the most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
In 1128 after granting a burgh charter to the 6th cent. Celtic town of Edinburgh (Edenesburg) (originally Din Eidyn) (modern-day pop. 794K/488K), David I of Scotland refounds Dunfermline Abbey as the #1 royal abbey, also founding the Augustinian Inchcolm Abbey on an island in the Firth of Forth (begun /by Alexander I), and the Augustinian Holyrood Abbey in Edinburgh on a site where he was allegedly miraculously saved from a stag attack when the lost holy rood (cross) fell from its antlers into his hands, causing the animal to turn and flee; Holyrood Church becomes a refuge for criminals and debtors; in the early 1300s it is expanded and turned into Holyrood House; in the 15th cent. it becomes a palace; in 1671-8 a new Holyrood Palace is built in a quadrangle layout; David I later founds the Augustinian Cambuskenneth (Stirling) Abbey; Edinburgh is not granted city status until 1889.
In 1135 the first known written mention is made of the 7th cent. C.E. W German farming-fishing town of Dusseldorf (Düsseldorf) (Dusseldorp), at the confluence of the Dussel and Rhine Rivers (modern-day pop. 619K/1.2M); in 1946 it becomes the capital of the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia.
In 1141 the town of St. Andrews in Fife, E Scotland (modern-day pop. 16.8K) is founded by Bishop Robert, later becoming the official ecclesiastical capital of Scotland, and the home of golf in 1754.
In 1144 The city of Montauban on the right bank of the Tarn River at its confluence with the Tescou River 31 mi. N of Toulouse in S France (modern-day pop. 61K) is founded with lands taken from the abbey by Count Alphonse Jourdan (Alfonso Jordan) of Toulouse (1103-48).
In 1146 the first written mention of the town of Bryansk (Debryansk) ("dense woodland") on the right bank of the Desna River 235 mi. SW of Moscow (modern-day pop. 426K) in the Hypatian Codex; in 1503 it is conquered by the Grand Duchy of Moscow, which turns it into a fortress; in 161034 it is occupied by the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth; in the 17th-18th cents. its economy is based on the annual Svenskaya Fair, largest in European Russia; in 1783 it becomes a manufacturing center for cannons and ammo for the Imperial Russian Navy.
In 1146 the Atlantic Ocean port city of Rabat, Morocco (Ribatu i-Fath = "stronghold of victory") at the mouth of the Bou Regreg River (modern-day pop. 577K/2.1M) opposite the ancient city of Sale (Salé) (Sallee) (Salli) in NW Morocco (founded ca. 1030) (modern-day pop. 890K) starts as a fortress built by Almohad ruler Abd al-Mu'min, becoming a favorite port for Barbary pirates in the 16th-18th cents.


In 1147 the village of Moscow (modern-day pop. 12.2M/17.1M) (precursor of the grand duchy of Moscow) on the Moskva River in Russia is founded by Prince Yuri (George) I Vladimirovich Dolgoruki (Long Arms) (1099-1157) of Suzdal-Vladimir (son of Vladimir II Monomakh) in C Russia on the Moscow (Moskva) River; in 1295 it becomes the capital of the principality of Moscow, going on to become the "Holy Mother of the Russians"; in 1482-95 the Moscow Kremlin (Russ. "fortress inside a city") in Moscow is built.
In 1155 the city of Bristol in SW England 105 mi. W of London and 45 mi. E of Cardiff across the Severn River estuary from South Wales (modern-day pop. 463K/742K) receives a royal charter, going on to become one of the top three English cities by the 13th cent. after London and York, and granted county status in 1373; in modern times it has the 8th largest pop. in England.
In 1158 the city of Munich (Munchen) (Ger. "Munichen" = "by the monks") (modern-day pop. 1.45M/2.6M) on the Isar River N of the Bavarian Alps in Bavaria in SE West Germany is first mentioned after being founded by Duke Henry the Lion on the site of an old Benedictine monastery, becoming the center of the salt trade and going on to become the most populous city in Bavaria and 3rd largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg - the birthplace of the Nazi movement in 1923?
In 1159 the N German town of Lubeck (Lübeck) on an island enclosed by the Trave River (modern-day pop. 216K) is rebuilt by Henry the Lion, duke of Saxony and Bavaria, becoming a free imperial city in 1227, and forming an alliance in 1241 with Hamburg, which became an imperial city in 1189; in 1356 the Hanseatic League holds its first gen. diet in Lubeck, growing to 170 cities and dominating Baltic maritime trade until 1800, incl. beer.
In 1166 the city of Birmingham (OE "Beormingham" = Anglian Beormingas tribe) on the Rea River in West Midlands, England (modern-day pop. 1M/3.6M) sees Lord of the Manor Peter de Bermingham obtain a market charter for his castle in an old 6th cent. B.C.E. settlement on the Birmingham Plateau, which builds the Bull Ring commercial center, becoming the 3rd largest town in Warwickshire in the 14th-16h cents., and the busiest shopping center in the U.K. by 2004 (36.5M visitors); in 1538 the city becomes a center for iron merchants, causing the pop. to become the 5th largest in England and Wales; in the 1640s it becomes a center for Parliamentarians, and in the 1660s for Nonformists, leading to the Birmingham (West Midlands) Enlightenment by 1750, along with a highly entrepreneurial economy based on thousands of small highly specialized workshops, making it a leading force in the Industrial Rev. (1760-1850) and a major financial center, incl. Lloyds Bank (1765), becoming known as "the first manufacturing town in the world" by 1791.
In 1167 the city of Copenhagen (Kobenhavn) (Lat. "Hafnia") on the E coast of Zealand Island across the Oresund Strait from Malmo, Sweden (modern-day pop. 600K/2M) is founded by Bishop Absalon, who builds a small fortress on Slotsholmen Island to defend against Wendish pirates; in 1177 St. Clemens Church is built, which is eventually destroyed by marauders and replaced in the late 14th cent. with Copenhagen Castle; Saxo Grammaticus in his 13th cent. Gesta Danormum (Deeds of the Danes) calls it Portus Mercatorum (Merchant's Harbor) (Kobmannahavn).
On Nov. 12, 1168 after reaching a pop. of 200K, Fustat (Fostat) (founded 641) is burned down by order of vizier (since Dec. 1162) Shawar (-1169) to keep the pesky Crusaders from stealing its wealth, and the remains are absorbed by nearby Cairo (al-Qahirah) ("the Conqueror") (modern-day pop. 9.5M/20.4M) N of Babylon-in-Egypt, founded in 969 by the Fatimids, which had turned into a rubbish dump.
In 1173 after floods cause a bridge to be built, the city of Amsterdam (originally Amstelredamme, "dam in the Amstel River") on the Amstel River in North Holland (modern-day pop. 866K/1.38M) is founded; in 1300 it is granted city rights, going on to become a major port.
In May 1177 after the Normans defeat the Ulaid of Ulster, Henry II holds a royal council in Oxford, dividing Leinster into three admin. areas, and with the approval of papal legate Cardinal Vivian, Henry II's 10-y.-o. youngest son Evil Prince John Lackland is made the first Lord of Ireland (ends 1542), requiring the principal Anglo-Norman landholders in Ireland to swear fealty to him; too bad, as a haughty Norman he soon begins treating the natives like serfs, giving large chunks of land to his friends, incl. Tipperary to his butler; a Norman earldom is established in Ulster (until 1333); he doesn't come to live in his new domain until 1185, and soon is recalled, leaving a group of haughty Normans behind to sow the seeds of centuries of ire?; the eternal battleground city of Belfast (modern-day pop. 340K/483K) on Belfast Lough, an inlet of the North Channel at the mouth of the Lagan River with a fine harbor is founded with a castle built to defend a ford over the river; 800+ years of direct English rule of Ireland begins.
In 1178 the first English invasion of Connaught, Ireland is repulsed, with the town of Galway (Gael. "Dun Gaillimhe" = fort at the mouth of the Gallimhe) (founded in 1124 by Connacht king Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair) on the Corrib River in Galway Bay (modern-day pop. 80K) becoming an anti-English citadel for cents., nicknamed "the city of the tribes" for its 14 merchant families.
In 1179 William I the Lion makes the first of several expeditions into N Scotland to fight the rebels, building new castles on the N side of Beauly and Cromarry Firths, and chartering the city of Aberdeen 130 mi. NW of Edinburgh between the estuaries of the Don and Dee Rivers (modern-day pop. 196K/214K) as a royal burgh, where it goes on to become known as the "Silver City by the Sea" and "Granite City", becoming the main city of N Scotland.
In 1179 the town of Durango in the Basque country of N Spain (modern-day pop. 29K) is first documented as a suzerain of the Kingdom of Navarre.
In summer 1187 the Pillage of Sigtuna on Lake Malaren (Mälaren) by the Karelians causes Birger Jarl to found the city of Stockholm, Sweden (Swedish "stock" + "holm" = log or fort + islet) (modern-day pop. 940K/2.2M); it is first mentioned in 1252.
In 1189 the town of Dundalk (Gael. "Dun Dealgan" = Dalgan's Fort) on the Castledown River in Ireland near the border with modern-day Northern Ireland halfway between Dublin and Belfast (modern-day pop. 39K/55K) is given a charter.
About 1200 William I the Lion of Scotland charters the highland capital Inverness (Gael. "mouth of the River Ness") (modern-day pop. 47K) as a royal burgh.
About 1200 the town of Tipperary (Gael. "Tiobraid Arann" = Well of the Ara) on the Ara River in Munster, S Ireland (AKA Tipp Town) (modern-day pop. 4.9K) is founded, becoming the home of the Clanwilliam barony and seat of County Tipperary; it goes on to house a large British army barracks that is used as a base by the Black and Tans; on Jan. 30, 1912 Jack Judge and Henry James "Harry" Williams compose the popular British music hall song It's a Long Way to Tipperary.
In 1201 after landing in Riga last year with 500 Westphalian crusaders on 23 ships, Bishop Albert of Riga (Livonia) (Latvia) (1165-1229) founds the city of Riga, Latvia on the Gulf of Riga (modern-day pop. 641K/1M), transferring the seat of the Livonian bishopric from Ikskile, and builds a cathedral in 1221. In 1202 the Livonian Knights (Order of Livonian Brothers of the Sword) (German Order of Swordbearers) (Militia of Christ of Livonia) of warrior monks are founded by Bishop Albert of Riga to convert the pesky pagan Finnish Livonians (N of the Lithuanians) to Christianity (finished 1236); Pope Innocent III sanctions them in 1204.
In 1204 the coal trade of Newcastle-upon-Tyne (2nd cent. C.E. Roman town of Pons Aelius and 5th cent. C.E. Anglo-Saxon Northumbrian town of Monkchester/Munucceaster) (modern-day pop. 300K/879K) is founded as King John accepts money in exchange for deforestation rights - later becoming the home of Eric Burdon and the Animals?
In 1207 the port city of Liverpool (OE "muddy pool") (modern-day pop. 485K/2.4M) on the E side of the Mersey Estuary in NW England is chartered by Beatle, er, King John as a borough; the name was first mentioned about 1190 as Liuerpul; King John designs the street plan, with seven streets laid out in an H shape, incl. Bank (later Water) St., Castle St., Chapel St., Dale St., Juggler (later High) St., Moor (later Tithebarn) St., and Whiteacre (later Old Hall) St.; since 18333 the inhabitants are called Liverpudlians, also Scousers (after the local stew scouse or lobscouse); in 1699 Parliament makes Liverpool a parish, and its first slave ship Liverpool Merchant sails for Africa; since Roman times the nearby town of Chester on the Dee River has been the principal Irish Sea port, but as it silts up Liverpool takes over; in modern times middle-class Liverpudlians are called Liverpolitans.
In 1207 Bishop Albert of Livonia begins fortification of the new (1201) bishopric town of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava River on the Gulf of Riga (modern-day pop. 641K/1M) with Philip of Swabia investing bishop Albert of Riga with Livonia as a fief and principality of the Holy Roman Empire; the Livonian Order is given one-third of all the land in order to create a standing army; Bishop Albert otains papal bulls giving German merchants a mandate to carry on all Baltic trade through Riga, insuring its commercial success, becoming the largest city in Latvia.

On June 15, 1219 the Battle of Lyndanisse (Tallinn) (Reval) is a decisive V for Christian Valdemar II of Denmark against the pagan Estonians after a red cloth with a white cross allegedly falls from the sky during the battle, and becomes the Dannebrog, the oldest nat. flag to survive to modern times; the first mention of the Estonian city of Tallinn (Reval) on the Gulf of Finland 50 mi. S of Helsinki (modern-day pop. 450K/602K), which is claimed by the Danes and receives city rights in 1249, becoming an important member of the Hanseatic League.
In 1233 the 8th cent. Danish Viking seaport city of Kiel on the SE Jutland Peninsula in Schleswig-Holstein across from the Kiel Fjord in N West Germany a few mi. S of the Danish border (modern-day pop. 248K/643K) is refounded as Holstenstadt tom Kyle by Holstein Count Adolf IV, and granted city rights in 1242 by his eldest son John I of Schauenberg; it goes on to be administered by Denmark in 1864, and annexed by Prussia in 1866, becoming part of Germany in 1871 and used as the HQ of their Baltic fleet.
In 1237 The town of Colln (Cölln) on former Slav settlements around the Spree River in Germany is founded, becoming the start of modern-day Berlin (modern-day pop. 3.7M/6M).
In 1242 after the 1st cent. C.E. Roman town of Zagreb (originally Andautonia) in Croatia on the S slope of Mt. Medvednica on the Sava River 230 mi. W of Belgrade (modern-day pop. 802K/1.1M) shelters him from a Tatar atttack, Hungarian King Bela IV bestows it a Golden Bull, making it a free royal city.
In 1256 Kublai Khan builds the city of Xanadu (Shangdu) (Chin. "Upper Capital") (original name Kaiping until 1264) in modern-day Inner Mongolia 220 mi. N of Peking, reaching 100K pop.; in 2002 a restoration effort begins; Marco Polo visits about 1275.
In 1270 the city of Rotterdam in S Holland on the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt River Delta on the North Sea (modern-day pop. 635K/1.1M) is founded after a dam is built on the Rotte River; in 1340 it is granted city rights by the count of Holland; it goes on to become the 2nd largest city in the Netherlands after Amsterdam, home of Erasmus U. (1913).
In 1276 the town of Gliwice ("gliw" = loam or wetland) in Upper Silesia in WC Poland (modern-day pop. 179K/2.7M) is first mentioned; in the mid-18th cent. it is taken along with most of Silesia by Prussia, and incorporated into the German Empre in 1871; in 1796 the first coke-fired blast furnace in Europe is build there.
About 1300 the city of Warsaw (Warszawa) (modern-day pop. 1.76M/3.1M) on the Vistula River in EC Poland is founded by Boleslaw II of Masovia, Prince of Plock, becoming the official capital of the Masovian Duchy in 1413 before being incorporated into the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland in 1526; in 1569 it becomes the seat of the Gen. Sejm, going on to become known as "the Paris of the East" until the German invasion of 1939, the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising in 1943, and the Warsaw Uprising of 1944, which destroys over 85% of its bldgs.; after WWII it becomes known as "the Phoenix City" for its reconstruction efforts.
In 1320 the city of Bialystok (Belostok) ("white slope") on the Bialy River (100 mi. NE of Warsaw) in NE Poland (modern-day pop. 297K/430K) is founded by Lithuanian Count Gedimin, becoming the largest city in NE Polnd.

In Oct. 1323 Lithuanian grand duke (1316-41) Gediminas (Gedymin) (1275-1341) is officially accepted into the Roman Catholic Church, and a compact is signed in Vilnius confirming it; too bad, the Teutonic Knights don't want Lithuania Christianized just yet, as they have their own designs, and after some shenanigans Gediminas is denounced by a synod of Prussian bishops in Elbing, causing him to refuse to see papal legates in Riga in Sept., keeping him from actually being baptized, and allowing him to play to the still large pagan constituency; the legates believe his assurances that he's really sincere, and forbid neighboring states to make war against him for the next four years; Gediminas moves the Lithuanian capital from Trakai to Vilna (Vilno) (Vilnyus) (Vilnius) on the Vilnia and Neris Rivers in SE Lithuania (modern-day pop. 545K/805K), where he builds Gedymin Castle; going on to house a large Jewish pop., causing it to be known as "the Jerusalem of Lithuania", and "the Jerusalem of the North" (Napoleon, 1812).
Why Mexico's emblem is an eagle and a snake? On Mar. 13, 1325 after getting in trouble for sacrificing and skinning the daughter of a Culhua ruler and being driven by the Toltecs into the swamps of Lake Texcoco (pr. tesh-KOH-koh), where they found an eagle warming itself, its wings stretched out towards the rays of the sun, and eating a snake, the Mexica (Aztecs) found the city of Tenochtitlan (pr. teh-noch-TEET-lahn) ("stone prickly-pear place") (modern-day Mexico City, pop. 8.9M/20.4M) on a marshy island in Lake Texcoco, later expanding it by filling in the lake, which is linked to the mainland by causeways; they build fertile floating gardens in Xochimilco (pr. show-chee-MEEL-koh) outside the city, enabling them to free manpower for armies which set out to conquer everything from the Gulf to the Pacific to Guatemala; the soldiers carry spirolina high-protein algae as rations; they never invent the wheel (except as a kiddie toy) or use a beast of burden, but they love human meat and practice ritual sacrifice religiously, considering it an honor to sacrifice one's yollotl (heart).
In 1345 the city of Manama (Arab. "place of rest/dreams") in N Bahrain Island on the Persian Gulf (modern-day pop. 157K/411K) is first mentioned.
In 1372 wealthy widow Lady Penh finds a Koki tree floating down the Tonle Sap River in Cambodia in a storm, containing four bronze Buddha statues and a stone statue of Vishnu, which are used to built a temple on the hill in what later becomes Phnom Penh ("Penh's Hill"), founded at the junction of the Mekong and Tonle Sap Rivers (modern-day pop. 2.1M); it becomes the capital of Cambodia in 1434-97, and 1865-.
By 1420 the town of Kishinev (Chisinau) (modern-day pop. 532K/685K) on the Byk River (tributary of the Dniester River) 90 mi. NW of Odessa is founded.
In 1423 the town of Lodz (pr. WUCH) in Poland is founded (modern-d pop. 687K/1.1M), going on to become Poland's 2nd largest city; it belongs to Russia until 1919.
In 1431 after pressure from Siam, King Pohnea Yat of Cambodia quits Angkor Wat for the new capital city of Phnom Penh ("Penh's Hill") (originally Kronk Chaktomuk, "City of Four Faces) on the Mekong, Tonle Sap, and Bassac Rivers (modern-day pop. 1.5M), switching from rice agriculture to maritime trade, with China granting them commercial initiatives; the religious culture begins shifting from priestly to monastic.
In 1441 the city of Ougadougou (originally Kumbee-Tenga = head war chief's village) on the upper Volta River (modern-day pop. 2.2M/2.5m) becomes capital of the Mossi Kingdoms (Empire) (ends 1896).
About 1560 the Incas subdue the Indians of Chimu in N Peru, and build the "Lost City of the Incas", Machu Picchu (Quechua "Old Peak") (7,875 ft. alt.) in the Urubamba Valley 50 mi. NW of Cuzco, with the cool Temple of the Sun, Room of the Three Windows, and Intihuatana (Quechua "Sun Tier") Temple situated at the NSEW alignnment point of the nearby mountains; after the Spaniards conquer the Incas, the city is overgrown with jungle and lost until 1911; about this time the Incas attempt to invade Chile across the Atacama Desert, but are stopped at the Maule River.
In 1450 the city of Cajamarca (Kashamarka) (Quechua "town of thorns") (alt. 8,900 ft./2750m) (modern-day pop. 226K) is founded in the Mashcon River Valley in the the highlands of N Peru by the Incas, becoming the scene of the Battle of Cajamarca on Nov. 16, 1532, in which a Spanish force of 168 led by cruel conquistador Francisco Pizarro defeats Incan emperor Atahualpa and his 3K-8K retinue, going on to be colonized by the Spanish, becoming Peru's 13th largest city.


In 1457 Edo (Chiyoda) Castle is built by samurai warrior-poet Ota Dokan Sukenaga (1432-86) in the Edo clan town of Edo in SE Honshu Island, Japan; in 1603 Shogun Tokugawa Ieyasu makes it his HQ; in the 18th cent. the pop. tops 1M; in 1868 Emperor Meiji moves his capital there from Kyoto, renaming it Tokyo ("eastern capital"), renaming Edo Castle to Tokei Castle then Tokyo Castle, then Palace Castle, which is destroyed on the night of May 24/25, 1945 by an Allied firebombing raid, after which in 1948 the new Tokyo Imperial Palace is built.

In 1459 the city of Jodhpur in Mandore in modern-day Rajasthan, India (modern-day pop. 1.0M/1.4M) is founded by Rao Jodha (1416-89).
In spring 1463 the Ottoman Muslims under Mehmed II invade Bosnia, killing Catholic king Stefan Tomasevic and capturing the country (until 1878); on May 28 Mehmed II grants the Ahdname (Charter) of Milodraz to the Bosnian Fransciscans in which he regulates their relationship with the Roman Catholic Church represented by the Bosnian custos Andjeo (Angel) Zvizdovic; Mehmet II erases all evidence of Bosnian statehood, destroying all 500 of its castles and forts and executing its nobility, then later importing elite Sephardic Jews after they are expelled from Spain in 1492, who convert to Islam in exchange for titles of nobility (bey and agha); Sarajevo (Turk. "saray" = palace) (modern-day pop. 275K/395K) on the Miljacka River in the Sarajevo Valley of the Dinaric Alps is founded by the Ottomans, becoming the capital of Bosnia and Herzegovina; Mehmed II's Bosnian conquests scare the Venetians into taking him on to protect their Aegean and Adriatic coastal possessions, and they begin the First Ottoman-Venetian War (ends 1479), seizing Morea (Peloponnesus), while the Hungarians retake Bosnia, only to see the Muslims retake it next year.
In 1496 the city of Ciudad Trujillo, capital of La Española (modern-day Santo Domingo, capital of the Dominican Repub., pop. 955K/2.9M) is founded, with Columbus' son Diego as its first viceroy, becoming the oldest continuous European settlement in the Americas, the first seat of Spanish govt. in the West Indies, and the oldest cathedral and univ. in the New World.


On Aug. 15, 1511 after Christopher Columbus' son Diego sends an expedition commanded by Spanish conquistador Diego Velazquez de Cuellar (Velázquez de Cuéllar) (1465-1524) to conquer Cuba, he founds the city of Baracoa on the E tip (modern-day pop. 82K), becoming the oldest Spanish settlement in Cuba and its first capital, giving it the nickname "Ciudad Primada" (First City). On Aug. 25, 1514 the city of Havana (San Cristobal de la Habana) (modern-day pop. 2.1M) in Cuba on the Almendares River near the Straits of Floida is founded by Diego Velazquez de Cuellar, and named by Panfilo de Narvaez (Pánfilo de Narváez) (1470-1528); on Dec. 20, 1592 Philip II of Spain grants it city status; it is later officially designated "Key to the New World and Rampart of the West Indies". In 1515 the city of Santiago de Cuba (modern-day pop. 431K) is founded by Diego Valazquez de Cuellar as the capital of Cuba; next year it burns down, and is rebuilt.










In 1518 Diego de Velazquez is appointed gov. of Cuba by the king of Spain; he and Hernán (Hernan) Cortes (1485-1547) organize a military expedition to Mexico, with Cortes countermanding Velazquez's orders and following the coast of Yucatan, clashing with Indians in Tabasco and reaching San Juan de Ulua (Ulúa) on the Gulf of Mexico near modern-day Veracruz; the Tabasco natives give Cortes several hot women, incl. Malitzin (Doña Marina) (Malinche), a Mexican slave who speaks Mayan and Nahuatl and becomes his common-law wife and official interpreter. In Feb. 1519 Spanish conquistador Hernan Cortes (Hernán Cortés) (1485-1547) renounces the authority of Diego de Velazquez, relocates the city of Havana (from the Indian name Guanabacoa meaning "site of the waters") in Cuba to the N coast as a Spanish naval base (modern-day pop. 2.1M), then takes off with on 11 ships with 400-600 men (70 musketeers, 40 crossbowmen, and several hundred Indian and Cuban servants), incl. 2nd-in-command Pedro de Alvarado y Contreras (1495-1541) and chronicler Bernal Diaz del Castillo (1496-1584) for New Spain (Mexico), and on Apr. 21 he lands in Veracruz with his well-armed men, 16 horses, 14 pieces of artillery, and a big pair of balls, and founds the city of Villa Rica de la Veracruz (Vera Cruz) (Sp. "true cross") (modern-day pop. 520K/702K) in Mexico after burning his own ships to keep his men from returning to Cuba; after his soldiers elect him as chief magistrate and send reps to the crown for confirmation, Cortes leaves a small garrison then begins travelling through Aztec villages, finding altars piled with skulls and smelling of rotten blood mixed with flowers while sending envoys to Emperor Montezuma (Moctezuma) II (1480-1520, who is zapped out by the belief that these white dudes are gods and Cortes is pale-faced feathered-serpent man-god Quetzalcoatl (whose arrival is predicted by the Mayan priests this year after some lost Viking stumbled ashore long ago?), and avoids confrontation; Cortes gains support from the Totonacs, then ends up in 11K-ft. mountains where their clothing is inadequate, and several servants die, then crosses desert salt lakes without food and water, until he comes to the independent city of Tlaxcala, and faces 149K fierce warriors with obsidian clubs and spears, holding out for two weeks on a little hill until they suddenly give up, welcome him as a friend, and offer him their daughters, then offer to help him fight their worst enemies the Aztecs (Mexica); on Mar. 12 Cortes and his men arrive in Potonchan (Potonchán) on the left bank of the Grijalva (Tabasco River), finding them hostile, after which on Mar. 25 they win a V over the Aztecs at the Battle of Centla, where Diego de Ordaz (1480-1532) distinguishes himself, going on to climb 17,802 ft. (5,426m) Popocatepetl (Popocatépetl) in C Mexico 40 mi. SE of Mexico City with two comrades, becoming the first white Euros, impressing Cortes native allies, after which HRE Charles V authorizes Ordaz to pus the volcano on his coat of arms; after passing through the narrow streets of Cholula (known for its Great Pyramid) Cortez and his men meet fierce resistance, incl. rooftop ambushes, and kill 3K and sack it, the news reaching Montezuma, who says his heart is "washed in chilies" with grief; Cortes brings horses to the Am. mainland for the first time? Fun in the sun of Mexico NOT, or How 500 white men conquered 7M-30M red men suffering from auto-reverse racism, and reduced their pop. to 3M in 50 years? In Mar. 1520 displeased at the resistance of Hernan Cortes to his authority as gov. of Cuba, Diego Velazquez sends an expedition under Panfilo de Narvaez (Pánfilo de Narváez) (1470-1528) from Havana, which lands at San Juan de Ulua on Apr. 23 and captures Cempoala; in May Cortes leaves Tenochtitlan under the protection of Pedro de Alvarado and 200 men, then defeats Narvaez on May 26 and takes him prisoner at Vera Cruz, persuading his men to join him. Like a cheating husband who won't go away? In June 1520 Cortes returns to Tenochtitlan, where Montezuma II always gets a kick out of watching Spanish soldiers play cards, and observes Aztecs (Mexica) writing with lead crayons (pencils?), but this time the cocoa bean-bartering Aztecs have had it up to there with Cortes and his cruel lt. Alvarado, who attacked warriors during religious celebrations, and believing their king has lost his aura, on June 30 they stone Montezuma II while trying to persuade them to kiss white Spanish butt from the palace roof (he dies on July 3), then trap and cut off Alvarado and his men, destroy the three bridges leading out of the island city, and siege them, but Alvarado makes a portable bridge out of ceiling beams and sneaks out at midnight; too bad, he is spotted halfway across, saves his life by jumping over Alvarado's Leap in the causeway, and loses three-fourths (800) of his men killed or captured (later used for sacrifices to the war god) before escaping and regrouping with Cortes under a huge ceiba (silk-cotton) (kapok) tree in what becomes known as La Noche Triste (the Sad Night), in which Cortes sits under the tree and weeps; after making sure his shipbuilder Martin Lopez is still with him, he says, "Okay, let's go, for we lack nothing", and they head back to their race-traitor allies in Tlaxcala; meanwhile Montezuma II (b. 1479) is succeeded as Aztec king by his younger brother Cuitlahuac (Cuitláhuac) (1476-120), who prepares to finish Cortes off, but on July 7 Cortes kicks their butts in the Battle of Otumba, with 100K-200K Aztecs getting their butts kicked by 500 Spaniards and a few hundred Tlaxcalans, losing only 73 Spanish KIA; in late Sept. after a reign of 80 days Cuitlahuac dies of the smallpox, and is succeeded by Montezuma II's nephew Cuauhtemoc (Cuautehmóc) (Cuitlahuac) (d. 1521), the last Aztec ruler; Cortes returns to Tlaxcala, receives reinforcements, and ends up making Texcoco his base on Dec. 31 while he prepares to return with 600 men and tens of thousands of native allies, having a stroke of genius and building a fleet of 13 40-ft. brigantines on land, which he has disassembled to be hauled overland by 8K native porters back to Tenochitlan for a final siege. On May 26 1521 Hernan Cortes sieges Tenochtitlan, and on Aug. 13 he defeats the Aztecs after 80 days of starving the 250K pop. (a tactic unknown in their history?), reducing them to eating lizards and grass, capturing 800 women and children foraging at night for food, then taking the city street by street until the Aztecs, reeling from starvation, white man's measles and smallpox make their last stand at the stacked pyramid of Tlatelolco, sister city of Tenochtitlan to the N; the Aztec Empire (founded 1428) ends (7M-30M people torpedoed by a few hundred Satanists, er, Saints, er, Spaniards?), and the Spanish Empire in Am. begins with the forceful seizure of Mexico, which becomes known as New Spain (until 1821), with Cortes as viceroy #1 (until Dec. 24), followed by Cristobal (Cristóbal) de Tapia (until Dec. 30), followed by Cortes again (until Oct. 12, 1524) after Tapia clears him of misconduct; Cortez sees bison in Montezuma's menagerie; in 1524 Mexico City is founded on the razed ruins of Tenochititlan after the lake is filled-in by Aztec slaves; king #4 (since 1487) Cosijoeza (Cocijoeza) (-1529) of the nearby Zapotecs in SE Mexico hears of the Spanish V and decides to lay low to avoid the same fate, allying with the Mixtecs (Mixteca) in modern-day Oaxaca, Guerrero and Puebla, but that doesn't stop the Spanish from attacking them next year, and subduing them by 1527, the Zapotec bat god and Mixtec jaguar god proving impotent against Spanish cannon, firesticks, and biological warfare.

On Aug. 15, 1519 Pascual de Andagoya (1495-1548) founds the city of Panama City (modern-day pop. 880K) as the seat of govt. for Pedro Arias de Avila, bringing in 400 (later 1.5K) settlers, incl. Hernando de Soto; Avila refounds Nombre de Dios on the Alantic side, and clears a route across the isthmus; Panama City becomes the base for Spanish exploitation of the W coast of South Am., incl. the unfortunate Incas, whose treasure later flows in from the coast, is loaded onto mules, and transported over the jungle trail to Porto Bello on the Caribbean for loading onto Spanish galleons.
In 1524 Pedro de Alvarado founds the city of Guatemala City (modern-day pop. 2.9M) at the base of the Volcan del Agua ("Volcano of Water") (a volcano with a water-filled crater) in Valle de la Ermita (Hermitage Valley) as the capital of the Spanish capt.-generalcy of Guatemala, which incl. most of Central Am.; it becomes the capital of Guatemala in 1776.
On June 22, 1527 ater conquering the 4th cent. C.E. city of Sunda Kelapa from the Portuguese, Javanese Demak Sultanate gen. Fatahillah founds the city of Jakarta (originally Jayakarta) (modern-day pop. 9.6M/30.2M), which on Mar. 4, 1621 is taken over by the Dutch, who rename it Batavia; on Aug. 8, 1942 it is renamed Jakarta, becoming the 2nd largest urban agglomeration after Tokyo.
In 1528 the city of Oaxaca (pr. hwah-SAH-kah) (from the Nahuatal word "Huaxyacac", the native guaje tree) In SE Mexico (modern-day pop. 3.9M) (which started as an Aztec fort in 1486) is settled by the Dominicans, who form a bishopric in 1535; in 1535 HRE Charles V gives it a charter.
In 1532 the city of Guadalajara in the Antemarac Valley near the Rio Grande de Santiago 275 mi. W of Mexico City (modern-day pop. 1.5M/4.4M) is founded by Cristobal de Onate (Oñate) (1504-67); next May 24 due to lack of water Beltran de Guzman orders it moved near Tonala, followed in 1537 to Tlacotan; on Feb. 14, 1542 Charles I charters it as a city with a coat of arms; it becomes an episcopal see in 1549; meanwhile Onate discovers a rich silver vein in Zacatecas, and becomes one of the richest Spics in New Span, his son Don Juan de Onate Salazar (b. 1552) going on to become gov. of New Spain.

In 1533 Pedro de Heredia y Bernandez (1505-54) founds the city of Cartagena de Indias on the NW coast of South Am. between Darien and Santa Marta in modern-day Colombia (modern-day pop. 970K/1M) under direct royal authority.
In May 1533 the first three Spaniards arrive in the Incan city of Cuzco (Cusco) (elev. 11,200 ft./3,400m) (modern-day pop. 435K) (founded by the Killke people about 900) in SE Peru in the Urubamba Valley at the E end of the Knot of Cuzco, followed in Nov. by big bad Francisco Pizarro and his conquistadors, plundering the palaces and temples then rebuilding the city.

On Dec. 6, 1534 after Francisco Pizarro's on-the-make lt. (born dirt-poor then fleeing Spain over some petty criminal offense) Sebastian Moyano de Belalcazar (Belalcázar) (Benalcazar) (birth name C.J. Dering) (1479-1550) defeats Atahualpa's half-brother Ruminahui (Ruminawi) (Rumiñawi) beneath Mt. Chimborazo and establishes control in Quito (elev. 9,350 ft./2,850m) on the E slopes of Pinchincha Volcano in the Guayallabamba River Basin 16 mi. S of the equator (modern-day pop. 2.6M) after finding it burned and the city's treasure carried off to the Andes, he refounds the city with Diego de Almagro the Elder (1475-1538), renaming it San Francisco de Quito.
On Jan. 18, 1535 Francisco Pizarro (d. 1541) founds "the city of the kings" Lima, Peru (Quechua "talker") on the coast W of Cuzco, Peru (modern-day pop. 9.7M/12.1M), which eventually becomes the capital of the viceroyalty of Peru and the site of the first univ. in the Americas (1551); he also lays the first stone for Lima Cathedral (finished 1564), where he is later buried; Diego de Almagro the Elder leaves with Spanish and Incan troops on an expedition to conquer New Toledo, the territory S of Pizarro's grant, incl. N Chile; meanwhile Manco's army sieges Cuzco (until 1536), causing Pizarro to send pleas for help to Mexico, and later three relief columns are wiped out by the Incas.
In 1535 Portuguese traders obtain the right to anchor ships in the harbor of Macau (Chin. "Magang" = harbor of Mazo, goddess of sailors) on the Pearl River (modern-day pop. 650K); it takes until 1552-3 to obtain permission to erect storage sheds onshore, followed by crude stone houses in Nam Van, establishing a permanent settlement in 1557 for 550 taels/year of silver (1 tael = 41.6 lbs.), which they hold until 1999.
In 1535 Jacques Cartier makes his Second Voyage to North Am., taking the St. Lawrence River to visit the Canadian Indian settlement near Cape Diamond on Oct. 11, which in 1608 becomes the city of Quebec City (Algonquin "shut-in place, narrow passage, strait") (modern-day pop. 531K/800K). capital city of the French-speaking province of Quebec; he also visits an Indian settlement at the foot of Mount Royal, future site of Montreal.
In 1535 the city of Recife, Brazil is settled by the Portuguese (modern-day pop. 1.5M).


On Feb. 2, 1536 the city of Buenos Aires (Sp. "fair winds") (Our Lady St. Mary of the Good Winds) (modern-day pop. 2.9M/13.6M) in Argentina on the estuary of the Rio de la Plata is settled by Spanish conquistadors led by Pedro de Mendoza (1487-1537), who began colonizing the year before; Juan de Ayolas (-1537) and Domingo Martinez de Irala (1509-56) lead expeditions up the Parana and Paraguay Rivers in search of a route to Peru; after fighting the Guarani, crossing the Chaco to the Andes, and seizing some booty, Ayola is killed along with his whole co. by the Payagua; meanwhile de Irala escapes, and next year is elected capt. gen. of the Rio de la Plata by his men, going on to relocate the pop. of Buenos Aires to Asuncion in 1841 before the city is abandoned; in 1552 he is confirmed by Charles V as gov., building encomiendas and forcing the native pop. into them.
On June 27, 1536 Spanish gov. of Guatemala Pedro de Alvarado y Contreras (1495-1541) founds the city of San Pedro Sula in NW coastal Honduras (modern-day pop. 661K/1.45M), which goes on to become Honduras' 2nd largest city after Tegucigalpa.
On July 25, 1536 Pizarro's lt. Sebastian de Belalczar founds the city of Santiago de Cali (modern-day pop. 2M/5M), followed by Pasto (1537) (modern-day pop. 480K), and Popayan (Jan. 13, 1537) (modern-day pop. 439K) in the Cauca River Valley of SW Colombia (1536-7); Pizarro's men bring back the potato to Europe.

In 1536 Spanish conquistador Diego de Almagro the Elder (1475-1538) founds the city of Valparaiso (Valparaíso) in C Chile (modern-day pop. 284K/930K), named by his lt. Juan de Saavedra after his hometown Valparaiso de Arriba in Cuenca Province, Spain.
On Aug. 15, 1537 after hostile Guarani attacks cause Buenos Aires to be abandoned, and Juan de Salazar de Espinoza (Emiliano Gomez Suarez) (1508-60) to lead colonists up the Parana and Paraguay Rivers, they found the seaport of Asuncion (Asunción) on the Paraguay River (modern-day pop. 525K/2.2M); the site becomes the launching point for the Jesuits until they are expelled in 1767.
In 1537 after being ruled by the Western Gangas, Cholas, and Hoysalas since the 4th cent., the modern city of Bangalore in the S Indian state of Karnataka (modern-day pop. 8.7M/12.3M) is founded by Kempe Gowda I (1510-69), vassal of the Vijayanagara Empire, which falls in 1565, after which it changes hands several times until the British capture it in 1799 in the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War; in 2006 it is renamed Bengaluru, becoming known as "the Silicon Valley of India".
On July 25, 1538 Spanish conquistador Francisco de Orellana founds the city of (Santiago de) Guyaquil, Ecuador (modern-day pop. 3.5M/5M), then heads N, entering the Cauca River Valley in Colombia in search of the Big Score, AKA El Dorado - by the 20th cent. it turns out be, not golden powder, but white?

On Aug. 6, 1538 the city of Bogota (Bogotá) (Santa Fe de Bogota on the Bogota Plateau (modern-day pop. 8M/10M) s founded on the site of the Chibcha town of Bacata by Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jimenez de Quesada (1495-1576), who began moving up the Magdalena River in 1536 on a commission from the govt. of Santa Marta on the coast, defeating and sacking Chibcha chiefdoms along the way; he names the new city after his native town of Santa Fe.
On Nov. 30, 1538 the city of La Plata (Ciudad de la Plata de la Nueva Toledo) (modern-day Sucre) in SC Bolivia (modern-day pop. 30K) is founded by Pedro Anzures, Marques de Campo Redondo, becoming the home of the Roman Catholic metropolitan see of Bolivia.
On Feb. 12, 1541 after penetrating Chile's central valley, Pedro de Valdivia founds the city of Santiago (Del Nuevo Extremo) (modern-day pop. 7.3M); hostile Indians siege the settlement until reinforcements from Peru arrive in Dec. 1543; once the city is established, he dumps his babe Ines Suarez?
On Oct. 20, 1548 the city of La Paz (La Ciudad de Nuestra Senora de La Paz) (The City of Our Lady of Peace) in W Bolivia (modern-day pop. 877K/2.3M) is founded by Spanish conquistadors on the site of an earlier settlement.
In 1548 the town of Helsinki (Helsingfors) (originally Helsinge fors or Helsinge Rapids) in S Finland on the shore of the Gulf of Finland (modern-day pop. 642K/1.47M) is founded in Finland is founded in Forsby Village, and chartered by Gustav I of Sweden as a trading town to rival the Hanseatic city of Reval (Tallinn), which turns out to be a dud; in 1710 a plague almost wipes out the pop.; in 1809 after Russia annexes it as the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland it begins a resurgence, becoming known as "the Daughter of the Baltic"; in 1812 Russian Tsar Alexander I moves the capital of Finland there to reduce Swedish influence and bring it closer to St. Petersburg.
In 1549 the city of Bahia (modern-day Cidade do Sao Salvador da Bahia de Todos os Santos) (City of Holy Savior of All Saints Bay) (modern-day pop. 15M) in Brazil is founded by Thome de Souza (-1560); Brazil is made a royal colony by Portugal; a Roman Catholic see is founded there by Pope Julius III in 1551.
On Oct. 5, 1550 the seaport-river city of Concepcion (Concepción) Concepción de la Madre Santísima de la Luz (Conception of the Blessed Mother of Light) (modern-day pop. 292K/1.3M) is founded in the Bio-Bio region of SC Chile by Pedro de la Gasca and Pedro de Valdivia.
In 1550 Don Francisco de Urdinola (Urdiñola) the Elder (1498-), who later strikes it rich with the Bonanza Mine founds San Luis Potosi (Potosí) in C Mexico (modern-day pop. 2.7M) (see 1583); in 1592 gold and silver are discovered, and the town is named in honor of silver-rich Potosi, Bolivia.
On Jan. 25, 1554 Sao Paulo in SE Brazil (modern-day pop. 12M/21.2M) is founded by Jesuit missionaries Manuel da Nobrega and Jose de Anchieta on an Indian campsite 45 mi. from the coast.
On Mar. 2, 1561 the Spaniards under Pedro del Castillo reach Cuyo, Chile and found the city of Mendoza (Ciudad de Mendoza del Nuevo Valle de La Rioja) in W Argentina (modern-day pop. 115K/1M), named after Chile gov. Garcia Hurtado de Mendoza, utilizing the old Huarpe irrigation system.

In 1563 the city of Durango in NW Mexico (first settled in 1556) (modern-day pop. 1.75M) is founded by silver-seeking Basque explorer Capt. Francisco de Ibarra (1534-75), who names it after his native town in Biscay, Spain, facing immediate challenges from the indigenous pop., who make it difficult to settle there.


On Feb. 13, 1565 Spanish conquistador Miguel Lopez de Legazpi (1502-72) and his navigator (Augustinian friar) Andres de Urdaneta (1498-1568) arrive from Acapulco, New Spain (Mexico) in the Philippines and on June 24, 1571 after conquistador Miguel Lopez de Legazpi conquers it from the Muslims found the city of Manila on Manila Bay in the South China Sea (modern-day pop. 1.8M/12.8M); in July they discover a good route back to Acapulco, which becomes known as Urdaneta's Route, and Legazpi returns as royal gov. of the Philippines to establish the "China route" through the "Spice Islands"; Augustinian friars follow and become a force in the islands, later joined by other orders, incl. Franciscans, Jesuits, Dominicans, and Recollects; tequila (distilled agave nectar) begins to be exported from Mexico via the Camino Real through the Sierra Madre Mts.; galleons are built in Barra de Navidad for the route from Veracruz to Spain.
On Mar. 1, 1565 the city of Rio de Janeiro ("January River") (Sao Sebastiao do Rio de Janeiro) (modern-day pop. 6.4M/12.3M) in Brazil is founded, becoming a favorite target for French buccaneers and pirates; on Jan. 27, 1763 the colonial admin. of Portuguese Am. is moved there from Salvador, after which in 1808 the Portuguese royal family and nobles flee Napoleon's invasion of Portugal there.

On Aug. 28, 1565 after Florida (Fla.) is settled by French Huguenots, troops sent by Spanish King Philip II, led by adelantado adm. Pedro Menendez de Aviles (Menéndez de Avilés) (1519-74) found the Spanish city of St. Augustine (San Augustin) (modern-day pop. 14K), with the parish church run by Padre Lopez, and build the massive coastal fort Castillo de San Marcos, designed by Ignacio Daza; on Sept. 20 they capture Huguenot-held Ft. Caroline, and in Oct. wipe out a Huguenot relief force under Jean Ribault in the Mantanzas Inlet, hanging their bodies with the legend "Not as Frenchmen but Lutherans"; the Spanish go on to build presidios and posts across the area and support the establishment of missions by Jesuits and Franciscans as far N as Va.
On Mar. 28, 1566 Hospitaller grandmaster Jean Parisot de la Valette founds the city of Valletta (modern-day pop. 6.4K) in Malta on the slopes of Mount Sciberras near Ft. St. Elmo, which held out to the Turks for 30 days; the city goes on to become known as "Superbissima" (Most Proud) as it holds out against pesky Muslims.

In 1567 Caracas (Santiago de Leon de Caracas) (modern-day pop. 1.9M/2.9M) in Venezuela is founded on July 25 by Diego de Losada (1611-69) in a fertile Caracas Valley 3K ft. above sea level (6 mi. SE of the Caribbean port of La Guaira) (in the crack of the valley's what?), becoming the first important settlement in Venezuela.

On July 6, 1573 after being appointed corregidor of Potosi, Peru in 1571, and commissioned by the gov. of Tucuman Province to explore NW Argentina, leaving Santiago del Estero last year with 100 men and 40 supply wagons, the city of Cordoba (Córdoba), Argentina on the Suquia River in the foothills of the Sierras Chicas Mts. 250 mi. S of Santiago de Estero and 435 mi. NW of Buenos Aires (modern-day pop. 1.3M/1.5M) is founded by Spanish conquistador Jeronimo (Jerónimo) Luis de Cabrera (1528-74), who names it after his wife's birthplace of Cordoba, Spain.
In 1573 after galleons began arriving there from Asia in 1550, causing 30 Spanish families to move there to establish a permanent base, building a port and a road to Mexico City in 1531, and the Marques Wharf between Bruja Point and Diamond Point in 1533, Spanish king Philip II declares the port city of Acapulco, Mexico (Nahuatl "Acapolco" = where the reeds are washed away) (modern-day pop. 687K) the official trading port of the Manila galleons in America, with a trading monopoly; the W end of the route in the Philippines is named Capul.

On Jan. 25, 1576 attracted by the silver mines of Cambambe, the Portuguese colonize Angola in Africa, and found the port city of Luanda (São Paulo da Assunção de Loanda) (modern-day pop. 2.8M) with 400 settlers (100 families) and 400 soldiers under Paulo Dias de Novais (1510-89) - luanda take a little boat trip?
In 1583 Mughal emperor Akbar the Great changes the name of the N Indian city of Prayag in Uttar Pradesh at the confluence of the Ganges and Yamuna Rivers (where Brahma allegedly offered his first sacrifice after creating the world) to Allahabad (City of Allah) (modern-day pop. 1.1M/1.2M).
In 1586 the city of Kuybyshev (Samara) in Russia on the Volga River (modern-day pop. 1.1M) is founded.
In 1589 the city of Hyderabad in Golconda, India, 400 mi. SE of Bombay (modern-day pop. 6.8M/7.7M) is founded by Kutb Shahi king Mohammed Kuli as the capital.
In 1589 the city of Volgograd (originally Tsaritsyn) is founded at the confluence of the Tsaritsa and Volga Rivers near the unstable S border of Russia; in 1925-61 it is renamed Stalingrad, becoming the scene of the surrender of the German Sixth Army in WWII after the largest and bloodiest battle in history (until ?); in 1961 it is renamed Volgograd.

In 1591 Qutb Shahi sultan #5 (1580-1611) Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah (1565-1612) establishes the city of Hyderabad (originally Baghnagar = city of gardens) on the S bank of the Musi River in SC India (modern-day pop. 6.8M/7.7M) to extend the fortified capital of Golconda, named after Quli Qutb's dancing girl babe Bhagmati, who converted to Islam under the name Hyder Mahal; it is laid out in a grid plan; it goes on to become known as "the City of Pearls" as well as a diamond trading center; in 1687 it is annexed by the Mughals.
On Sept. 20, 1596 the city of Monterrey (Ciudad Metropolitana de Nuestra Señora de Monterrey) in the foothills of the Sierra Madre Mts. in NE Mexico (modern-day pop. 1.1M) is founded by new gov. #1 Diego de Montemayor (1530-1610) as the capital of the state of Nuevo Leon (Sp. "New Lion").
In 1600 daimyo Date Masamune (1567-1636), "the One-Eyed Dragon", known for his crescent-moon-bearing helmet abandons his stronghold of Iwadeyama for better digs (easier access to Edo) and founds the city of Sendai on Honshu Island (modern-day pop. 1.806M), changing its kanji from "a thousand generations" to "immortal hermit on a mountain", and building Sendai (Aoba) Castle in Dec.; it goes on to become known as "the City of Trees" for its zelkova trees, becoming the 2nd largest Japanese city N of Tokyo.
In 1606 Mannheim in SW Germany at the confluence of the Rhine and Neckar Rivers (10 mi. W of Heidelberg) (modern-day pop. 305K) is turned from a village (first mentioned in 764) to a major town by Frederick IV, elector palatine of the Rhine, becoming a mecca for Protestant refugees from Holland.
On Sept. 14, 1607 Irish rebel leader Hugh O'Neill, 2nd earl of Tyrone, fearing arrest for attempted insurrection for a new intrigue flees Ulster to Spanish-controlled Flanders with a boatload of 90 Irish noblemen incl. Rory O'Donnell, 1st earl of Tyrconnell in the Flight of the Earls, ending the era of tribalism in Ireland; using the ancient feud between the earls of Tyrone and Tyrconnell as a pretext, James I confiscates O'Neill's lands, along with the land in six counties of N Ulster, then creates 40 fake boroughs from small hamlets to give the English crown a permanent majority in the Irish Parliament; James I then gives the land in Northern Ireland to English and Scottish Protestants, who found the Plantation of Ulster in 1609, which eventually leads to a Protestant majority there, incl. in the ancient city of Belfast (Gael. "Beal Feirsde" = mouth of the sandbar or tidal river ford) on the Lagan River (modern-day pop. 333K/672K), which is granted city status in 1888, becoming known as "Linenopolis" for its linen industry, as well as shipbuilding industry, which builds RMS Titanic, going on to be equally split in the 20th cent. between Roman Catholic and Protestant pops. in eternal religious war; meanwhile James I proposes the Union of England and Scotland on equal terms, but is rejected by the English Parliament - pass the poteen, I think I need it?
In 1608 the city of Dacca (Dhaka) ("watchtower"?) on the E bank of the Buriganga River in the Bengal Delta in SE India (modern-day pop. 14.4M/18.8M) is founded by the Mughal Empire as the capital of its Bengal Province (until 1639, then 1660-1704), going under the name Jahangir Nagar in the 17th cent., going on to develop a Muslim-majority pop. that wars with the Hindu-majority pop. of Calcutta, becoming known as the City of Mosques, and Venice of the East; in 1947 it is granted city status; in 1947 it becomes the admin. capital of East Pakistan, followed by the legislative capital of Pakistan in 1962, and capital of Bangladesh in 1971; in 1983 the spelling is changed to Dhaka.
In 1614 a group of Dutch colonists led by Capt. Hendrick Christiaensen (-16169) founds Ft. Nassau (van Nassouwen) in New Netherland on the ruins of an old French fur trader fort on Castle Island on the W bank of the Hudson River 10 mi. S of its confluence with the Mohawk River opposite the site of modern-day Albany, N.Y. (modern-day pop. 98K/1.2M), becoming the first Dutch settlement in North Am., followed in 1624 by Ft. Orange on the W bank of the Hudson River, engaging in fur trade with the Mahicans and Mohawks, causing more settlers to found the village of Beverwijck (Beverwyck) nearby to the N on the future site of Albany; in 1664 the English take over, renaming the city in honor of the Duke of Albany, future James II of England, officially chartering it in 1686; in 1797 it becomes the capital of N.Y. state; it goes on to become the longest continuously-chartered U.S. city.
The long-awaited Promised Land for International Jewry? In 1614 after setting out late in 1613 to New York harbor in the Tijger (Tiger), Dutch navigator Adriaen (Aerjan) Block (1567-1627) anchors in the harbor, his ship burns, and he and his crew camp on Manhattan Island, where they build the Onrust (Restless), then explore Long Island Sound N beyond Cape Cod, discovering the Connecticut River and Block Island (9 mi. SW of Point Judith, Rhode Island); he claims Connecticut (Conn.) (Algonquin "Quinnehtukqut" = "beside the long tidal river") for the Netherlands, and names it Rhode Island (R.I.) for its red clay; he later pub. Figurative Map of 1614, the first to show Manhattan Island as separate from Long Island; in 1623 fur traders from New Amsterdam set up Ft. Goede Hoop (Ft. Good Hope) at the confluence of the Connecticut and Park Rivers, which is abandoned in 1654, after which English settlers begin arriving in 1637, founding Newtown, which soon becomes Hartford, Conn. (modern-day pop. 124K/1.4M), named after Hertford, England; it is incorporated as a city in 1784, and consolidated in 1896; the city seal depicts a male hart (deer) crossing a you know what.
In 1614 the city of Tirana, Albania in C Albania 19 mi. E of Durres, 95 mi. SW of Skopje, 82 mi. SE of Podgorica, and 310 mi. N of Athens (modern-day pop. 860K) is founded by Sulejman Pasha Bargini as the site of a market, Turkish bath, and mosque, going on to become the cultural hub and seat of govt. in Albania; in 1912 after Albania declares independence, it becomes the capital.
In 1619 after deciding to turn the Dutch warehouses into a fort, and allowing the English to take the town while he's away on an expedition, Dutch East India Co. gov.-gen. Jan Pieterszoon Coen reconquers Jakarta but burns it down in the process, rebuilding it and founding Batavia (modern-day Jakarta) in Java (modern-day pop. 33.4M/10.7M), which becomes HQ of the spice-is-nice Dutch East India Co. (VOC); he tries unsuccessfully to get the town named Nieuw Hoorn after his hometown, and also tries unsuccessfully to dig canals there like in Amsterdam.
In 1624 the town of Duxbury, Mass. (originally Duxborough) (modern-day pop. 15.5K) on the South Shore near Plymouth is founded by Capt. Myles Standish, William and Love Brewster, John Alden and Priscilla et al., named after his family's Duxbury Manor in Lancashire; it starts out as a farming community then in the 19th cent. becomes a shipbuilding center, and by the 1870s a tourist mecca; in 1638 Myles Standish Burial Ground is founded there.


On Mar. 22, 1630 (Apr. 7?) 700-odd (400-odd?) Massachusetts Bay Colonists seeking to escape the Thirty Years' War and its economic slump sail in seven ships from Southampton, England for North Am.; Arabella carries John Winthrop (1588-1649) and the charter; en route John Winthrop delivers the sermon Model of Christian Charity, exhorting good Puritans to be like a "City Upon a Hill" and work to construct a Bible-thumping theocratic society in America that will "shame the faces of many of God's worthy servants", else face God's wrath, shaping American politics seemingly forever (until ?); after landing at Salem, Mass. on June 25, on Sept. 17 (Sat. Old Style) (Tues. New Style) they found the town of Boston (formerly Shawmut) (modern-day pop. 4.2M/4.6M) on the 800-acre Shawmut Peninsula surrounded by tidal marshes, deeply indented by coves, creeks and inlets, and dominated by three hills, with a narrow 1-mi.-long frequently-submerged neck joining it with the mainland; a few mo. earlier the town of Dorchester, Mass. near Boston (modern-day pop. 92K) is founded by English Puritan settler Israel Stoughton (1602-45) (remote ancestor of U.S. pres. FDR) et al. from Dorchester, Dorset, England; John Endicott (Endecott) (1588-1665) becomes gov. #1 of the Mass. Bay Colony, with capital at Charlestown, Mass. (originally Mishawum) on the Mystic River; the first law against gambling in Britsh North Am. is enacted; over the next few cents. the area is gradually filled in, increasing it to 1.8K acres; Medford, Mass. (originally Mistik) is founded as part of Charlestown; John Winthrop (gov. #1 of Mass. Bay Colony) begins keeping a Journal; on Nov. 9 the Boston-Charleston Ferry opens, starting at Noddle's Island, where English Anglican settler Samuel Maverick (1602-70) buys black slaves in 1638, becoming one of the earliest slave owners in Mass.; by the end of the year 17 more ships with another 1K colonists arrive, and by 1642 16K more follow; over 80K colonists leave England for greener pastures (New World, Ireland, Netherlands, Rhineland) in the Great Puritan Migration in this decade (1620-40), mostly Puritans fleeing Charles I for the Mass. Bay Colony, many of them as indentured servants; by 1640 20K settle in Mass. Bay Colony, and 55K total go to the New World, half settling in New England; the total pop. of the Am. colonies this year is only 4.6K; 35 mi. x 1 mi. Newtown (Newe Towne) (New City) is founded in Mass. on the N side of the Charles River opposite Boston 10 years after the Pilgrims land at Plymouth Rock; in 1638 it changes its name to Cambridge, Mass. (modern-day pop. 110K), becoming a univ. town.; it is later subdivided to form the additional towns of Newton (1691), Lexington (1713), Brighton (1837), and Arlington (1846).
In 1632 the city of Portland, Maine (modern-day pop. 66K/519K) is settled as the fishing village of Casco on Casco Bay, which is taken over by the Mass. Bay Colony in 1658 and changes its name to Falmouth, which is destroyed by the Abenaki in 1676 during King Philip's War, then destroyed again by French and Indian allies in the 1690 Battle of Fort Loyal, then burned down by the British Royal Navy on Oct. 18, 1775; in 1786 it is refounded as Portland, named after the Isle of Portland off the coast of Dorset, England; in 1820 Maine becomes a U.S. state, with Portland as its capital until 1832, when it is moved N to Augusta; in 1851 Maine becomes the first state to pass a prohibition law, leading to the Portland Rum Riot on June 2, 1855; Portland, Ore. is later named after it.

In 1634 French explorer Jean Nicolet (1598-1642) crosses Lake Michigan and lands at Green Bay (originally La Baie des Puants, "Bay of Stinking Waters") (modern-day pop. 104K/312K), home of the Menominee and Winnebago (Ho-Chunk) people to explore the region; expecting Chinese, he dresses in bright-colored flowery Chinese robes; the city grows up at the mouth of the Fox River 112 mi. N of Milwaukee, Wisc.
On Aug. 22, 1639 Francis Day (1605-73) of the British East India Co. (which is still smarting from their boinging at Amboina in 1623) acquires a trading station in Madras (Chennai) on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal in SE India (modern-day pop. 7M/8.9M), with permission from the local nayak Damerla Venkatapathy to build a factory and warehouse.
In 1639 the city of (The) Bronx, N.Y., NE of the Harlem River on the Bronx River (modern-day pop. 1.4M) is settled by Swedish immigrant Jonas (Jonasson) (Jonassne) Bronck (Bronk) (Brunk) (1600-43), who builds the Emmanus farm.
In 1639 Shah Jahan erects the walled city of Old Delhi (the Red Fort) (Shahjahanabad), becoming the 6th Delhi city.
In 1639 Newport, R.I. (modern-day pop. 25K) is founded on Aquidneck Island, becoming a main base for Baptists in 1640 and Jews in 1658, followed by more Portuguese Jews in 1745, who make the manufacture of sperm oil and candles its main industry, making the town rich; in 1663 the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations receives a royal charter, with capital at Newport, and Benedict Arnold as gov. #1; in the 19th cent. it attracts millionaires who set up summer mansions, with elaborate ballrooms and chandeliers spraying perfume; during the admins. of U.S. presidents Dwight D. Eisenhower and John F. Kennedy it hosts Summer White Houses.
In 1639 the city of Ulan Bator (Ulaan Baatar) (Mongolian "red hero") (original name Urga) (modern-day pop. 1.37M) in NC Mongolia on the confluence of the Tuul and Selbe Rivers is founded as a nomadic Buddhist monastic center.

On May 17, 1642 the city of Montreal (originally Ville-Marie) in SW Quebec, Canada at the foot of Mount Royal on the S shore of Montreal Island in the St. Lawrence River (modern-day pop. 1.7M/3.5M) is founded by a group of French colonists led by Paul de Chomedey, Sieur de Maisonneuve (1612-76) on the site of an Iroquois encampment; too bad, the Iroquois don't like it, and begin attacking it, reducing the pop. to 50 by 1653 when 100 volunteers arrive to save it, after which the pop. rises to 600 by 1685, living mainly by the fur trade.
In 1642 the town of Lexington, Mass. (modern-day pop. 31K) is first settled as part of Cambridge, Mass., and incorporated in 1691 under the name Cambridge Farms, then reincorporated as an independent town in 1713 under the name Lexington, becoming the breadbasket of Boston, gaining fame for the first shots of the Am. Rev. War in the Battle of Lexington on Apr. 19, 1775; in 1846 the Lexington and West Cambridge Railroad reaches it, boosting pop.
In 1642 French missionaries hold services for 2K Ojibwas at the NE end of Michigan's Upper Peninsula on the U.S.-Canada border 346 mi. from Detroit on the future site of the city of Sault Sainte Marie, Mich. (Fr. "St. Mary's Falls") (modern-day pop. 14K), giving the French dibs to the area; twin city Sault Sainte Marie, Ontario on the other side of the St. Marys River (modern-day pop. 73K) is separated after the War of 1812 establishes the border at the river.
In 1645 Dahomey king (since 1620) Dakodonou dies, and his nephew Aho Houegbadja (-1685) becomes king #3 of Dahomey in W Africa (until 1685), founding the capital city of Abomey (Agbome) ("middle of the ramparts") near Guedevi (modern-day pop. 90K).
In 1645 the city of Brooklyn (Dutch "Breuckelen" = marshland) on the East River at the SW end of Long Island in New Amsterdam (modern-day pop. 2.6M), named after the town of Breukelen near Utrecht is founded near the modern-day borough hall; on Jan. 1, 1898 it is merged into the City of New York as one of five boroughs, although as a city it becomes the 3rd most populous city in the U.S. after Los Angeles, Calif. and Chicago, Ill.

On Apr. 6, 1652 three ships of strict Calvinist Dutch settlers led by Johan Anthoniszoon "Jan" van Riebeeck (1619-77) of the Dutch East India Co. arrive in Table Bay (beneath Table Mountain) at the N end of the Cape of Good Hope in SW South Africa, and found Cape Colony and Cape Town (Kapstaad) (modern-day pop. 433K/4M) as a Dutch East India Co. supply station; their descendants become known as Boers ("farmers"); the Dutch dialect in this isolated area begins to absorb words from French, German, Scandinavian, and Malay-Portuguese, evolving into the Afrikaans language.

In 1653 the city of Kingston, N.Y. 91 mi. N of New Amsterdam (modern-day pop. 23K/177K) is settled by Dutchman Thomas Chambers from Rensselaerswyck under the name Esopus, and in 1661 Peter Stuyvesant grants it a charter under the name Wiltwyck, becoming one of three large Hudson River settlements in New Netherland after Beverwyck (Albany) and New Amsterdam (New York City); in 1664 the British seize New Netherland; in 1669 is is renamed Kingston in honor of the family seat of the mother of New York gov. #2 (1668-73) Francis Lovelace (1621-75); 1777 it becomes New York's first capital before being burned by the British on Oct. 13, 1777; in the 19th cent. natural cement is discovered, turning it into a major transport hub.
In 1654 the city of Kharkhiv (Kharkov) ("kharka" = swan) in NE Ukraine (modern-day pop. 1.4M/1.7M) is founded as an outpost of Moscow, becoming the 2nd largest city in Ukraine.
In 1661 the Swedes establish a fortress colony in Christiansborg on the Gold Coast near modern-day Accra ("soldier ants") (modern-day pop. 1.6M/2.0M) in Ghana, which ships slaves, ivory, and gold to Europe in exchange for liquor and cowrie shells to buy them with, and weapons and gunpower to enforce the deals.
In 1661 the first Western reference to the 2nd cent. C.E. city of Kathmandu ("kastha" + "mandap" = wood + covered shelter) (modern-day pop. 1.4M/2.5M) by Jesuit travelers Johann Grueber and Albet d'Orville en route from Tibet to India; in Sept. 1768 the Battle of Kathmandu sees King Jaya Prakash Malla defeated by Gorhka king Prithvi Narayan Shah, ending the Gorkha Kingdom (begun 1559) and founding the Shah Dynasty in Nepal (ends May 28, 2008), with capital in Kathmandu.
In Jan. 1664 the Second Anglo-Dutch War (ends 1667) is started by the Earl of Clarendon; on May 25 Duke James II of York (eventual successor Charles II) sends an expedition of 300 troops from Portsmouth to capture New Netherlands from Connecticut to Delaware, incl. Ft. Orange, renaming it Albany; on Sept. 8 they capture New Amsterdam from the Dutch, who surrender it peacefully, renaming it New York City (modern-day pop. 8.5M/23M) after the Duke of York (both the city and the province), with Richard Nicolls (1624-72), groom of the duke's bedchamber as British gov. #1 (until 1672); the region of Pennsylvania is captured along with it; Charles II also grants the province of Maine (named after the French province, or because the mainland is distinct from its many coastal islands?) to the the Duke of York, who grants the province of New Jersey (named after Carteret's native island of Jersey, or Nova Caesaria) to Sir George Carteret and Lord John Berkeley (brother of the gov. of Va.); after the surrender Dutch gov. of New Holland Peter Stuyvesant goes to Holland for debriefing, then returns, spending the rest of his life cultivating his large farm called the Bouwerij (Bowery) in Manhattan (Algonquian word for island?) (until 1672).
In 1666 the modern-day city of Newark (New Ark of the Covenant) on the Passaic River in the New Jersey Colony (modern-day pop. 277K) is founded by Connecticut Puritans led by Robert Treat (1622-1710); on Oct. 31, 1693 it is reorganized as a township, and granted a royal charter on Apr. 27, 1713, then incorporated on Feb. 21, 1798; on Apr. 11, 1836 is is incorporated as a city.
In 1670 South Carolina (originally the Province of Carolina) is finally settled by English Puritans from Bermuda at Albemarle Point on the W bank of the Ashley River, who find poor soil conditions and found the city of Charles Town (Charlestown) (named after Charles II) (modern-day pop. 120K/744K) a few mi. SE between the Ashley and Cooper Rivers.
On Nov. 2, 1675 the city of Medellin (Medellín) (Villa de Nuestra Señora de la Candelaria de Medellín) in NW C Colombia (modern-day pop. 2.4M/3.7M) is founded by queen consort Mariana of Austria.
In 1677 France takes the island of Goree (Gorée) (Dutch "Goedereede" = good roadstead) off the coast of Cape Verde Peninsula from the Portuguese, becoming the start of the city of Dakar, Senegal (modern-day pop. 1.1M/2.4M), westernmost city on the African mainland and the Old World.

The Indians finally yuck it up on the Conquistadors? On Aug. 10, 1680 after a decade of drought, white man's diseases, and suppression of their medicine men, the Pueblo (Po'pay's) (Pope's) (Popé's) Revolt (ends 1692) begins in the Pueblo of Isleta in New Mexico 13 mi. S of Albuquerque against the Spanish, led by pagan Tewa religious leader Po'pay Pope (Popé) (1630-88) ("pumpkin mountain"), who stages a blitzkrieg attack, killing 380 Spaniards, incl. 21 of 40 Franciscans, followed by a siege of Santa Fe, causing Spanish settlers to flee S on Aug. 21 to El Paso del Norte (until 1691), closing El Camino Real and becoming the most successful Indian revolt in history, after which Po'pay sets himself up in the governor's palace and orders all vestiges of Roman Catholicism destroyed, washing Catholic converts in yucca juice to get rid of the yucky white man's stink; El Paso (modern-day pop. 650K/1M) is founded near El Paso del Norte (modern-day Ciudad Juarez) as a temporary capital of the New Mexico territory until Santa Fe is reconquered in 1692, remaining the largest settlement in N.M. until 1848, when it becomes part of Tex., after whch it is incorporated in 1873; meanwhile in 1682 Spanish fugitives from the revolt, joined by Tigua (Tiwa) Indians found La Purisima del Socorro Mission (Nuestra Senora de la Concepcion del Soccoro) halfway between Santa Fe and El Paso, waiting for the various Pueblo tribes to begin infighting and play into their hands, and Spanish fugitives found the Ysleta Mission in El Paso.
The first planned American housing development? On Feb. 2, 1683 the Penn. Gen. Assembly rejects the First Frame of Government, and adopts the Second Frame of Government as their constitution, passing "at least seventy laws without one dissent" (William Penn); William Penn sets up a provincial postal system; on Oct. 6 13 families from Krefeld, Germany on the Rhine River (founded 1105) (one of the few towns spared the horrors of the Thirty Years' War of 1618-48, causing it to become overpopulated, unlike its sister town Uerdingen, which was almost wiped out) found Germantown (modern-day pop. 76K); meanwhile William Penn learns the Delaware language (how?), and in Oct. enters into a Treaty of Perpetual Friendship with the Lenni-Lenape tribe of the Delaware River Valley under Tammany (Tamanend) (Tamanent) (Tamine) (1628-98) ("affable") while standing under Treaty Oak tree in Shakamaxon (Kensington, later part of Philadelphia), which lasts 50 years after Tammany utters the soundbyte that they would "live in peace as long as the waters run in the rivers and creeks and as long as the stars and moon endure" (a fairy tale?); Penn then allegedly sights the city of Dover, Del., and the planned city of Philadelphia, Penn. (Philly) (Gr. "brotherly love") (modern-day pop. 1.56M/6M), founded last Oct. 27 1 mi. from Shackamaxon at the junction of the Delaware and Schuylkill ("hidden channel") (pr. SKOOL-kuhl) Rivers in SE Penn., becoming the first city in North Am. with public parks?; it is incorporated on Oct. 25, 1701; land is purchased from the Lenape by William Penn that later becomes Abington Township, Penn. N of Philly - so what's your tire size?
In 1686 the city of Poughkeepsie (Wappinger "U-puku-ipi-sing" = reed-covered lodge by the little water-place) in the Hudson River Valley midway between Albany and New York City (modern-day pop. 30K/423K) is purchased from the Wappinger Indians by Englishman Robert Sanders and Dutchman Myndert Harmense Van Den Bogaerdt, and settled by the Dutch, who found the Reformed Church of Poughkeepsie in 1720, and incorporate it as a town on Mar. 27, 1799; it is chartered as a city on Mar. 28, 1854, becoming the 2nd capital of N.Y. during the Am. Rev., hosting the U.S. constitution ratification convention for N.Y. and becoming the county seat of Dutchess County, known as "the Queen City of the Hudson".
On June 7, 1692 an earthquake strikes Jamaica, causing the capital city Port Royal to disappear in the sea; on June 24 the new capital city of Kingston (originally Sunda Kelapa) on the SE coast of Jamaica (modern-day pop. 662K) is founded as a haven for refugees from the earthquake, going on to become the largest city in Jamaica and the largest English-speaking city S of the U.S.

In 1698 Md. gov. (since 1694) Francis Nicholson (1655-1728) returns from Md. to Va., becoming lt. gov. (until 1705), moving the capital from Jamestown to Middle Plantation between the James and York Rivers (founded 1632), which is renamed Williamsburg (modern-day pop. 14), becoming capital of the Colony and Commonwealth of Va. until 1780.
In 1698 the city of Pensacola, Fla. (modern-day pop. 53K/461K) in the W Fla. Panhandle on Pensacola Bay, protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa that connects to the Gulf of Mexico is founded by the Spanish as a presidio, named after the Muskogean-speaking Pensacola tribe, going on to be nicknamed "the City of Five Flags" (Spain, France, Great Britain, U.S., Confed. States of Am.), "America's First Settlement", and "Emerald Coast"; in 1913 the Naval Air Station Pensacola is founded, becoming the first in the U.S., giving the city the nickname "Cradle of Naval Aviation"; it goes on to become known for "the world's whitest beaches", and "the red snapper capital of the world".

In 1698 as part of their campaign to expand S, Vietnamese gen. Nguyen Huu Canh (1650-1700) is sent by sea by the Nguyen rulers of Hue to detach the area around Saigon ("firewood/cotton stick/palisade") (modern-day pop. 8.4M) from Cambodia, turning it into a major city; on July 2, 1976 it is renamed Ho Chi Minh City.


In 1699 French colonizers (from Montreal) Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne, Sieur de Bienville (1680-1767) and his older brother Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (1661-1706) sight an Indian portage to Lake Ponchartrain and the Gulf of Mexico, and found the first European settlement in La. at Ft. Maurepas (modern-day Ocean Springs, Miss., pop. 17.4K); the Quapaw ("downstream") (AKA Arkansas) Sioux Indian tribe allies with them; meanwhile Iberville lands in Ships Island then founds Biloxi, Mississippi (modern-day pop. 45K), exploring the Mississippi Gulf Coast; the first Mardi Gras (Shrove Tuesday) is celebrated on the Mississippi River.
On Sept. 6, 1700 the town of Mount Kisco, N.Y. on the Kisco River in modern-day Westchester County (Munsee "asiskuw" = mud") (modern-day pop. 10.8K) is first mentioned, becoming the home of New York Times pub. Arthur Ochs Sulzberger Jr., Walt Disney CEO Michael Eisner, TV personalities Bennett Cerf and Arlene Francis, and composer Samuel Barber.

Detroit really is the original home of Cadillac? On July 24, 1701 French king Louis XIV gives permission for the settlement of Detroit (Fr. "le Detroit" = the Straits) (modern-day pop. 3.7M/5.3MM), originally Fort Pontchartrain du Detroit (Détroit) to ever-broke Gascony, France-born explorer and scoundrel Antoine Laumet de La Mothe, Sieur de Cadillac (1658-1730) on a peninsula joining Lake Huron and Lake Erie to control Illinois trade; the settlement is begun in July; Cadillac arrived from France at Point Royal in 1683, added "de La Mothe Cadillac" to his name after Cadillac in SW France,, and spent four years exploring the New World down to the Carolinas, getting a promotion to cmdr. of Fort de Buade (Michilimackinac) (near modern-day St. Ignace, Mich.) in 1694, exploring the Great Lakes in 1695 until he got into trouble for selling alcohol to the Indians and returned to Montreal in 1696, traveling back to France in 1697 to talk them into building Fort Pontchartrait on the straits; too bad, it burns down in 1703, and he returns to Quebec, getting charged with trafficking in alcohol and furs, taking until 1708 to clear his name, after which in 1710 he is appointed gov. of Louisiana, founding Mine La Motte in modern-day Madison County, Mo., the first lead mine in Missouri, worked by the first African slaves in Mo.; in 1716 he is fired, and returns to France in 1717, gaining an undeserved rep as a hero until the 1950s; Detroit is incorporated on Sept. 13, 1806.
In 1701 Philadelphia, Penn. at the junction of the Delaware and Schuylkill Rivers (modern-day pop. 2M/5M) is first chartered as a city (rechartered in 1789).


In 1702 Alabama (Ala.) (Muskogee "town") (named after the Alabama or Alibamon tribe of the Creek confederacy) is founded at Ft. Louis de la Louisiane on the Mobile River by French Canadian brothers Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (1661-1706) and Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne, Sieur de Bienville (1680-1767), becoming the site of the city of Mobile, Ala. (modern-day pop. 195K/619K), which is incorporated as a town on Jan. 20, 1814 and as a city on Dec. 17, 1819.





On May 1, 1703 the Russians take Nienshanz Fortress at the mouth of the Neva River, and drive the Swedes from the Neva Delta, then seize Noteburg and rename it Schlusselburg; on May 16 Tsar (1682-1721) Peter I the Great (1672-1725) pissed-off at his Moscow nobles failing to become kulturny and adopt Western culture, officially founds St. Petersburg (modern-day pop. 5.3M) on the banks of the Neva River on territory he just took from Sweden as Russia's "Window on the West", and builds the Fortress of St. Peter and St. Paul on a small island in the river in On May 27, 1703-1740, designed by Swiss Italian architect Domenico Trezzini (1670-1734), who goes on to design Kronstadt (1704) on Kotlin Island 19 mi. W of St. Petersburg, St. Peter and St. Paul Cathedral (1712-33) (world's tallest Orthodox Catholic bell tower), Peter the Great's Summer House (1710-14), the Alexander Nevsky Monastery (1710-13), / and the Twelve Collegia (Colleges) Bldg. Complex (1722-44) (main bldg. of St. Petersburg U.), founding Petrine Baroque, which departs from the Naryshin Baroque of Moscow and follows the Dutch, Danish, and Swedish styles; his architect son Pietro has Peter I the Great as a godfather; "A giant built it; lacking stones/ "He paved the swamps with human bones" (Mikhail Dmitriev); this year 8-y.-o. black African slave Abraham (Ibrahim) Petrovich Gannibal (Hannibal) (1696-1781), who claims he was kidnapped from a royal tribal family in Africa is presented by a Russian diplomat as a gift to Peter I the Great, becoming his adopted son, and rising quickly to a 5-language linguist, civil engineer, diploma,t and gen. (Europe's first black intellectual?) - so cute everybody should own one?

On Feb. 7, 1706 new viceroy of New Spain (since Nov. 27, 1702) Francisco Fernandez de la Cueva (Cuervo) Enriquez, Marques de Cuellar, 10th Duke of Alburquerque (1666-1724) founds the villa of Albuquerque (Villa of San Francisco de Alburquerque) (modern-day pop. 560K/1.7M) , and stocks it with 12 families, writing the viceroy about it after the fact, breaking Spanish law requiring permission, and lying that there are the required min. of 35 families; he is called to Mexico City for punishment, and loses his planned appointment as permanent gov., having to leave in 1711; the villa later becomes known as "Duke City"; in 1988 the city council declares Founder's Day in Albuquerque's honor, complete with a statue; since the Spanish have less than 60 soldiers to guard all the settlers and their farms, they relocate their homes into a single square, creating the Old Town Plaza for mutual defense, Mexico's first?; Albuquerque is incorporated in 1891.
In 1709 Taipei (modern pop. 2.7M/8.5M) on the Danshui River on N Taiwan Island, home of the Ketagalan tribes is settled by mainland Han Chinese immigrants.

In 1721 Norwegian Lutheran missionary Hans Egede (1686-1758) sails in the ship The Hope from Norway to Greenland to convert Norse farmers, becoming the first new European in Greenland in 200 years; too bad, the Inuits tell him that there are no Norse there anymore, showing him crumgling stone church walls, causing the mystery of their disappearance to arise, which isn't solved until ? (the Little Ice Age?); he founds Godthab (Good Hope) on Kangeq (Kangek) Island on the W coast, establishing trade with Denmark and beginning missionary work among the Skraelings, er, Inuit, becoming known as "the Apostle of Greenland"; in 1728 Danish-Norwegian gov. Maj. Claus Enevold Paarss (1683-1762) moves Godthab to the mainland, becoming the world's northernmost capital ahead of Reykjavik; in 1979 it is renamed Nuuk ("cape").

On Nov. 18, 1723 the city of Ekaterinburg (Yekaterinburg) (named after Peter the Great's wife Yekaterina AKA Tsar Catherine I) on the Iset River E of the Ural Mts. of Russia (modern-day pop. 1.34M/1.49M) is founded, becoming Russia's mining capital, known as "the window to Asia" after Tsar Catherine II builds the Siberian Route (Tea Road) (Moscow Highway) (Great Highway) from Russia to Siberia to China through it; in 1924-91 it is renamed Sverdlovsk after deceased Bolshevik leader Yakov Mikhailovich Sverdlov (1885-1919), becoming an industrial center, known for some of Russia's tallest skyscrapers.

In 1724 after the Portuguese begin fortifying the heights around the Bay of Montevideo in Uruguay, a Spanish force from Buenos Aires led by Spanish soldier Bruno Mauricio de Zabala (1682-1736) forces them back to Colonia, and Zabala founds a fortress that becomes the city of Montevideo (San Felipe y Santiago de Montevideo) on the NE bank of the Rio de la Plata River 68 mi. E of Buenos Aires (modern-day pop. 1.3M/1.9M), continuing the turf war, while the British and Portuguese carry on what they claim to be illicit trade in the Rio de la Plata region; Montevideo goes on to become the center of Spanish control over the Banda Oriental, capital and largest city of Uruguay, and southernmost capital city in the Americas.

On Nov. 18, 1727 the city of Jaipur in Rajasthan, India (modern-day pop. 3.1M) 167 mi. from modern-day New Delhi is founded as a trading city and new capital by Rajput maharaja (1699-1743) and astronomer Sawai Jai Singh II (1688-1743) of Amber, becoming known for its Havelis, courtyard mansions; in 1876 the city is pained pink to welcome English Prince Albert Edward of Wales (future Edward VII) , causing the city to be nicknamed "the Pink City"; the Jantar Mantar (magical device), a network of three observatories based in and S of Delhi is built there by the maharaja, who designs masonry structures and crude instruments because his Jesuit advisers were prohibited by the Church from accepting the views of Galileo and Copernicus; the city is designed according to Hindu doctrine in seven rectangular areas according to the caste system, with the palace in the 7th and holiest one, and the observatory in the place of the temple; other observatories are built in Delhi, Mathura, Ijjain, and Varanasi.
In 1727 the city Concord, N.H. (originally Penacook) on the Merrimack River (modern-day pop. 42K) is founded by colonists from Haverhill, Mass. led by Capt. Ebenezer Eastman on the site of the main Pennacook Indian village; originally named Penacook, the name is changed to Rumford in 1733, and incorporated on Feb. 9, 1734; in 1765 after a 20-year boundary dispute with Mass. (which claims the Merrimack River) it is reincorporated as Concord to celebrate peace being declared with them; it goes on to become the capital of N.H.
In 1729 the city of Baltimore, Md. (AKA B'more, Charm City, Mobtown, Monument City, Ravenstown, City of Firsts) on the upper Cheseapeake Bay at the mouth of the Patapsco River (modern-day pop. 620K/2.7M) is founded as a tobacco port, becoming the largest independent city in the U.S. by modern times (until ?), becoming known as the home of celebs Edgar Allan Poe, Frederick Douglass, H.L. Mencken, Eubie Blake, Babe Ruth, Billie Holiday, and Francis Scott Key's nat. anthem "The Star-Spangled Banner".
In 1729 the city of Karachi on the Arabia Sea is founded as the fortified village of Kolachi; in the mid-19th cent. the British East India Co. arrives, turning it into a major seaport and railroad hub, growing to 400K pop. by 1947, after which the partition of British India causes it to be flooded with millions of Muslim refugees, reaching 14.9M pop. in 2017, becoming the most populous city in Pakistan and #5 in the world, hosting 2M immigrants from Bangladesh, 1M from Afghanistan and 400K Rohingyas from Myanmar, also becoming its industrial and financial center.
In Sept. 1732 the city of Wilmington, N.C. on the Cape Fear River (modern-day pop. 117K/282K) is founded on land owned by John Watson by royal gov. George Burrington, who calls it New Carthage, then New Liverpool, then New Town (Newton); on Feb. 20, 1739 it is incorporated under the name Wilmington in honor of Spencer Compton, Earl of Wilmington; in the 20th cent it develops the 1-mi.-long Riverwalk; in 2003 it is designated by Congress as a Coast Guard City.

In 1732 German-Am. Seventh-Day Adventists under German-born Johann Conrad Beissel (1691-1768) found Ephrata Cloister in modern-day Lancaster County, Penn.; on July 27, 2008 Marie Kachel Bucher, its last surviving resident dies.
In 1732 the town of Selma, Ala. (meaning: "high seat or throne", from the poem "The Songs of Selma" by Ossian) (modern-day. pop. 21K) on the Alabama River is first explored by French explorers, who call it Ecor (Écor) Bienville; in 1815 Anglos settle it, calling it Moore's Bluff; it is incorporated in 1820 after being planned and named by future U.S. vice-pres. William R. King; during the U.S. Civil War it becomes the 2nd most important military manufacturing center after Tredegar Iron Works in Richmond, Va.


On Feb. 2, 1733 Oxford-educated Methodist resident trustee gen. James Edward Oglethorpe (1696-1785) along with some Moravian Protestants land in Savannah, and found the colony of Jaw-Jaw, er, Georgia (Ga.) (named after George II of England) as a refuge for debtors and criminals after getting the idea from English Anglican clergyman Thomas Bray (1656-1730); he leads 120 colonists to the colony, then with surveyor col. William C. Bull lays out the capital city of Savannah (modern-day pop. 136K/384K) on the coast in a geometrical pattern with 22 squares, starting with Johnson Square on Bull St. between Bryan and Congress Sts.; the colony tries to be both a military buffer against Spanish Fla. and a philanthropic experiment for the poor and persecuted.
In 1733 Cape Girardeau, Mo. (modern-day pop. 38K/134K) at a rocky promontory overlooking the Mississippi River is founded as a trading post by French soldier Jean Baptiste de Giardot in Kaskaskia in the French colony of La Louisiane; in 1793 after it becomes kaput, French-Canadian trader Louis Lorimier establishes another trading post there; at the same time Baron Carondelet grants land to the Black Bob Band of the Hathawekela Shawnee, who are removed by the U.S. govt. in 1833; in 1799 Am. settlers found the first English school W of the Mississippi River there at Mt. Tabor; the town is incorporated in 1818, after which it becomes the biggest port on the Mississippi River between St. Louis and Memphis.
In 1743 the city of Magnitogorsk (modern-day pop. 408K) is founded on the E side of the S Urals by the Ural River, named after 60%-iron-containing Mount Magnitnaya, launching iron ore production in 1759; in 1928 the Soviets travel to Cleveland, Ohio to meet with consulting co. Arthur G. McKee to discus plans to copy the U.S. Steel mill in Gary, Ind., also modeling their Magnitogorsk Iron and Steel Works after Pittsburgh, Penn.; in 1931 it is granted city status ; Motto: "The place where Europe and Asia meet".

On July 9, 1746 Spanish king (since Nov. 1, 1700) Philip V (b. 1683) dies, leaving Spain stripped of its European possessions incl. Gibraltar and Minorca, and is succeeded by his 4th son (by Mari Luisa of Savoy) Ferdinand VI (the Learned) (1713-59), who becomes Spanish Bourbon king #3 (until Aug. 10, 1759), going on to patronize castrato Farinelli, end the influence of widow (of Philip V) Queen Elisabeth Farnese of Parma and her Italian courtiers, who retires fro the court, and pursue a policy of neutrality between France and Britain without renouncing its claim to Gibraltar; he builds up the royals-and-nobles-only city of Aranjuez 26 mi. S of Madrid (modern-day pop. 58K) on the site of the ancient town of Ara Jovis (Lat. "altar of Jove") and a royal summer palace built by HRE Philip II (1527-98), allowing non-royals to stay overnight in 1752; his treasury secy. the Marquis of Ensenada modernizes Spain, creating the Giro Real bank in 1752, registering ships to trade freely in the Americas, modernizing the navy, founding the Royal Academy of the Fine Arts of San Fernando in 1752, which patronizes composer Domenico Scarlatti, and improving relations with the Church.
On May 2, 1749 after help from young surveyor George Washington, the city of Alexandria, Va. at Hunting Creek Warehouse in Fairfax County on the W bank of the Potomac River 7 mi. S of modern-day Washington, D.C. (modern-day pop. 139K) is founded as Belhaven; it is incorporated as Alexandria in 1779; in 1791 it becomes part of the District of Columbia.
On June 1, 1749 Francois Piquet founds a mission at Oswegatchie (Ogdensburg), N.Y. at the confluence of the Oswegatchie and St. Lawrence Rivers (modern-day pop. 11K), which attracts many Iroquois to the French side; on June 21 Father Le Loutre's (Anglo-Micmac) (Indian) War begins when Gen. Edward Cornwallis arrives with 13 transports carrying 1,176 settlers and their families along with a war sloop to found the Atlantic seaport of of Halifax (named after the 2nd Earl of Halifax) in Nova Scotia on a hill overlooking Chebucto Bay (Halifax Harbor) (modern-day pop. 403K) as a countermeasure to the fortress of Louisbourg, going on to become Canada's main Atlantic seaport and capital of Nova Scotia.
In 1749 the city of Port-au-Prince (formerly Hopital) (allegedly named for the ship Le Prince that sailed there in 1706) on the Gulf of Gonave in the French part of Hispaniola (Saint-Domingue) (modern-day Haiti) (modern-day pop. 987K/2.6M) is built; in 1770 it replaces Cap-Francais (modern-day Cap Haitien) as the capital; in 1804 it becomes capital of independent Haiti.
In 1749 the city of Rostov-on-Don at the confluence of the Don and Temernik Rivers (modern-day pop. 1M) is founded as a customs house by Empress Elizabeth to control trade with Turkey; it is chartered in 1796.
In 1755 the city of Charlotte, N.C. (originally Charlotte Town) E of the Catawba River, named after British queen consort Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (modern-day pop. 731K/2.4M) is settled on land depleted by smallpox of the native Catawba tribe by Thomas Spratt and Thomas Polk (grand-uncle of U.S. pres. James K. Polk) (who marries his daughter), followed by a large number of Scots-Irish Presbyterians and a smaller number of Germans, with the city flag based on the St. Andrews Flag of Scotand; it is incorporated in 1768; it later gets the nicknames "Queen City" and "the Hornet's Nest" after British Gen. Charles Cornwallis calls it "a hornet's nest of rebellion".
On Nov. 24, 1758 the British led by Fife, Scotland-born Gen. John Forbes (1707-59) retake Ft. Duquesne in Penn. from the British after the French defeat their advance party then give up and destroy and abandon it; on Nov. 27 after occupying it on Nov. 25 Forbes renames it Pittsburgh (pr. PITS-buh-rah) (modern-day pop. 306K/2.66M) Pittsburgh (pr. PITS-buh-rah) (modern-day pop. 306K/2.66M) in honor of PM William Pitt the Elder, then construct the new smaller Ft. Pitt during the winter of 1758-9; it is incorporated as a township in 1771, and as a borough on Apr. 22, 194; Pittsburgh goes on to become known as Steel City for its 300 steel-related businesses, and the City of Bridges for its 446 bridges along the Allegheny, Monongahela, and Ohio Rivers; in 1909 Forbes Field, home of the Pittsburgh Pirates and Pittsburgh Steelers is named for Forbes.


On Feb. 14, 1764 (Valentine's Day) the river town of St. Louis (modern-day pop. 311K/2.9M) on the W bank of the Mississippi River in modern-day Mo. on the border with modern-day Ill. 18 mi. downstream from the confluence of the Missouri River is founded by French fur traders Pierre Laclede (Laclède) (1729-78) and his stepson (common law wife's son) Rene (René) Auguste Chouteau Jr. (1749-1829), and named after French king Louis IX; in 1803 it becomes U.S. territory; it is incorporated in 1822, becoming the 4th largest U.S. city by 1870.
In 1770 the city of Casablanca (Sp. "white house") (Dar el-Beida) (modern-day pop. 4M) is founded in Morocco by Sultan Sidi Mohammed ben Abdallah after an earthquake levels the Portuguese installation of Casa Branca (Port. "white house") in 1755; by 1860 its pop. is only 8K.
In 1770 the city of Monterey, Calif. at the S end of Monterey Bay on Monterey Peninsula (modern-day pop. 27K) is founded as a Presido, becoming the first military establishment W of the Rocky Mts. and the capital of Alta Calif.
By 1770 the town of Pittsburgh, Penn. (modern-day pop. 305K) (founded 1758) has 20 log houses, and a small village flourishes on the site of modern-day city Wheeling, W. Va. on the Ohio River (modern-day pop. 28K), founded during the winter of 1769-70 by Col. Ebenezer Zane (1747-1811) and his brothers, who erect Ft. Fincastle in 1774, renaming it Ft. Henry in 1776 in honor of Patrick Henry.
On Oct. 22, 1777 the city of Stavropol (Gr. "stauropolis" = City of the Cross) in W Russia (modern-day pop. 433K) founded as a military encampment by Prince Grigory Potemkin as one of 10 fortresses built between Azov and Mozdok at the request of Catherine II the Great; in 1785 after being settled by Don Cossacs from the Khopersky Regiment, it is granted city status; in 1809 Tsar Alexander I invites several Armenian family to settle there; it goes on to become a strategic base for Russian conquest of the Caucasus.

In 1779 the city of Chicago, Ill. (Ill. Tribe word for "striped skunk", meaning wild leek) (modern-day pop. 2.7M/9.5M) is founded by Jean Baptiste Pointe du Sable (DuSable) (1745-1818), a black fur trapper from Haiti, who sets up a trading post in modern-day Pioneer Court on the NE side of Michigan Ave. Bridge; it is incorporated as a town on Aug. 12, 1833, and as a city on Mar. 4, 1837; on Oct. 26, 1968 the state of Ill. recognizes du Sable as the father of Chicago; in 1957 the DuSable Museum of African-Am. History is founded at 57th St. S at Cottage Grove in Chicago.
In 1779 the town (borough) of Glassboro, N.J. (modern-day pop. 29K) is founded by Solomon Stanger as "the Glass Works in the Woods", becoming home to several glass manufacturers; in 1923 Rowan U. (originally Glassboro State College) is founded there.
In 1779 the city of Nashville, Tenn. on the Cumberland River (Davidson County) (modern-day pop. 684K/1.8M) is founded, named after Brig. Gen. Francis Nash (1742-77), who was mortally wounded in the Oct. 4, 1777 Battle of Germantown.
On Sept. 4, 1781 Spanish gov. of Calif. (1777-82) Felipe de Neve (1724-84) along with the Franciscans found El Pueblo de la Reina de Los Angeles (Town of the Queen of the Angels) (modern-day pop. 3.8M/18.6M) from an Indian village named Yangma; 29 of the first 44 Spanish settlers (Los Pobladores) are of African ancestry.

On Apr. 6, 1782 mad king (since Dec. 28, 1767) Taksin the Great (b. 1734) is executed by a coup after they reject his offer to become a monk; on Apr. 6 after defeating the rebels, gen. Chao Phraya Chakri becomes king Rama I (Phra Phutthayotfa Chukalok) (Thongduang) (1737-1809) of Siam (until Sept. 7, 1809), founding the Chakri (Thai "chakra" = discus") Dynasty in Siam (Thailand) (ends ?) on Apr. 21 at 54 min. after sunrise by placing the City Pillar for the new capital city of Bangkok (originally Rattanakosin) on the Chao Phraya ("River of Kings") River (modern-day pop. 8.3M/14.6M).
In May 1783 the Black Sea port city of Sevastopol (modern-day pop. 418K) is founded, becoming the main base of the Russian Black Sea fleet.
In 1784 to reward them for siding with the British in the Am. Rev. War, Mohawk Chief Joseph Brant and the Six Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy settle in the Six Nations of the Grand River Reservation 12 mi. from Brantford (modern-day pop. 97K/134K) (founded May 31, 1877), the seat of Brant County, Ont., 26 mi. SW of Hamilton on the Grand River; it later becomes famous as the location of the first successful test of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell at his father's home Melville House, causing it to become known as "the Telephone City", later becoming the birthplace of NHL hockey star Wayne Gretzky.

In 1786 the city of Dearborn, Mich. (modern-day pop. 98K) is settled by Europeans, named after U.S. Am. Rev. War. gen. Henry Dearborn (1751-1829); it becomes Dearborn Township in 1833, and Dearbornville village in 1836; in 1893 it is incorporated as a village, and in 1927 as a city, becoming the world HQ of the Ford Motor Co.
In 1786 the city of Knoxville, Tenn. (modern-day pop. 179K/868K) in the Tennessee Valley is settled by Rowan County, N.C.-born Am. Rev. War brig. gen. James White and James Connor, who build White's Fort near the mouth of First Creek; on July 2, 1791 the Treaty of (the) Holston settles territorial boundaries with the Cherokees, also establishing that the Cherokee tribes fall under the protection of the U.S., which will manage all their foreign affairs; the city is incorporated in 1815; the arrival of the railroad in 1855 causes an economic boom.
In 1787 the city of Dnepropetrovsk (Ekaterinoslav until 1925, Dnipro since May 2016) is founded on the Dnieper River 243 mi. SE of Kiev in SC Ukraine by the Cossacks (modern-day pop. 980K/1.4M)).


Is there any continent on Earth not being taken over by whitey? On Jan. 18, 1788 (8 mo. after setting sail on May 13, 1787) the 11-ship First Fleet containing the first white English (European) settlers (732 convicts), led by British Navy Capt. (later Adm.) Arthur Phillip (1738-1814) of the Sirius arrive in Botany Bay in SE Australia (New Holland), and on Jan. 26 after realizing there's no water or secure anchorage they move to Port Jackson, and land the marines and convicts at Sydney Cove, which Phillip names in honor of British home secy. (1783-9) catch-the-mystery-of-white (well-meaning angel or devil?) Thomas Townshend, 1st Viscount Sydney (1732-1800), who appointed him gov. #1 of New South Wales (until 1792), which he rules from Port Jackson, while his marines guard the farmer-prisoners, who become Australia's first settlers; the first horses in Australia arrive with the First Fleet from Cape Town, South Africa; on Feb. 15 Capt. Phillip sends men to establish a 2nd colony in Norfolk Island, and claims Australia E of 135 E longitude for Britain, establishing Botany Bay Penal Colony as a place to dump English undesirables a good safe 13K mi. from London; Sydney (modern-day pop. 5M) becomes the first British settlement in Australia, with Sydney Hospital established on George St. on The Rocks as a tent hospital before being moved to Macquarie St. in 1811; the newcomers (who are watched by the indigenous Eora Tribe, which Phillip makes a hanging offense for his men to kill) have virtually no clothes or equipment, are covered with vermin and riddled with disease, are not farmers, and the seed brought on the journey is spoiled by sea-damp and fails to germinate; they do bring along 100 Bibles and 100 copies of the bestseller "Exhortation to Chastity", but who can read, and since there aren't enough women for the men, Capt. Phillip writes back to England to send women of childbearing age, and of course they send whores; finding the marines also undisciplined slackers, Phillip, uttering the soundbyte "In a new country there will be no slavery and hence no slaves" sets some convicts up as overseers, and also sets up two civil courts where prisoners can get around the usual laws against felons being able to sue, beginning the gradual process of emancipation, which is helped by the little fact that after the convicts serve their sentences they find it too expensive to leave, causing Australia to become known as "the country where people got stuck", and their usually illegimate children to become known as cornstalks.



On Aug. 25, 1788 after Riverhead, N.J.-born John Cleves Symmes (1742-1814) of N.J. (father-in-law of Pres. William Henry Harrison) negotiates the 330K-acre Symmes (Miami) Purchase (Ohio River to Great Miami River to Little Miami River) from Congress for $225K, and Morristown, N.J.-born surveyor Israel Ludlow (1765-1804) surveys the 1.5M-acre Ludlow Survey (Scioto River to Little Miami River) for the Ohio Co. of Associates, separated from the Symmes Purchase by the disputed Ludlow Line, the city of Cincinnati, Ohio at the N side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio Rivers (modern-day pop. 296K/2.1M) is founded by Col. Robert Patterson (1753-1827), surveyor John Filson (1747-88), and Mathias Denman, settled on Dec. 28 by 26 more people, and named Losantville ("city opposite the mouth of the Licking River") by Filson, then renamed in 1790 by Arthur St. Clair after the 1783 Society of the Cincinnati, becoming the first U.S. boomtown; it is incorporated as a village in 1802, and as a city in in 1819; as settlers from N.J. and other mideastern U.S. states purchase 1M acres along the Ohio River and establish several settlements, Cincinnati becomes the Gateway to the South for steamboats on the Ohio, which are introduced in 1811, with its pop. zooming from 9,642 in 1910 to 24,831 in 1830 and 115K in 1850; in 1827 the Miami and Erie Canal opens, connecting Cincinnati with Middletown and Toledo.
In 1788 the city of Charleston, W. Va. at the confluence of the Elk and Kanawha Rivers (modern-day pop. 51K/222K) is founded as Ft. Lee, becoming the seat of Kanawha County, and the state capital of W. Va.; members of the Kanawha County Assembly incl. Daniel Boone.
In 1788 after settling in 1785 on the Mississippi River opposite the modern-day Wisc.-Ill. boundary on the site of modern-day Dubuque, Iowa (modern-day pop. 57K/96K), French-Canadian Quebecois pioneer Julien Dubuque (1762-1810) receives permission from the local Meskwaki tribe and the Spanish govt. to mine lead; after the Meskwaki are forced out of the region in 1830, the first permanent settlement is founded in 1833.
In 1788 after the N.C. assembly chooses it as the site of the new capital to replace New Bern (1743), the city of Raleigh, N.C. (modern-day pop. 403K/2.2M), located on land owned by Wakefield mansion owner Joel Lane is named in honor of Sir Walter Raleigh; it is chartered on Dec. 31, 1792.
In 1788 after the pesky Iroquois are forced into Canada, where Britain gives them a large land grant on the Grand River, the city of Rochester, N.Y. (modern-day pop. 210K/1.1M) is first settled by English Puritans from New England, it is incorporated as a village on Mar. 21, 1817, and as a city on Apr. 28, 1834 after reaching a pop. of 9.2K, becoming the largest flour-producing city in the U.S. by 1838, known as "the Flour City", and "the Young Lion of the West" for doubling its pop. in 10 years, becoming the first U.S. boomtown; by 1850 it becomes known as "the Flower City" for its nurseries; it goes on to become the home of revivalist Charles Finney, Frederick Douglass, Susan B. Anthony, John Jacob Bausch and Henry Lomb, George Eastman, and Emma Goldman.
On Sept. 25, 1789 a force of Russian and Zaporozhian Cossack troops under Gen. Count Ivan Vasilyevich Gudovich (1741-1820) capture the Turkish citadel of Khadjibey in Ukraine, which is renamed Odessa (modern-day pop. 1M); the Jews begin to settle there.
In 1789 after the pesky Iroquois are herded into the Buffalo Creek Rez to the W, the city of Buffalo, N.Y. (named after a Seneca Indian who lived there) (modern-day pop. 260K/1.2M) near Buffalo Creek on the E shore of Lake Erie at the head of the Niagara River 17 mi. SSE of Niagara Falls is settled by Dutch trader Cornelius Winney from Albany and ex-slave Joseph "Black Joe" Hodges, followed by Iroquois interpreter Capt. William Johnston; it is officially founded in 1801; in 1802 the first road from the Conn. Western Reserve in Ohio to Penn. is built through it; in 1804 a spoke-diagonal street plan mimicking Washington, D.C. is designed by D.C. surveyor Joseph Ellicott for the 400 pop.; it is incorporated as a city in 1832 after the completion of the Erie Canal in 1825 causes pop. to zoom, attracting Roman Catholic Irish and German immigrants along with fugitive black slaves; Buffalo goes on to become known as "the City of Light" for its early embrace of electric power, and the 2nd largest city in N.Y.
In 1789 the city of Hammerfest, Norway (Norse "hamran" = steep mountainside), the northernmost town in Europe (modern-day pop. 10.5K) is founded; it is incorporated on Jan. 1, 1838.
The Great American White-Is-Right Dream begins with the Father of the Country? On Mar. 26, 1790 Pres. Washington signs the U.S. Naturalization Act of 1790, barring anyone not a "free white person" from becoming a U.S. citizen; when Puerto Rico's citizens are allowed to become U.S. citizens in 1917, the govt. looks the other way and classifies them all as white.
On Sept. 22, 1791 the city of Paterson, N.J. (modern-day pop. 147K) is founded by the Society for the Establishment of Useful Manufactures (SUM), founded by U.S. treasury secy. Alexander Hamilton, and named for N.J. gov. William Paterson, becoming the cradle of the Industrial Rev. in the U.S.; it is incorporated as a town on Apr. 11, 1831, and as a city on Apr. 14, 1851.


In 1791 Paris-born French engineer (Valley Forge veteran) Maj. Pierre Charles L'Enfant (1754-1825) draws up the original plan for the District of Columbia (Washington, D.C.); a gridwork of parallel streets are overlaid with diagonal "grand avenues" which radiate from Jenkins' Hill (Capitol Hill) (site of the U.S. Capitol) and the Executive Mansion, which face each other along Pennsylvania Ave., with the President's Park to be located N of the President's House, later becoming Lafayette Square, and the President's Park South to be located S of the President's House, with the 1km circumference street in it called the Ellipse; a third focus is planned for the Supreme Court, but it ends up being put in the basement of the Capitol instead; there were a lot of Freemasons among the the Am. Founding Fathers, and they even laid out Washington, D.C. in a Masonic configuration? - the Satanic hexagram design is an Illuminati symbol in disguise? In 1791 Alexandria, Va. (founded in 1749; incorporated as a town in 1779) (modern-day pop. 150K) 7 mi. S of Washington, D.C becomes part of the District of Columbia (until 1846), making big money trading slaves; it is incorporated as a city in 1852, and becomes independent in 1870.
In 1791 the city of Jacksonville, Fla. (modern-day pop. 880K/1.6M) on the St. Johns River 25 mi. S of Ga. and 340 mi. N of modern-day Miami, Fla. is founded as Cow Ford on the King's Road to Ga.; on Feb. 9, 1832 it is chartered as a town and named after Andrew Jackson.
In 1791 Misson Santa Cruz is founded on the N edge of Monterey Bay in Calif. 75 mi. S of modern-day San Francisco by missionary priest Juan Crespi; in 1797 Villa de Branciforte is founded by the Spanish colonial govt. of Alta Calif. on the E bluff of the San Lorenzo River facing the mission on the other side; in 1866 the city of Santa Cruz, Calif. (modern-day pop. 64K/262K) is incorporated, and chartered in Apr. 1876; in 1905 Branciforte is annexed; in the 20th cent. it calls itself "Surf City", becoming a center of progressive liberal activism.
On Dec. 31, 1792 the city of Raleigh, N.C. (modern-day pop. 468K/2.2M), named for Sir Walter Raleigh is incorporated as the capital of N.C., replacing New Bern; a planned city, its location is chosen because it's only 11 mi. from Isaac Hunter's Tavern, a favorite of state legislators; the city plan is based on the 1682 Thomas Holme plan for Philly; on Jan. 21, 1797 it is granted a city charter.
In 1793 the city of Abu Dhabi (Arab. "father of the gazelle/deer") (modern-day pop. 1.5M) is founded by Bani Yas bedouins from the Liwa Owasis; the Al Nahyan family goes on to become the rulers of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi; the city goes on to become the 2nd most populous city of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) after Dubai.
On Sept. 2, 1794 the port city of Odessa, Russia (modern-day pop. 1M) is founded on the shores of the Black Sea by a bunch of mostly Jews from Italy (Genoa, Naples, Venice, Palermo) - wearing the perfect shade of lipstick?
In 1795 the city of Arak in WC Iran (modern-day pop. 609K) is founded by pro-Iranian Georgian warlord Yusef Khan Gorji, who was given refuge by Agha Mohammad Khan after a territorial dispute with Catherine II the Great.
In 1795 The borough of Braddock in Allegheny County, SW Penn. on the Monongahela River E of Pittsburg (modern-day pop. 2K) is settled on the site of Edward Braddock's 1755 ambush, becoming the site of the Carnegie steel mills, the first Bessemer steel process, and the first Carnegie free public library.
In 1795 the city of Milk, er, Milwaukee, Wisc. (Algonq. "millioke" = pleasant land") (modern-day pop. 595K/2M) is settled by French-Canadian fur trader Jacques Vieau (Vieaux) (1757-1852), becoming known for beer brewing.
In 1795 the city of Williamsport, Penn. (modern-day pop. 29K) is founded, becoming an incorporated borough on Mar. 1, 1806 and a city on Jan. 15, 1866, then hosting Little League Baseball in 1939.
On Feb. 9, 1796 Whitestown, N.Y. surveyor John Young (1764-1825) purchases 15,560 acres from the Western Reserve Land Co. for $16,085, founding the city of Youngstown, Ohio in NE Ohio at the confluence of the Mahoning River and Mill Creek 65 mi. SE of Cleveland, Ohio, 61 mi. NW of Pittsburgh, Penn., and 10 mi. W of the Penn. border halfway between Chicago, Ill. and New York City (modern-day pop. 66K/555K), attracting settlers from Conn. along with Scots-Irish from Penn., followed by blacks in the early 20th cent. and Latinos in the 1950s, going on to become one of the top steel producers in the U.S. until the steep decline of the 1970s.
On Apr. 1, 1796 the city of Dayton, Ohio on the Great Miami River in SW Ohio (modern-day pop. 141K/799K) is founded by the 12-person Thompson Party from Cincinnati, Ohio, becoming the birthplace of aviation pioneer Orville Wright.

On July 22, 1796 the city of Cleveland, Ohio (modern-day pop. 397K/3.5M) on the Cuyahoga River is founded by land surveyor Moses Cleaveland (OE "hilly area") (1754-1806) of the Conn. Land Co.; the first settler is Lorenzo Carter; the village of Cleaveland is incorporated on Dec. 23, 1814, and incorporated as a city on Mar. 6, 1836 after the completion of the Ohio and Erie Canal in 1832 allows shipping down the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico, and iron ore begins to be shipped in from Minn. - Levon calls his child Jesus?

On July 17, 1797 Ferdinand von Hompesch zu Bolheim (1744-1805) becomes Knights of Malta grandmaster #71 until July 6, 1799 (first German); he bestows the title of Citta Beland (his mother's surname) on the town of Zejtun (Arab. "olive")(formerly Casal Santa Caterina) in SE Malta (modern-day pop. 11K); too bad, he disregards warnings and fails to take action against an invasion prior to the French invasion next June 6.
In 1797 the city of Baltimore, Md. (founded 1729) (modern-day pop. 620K/2.2M 1M) on Chesapeake Bay is incorporated, becoming the 2nd largest seaport in the Mid-Atlantic; its Inner Harbor becomes the #2 part for immigrants to the U.S.; in 1876 Johns Hopkins U. is founded there, followed in 1889 by Johns Hopkins Hospital; it goes on to have more public statues and monuments per capita than any U.S. City. famous residents incl. Edgar Allan Poe, Frederick Douglass, W.E.B. Du Bois, Ogden Nash, Gertrude Stein, F. Scott Fitzgerald, Dashiell Hammett, Upton Sinclair, H.L. Mencken, Edith Hamilton, Eubie Blake, Billie Holliday, Cab Calloway, Frank Zappa, John Waters, Barry Levinson, Babe Ruth, Michael Phelps, Thurgood Marshall, Nancy Pelosi, and Ben Carson.
In 1800 the city of Johnstown, Penn. (modern-day pop. 21K/140K) on the Conemaugh River at its confluence with Stony Creek 75 mi. SE of Pittsburgh is founded as Schantzstadt by Swiss German settler Joseph Schantz Johns (Jahns) Sr. (1749-1813), becoming a coal and iron ore mining center for Tunkers (Germ. "tunken" = to dip), located at the head of the W branch of the Penn. Main Line Canal; not to be confused with Johnstown, N.Y. - johnson jokes here?

On July 25, 1801 U.S. Rep. (Dem.-Repub., Ga.) (1795-1802) John Milledge (1757-1818) founds the city of Athens, Ga. (modern-day pop. 115K/192K) on the Oconee River as a site for the U. of Ga. (incorporated Jan. 27, 1785); on Nov. 4, 1802 he becomes Ga. gov. #26 (until Sept. 23, 1806), founding a land lottery for fair distribution of former Creek lands, reorganizing the state militia, and building a road to Tenn. through Cherokee lands; in 1804 he founds the city of Milledgeville, Ga. on the Oconee River in C Ga. NE of Macon (modern-day pop. 18.9K) as the Ga. state capital (until 1868); on June 19, 1806 he becomes U.S. Sen. from Ga., resigning on Nov. 14, 1809.
In Oct. 1802 the city of Ashburn, Va. (modern-day pop. 43K) (originally Old Farmwell Station) 30 mi. NW of Washington, D.C. starts out as a 1,236-acre plantation owned by George Lee III; in 1841 Quaker atty. John Janney purchases a 580-acre tract W of Ashburn Road, calling it Ashburn Farm; it goes on to host campuses of George Washington U., Strayer U., and George Mason U., and become a hub for 70% of the world's Internet traffic.

In 1804 the city of Hobart (originally Hobart Town) (modern-day pop. 222K) is founded as a British colony in Sullivans Cove in Van Diemen's Land (later Tasmania), named after British secy. of state for war and the colonies (1801-4) Robert Hobart, 4th Earl of Buckinghamshire (1760-1816), becoming the capital in 1856 when the colony is granted its own govt.
In 1804 after Canada grants 675K acres in 1784 to the League of Six Nations for help during the Am. Rev., and they turn around and sell 93K acres by 1798, the city of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada 60 mi. W of Toronto (modern-day pop. 104K/523K) is first settled by Mennonites from Penn., and in 1816 it is named after the 1815 Battle of Waterloo, attracting German settlers, who found the twin city of Kitchener (Berlin until 1916) in 1830 to the SE (modern-day pop. 233K/523K);; Waterloo is incorporated on May 27, 1857; in 1873 the city of Cambridge S of Kitchener at the confluence of the Grand and Speed Rivers (modern-day pop. 128K) is formed by the merger of Galt, Peston, Hespeler, and Blair.

In 1805 the city of Canton, Ohio on Nimishillen Creek 24 mi. S of Akron and 60 mi. S of Cleveland (named after Canton, China) (modern-day pop. 73K) is founded by surveyor Bezaleel Wells, incorporated as a village in 1822, and as a city in 1838, becoming the home of the Nat. Football League in 1920 and NFL Pro Football Hall of Fame in 1963.
In 1805 "Crescent City" New Orleans, La. is incorporated; highest altitude is 15 ft. (much of it 10-20 ft. below sea level); map of Orleans territory - who will give it shelter from the storm?
In 1805 Zebulon Montgomery Pike explores Minnesota, searching for the headwaters of the Mississippi River and stopping on Dec. 25 in Ojibwe territory at the site of the future city of Brainerd, Minn. (founded 1870, incorporated 1873) (modern-day pop. 13K), becoming the site of Ft. Ripley in 1849-77; he negotiates a treaty with the Sioux (Dakota) ceding 100K acres, incl. most of Mineapolis and St. Paul at the confluence of the Minnesota and Mississippi Rivers.


In 1806 the city of Macon, Ga. in C Ga. on the fall line E of the Ocmulgee River (modern-day pop. 153K/231K) on the Ocmulgee Oil Fields at the most inland point of navigation from the S.C. Low Country starts out as Ft. Benjamin Hawkins, named for N.C.-born U.S. Supt. of Indian Affairs (1796-1816) Benjamin Hawkins (1754-1816), founded after Pres. Jefferson forced the Creeks to cede their lands E of the river, going on to be used during the War of 1812 and 1813 Creek War until being decommissioned in 1828, after which European immigrants (esp. from N.C.) rename it Newtown, becoming the county sea of the new (1822) Bibb County in 1823 and named in honor of N.C. politician Nathaniel Macon (1757-1837), becoming known for its 250-acre Central City Park and ordinances requiring shade trees to be planted in front yards, becoming known as "the Heart of Georgia", home of Mercer U. (1833), oldest private univ. in Ga., and music stars incl. Little Richard, the Allman Brothers, Jason Aldean et al.
On Dec. 23, 1809 after their 1805 treaty causes the Chickasaws to clear out, and their 1806 Treaty of Washington causes the Cherokees to do ditto, the city of Huntsville, Ala. (modern-day pop. 193K/441K) in NW Ala. N of the Tennessee River is founded by Freemason LeRoy Pope (1765-1844) from Madison County, Ala., who names it Twickenham after the home village of his distant relative Alexander Pope, and lays out the streets in a NE-SW dir. parallel to Big Spring; it is incorporated as a town on Dec. 9, 1811, and a city on Feb. 24, 1860.
On Sept. 25, 1810 the 90%-Muslim city of Bandung (Bandoeng) in W Java, Indonesia (founded in 1488) is consolidate (modern-day pop. 2.5M/8.5M).
In 1811 the port city of Astoria, Ore. near the Columbia River (modern-day pop. 9.5K) is founded by the Am. Fur Co. of John Jacob Astor as Ft. Astoria, becoming the first permanent U.S. settlement on the Pacific coast, and first to have a U.S. post office W of the Rocky Mts.
On Feb. 14, 1812 after the Ohio state legislature chooses the name, the city of Columbus, Ohio (after Christopher Columbus) at the confluence of the Scioto and Olentangy Rivers (modern-day pop. 787K/2.4M) is founded as the capital of Ohio after Ohio City is outvoted; it assumes the official functions in 1816.
On Jan. 16, 1817 the city of Baton Rouge, La. (Fr. "red stick") (founded in 1699 and settled in 1721) (modern-day pop. 229K/830K) on the E bank of the Mississippi River is incorporated, becoming the first U.S. state capital with a 2-word French name (next is Des Moines, Iowa).

On Jan. 28, 1819 Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles (1781-1826), gov. of Java (1810-15) and Benckulen, Sumatra (1818) lands in Singapore, and on Feb. 6 establishes a British East India Co. trading settlement on the island of Singapore (modern-day pop. 5.6M) which was destroyed in 1365; ill health forces him to sail for Plymouth, England in 1824, and his ship catches fire, destroying all his possessions, incl. his natural history collection and mss. valued at $100K; Singapore goes on to eclipse Malacca and become the commercial and military center of the region.


On May 22, 1819 the city of Memphis, Tenn. (modern-day pop. 647K/1.34M) on the 4th Chickasaw Bluff S of the confluence of the Mississippi and Wolf Rivers is founded on land donated by future U.S. pres. Andrew Jackson and other wealthy landowners incl. Louisa County, Va.-born judge John Overton (1766-1833) and War of 1812 brig. gen. James Winchester (1752-1826).
In 1819 the city of Managua on the SW shore of Lake Managua (modern-day pop. 1M/1.4M) is incorporated as Leal Villa de Santiago de Managua; it becomes the capital of Nicaragua in 1852.
On Jan. 6, 1821 the planned state capital of Indianapolis, Ind. ("Indian City or Land") near the White River (modern-day pop. 820K/2.3M) is sited in the geographic center of the state of Ind. even though not on a navigable waterway, and later becomes a nexus for nationwide agricultural and industrial traffic, plus auto racing, with the nickname "Crossroads of America".
In 1821 Possum Town on the Tombigbee River is renamed Columbus, Miss. (modern-day pop. 42K), becoming home to landed cotton gentry who build stately mansions in the Greek Revival style.

In 1821 after the name "Missouriopois" is rejected, the Mo. legislature chooses the village of Lohman's Landing on the Missouri River at the center of the state midway between St. Louis (107 mi. to the E) and Kansas City (157 mi. to the W) to replace St. Charles as the new Mo. capital under the name Jefferson City, Mo., named after Pres. Thomas Jefferson and sited by Daniel Boone's son Israel Boone (1759-82); it is it is incorporated as a city in 1825, and the legislature meets there for the first time in 1826; Mo. State Penitentiary opens there in 1836 (until 2004); the Mo. Rhineland is established in the Missouri River Valley in the mid-1800s by German immigrants, stretching from Marthasville, Mo. W to Jefferson City.
In 1821 having secured Sudan, heavy-handed Egyptian pasha Mehmet Ali's sends his son Ibrahim Pasha to found the city of Khartoum (Arab. "elephant's trunk") (modern-day pop. 5M) at the junction of the Blue and White Nile Rivers 15 mi. N of the ancient city of Soba as an outpost for the Egyptian army, becoming a center of the slave trade; in 1830 it becomes capital of Egyptian Sudan; eventually the White Nile junction moves several mi. to the N; meanwhile Mehmet's forces begin capturing slaves from the Nuba Mts. W and S of Sudan, forcing them into the Gihadiya foot regiment.
On Mar. 25, 1822 U.S. Lt. Cmdr. Matthew C. Perry of the schooner Shark claims the 4 mi. x 1 mi. island of Key West, Fla. at the southern tip of the Fla. Keys 94 mi. from Cuba and 129 mi. SW of Miami for the U.S., becoming home to the city of Key West, Fla. (modern-day pop. 26K), which later becomes the home of writer Ernest Hemingway and the Winter White House of Pres. Harry S. Truman.
In 1822 St. Louis, Mo. on the Mississippi River is incorporated (modern-day pop. 311K/2.9M); river steamboats begin navigating the upper Mississippi River.

In 1823 the fairyland foothill town of Mussoorie (alt. 6,170 ft.) in Uttarakhand, N India 35 mi. from Dehradun and 180 mi. N of modern-day New Delhi (modern-day pop. 30K0 is founded by British lt. Frederick Young (1786-1874) of the British East India Co. as a hunting lodge; he raises the first Gurkha regiment there, and plants the first potatoes and tea in the Himalayas.

In Jan. 1824 the U.S. Army establishes the frontier outpost of Ft. Brooke at the mouth of the Hillsborough River on Tampa Bay in W Fla., which on Jan. 18, 1849 after Fla. becomes U.S. state #27 in 1845 becomes the village of Tampa, Fla. (modern-day pop. 336K/3M), reincorporated as a town on Dec. 15, 1855. In 1885 Ybor City NE of Tampa, Fla. is founded by Spanish-born cigar manufacturer Vicente Martinez Ybor (1818-96), who moves his cigar factory from Key West, Fla. and attracts workers from Cuba and SW Sicily, becoming known as "Cigar City" (cigar capital of the U.S.), peaking by 1900 (pop. 16K), becoming known as "Florida's Latin Quarter", then starting a downhill slide in the 1930s when the Great Depression and mechanization begins cutting employment, reducing the pop. to nil by the late 1970s; in the late 1990s part of it is revived as a night club and entertainment district; in 2018 mysterious tunnels are discovered, and speculated to be part of a network that transported Chinese hos from Cuba in the early 1900s.

On Aug. 24, 1824 old fart Am. Rev. War hero Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de Lafayette (1757-1834) arrives in New York City as a "guest of the nation" to begin a year of being feted; New Yorkers become embarrassed when they realize they have no fine restaurants to toast him in, only oyster bars and taverns; on Sept. 2 he visits Concord, Mass., where a speech made by Samuel Hoar that Concord is the spot where "the first forcible resistance" to British arms was made starts an eternal spitting war with nearby Lexington; since he's a friend of Nelly Custis Lewis, Laffy stays at Woodlawn Plantation in Mount Vernon, Va., and spends a week with Thomas Jefferson in Monticello, Va., after which the wine cellar has to be restocked; after the U.S. Congress votes him $200K to match his donation to the struggling colonies in 1778, along with the 36 sq. mi. Lafayette Land Grant in Leon County, Fla. the town of Tallahassee, Fla. (modern-day pop. 190K/380K) is founded as the capital of Fla. Territory, smack dab in the heart of the Fla. Cotton Belt in the Fla. Panhandle, center of the Fla. slave trade.
On Mar. 4-5, 1825 Marquis de Lafayette visits a town in N.C. on the Cape Fear River that was founded in 1783 and named in his honor as Fayetteville, N.C. (modern-day pop. 200K/377K), becoming the first U.S. town named for him, later becoming the home of U.S. Army Fort Bragg and receiving the All-American City Award from the Nat. Civic League 3x.
On Apr. 21, 1825 the city of Ypsilanti, Mich. (modern-day pop. 21K) near Ann Arbor is founded by settlers in honor of Greek hero Demetrios Ypsilanti.
In 1825 the city of Akron, Ohio in Summit County (modrn-day pop. 199K) is founded, named after the Greek word for summit since it's the highest city on the Ohio & Erie Canal; after Goodrich Corp. (1869), Goodyear Tire and Rubber Co. (1898), Firestone Tire and Rubber Co. (1900), and Gen. Tire (1915) locate there, it becomes known as the Rubber Capital of the World.
In 1825 the city of Doha (Arab. "big tree"), Qatar on the coast of the Persian Gulf (modern-day pop. 1.3M) is founded.
In 1825 the city of New Harmony (modern-day pop. 800) is founded on 30K acres in Indiana purchased by reformer Robert Owen and his son Robert Dale Owen (1801-77), but a misselection of personnel leaves several occupations underrepresented and the colony soon folds (1828).

In 1826 after news that that British authorities are extending the N end of the Rideau Canal there causes hundreds of land speculators to show up, the city of Ottawa (Algonquin "adawe" = to trade) (originally Bytown) (modern-day pop. 930K/1.3M) is founded on the S bank of the Ottawa River at its confluence with the Rideau River (100 mi. W of Montreal) around the canal (extending to Kingston on Lake Ontario), named after English engineer Lt. Col. John By (1779-1836), chief engineer of the Rideau Canal, which eventually divides the city into Upper Town (English) and Lower Town (French), with Parliament Hill dominating the view 125 ft. above the Ottawa River; the canal provides a secure route between Montreal and Kingston on Lake Ontario bypassing the stretch of the Lawrence River bordering New York that had been vulnerable to enemy fire during the War of 1812.
On June 4, 1829 Capt. James Stirling, Thomas Peel et al. found the city of Perth in SW Australia on the Swan River (modern-day pop. 2M), which leads a precarious existence for many years because of insufficient immigration.
In 1829 the village of Tijuana (modern-day pop. 1.7M) is founded in Baja Calif. Norte as Rancho Tia Juana (Aunt Jane Ranch); the city is founded on July 11, 1889 - not to be confused with Alta Calif.?
In 1831 the city of Kansas City (originally just Kansas) (named after the Kansas Indians) (modern-day. pop. 481K/2.4M) is founded at the confluence of the Missouri and Kansas Rivers by a group of Mormons from N.Y., building the first school in Kan. Territory until they are chased out by mobs in 1833, after which the Kansas Town Co. is formed to settle the area; it is incorporated as a town on June 1, 1850, and as a city on Mar. 28, 1853, going on to become the largest city in Mo.

In 1832 the city of Fort Pierre, S.D. (modern-day pop. 2K) is founded as a trading post by St. Louis, Mo.-born fur trader Pierre Chouteau Jr. (Pierre Cadet Chouteau) (1789-1865) on the N side of the mouth of the Bad River to replace Fort Tecumseh (founded 1817).
In 1832 the city of Saint (St.) Paul, Minn. (originally named Pig's Eye) (modern-day pop. 285K/3.5M) is first settled by 1-eyed Pierre "Pig's Eye" Parrant (Parent); it is incorporated on Mar. 4, 1854.
On Aug. 12, 1833 the "Windy City" of Chicago, Ill. (Algonquian "place of the wild onion or garlic") (modern-day pop. 2.6M/9.8M) on the lower W shore of Lake Michigan near a portage between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River watershed is incorporated as a town with a pop. of 200, growing to 4K by 1840; the city of Chicago is incorporated on Mar. 4, 1837.

On June 23, 1835 the city of Durban (Zulu "itheku" = bay/lagoon) (modern-day pop. 595K/3.8M) on the Indian Ocean coast of South Africa is founded by 35 Voortrekkers, named after Cape Colony gov. (1834-8) Lt. Gen. Sir Benjamin Alfred d'Urban (1777-1849), going on to become South Africa's busiest port and a center of tourism.

On Mar. 6, 1834 the city of York in Ontario, Canada (pop. 10K) on the NW shore of Lake Ontario (modern-day pop. 2.7M/5.9M) is incorporated as Toronto (Iroquois "tkaronto" = "place where trees stand in water"), with William Lyon Mackenzie (1795-1861) becoming mayor #1 next year.

On Aug. 30, 1835 the city of Melbourne (originally Batmania) (modern-day pop. 4.7M) (named after British PM William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne) by N.S.W. gov. Sir Richard Bourke) is founded in S Australia by Tasmanian settler John Batman (1801-39), who crossed the Bass Strait and picked a site on the Yarra River, then bought 775 sq. mi. of land around it from the aborigines for clothing, blankets, knives, scissors and tomahawks in Batman's Treaty of June 6, becoming Britain's greatest land grab from helpless natives, declared void by Bourke on Aug. 26; Queen Victoria officially declares Melbourne a city in 1847, going on to become large and wealthy from the 1851 Victorian Gold Rush.
In 1835 Mich. and Ohio almost go to war over the new city of Toledo, Ohio at the W end of Lake Erie at its confluence with the Maumee River on in NW Ohio on the Mich. border (modern-day pop. 287K/608K), founded in 1833; in 1845 the Miami and Erie Canal is completed, causing pop. to grow, becoming known as "the Glass City" for its glass industry.

On Apr. 20, 1836 Wisconsin Territory (Wisc., Iowa, Minn.) is established by the U.S. Congress, with Henry Dodge (1782-1867) as Dem. gov. #1 on Apr. 30 (until Sept. 13, 1841); the city of Oshkosh on the W shore of Lake Winnebago at the mouth of the Fox River (75 mi. NNW of Milwaukee) (modern-day pop. 66K/160K) is settled about this time, and named in honor of Menominee Indian chief Oshkosh (Ojibwe "claw") in 1840.

On Aug. 26, 1836 the town of Houston, Tex. (named after Sam Houston) (modern-day pop. 2.1M/6.3M) is founded on Buffalo Bayou (modern-day Allen's Landing) by Canaseraga Village (modern-day Sullivan), N.Y.-born brothers Augustus Chapman Allen (1806-64) and John Kirby Allen (1810-38) after purchasing 6,642 acres from John Austin's widow Elizabeth E. Parrott for $5K; it becomes the capital of the Repub. of Texas on Nov. 30, and is incorporated next June 5.
On Dec. 28, 1836 the city Adelaide on the SE coast of South Australia on the Torrens River between Gulf St. Vincent and the Mount Lofty Ranges (modern-day pop. 1.3M) is founded, named after William IV's consort Queen Adelaide; the original pop. of 1K Kaurna (pr. GAR-ner) aborigines lose their way of life within 20 years, and the last surviving full-blood woman named Ivaritji dies in 1931.
In 1836 the city of Tulsa, Okla. (modern-day pop. 391K/1.1M) is founded in Indian Territory near the Arkansas River by the Lochapoka and Creeks under the Creek Council Oak Tree (Cheyenne and 18th St.) after Chief Tukabahchi is reminded of their old tree in Talisi, Ala., naming the settlement Tallasi (Creek "old town"); more members of the Five Civilized Tribes later settle there, incl. the Cherokee and Osage; it is officially incorporated on Jan. 18, 1898.

In 1837 the city of Atlanta, Ga. (modern-day pop. 420K/6.3M) E of the Chattahoochee River is founded as a transportation hub at of the Western & Atlantic Railroad; in 1842 its pop. of 30 names it Marthasville in honor of the daughter of the Ga. gov.; on Dec. 29, 1847 it is incorporated as Atlanta, short for Atlantica-Pacifica, the name proposed by Georgia Railroad chief engineer J. Edgar Thomson; in 1860 the pop. is 9,554; on Nov. 11, 1864 Union troops burn it to the ground, after which it is slowly rebuilt, replacing Milledgeville as the state capital in 1858, becoming known as the unofficial capital of the New South, and "the City in a Forest" for its dense tree cover, making it the laid-back New York City and Sherwood Forest combined.
On Nov. 9, 1838 Ft. Gatlin in C Fla. (modern-day pop. 238K/3.1M) is established by the 4th U.S. Artillery led by Ltc. Alexander C.W. Fanning for use in the Second Seminole War, named after Army physician Dr. John S. Gatlin, who was KIA in Dade's Massacre on Dec. 26, 1835; in 1838 the fort is abandoned, and settlers found the town of Jernigan, named after cattlemen Isaac and Aaron Jernigan; in 1856 it becomes the county seat of Orange County; in 1857 it is renamed Orlando after a local grave of a man named Orlando Reeves who died in 1835; it was really named after a char. in Shakespeare's "As You Like It"?; it goes on to become known as "the City Beautiful" and "Theme Park Capital of the World" after Walt Disney World opens in 1971 and Universal Orlando Resort opens in 1999.
On Sept. 20, 1839 the ship Tory carrying the New Zealand Co. begins settling the city of Wellington, New Zealand at the SW tip of North Island between Cook Strait and the Rimutaka Range (modern-day pop. 416K) (named after Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington), followed next Jan. 22 by 150 more settlers on the ship Aurora; in 1865 it replaces Auckland as the capital of New Zealand, becoming the closest nat. capital to Antarctica.
In 1839 the city of Corpus Christi, Tex. (Lat. "Body of Christ") (modern-day pop. 305K/320K) in coastal S Tex. is founded by Col. Henry Lawrence Kinney (1814-62) as Kinney's Trading Post to sell supplies to a Mexican rev. army.
In 1839 after Ross' Landing was used last year by the U.S. Army as the site one of three large internment camps (along with Fort Payne, Ala. and Ft. Cass, Tenn.) for Cherokees on their way down the Trail of Tears, the city of Chattanooga, Tenn. (modern-day pop. 168K/548K) in SE Tenn. on the Tennessee River 120 mi. NW of Atlanta, Ga., 120 mi. SW of Knoxville, Tenn., 135 SE of Nashville, Tenn., 120 mi. NE of Huntsville, Ala., and 148 mi. NE of Birmingham, Ala. is incorporated, becoming a boom town after the arrival of the railroad in 1850, with the slogan "Where cotton meets corn".

On Feb. 6, 1840 the Treaty of Waitangi is signed with the Maori, promising British protection of Maori land in protection for recognizing British rule, and the British formally annex New Zealand, founding the city of Auckland on the Tasman Sea on the N side of North Island (modern-day pop. 1.6M), named for India gov.-gen. (1836-42) George Eden, 1st Earl of Auckland (1784-1849), which next year becomes the capital until 1865 - I roamed under it as a tired nude Maori?

In 1840 Mzilikazi (Mosilikatze) ("Great Road") (1790-1868), a former lt. of Shaka Zulu who rebelled in 1823 and fled to exile with his Khumalo tribe, first to Mozambique then to Transvaal founds Matabeleland in modern-day Zimbabwe between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, with capital in the city of Bulawayo ("town of the persecuted one") (modern-day pop. 1.2M), named after Shaka Zulu's capital.

In 1840 Swiss immigrant John Augustus Sutter Sr. (Johann August Suter) (1803-80), who arrived via Oregon, Hawaii, and Alaska in Calif.'s remote Central Valley on Aug. 13, 1839, and persuaded the Mexican govt. to give him a 48K-acre land grant on the American River near its junction with the Sacramento River (modern-day Sacramento) erects a fort called New Helvetia (Sutter's Fort) with 18-ft.-high walls, living like a feudal baron while entertaining illegal gringo immigrants arriving over the California Trail through the Sierras, stretching his credit to buy 2K fruit trees in 1847, founding the Sacramento Valley agriculture industry, and hiring James Marshall to build a sawmill.
In the early 1840s the city of Plano, Tex. (Sp. "flat") 17 mi. NE of modern-day Dallas, Tex. (modern-day pop. 2670K/7.1M) is founded by Euro settlers.

In 1840 the unincorporated city of Silver Spring, Md. N of Washington, D.C. (modern-day pop. 79K) is founded by Francis Preston Blair Jr. (1791-1876) as a summer home near a mica-flecked spring near 7th St. Pike in modern-day Acorn Park; it goes on to become the HQ of the U.S. Food and Drug Admin. (FDA), the Nat. Oceanic and Atmospheric Admin. (NOAA), the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community, and the Seventh-Day Adventist Church; Blair goes on to help found the Repub. Party along with his daughter Elizabeth, who marries Samuel Phillips Lee, 3rd cousin of Robert E. Lee, whose son Francis Preston Blair Lee becomes the first popuarly-elected U.S. Sen.; Blair's son Montgomery Blair goes on to become U.S. postmaster gen. under Pres. Lincoln, representing Dred Scott before the SCOTUS.
On Jan. 20, 1841 the island of Hong Kong ("fragrant harbor") at E side of the mouth of the Pearl River S of the Chinese province of Guangdong and E of Macau (modern-day pop. 7.4M) is ceded to Britain by China, and on Jan. 26 Britain formally occupies it (ends 1997); too bad, China failed to fortify the Pearl and Yangtze Deltas against British warships, turning into a major disaster; in 1860 the colony expands to the Kowloon Peninsula; in 1898 it signs a 99-year lease with China (ends 1997).

In Nov. 1841 the city of Dallas, Tex. (Gael. "dwellers by the waterfall") (modern-day pop. 5.1M/7.7M) in NE Tex. on 640 acres overlooking the Three Forks area of the Trinity River is settled by Tenn. trader-atty. John Neely Bryan (1810-77); the site is where JFK is assassinated on Nov. 22, 1963; in 1846 after attracting Anglo-Am. (non-Hispanic) settlers, it and the surrounding county are named after Philly-born Anglo U.S. vice-pres. #11 (1845-9) George Mifflin Dallas (1792-1864) - shouldn't that be Houston-Mufflin? In 1872 the town of Dallas, Tex. begins a boom after the arrival of the Houston and Texas Central Railroad this year, the Texas and Pacific Railroad next year, and several other railroads within a short period - only 91 years to go until JFK's fatal visit?


In May 1842 after Bent's Fort misses a shipment of hides wanted by the East, causing them to see their chance, Pueblo, Colo. on the N bank of the Arkansas River at its confluence with Fountain Creek in S Colo. on the border of the Louisiana Purchase (modern-day pop. 110K) is founded as Ft. Pueblo (El Pueblo) by Bent's Fort trader George Simpson et al., who build a log fort to protect against hostile Utes, attracting Va.-born part-black mountain man James P. "Jim" Beckwourth (1798-1867), white mountain man Christopher Houston "Kit" Carson (1809-68), et al. while reaching 100 pop., encouraging farming and ranching; in winter 1846 a party of several hundred Mormons from Miss. arrive, and are joined by a group of sick members of the Mormon Battalion incl. women and children, who all leave for the Salt Lake Valley next July; too bad, the 1848 Mexican-Am. War and the 1849 Calif. Gold Rush deplete it, and by 1854 only 15-20 live there.
On Sept. 29, 1843 the Treaty of Bird's Fort between the Repub. of Tex. and "the Indigenous Nations of the Delaware, Chickasaw, Waco, Tawakani, Keechi, Caddo, Anadahkah, Ionie, Biloxi, and Cherokee", negotiated by Edward H. Tarrant and George W. Terrell and signed in modern-day Haltom City, Tex. ends years of warfare, establishing the border of Indian territory as a "line of trading houses" at the junction of the Clear Fork and West Fork of the Trinity River in modern-day Fort Worth, Tex. (modern-day pop. 854K/7.1M) which is founded by the U.S. Army in 1849 as Camp Worth, becoming the northernmost fort protecting the Am. Frontier after the Mexican-Am. War.


In 1843 the city of St. Joseph, Mo. (AKA St. Joe) on the Missouri River in NW Mo. (modern-day pop. 76K) is founded and incorporated by French trapper Joseph Robidoux III (1783-1868), becoming the starting point of the Pony Express and death place of outlaw Jesse James; Robidoux goes on to build Robidoux Row, the first apt. bldg. W of the Mississippi River.
In 1844 the city of Portland, Ore. (originally the Clearing, Stumptown) (modern-day pop. 584K/3.1M) at the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia Rivers at the end of the Oregon Trail is founded; the name is decided on a coin toss, with loser Asa Lovejoy of Boston, Mass. wanting Boston, and winner Francis W. Pettygrove of Portland, Maine wanting Portland; it is incorporated on Feb. 8, 1851.

In 1845 a group of Boston industrialists led by former U.S. Rep. (Whig-Mass.) (1835-7) Abbott Lawrence (1792-1855) found the town of Lawrence, Mass. on the Merrimack River 25 mi. NNW of Boston (modern-day pop. 80K) on land purchased from Andover and Methuen as a site for manufacturing plants; it is incorporated as a town in 1847, and as a city in 1853; it later becomes the childhood home of poet Robert Frost.

In 1845 Kamehameha III moves his royal court from Lahaina on Maui to Honolulu (Hawaiian "sheltered harbor", "calm port") on Oahu (modern-day pop. 350K/950K), modernizing it and turning it into a major commercial center, making 'Iolani Palace the official royal residence; he allows commoners to own land in Makawao in E Maui on the NW slope of Haleakala, causing vast sugar cane plantations and ranches to be built; Baldwin Ave. becomes a retail center.

On Feb. 19, 1846 the Texas state govt. is formally installed in Austin, Tex. (settled 1835; incorprated Dec. 27, 1839) (modern-day pop. 967K/2.1M), with Lincolnton, N.C.-born atty. James Pinckney Henderson (1808-58) as gov. #1 (until Dec. 21, 1847); on Feb. 21 Sam Houston becomes the first U.S. sen. from Tex. (until Mar. 4, 1859), and goes to Washington, D.C., counseling Pres. Polk against war with Mexico, lobbying for peaceful purchase of western lands, and attending a Baptist church; in Apr. after the Mexican-Am. War breaks out, Henderson takes a leave of absence to command a troop of Texas Rangers with the rank of maj. gen. under Gen. Zachary Taylor.
In 1846 the city of Bloemfontein (Dutch "fountain of flowers") (Sesotho "Mangaung" = place of cheetahs) in South Africa (modern-day pop. 256K/747K) is founded as a fort by British army Maj. Henry Douglas Warden on the farm of Johannes Nicolaas Brits (b. 1790), known for absence of horse sickness; it goes on to become one of South Africa's three nat. (judicial) capitals along with Cape Town (legislative) and Pretoria (administrative), with a 56% black and 13% black pop.

In 1846 the city of Eugene, Ore. (originally Skinner's Butte or Mudhole) at the S end of the Willamette Valley near the confluence of the Willamette and McKenzie Rivers 50 mi. E of the Ore. coast (modern-day pop. 156K/369K) is founded by Essex, N.Y.-born settler Eugene Franklin Skinner (1809-64) and 1.2K other colonists; in 1853 it is named Eugene City; in 1862 it is incorporated as a city, and renamed Eugene in 1889.
In 1846 the city of Fort Benton, Mont. (modern-day pop. 1.4K) is founded by St. Louis fur traders Pierre Chouteau Jr. and Auguste Chouteau as the last fur trading post on the Upper Missouri River, becoming the terminus of the 642-mi. Mullan Road for wagons (completed in 1860) from Ft. Benton in S.D., which, along with steamboats from St. Louis carrying immigrants to the Am. West (Ft. Walla Walla, Wash., Mont., Idaho, and Canada) until 1890, when railroad transport takes over.
In 1846 after settlement by French Canadian explorer Solomon Laurent (Laurent-Salomon) Juneau (1793-1856) (cousin of Juneau, Alaska founder Joseph Juneau) in 1818, followed by mass immigration of Germans since 1840, the famous city of Milwaukee, Wisc. (Algonq. "good land") in SE Wisc. (alt. 580.6 ft.) at the confluence of the Milwaukee and Menominee Rivers on the W shore of Lake Michigan (modern-day pop. 594K/ 2M) is incorporated, becoming known as the "Deutsche Athen" (German Athens).


Eureka, greedy gringos go for the gold in somebody else's territory, haha, their territory? On Jan. 24, 1848 (Wed.) a gold nugget is discovered by Sutter's partner James Wilson Marshall (1810-85) in the tailrace of Sutter's Mill (Sawmill) in Coloma on the Trinity River in the foothills of the Sierras in N Calif. 50 mi. NE of Sutter's Fort on the South Fork of the American River, launching the Calif. Gold Rush (ends 1855) (300K rush in, 100K+ stay, 28.4M troy oz. of gold at $18.89 an oz. worth $536M by 1859) after a publicity stunt is staged by Sutter's Fort store owner Samuel Brannan (1819-89), a Mormon elder hoping to make a fortune outfitting gold seekers in San Francisco, causing most of the town's 800 residents to head for the gold fields within a few days; Brannan becomes the first millionaire of the gold rush; on Aug. 19 the New York Herald reports the discovery, turning on the 500K pop. crowded in too small a space and plagued by horse manure, wild dogs and pigs, and drunks from cheap whiskey; several lucky early miners make sizeable fortunes fast and easy, the news feeding "gold fever"; in Aug. Sutter's son John Augustus Sutter Jr. (1826-97) arrives to help save the claim from squatters and thieves, in vain, causing Sutter Jr. to begin laying out the city of Sacramento, Calif. 2 mi. S of New Helvetia on the Sacramento River (modern-day pop. 490K/2.4M), incorporating on Feb. 27, 1850 (oldest incorporated city in Calif.), which becomes an overnight success, causing the father to grow bitter at the son; it is chartered as a city in 1920; on Dec. 5 Pres. Polk confirms the discovery in his Fourth Annual Message, complete with an oyster tin full of gold, starting a nationwide and later a worldwide stampede known as the Forty-Niners, ruining Sutter's land grant with claim jumping, while gold fever is further pumped up by newspaper stories about gold nuggets lining the streets and gold dust so easy to harvest that one could coat oneself with sticky stuff and roll down a hill to collect it; others see the easy riches as proof that the Am. West is God's promised land for whites, and that the U.S. was meant to have Calif. not Indians and beaners; the mining puts mercury in San Francisco Bay, which ends up in fish.
On Feb. 2, 1848 the first Chinese immigrants to the former Spanish mission (founded June 29, 1776) of San Francisco in Calif. (modern-day pop. 870K/8.7M) arrive in the Eagle one week after the Calif. Gold Rush starts, adding to the seven already there; the city's pop. grows from 1K in 1848 to 25K in Dec. 1849; the city is incorporated on Apr. 15, 1850.
On Mar. 1, 1849 after Neil McLennan settles in the area in 1845, Waco, Tex. (modern-day pop. 134K/265K) on the Brazos River is founded on lands formerly inhabited by the Waco (Huaco) tribe.

On June 6, 1849 the city of Ft. Worth, Tex. (modern-day pop. 854K/7.1M) ("Where the West begins") is founded 30 mi. W of Dallas as the northernmost of a chain of 10 forts for protecting the U.S. frontier, named after maj. gen. William Jenkins Worth (1794-1849) (who died in Feb. of cholera while trying to establish 10 new forts to mark the W Texas frontier from Eagle Pass to the confluence of the West and Clear Forks of the Trinity River), later being called "Cowtown" after the Chisholm Trail runs through it; it is incorporated in 1873.
Waffle and chicken restaurants right ahead? On Mar. 27, 1850 the officially WASP gringo Calif. cities of San Jose (Spanish mission founded Nov. 29, 1777) (modern-day pop. 1M/8.7M) and San Diego (Spanish mission founded July 16, 1769) (modern-day pop. 1.3M/3.3M) are incorporated, followed by Los Angeles (Apr. 4) (Spanish mission founded Sept. 4, 1781) (modern-day pop. 3.8M/18.7M), and San Francisco (Apr. 15) (Spanish mission founded June 29, 1776) (pop. 870K/8.7M).
On Jan. 9, 1851 Salt Lake City (originally Great Salt Lake City) (modern pop. 180K/560K) is incorporated; a territorial legislature is established on Apr. 5; the pop. of Utah is 11,354 - one Mormon cock to every how many dozen Moron pussies?
In July 1, 1851 the city of Melbourne (founded Aug. 30, 1835) (modern-day pop. 4.7M) becomes the capital of the new British colony of Victoria in S Australia; meanwhile in Feb. gold is discovered in New South Wales at Bathurst by Edward Hargraves, who had just come from the gold fields of Calif.; on Aug. 21 gold is discovered in Victoria at Golden Point near Ballarat, and in Sept. at Bendigo Creek, sparking a new gold rush that swells Melbourne's pop. by 500K in a decade (3x), the whites systematically pushing the aborigines out of the way onto reserves and missions.


On Sept. 14, 1851 the town of Seattle, Wash. on Puget Sound at the mouth of the Duwamish River is claimed by a large party of settlers led by Luther Collins; on Nov. 13 another party from Knox County, Ill. via Portland, Ore. led by Salem, Ind.-born Arthur Armstrong Denny (1822-99) land at Alki (Battery) (Roberts) (Me-Kwah-Mooks) Point (West Seattle), moving to the E shore of Elliott Bay at modern-day Pioneer Square and naming their settlement after Duwamish-Suquamish chief Seattle (Sealth) (Si'ahi) (1786-1866).
In 1851 the city of Oakland, Calif. on the E side of San Francisco Bay (modern-day pop. 420K) is founded by Galway, N.Y.-born Horace Walpole Carpentier (1824-1918), Edson Adams, and Andrew Moon; it is is incorporated on May 4, 1852, and reincorporated on Mar. 25, 1854, with Carpenter as mayor #1 (until Mar. 8, 1855).

In 1851 the city of Pendleton, Ore. (modern-day pop. 16.6K) is founded on the Oregon Trail near the Umatilla Nat. Forest as a trading post by Dr. William C. McKay; on Apr. 21, 1865 a U.S. post office is established under the name Marshall; in 1868 it is named for 1864 U.S. Dem. vice-pres. candidate George Hunt Pendleton (1825-99) of Ohio, and incorporated as a city on Oct. 25, 1880, later becoming the cultural center of E Ore., famous for its annual cattle roundup.
In 1851 the city of San Bernardino, Calif. (modern-day pop. 209K/4.2M) (originally the 1810 Spanish settlement of Politana, named for Bernardino of Sienna) is founded by Mormons, who form San Bernardino County in 1853, and incorporate the city in 1857; in 1857 most of the colonists are recalled to Utah by Brigham Young to fight the Utah War; in 1860 William F. Holcomb discovers gold in nearby Holcomb Valley, causing a pop. spurt.
In 1852 the city of Revere, Mass. 5 mi. N of Boston (modern-day pop. 51K) is incorporated from the 1626 settlement of Rumney Marsh, which was annexed on Sept. 25, 1634 to Boston until 1739, when it became part of Chelsea, known as North Chelsea; Pullen Poynt secedes from North Chelsea, becoming the town of Winthrop.
On May 30, 1854 after a push by Northern Dem. Senators Stephen Douglas of Ill. and Lewis Cass of Mich. to help the North catch up with Pres. Pierce's deal for a southern-route transcontinental railroad, the Missouri Compromise of 1820 is repealed, and the U.S. Kansas-Nebraska Act is passed, creating the territories of Kansas and Nebraska, while permitting a local option on slavery (popular sovereignty) (Tex. Sen. Sam Houston votes against it); both slave owners and free soilers rush in, riots ensue, and the War for Bleeding Kansas begins, trashing the existing political party system, destroying the Whigs and dividing the Dems; the city of Lawrence, Kan. (modern-day pop. 95K) is founded in NW Kan. between the Kansas and Wakarusa Rivers near Hogback Ridge on the Oregon Trail, becoming a hotbed of anti-slavery sentiment, going on to be the site of the Wakarusa War (1855), the Sack of Lawrence (1856), and the Lawrence Massacre (1863); after the U.S. Civil War ends, it becomes home to the U. of Kan. in 1866, and Haskell Indian Nations U. in 1884.
In 1854 after Sgt. Charles Floyd dies there on Aug. 20, 1804, becoming the only death during the 2.5-year Lewis and Clark Expedition, the city of Sioux City, Iowa on the navigational head of the Missouri River in NW Iowa (modern-day pop. 82K) is founded as a stop on the Great Plains for Mormons headed to Salt Lake City and prospectors heading to Wyo.; during Prohibition it becomes known as "Little Chicago" for its speakeasies.
On Mar. 28, 1855 the port city of Hoboken, N.J. ("place of the tobacco pipe") (modern-day pop. 50K) across the Hudson River from New York City is incorporated.
On June 14, 1855 Mormon missionaries arrive at the site of Las Vegas Springs in modern-day Las Vegas, Nevada ("the meadows") (modern-day pop. 2.2M/650K), and select the site of Old Mormon Fort, which protects the midpoint of the Mormon trail from Salt Lake City to Los Angeles from Indian attacks; it is abandoned in 1857.
In 1855 the city of Managua on Lake Managua is founded as the capital of Nicaragua to end a feud (modern-day pop. 1.4M/1M).
In 1855 the city of Minneapolis, Minn. (modern-day pop. 3.6M/382K) on the W bank of the Mississipi River opposite St. Anthony Falls near Ft. Snelling (built 1819) is founded by Scandinavian immigrants from land stolen, er, purchased from 21 Dakota Sioux, incl. Taoyateduta (Little Crow) (1810-63); it is incorporated in 1867 as rail service begins with Chicago.
In 1855 the city of Pretoria in Transvaal (later Gauteng), South Africa (modern-day pop. 740K/2.9M)), named after recently-deceased Boer Great Trek leader Andries Wilhelmus Jacobus Pretorius (1798-1853) is founded by his son Marthinus Wessel (Wessels) Pretorius (1819-1901); in 1860 it becomes the capital of Transvaal; in 2005 it is renamed Tshwane over the objections of whites.
In 1857 the town of Abilene, Kan. (modern-day pop. 6.8K) is founded as a stage coach stop in new Dickinson County, and named in 1860 after a passage in the Bible (Luke 3:1) meaning "city of the plains"; in 1867 the Kansas Pacific Railway reaches it, and on Sept. 5 after Joseph G. McCoy builds stockyards for 2K heads of cattle, and the railroad puts in a switch enabled cattle cars to be loaded, the first 20 carloads are sent to Chicago, Ill., causing the Chisholm Trail to end there, making Abilene the Wild West's first cowtown, with 35K heads shipped in 1867, and 440K by 1871.
On Jan. 17, 1858 the city of Canon (Cañon) City, Colo. in Fremont County on the Arkansas River in SC Colo. (modern-day pop. 16K), named for the nearby Royal Gorge of the Arkansas River is laid out for Pikes Peak Gold Rush miners by people who never live there, after which in late 1859 a new party jumps their claim, putting up the first bldg. in Feb. 1860 as a commercial center for mining in South Park and the Upper Arkansas River; a gringo journalist leaves the tilde out of the Spanish word for canyon and it takes decades to put it back in; it is incorporated on Apr. 3, 1872; in 1861 the town sends two cos. of volunteers to serve with the 2nd Colo. Infantry, fighting in N.M., Okla., and Mo. until 1865; in 1862 A.M. Cassaday strikes oil 6 mi. N of town, becoming the first commerical oil well W of the Mississippi River; after gold is discovered in Cripple Creek in 1891, several smelters are built; it goes on to become the home of nine state and four federal prisons, incl. the Colo. Territorial Correctional Faciity (1871), with a Welcome sign reading "Corrections Capitol of the World"; it also calls itself the climate capital of Colo.



On May 23, 1858 a party from Auraria, Ga. led by William Greeneberry "Green" Russell (1818-77) arrives at the head of Cherry Creek in Colo. near the South Platte River at the W edge of the Great Plains on the 150-mi. Front Range of the Rocky Mts., and come up empty, going on to prospect on all the streams N to the Cache la Poudre River, returning in early July to the Platte River and camping in Little Dry Creek S of modern-day Denver, discovering gold and taking 20 oz. (several hundred dollars' worth), after which old trader John Cantrell returns to Kansas City with the good news backed up by samples, causing newspapers to start the Colo. (Pike's Peak) Gold Rush, during which 50K migrate within a year and 100K+ migrate by the time of the creation of Colo. Territory on Feb. 28, 1861, with the motto "Pike's Peak or Bust", although no gold is discovered within 50 mi. of it; meanwhile in Oct.-Nov. a party from Lawrence, Kan. that arrived near Pueblo on July 4 settles on the Platte River N of Denver, building 20-30 log cabins, which they call Montana City; on Oct. 29 a large number of prospectors that heard of the Russell discovery begin settling on both sides of Cherry Creek; on Nov. 1 the town of Auraria SE of the confluence of Cherry Creek and the South Plate River is founded three weeks before Denver by the Russell party; on Nov. 6 an election is held, and H.J. Graham is selected to travel to Washington, D.C. to talk Congress into organizing a new territory in vain, while A.J. Smith is sent to the Kan. Territorial legislature to do ditto, and they bite, establishing Arapahoe County in the W part of Kan. Territory to the crest of the Rocky Mts.; next Apr. a convention is held there to create the provisional State of Jefferson, which is never recognized by the U.S. govt.; on Nov. 22 Leavenworth, Kan. settler "General" William H. Larimer Jr. (1809-75) arrives, settling on a hill across Cherry Creek from Auraria, laying cottonwood logs along a 1 sq. mi. parcel of land to stake his claim, which he calls the mile-high (5,280 ft. elev.) city of Denver, Colo. (modern-day pop. 690K/2.8M), named after Winchester, Va.-born Kansas Territorial Gov. #5 (since Dec. 1857) James William "Jim" Denver (1817-92), opening the first store in Denver to service miners working in placer mines, founding the Denver Land Co. to sell tracts, calling Colo. "the most picturesque country in the world, with fine air, good water, and everything to make a man happy and live to a good old age" and trading tracts in Denver for grubstakes and gambling debts until the mines peter-out by 1860, causing tens of thousands to return home; the Denver streets are laid out parallel to the S bank of Cherry Creek near its confluence with the Platte Rive*r, ending up diagonal to the four cardinal directions, running from 13th St. N to 38th St., and E from Wawatta St. to Wazee St., Blake St., Market St., Larimer St., Lawrence St., Curtis St., Champa St., Stout St., California St., Walton St., Glenarm Pl., Tremont Pl., and Court Pl., ending at the intersection of W Colfax Ave. and Broadway, site of Civic Center Park and the Colo. State Capitol; on Apr. 6, 1860 Auraria is incorporated into Denver, becoming known as West Denver; Southern Arapaho chief Little Raven (Crow) (Hosa) (Oh-has-tee) (1810-89) welcomes the paleface settlers to the Denver gold camp, causing them to name Arapahoe St.; the Indian tribes are pushed S into the Arkansas River Valley; next year Larimer founds Mount Prospect (Prospect Hill) Cemetery in Denver on Arapaho land, which is converted to Cheesman Park in 1907; the real Denver visits Denver in 1875 and 1882 and receives little attention?
In 1858 the city of Carson City, Nev. on the E edge of the Carson Range of the Sierra Nevadas 30 mi. from modern-day Reno (alt. 4.8K ft.) is founded as a trading post, named for Kit Carson, experiencing a pop. surge from the 1859 Comstock Lode strike; in 1864 it becomes the capital of Nev., with the Virginia and Truckee Railroad connecting it with Virginia City, along with a log flume; in 1870-93 the Carson City Mint strikes gold and silver coins; by 1880 it becomes home to 1K+ Chinese immigrants (railroad workers), 20% of the pop.; too bad, after the Central Pacific Railroad builds a line through Donner Pass to the N, pop. begins to decrease.
In 1858 Ancient Corinth in Greece is destroyed by a 6.5 earthquake, and the city of New Corinth (Nea Korinthos) (modern-day pop. 38K/58K) is built 1.9 mi. to the SW on the Gulf of Corinth 48 mi. W of Athens; in 1928 a 6.3 earthquake destroys it, and it is rebuilt, and ditto after a great fire in 1933.

On Aug. 13, 1859 Colorado Springs, Colo. (originally Colorado City) on the Colo. Front Range at the confluence of Fountain and Camp Creeks (modern-day pop. 465K/712K) is formally organized, serving as the capital of Colo. Territory from Nov. 5, 1861 to Aug. 14, 1862, when the capital is moved 70 mi. N to Denver; in Aug. surveyors M.S. Beach and Rufus Cable discover Garden of the Gods rock formation near Colorado Springs, with Beach suggesting that it would make a great place for a beer garden, and Cable replying "Beer garden! Why, it is a fit place for the gods to assemble"; it becomes a U.S. nat. park in 1909, and is designated a nat. natural landmark in 1971.

In Nov. 1859 Champion, N.Y.-born George Eliphaz Spencer (1836-93) founds the town of Breckenridge, Colo. just W of the Continental Divide in Summit County (modern-day pop. 4.5K), named after U.S. vice pres. #14 John C. Breckinridge of Ky. in hopes of flattering the federal govt. into putting a post office there, which becomes the first between the Continental Divide and Salt Lake City, Utah; too bad, Breckinridge sides with the Confeds., causing the citizens to change the name; Spencer joins the Union Army on Oct. 16, 1862, rising to brig. gen. then becoming a Repub. U.S. Sen. in Ala. in 1868-79; skis (from the Nordic word for sticks) are first used in the state when 10 men in a snowbound mining camp along the Blue River near Breckenridge build their own skis to travel down the valley, where they begin the town of Eldorado West; Breckenridge Ski Resort opens on Dec. 16, 1961.
In 1859 gold is discovered in California Gulch near the headwaters of the Arkansas River at 10,152 ft. alt. in the Rocky Mts. of Colo., causing the town of Oro (sp. "gold") City, Colo. to spring up, reaching 5K pop. next year; too bad, the gold runs out and the town is abandoned, but in 1874 silver is discovered there, causing people to return, founding Leadville, Colo. (modern-day pop. 2.6K), which is incorporated on Feb. 18, 1878, becoming the highest incorporated city in the U.S.
In 1859 the city of Casper, Wyo. in EC Wyo. at the foot of Casper Mountain and the N end of the Laramie Mountain Range (modern-day pop. 59K) starts out as a ferry on the Emigrant Trail built in 1847 during the first Mormon wagon train to Utah by Brigham Young, growing into several ferries over the North Platte River for settlers along the Oregon, Calif., and Mormon trails, followed by a bridge and trading post built this year by Louis Guinard, after which Ft. Caspar (originally Platte Bridge Station) is founded under the command of Lt. Col. William O. Collins, and named after his son 2nd. Lt. Caspar Collins, who is KIA by Indians in July 1865; in 1857 the troops abandon the fort in favor of Ft. Fetterman downstream on the North Platte River on the Bozeman Trail, allowing developers to found a town as a stopping point for the Wyo. Central Railway; a typo causes the name change during registration; after development of the Salt Creek Oil Field, Caspar becomes known as "Oil City"; residents later incl. Dick, Lynne, and Liz Cheney.
The ugly but useful butthole of the Colo. Front Range? In 1859 the city of Commerce City, Colo. in Kansas Territory (modern-day pop. 54K) starts out as a trading post-hotel-ranch on Henderson Island in the South Plate River S of Denver, founded by Kan. Territory pro-slavery politician, Leavenworth Journal ed., and Bleeding Kansas col. John D. "Colonel Jack" Henderson, becoming the first permanent settlement in the South Plate River Valley between Fort St. Vrain in Neb. Territory and Cherry Creek in Kan. Territory; on Jan. 29, 1861 the E side of Kansas Territory becomes the state of Kansas, and on Feb. 28 the W side becomes part of Colo. Territory, which on Nov. 1 creates Arapahoe County, which stretches from modern-day Sheridan Blvd. 160 mi. E to the Kansas border, and from modern-day County Line Rd. 30 mi. N to Parallel 40 deg. North (168th Ave.), wich Denver as the county seat until 1902; in 1876 after Colo. becomes a state on Aug. 1, Riverside Cemetery (the metro Denver area's oldest cemetery) is founded in Commerce City, followed in 1892 by Rose Hill Cemetery, founded by the United Hebrew Cemetery Assoc.; the town of Derby is founded in 1889 along with Irondale, followed by Adams City in 1903; on Apr. 15, 1901 the Colo. legislature splits Arapahoe County into Adams County, a new consolidated City and County of Denver, and South Arapahoe County, which is renamed Arapahoe County on Apr. 11, 1903, with Littleton as the county seat; on Nov. 8, 1904 Brighton, Colo. (incorporated on Sept. 1887 and named for Brighton Beach, N.Y.) becomes the county seat of Adams County; in Dec. 1942 Rocky Mountain Arsenal is founded to the E of Commerce City (closed in 1992); on July 27, 1949 after Amendment 2 legalizing pari-mutuel betting on horses and greyhounds is approved in 1948, Mile High Kennel Club is founded in Commerce City for greyhound racing; on Dec. 18, 1952 Commerce City is incorporated as Commerce Town, changed in 1962 to Commerce City; in 1989 53 sq. mi. of Adams County is transferred to the City and County of Denver for the new Denver Internat. Airport (DIA); on Nov. 15, 2001 the NW corner is transferred to the City and County of Broomfield.
In 1859 the seaside resort town of Eastbourne on the S coast of England right E of Beachy Head (highest chalk sea cliff in Britain) and 19 mi. E of Brighton (modern-day pop. 103K) is created from four separate hamlets under the direction of the Duke of Devonshire, becoming known for its string of large beachfront Victorian hotels, its pier, a Napoleonic fort, and military museum.
In 1859 the city of Kuala Lumpur ("muddy confluence") in Malaysia (modern-day pop. 1.7M/7.2M) is founded as a tin-mining settlement, going on to become Malaysia's cultural, financial, and economic center, home of the Maylasian king, and home of the Malaysian Parliament.
In 1859 the city of Logan, Utah on the Logan River on the W slopes of the Bear River Mts. and the E edge of Cache Valley in N Utah 47 mi. N of modern-day Ogden and 82 mi. N of Salt Lake City (modern-day pop. 48K) is founded by Mormon settlers sent by Brigham Young to build a new fort, named for fur trapper Ephraim Logan; it is incorporated on Jan. 17, 1866; on Aug. 6, 1877 Brigham Young College is founded there (until 1926), followed on Mar. 8, 1888 by Utah State U. (of Agriculture and Applied Science) (originally Agricultural College of Utah until 1957).

The gold vs. silver wars start just before the U.S. Civil War? In 1859 the Comstock Silver Lode is discovered in Six-Mile Canyon (Eagle Valley) on the E slope of Mt. Davidson in the Va. Range in W Nevada; to the W the city of Virginia City (named after a miner nicknamed Virginia?) is founded near Reno (modern-day pop. 800); San Francisco robber baron William Sharon (1821-85) (Repub. U.S. Sen. from Nev.) and his Bank Ring gain control of the Comstock, becoming known as "King of the Comstock".
On June 6, 1860 (July 2 Old Style) the Russian military supply ship Manchur commanded by Capt.-Lt. Alexey K. Shefner founds the outpost of Vladivostok (Russ. "ruler of the East") (modern-day pop. 600K) on the Golden Horn Bay near the Russian borders with China and Korea; town status is granted on Apr. 22, 1880; in 1916 the Trans-Siberian Railway connecting Vladivostok to Moscow is completed, giving a royal road to Europe.
On Dec. 7, 1860 after the railroad reaches it on July 4, the city of Valdosta, Ga. ("the Azalea City") 140 mi. S of Macon (modern-day pop. 56K) is incorporated, becoming the center of long-staple cotton growing manned by black slaves; in 1897 the world's 2nd Coca-Cola bottling plant opens there; in 1899 the cotton mill town of Remerton is founded 2 mi. away; Valdosta later becomes known for its sweet mild Valdosta Onions.
In 1860 the city of Bakersfield, Calif. at the S end of the San Joaquin Valley (modern-day pop. 376K/839K) is founded by German immigrant Christian Bohna; too bad, it is swept away by floods in 1862, after which Ohio settler Thomas Baker refounds the town at Baker's Field in 1863, growing to 600 pop. by 1870 and incorporating as a city in 1873, becoming the seat of Kern County in 1874 until bad sheriff Alexander Mills causes the town to disincorporate in 1876, not reincorporating until Jan. 11, 1898, going on to become known for agriculture and oil production, and as the birthplace of the Bakersfield Sound.


On Apr. 12, 1861 - May 9, 1865 the horrific U.S. Civil War sees the invention of the first modern weapon when N.C.-born agricultural equipment maker Richard Jordan Gatling (1818-1903) patents the 10-barrel hand-cranked hundreds-of-rounds-per-min. Gatling Gun (the first practical machine gun) just in time for use on some Johnny Rebs; it is first used by the Union Army in 1864, but luckily never sees extensive use.
In 1862 the desert resort city of Palm Springs, Calif. E of Mount San Jacinto in the Coachella Valley 55 mi. E of San Bernardino, 107 mi. E of Los Angeles, 123 mi. NE of San Diego, and 268 mi. W of Phoenix, Ariz. (modern-day pop. 44K) (named after the Calif. fan palm Washingtonia filifera) is founded by Jack Summers as a stagecoach station on the Bradshaw Trail; in 1876 the Southern Pacific Railroad bypasses it 6 mi. to the N, stifling pop. growth; in 1886 Dr. Welwood Murray founds Murray Hotel for health tourists; in 1906 health nut George Wharton James pub. The Wonders of the Colorado Desert (2 vols.), which praises it for its "great charms and attractiveness", making fans of U.S. vice-pres. Charles Fairbanks, naturalist John Muir, and Robert Louis Stevenson's widow Fanny Stevenson before it is demolished in 1909; in 1920 J. Smeaton Chase pub. Our Araby: Palm Springs and the Garden of he Sun, causing Pearl McCallum and her husband Austin G. McManus to build the Art Deco Oasis Hotel in 1924, designed by Frank Lloyd Wright, starting a luxury resort hotel boom that makes it popular with Hollywood stars in the 1930s.
On July 4, 1863 Ft. Boise 110 mi. N of the modern-day Nev. border and 41 mi. E of the modern-day Ore. border on the Boise River on the Oregon Trail and a major road to to Boise Basin and Owyhee 50 mi. E of the old Hudson's Bay Co. fort is founded, spawning the city of Boise, Idaho (Fr. "Le bois" = the woods) (modern-day pop. 205K/664K), becoming the largest city in the NW U.S.

On May 26, 1864 the Territory of Montana (Mont.) is created out of Idaho Territory by Congress, with capital at Bannack, Mont. on Grasshopper Creek in SW Mont. until Feb. 6, 1865, followed by Virginia City, Mont. in SW Mont. until Apr. 19, 1875; on July 14 gold is discovered in Last Chance Gulch, Mont. by the Four Georgians; on Oct. 30 3,875-ft. alt. Helena, Mont. in WC Mont. (modern-day pop. 31K) is founded; by 1868 $16M in gold is dug up from Last Chance Gulch, and the town pop. reaches 7.5K, incl. 50 millionaires, most per capita on Earth; on Apr. 19, 1875 it becomes the capital of Mont. Territory, and capital of the state of Mont. on Nov. 8, 1889; Last Chance Gulch takes 20 years to peter out; meanwhile in Aug. the city of Bozeman, Mont. in SW Mont. (modern-day pop. 45K/97K) is founded, named after Bozeman Trail founder John M. Bozeman (1835-67); it is incorporated in 1883, becoming home to Mont. State U. (1893).

In 1865 the city of Dar es Salaam (Arab. "House of Peace") (modern-day pop. 4.3M) is founded by sultan #1 (1856-70) Majid bin Said Al-Busaidi (1834-870) of Zanzibar near the Indian Ocean Swahili coastal fishing village of Mzizima (Swahili "healthy town"); in 1887 the German East Africa Co. establishes a station there, making it the administrative-commercial center of German East Africa and hub of the Central Railway Line; during WWI the British capture German East Africa, renaming it Tanganyika and importing workers from British India; in Dec. 1961 Tanganyika attains independence, with Dar es Salaam as capital, becoming the largest and most populous Swahili-speaking country on Earth, continuing as capital in 1964 when Tanganyika merges with Zanzibar to form Tanzania; in 1973 the capital begins moving to Dodoma, which is completed in 1996.
About 1865 the town of Laramie, Wyo. (modern-day pop. 32K) is settled by white settlers from New England, Mich., Wisc., and Iowa as a tent city near the Overland Stage Line route and the Union Pacific segment of the Transcontinental Railroad N of Ft. Sanders, and named after French-Canadian trapper Jacques La Ramie (Ramee) (Ramée) (1784-1821); the first regular passenger service begins on May 10, 1868.

In 1866 German immigrant Adolf Pfannenschmidt from Rinteln founds the town of Pfannenschmidtstadt on the site of Nopalera (founded 1853) in the Cahuenga Valley of the Santa Monica Mts. in warm sunny S Calif. (355 days of sunshine a year), which in 1886 is named Hollywood by Toronto, Canada-born "Father of Hollywood" Hobart Johnson "H.J." Whitley (1847-1931) on a honeymoon with his wife Gigi after he sees a Chinese man carrying wood in a wagon and uttering the soundbyte "I holly wood"; in 1903 it is incorporated as Hollywood, Calif. becoming known for orange groves, joining the city of Los Angeles in 1910 and becoming the HQ of the U.S. film industry.

In 1866 the city of Loveland, Colo. in Larimer County S of Fort Collins and 46 mi. N of Denver (modern-day pop. 76K) is founded along the newly constructed line of the Colo. Central Railroad near its crossing of the Big Thompson River, named in honor of its pres. William Austin Hamilton Loveland (1826-94), going on to become known for sugar beets and sour cherries; in 1901 the Great Western Sugar Co. opens a factory there, which closes in 1977; in the late 1920s the Spring Glade Orchard becomes the largest cherry orchard W of the Mississippi River, dwindling under killer freezes and blights until it closes in 1960.
On Mar. 1, 1867 "Cornhusker State", "Beef State" Nebraska (Neb.) (Oto Indian "flat water") is admitted as the 37th U.S. state, with the village of Lancaster, Neb. (pop. 30) (founded 1856), located in a salt marsh basin on Salt Creek (tributary of the Platte River), changing its name to Lincoln, Neb. (modern-day pop. 258K/348K), becoming the last state to name its capital city after a U.S. pres.; it was renamed after dead Pres. Lincoln by interests partial to keeping it Omaha (capital of Nebraska Territory since 1854), thinking that Confed. sympathies of senators living S of the Platte River would derail it, which backfires; the 2-story native limestone Nebraska State Capitol is completed on Dec. 1, 1868, and replaced with a 2nd bldg. in 1888, a 3rd bldg. in 1924, and a 4th bldg. in 1932, becoming the 2nd-tallest capitol bldg. in the U.S.

 On Nov. 16, 1867 after starting a gold rush in Yavapai County in the C highlands of Ariz. Territory in 1863, Anderson, S.C.-born Confed. veteran
John W. "Jack" Swilling (1830-78)
forms the Swilling Irrigating and Canal Co. in Wickenburg, Ariz, pioneering modern irrigation canals in the Salt Valley of Ariz. modeled on ancient Hohokam canals;
next summer he founds the city of Phoenix, Ariz. (modern-day pop. 1.68M/1.45M).
in the Salt River Valley, with Kent, England-born settler "Lord" Phillip Darrell Dupa (1832-92)
suggesting the name, establishing their first post office on June 15 and becoming postmaster and justice of the peace.
On Nov. 16, 1867 after starting a gold rush in Yavapai County in the C highlands of Ariz. Territory in 1863, Anderson, S.C.-born Confed. veteran
John W. "Jack" Swilling (1830-78)
forms the Swilling Irrigating and Canal Co. in Wickenburg, Ariz, pioneering modern irrigation canals in the Salt Valley of Ariz. modeled on ancient Hohokam canals;
next summer he founds the city of Phoenix, Ariz. (modern-day pop. 1.68M/1.45M).
in the Salt River Valley, with Kent, England-born settler "Lord" Phillip Darrell Dupa (1832-92)
suggesting the name, establishing their first post office on June 15 and becoming postmaster and justice of the peace.
In 1867 the cow town of Abilene, Tex. in Taylor County, 150 mi. WSW of Ft. Worth (modern-day pop. 120K/165K) is founded by Chicago cattle dealer Joseph McCoy, and named after Abilene, Kan., becoming the original endpoint for the Chisholm Trail; it is incorporated as a town in 1881, becoming county seat of Taylor County in 1883; in 1910 the pop. is 9,204.
In 1867 the city of Minneapolis, Minn. near Saint Anthony Falls, highest waterfall on the Mississippi River at its confluence with the Minnesota River (modern-day pop. 382K/4.1M) is founded, with the city's first schoolmaster Charles Hoag (1808-88) naming it from the Dakota Sioux word "mni" = water.
In 1867 the port city of Redwood City, Calif. on San Francisco Bay 27 mi. S of San Francisco and 24 mi NW of San Jose (modern-day pop. 84K) is incorporated, becoming the county seat of San Mateo County in 1866, and the only deepwater port on San Francisco Bay S of San Francisco.

On May 9, 1868 the city of Reno, Nev. in N Nev. on the Truckee River 22 mi. SW of Lake Tahoe (modern-day pop. 225K/425K) is founded at Lake's Crossing on the Central Pacific Railroad in Truckee Meadows at the foot of the Sierra Nevada Mts., named for U.S. Gen. Jesse Lee Reno (1823-62); it is incorporated on Mar. 16, 1903, going on to become known as "the Biggest Little City in the World" for its hotels and casinos.

In 1868 the city of Wichita, Kan. (modern-day pop. 382K/680K) on the Arkansas River in SC Kan. is founded as a trading post on the Chisholm Trail by New Haven, Vt.-born James R. Mead (1836-1910), becoming a destination for cattle drives from Tex. and gaining the nickname "Cowtown"; after the railroad arrives, it is incorporated as a city on July 21, 1870.

On Feb. 5, 1869 the city of Darwin on the Timor Sea in Australia's Northern Territory (modern-day pop. 145K) is founded by South Australia surveyor-gen. George Woodroffe Goyder (1826-98), originally named after British PM Lord Palmerston until 1911, when it is named after Charles Darwin, who surveyed the area on Sept. 9, 1839; in the 1870s telegraph pole diggers discover gold, causing a gold rush that boosts the white pop. to 300; the city ends up being rebuilt 4x after cyclones in 1897, 1937, and 1974, and Japanese air raids in WWII.
In 1869 the city of El Cajon, Calif. (Sp. "the box") 12 mi. E of San Diego in a boxed-in valley (modern-day pop. 100K) is founded; it is incorporated on Nov. 12, 1912.
In 1869 the city of Livermore, Calif. on the E edge of the San Francisco Bay Area (modern-day pop. 89K/4.5M) is founded by William Mendenhall, who names it for the Livermore Ranch of Springfield, Essex, England-born Robert Livermore (1799-1858), becoming the home of Lawrence Livermore Nat. Lab. and the namesake of the chemical element livemorium.
In 1869 the city of Santa Ana, Calif. (Sp. "Saint Anne") on the Santa Ana River 10 mi. from the coast of S Calif. (modern-day pop. 329K) is founded by Ky. immigrant William H. Spurgeon from the Rancho Santiago de Santa Ana 1810 Spanish land grant; in 1877 the Southern Pacific Railway builds a branch line from Los Angeles, followed in 1887 by the Calif. Central Railway, which later becomes part of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway; it is incorporated as a city in 1886 with a pop. of 2K, becoming the seat of newly-formed Orange County in 1889; during WWII Santa Ana Army Air Base is built there, boosting pop. growth after veterans move there after the war, with the Santa Ana Freeway connecting it with Los Angeles; the Santa Ana Mountains straddle the border between Orange and Riverside counties, becoming known for their Santa Ana winds that fuel seasonal wildfires.
In 1869 after deciding last year to move the admin. center out of the port city of Hakodate, the Japanese Meiji govt. develops their northernmost island of Hokkaido, founding the city of Sapporo (modern-day pp. 1.4M).

On Nov. 8, 1870 the city of Modesto, Calif. on the Tuolumne River 25 mi. SE of Stockton (modern-day pop. 201K/504K) is founded as a stop on the railroad between Los Angeles and Sacramento, allegedly named Modesto because San Francisco financier William Chapman "Billy" Ralston (1826-75) (founder of the Bank of Calif.) was too modest to let his name be used; it is incorporated on Aug. 6, 1884; too bad, Ralston commits suicide on Aug. 27, 1875 after his financial empire collapses.


In 1870 obeying Horace Greeley's 1865 exhortation to "Go West, young man", Ohio-born Nathanial "Nathan" Cook Meeker (1817-79) arrives in Colo. and founds the utopian Union Colony, which later becomes Greeley, Colo. (modern-day pop. 103K), known for its frequent stench from the JBS Swift & Co. slaughterhouse; each of 300 families pays $155 to be part of the initial "joint stock venture"; meanwhile on Dec. 1 after the Colo. Central Railroad lays tracks through it to link Golden, Colo. with Jersey Junction 5 mi. N of Denver, N.Y.-born Benjamin F. Wadsworth and Louis A. Reno (1833-1906) found Arvada, Colo. (modern-day pop. 110K), named after Hiram Arvada Haskin, brother-in-law of settler Mary Wadsworth, wife of Benjamin Wadsworth, who becomes its first postmaster; it incorporates on Aug. 14, 1904.
In 1870 after settlers buy 1-acre plots from the State of Calif. for $1, and the 105-ton steamer The Vaquero captained by Samuel S. Dunnells ignores posted warnings and safely steers through Lower Newport Bay and Upper Newport Bay, the city of Newport Beach, Calif. is named by County Down, Ireland-born James Irvine (1827-86) of San Francisco; in 1905 the Pacific Electric Railway connects it with downtown Los Angeles; on Sept. 1, 1906 the 206 citizens incorporate it as a city, going on to become a favorite beach resort and home of wealthy celebs incl. John Wayne, Humphrey Bogart and Lauren Bacall, George Burns, Buddy Ebsen, Shirley Temple, Mamie Van Doren, Dean Koontz, Kelly McGillis, Chuck Norris, and Nicolas Cage. hosting the annual Christmas Boat Parade starting in 1908; in 1878 James Irvine acquires the 110K-acre Irvine Ranch stretching from the Pacific Ocean to the Santa Ana River, becoming home to the Marine Corps Air Station El Toro in 1942-99, and the Irving campus of the U. of Calif. in 1959, and incorporating as the city of Irvine, Calif. (modern-day pop. 266K) on Dec. 28, 1971; in 2003 Irvine annexes the closed 7.3 sq. mi. El Toro Marine Corps Air Station.
On June 1, 1871 the city of Birmingham, Ala. (modern-day pop. 217K/1.1M) is founded at the planned crossing of the Alabama & Chattanooga and South & North Alabama Railroads from three farm towns by the Elyton Land Co., named after Birmingham, England to emphasize its industrial goals; in the early 1900s it becomes known as "the Magic City" and "the Pittsburgh of the South" for its rapid growth, mainly Irish and Italian non-union laborers along with African-Ams. from rural Ala., rivaling Atlanta, Ga. as a Deep South railroading hub and banking center; in 1902-12 four skyscrapers are built in downtown, becoming known as "the Heaviest Corner on Earth".
In 1871 the steamboat stop city of Fargo, N.D. (originally Centralia) on the Red River (modern-day pop. 105K/238K), named after Wells Fargo founder William Fargo is founded, going on to hook up with the Northern Pacific Railroad and gain the nickname "Gateway to the West", and become the divorce capital of the Midwest in the 1880s because of lenient divorce laws.
In 1871 the city of Ivanovo 160 mi. NE of Moscow (modern-day pop. 408K) is founded by merging the 16th cent. village of Ivanova with the new digs of Voznesensk; until 1932 it is called Ivanovo-Boznesensk.
In 1871 the city of Spokane, Wash. on the Spokane River on the former site of the Spokane "children of the sun" people (modern-day pop. 209K/710K) is settled by cattle ranchers J.J. Downing and S.R. Scranton; on June 20, 1881 the railroad reaches the city, bringing Euro settlement, and it is incorporated on Nov. 29 with 1K pop.; in 1883 gold, silver, and lead are discovered in the Coeur d'Alene region of N Idaho, causing Spokane to become a mining-smelting town until the Great Fire on Aug. 4, 1889 burns down 32 blocks of downtown, which doesn't stop it from being rebuilt and reincorporated in 1891, becoming known as "the Lilac City".
In 1872 "Cowboy Capital of the World", "Wickedest Little City in the West", "Queen of Cowtowns" Dodge City, Kan. on the Arkansas River in SW Kan. (on the meridian separating Central and Mountain time) 5 mi. W of Ft. Dodge (modern-day pop. 27K) (founded last year as an outpost on the Santa Fe Trail and originally called Buffalo City) becomes connected to the Atchison, Topeka, and Santa Fe Railway, becoming a main shipping point for Texas cattle (unti 1885), famous for lawmen Wyatt Earp and Bat Masterson, Front St., and Boot Hill (where they bury them with their boots on).
In 1872 the city of Fresno, Calif. on the San Joaquin River in the geographical center of Calif. 220 mi. N of Los Angeles, 170 mi. S of Sacramento, and 180 mi. SE of San Francisco (modern-day pop. 494K/972K) is founded as a station of the Central Pacific Railroad; it is incorporated in 1885.
In 1872 the city of Pawhuska, Okla. (originally Deep Ford) (modern-day pop. 3.5K) named after Osage chief Paw-Hiu-Skah ("white hair") (1763-1809) is established on the new Osage Nation Rez in Indian Territory (Okla.); the first Boy Scout troop in the U.S. is organized there in 1909.
Don't let your buds down? On Nov. 17, 1873 the 1st cent. C.E. Celtic cities of Buda and Obuda on the W bank and pesky Pest on the E bank unite with Margret Island on the Danube River to create the city of Budapest (modern-day pop. 1.75M/3.3M), which becomes the co-capital of the Austro-Hungarian Empire (until 1918).

In 1873 the city of Fort Worth, Tex. on the Trinity River (modern-day pop. 400K/800K), founded in 1849 as a military camp and named after U.S. gen. William Jenkins Worth (1794-1849) is incorporated, becoming known as a cattle drive terminus.
In 1875 the city of Calgary in Alberta, Canada (modern-day pop. 1.2M/1.4M) at the confluence of the Bow and Elbow Rivers 50 mi. E of the Canadian Rockies Front Range is founded as a Northwest Royal Canadian Mounted Police post; in 1883 the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) reaches the city, causing it to grow; on Nov. 7, 1884 it is incorporated as a town, and as a city on Jan. 1, 1894; in 1996 the CPR HQ moves there from Montreal.
On Mar. 14, 1876 after the Colo. legislature passes legislation on Nov. 7, 1861 naming the city of Boulder, Colo. (25 mi. NW of Denver) (modern-day pop. 108K/313K) as the site, and the cornerstone for the Old Main Bldg. is laid on Sept. 20, 1875, the U. of Colo. (CU) (home of the Buffaloes) is founded via an amendment to the state constitution before formal admission to statehood, which later causes its regents to consider themselves equal to or above the state legislature; it officially opens on Sept. 5, 1877; in 1912 the U. of Colo. Denver is founded; in 1965 the U. of Colo. Colorado Springs is founded.
In 1876 the city of Flagstaff, Ariz. (modern-day pop. 71K/139K) is founded by Thomas F. McMillan, who builds a cabin on Mars Hill on the W side of town; it is named after a centennial ponderosa pine flagpole erected there by a scouting party from Boston, Mass.; the town is only a 2-day ride to the S rim of the Grand Canyon; it is incorporated in 1928.

In 1877 Ariz. Territory capital (since 1867) Tucson, Ariz. (O'odham "Cuk Son" = base of the black hill) (founded on Aug. 20, 1775 as Presidio San Agustín del Tucsón) on the Santa Cruz River in the Sonoran Desert (modern-day pop. 530K/1M) is incorporated; in 1889 the Ariz. capital is moved to Phoenix, which passes Tucson in pop. in the 1910s; 60 mi. SE the town of Tombstone, Ariz. (modern-day pop. 1.3K) is founded in 1879 as a silver mining strike by Wellsboro, Penn.-born prospector Edward Lawrence "Ed" Schieffelin (1847-97), who was told that is the only kind of stone he'd find in Goose Flats (he ends up finding silver and founding the Contention, Lucky Cuss, and Tough Nut mines); the town is incorporated in 1881, becoming known for its frontier main street ended by the Bird Cage Saloon with a 24/7/365 basement poker game attracting players incl. Diamond Jim Brady, Doc Holliday, and Bat Masterson, and the Gunfight at the O.K. Corral on Oct. 26, 1881 at the other end towards Boot Hill at the NW corner of town; by the mid-1880s local mines produce $40M-$85M in silver bullion, becoming one of the last Am. Frontier boom towns.
In 1878 U.S. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman builds a fort on the future site of Coeur d'Alene (Fr. "heart of an awl"), Idaho on the N shore of 25-mi.-long Lake Coeur d'Alene 30 mi. E of Spokane, Wash. (modern-day pop. 50K/679K), attracting miners and settlers after gold, silver, and lead are discovered in 1883.

On Sept. 10, 1880 after talking Bateke king Illoh Makoko into placing his kingdom under protection of the French flag, the city of Brazzaville on the N bank of the Congo River and the Pool Malebo (Stanley Pool) (Lake Nkunda) (modern-day pop. 1.8M) is founded by French explorer Pierre Paul François Camille Savorgnan de Brazza (Pietro Paolo Savognan di Brazzà (1852-1905), becoming the capital of the Repub. of the Congo; meanwhile in 1881 the city of Leopoldville (later Kinshasa) on the S bank of the Congo River and the Pool Malebo opposite Brazzaville (modern-day pop. 11.8M), named after Leopold II of Belgium is founded by Henry Morton Stanley in the Belgian Congo (modern-day Dem. Repub. of the Congo), becoming the 3rd largest urban area in Africa after Cairo and Lagos, and 2nd largest Francophone urban area in the world after Paris; French is the official language, although Lingala (Bangala) (Bangi), Tshiluba, and Swahili are also spoken; in 1971-97 the Dem. Repub. of Congo is called Zaire.

On Oct. 18, 1880 after receiving help from native guide Chief Kowee and making the first major gold discovery in the panhandle in the Gastineau Channel at the base of Mt. Juneau across from Douglas Island, Quebec-born miner Joseph "Joe" Juneau (1836-99) and Irish-born miner Richard Tighe Harris (1833-1907) found Juneau, Alaska (originally ROckwell) (modern-day pop. 32K/24K), taking 1K lbs. of gold ore back to Sitka; Juneau replaces Sitka as the capital of Alaska in 1906; the city and borough incl. 3,255 sq. mi. of territory, as large as the states of R.I. and Del. combined.
On Oct. 30, 1880 the city of Tegucigalpa (Nahuatal "Taguz-galpa" = hills of silver) in SC Honduras (claimed by the Spanish on Sept. 29, 1578) (modern-day pop. 1.1M) becomes the capital of Honduras; the twin city of Comayaguela lies on the opposite (W) bank of the Choluteca River - why does that name give me goosebumps?
In 1880 the city of Long Beach, Calif. 20 mi. S of Los Angeles (modern-pop. 462K/17.8M) is founded by William E. Willmore, who buys 4K acres of the Rancho Los Cerritos from Jotham Bixby, "the Father of Long Beach", then tries to create the farming community of Willmore City, fails, and sells out to a Los Angeles syndicate; it is incorporated on Dec. 13, 1897, later becoming known as "Iowa by the sea" for its major immigrant group.

In 1880 the city of Pierre, S.D., named after St. Louis, Mo.-born fur trader Pierre Chouteau Jr. (Pierre Cadet Chouteau) (1789-1865) is founded on the E bank of the Missouri River opposite Fort Pierre (founded 1832) in the geographic center of the state, becoming the capital of S.D. on Nov. 2, 1889 after defeating rival town Huron.


In 1880 the town of Winslow, Ariz. (Navajo name Beeshsinil = "iron lying down") 58 mi. E of Flagstaff in the high plateau country of NE Arizona (4,850 ft.) in the Little Colorado River Valley ) (modern-day pop. 10K) is founded as a div. point for the Santa Fe Railway, named after prospector T.L., er, Tom Winslow and/or Augusta, Maine-born U.S. Civil War Union Gen. Edward Francis Winslow (1837-1914), pres. of the St. Louis & San Francisco Railroad, which passes through; it is incorporated in 1900.
On Feb. 25, 1881 the city of Phoenix, Ariz. near the confluence of the Salt and Gila Ribvers in the Valley of the Sun in the Salt River Valley of Maricopa County (settled in 1867) is incorporated (modern-day pop. 1.68M/1.45M), becoming the state capital of Ariz. in 1889, and the most populous city in Ariz., also the first state capital with 1M residents (until ?).

On Aug. 28, 1881 after Congress passes the U.S. Ute Removal Act, reneging on a guarantee of 12M acres in perpetuity, the former Ute Indian Territory is abolished and the Utes removed from their "Shining Mountains" to a rez in E Utah so that the U.S. govt. can open the area to white settlers, incl. Clinton County, Penn.-born George Addison Crawford (1827-91), who next July 22 incorporates the town of Grand Junction, Colo. (AKA River City, Ol' Grandy, Capital of the Western Slope) in Grand Valley on the W slope of the Rockies at the confluence of the Grand (Upper Colorado) and Gunnison Rivers (modern-day pop. 60K/147K), and plants the first vineyard in Colo. near Palisade, after which the area becomes known as the Colo. Wine Country.
In 1881 the city of Aberdeen, S.D. in NE S.D. 125 mi. NE of Pierre (modern-day pop. 28K) is founded in one of the richest farm areas in the U.S., becoming known as the "Hub of the Two Dakotas".
In 1881 the town of Calico, Calif. in the Calico Mts. of the Mojave Desert 3 mi. NE of modern-day Barstow, Calif. is founded near the site of a major silver strike, shipping $13M-$20M worth of silver by the time it becomes a ghost town in 1900; in 2005 Calif. Gov. Arnold Schwarzenegger proclaims it Calif.'s Silver Rush Ghost Town.
In 1882 the city of Regina (Lat. "Queen") in Saskatechewan, Canada (modern-day pop. 214K/236K) (originally Wascana = "Buffalo Bones" in Cree), named for Queen Victoria is established after being picked by Victoria's daughter Princess Louise, wife of the Marquess of Lorne, gov.-gen. of Canada; the capitol bldg. is at Victoria Ave. and Albert St.; the city of Saskatoon (Cree "place of many saskatoon berries") on the South Saskatechewan River in Saskatchewan, Canada (modern-day pop. 246K/295K) is founded by the Toronto-based Temperance Colonization Society as a dry community, going on to become the largest city in Saskatechewan.
In 1883 after the railway arrives there, the city of Virginia Beach, Va. in Princess Anne County on the Atlantic Ocean at the mouth of Chesapeake Bay near Cape Henry where English Jamestown colonists first landed in 1607 (modern-day pop. 452K/1.7M) is settled, and incorporated as a town in 1906, becoming a popular vacation spot with casinos and amusement parks; in 1952 it is incorporated as a city, becoming the most populous in Va.

On Feb. 21, 1886 the city of Fort Myers, Fla. (modern-day pop. 75K), named after Confed. quartermaster gen. Abraham Charles Myers (1811-89) is founded on an abandoned U.S. Army fort by U.S. Civil War Union vet Manuel A. Gonzalez (1832-1902) and his 5-y.-o. son Manuel S. Gonzales from Key West; it goes on to become a major winter resort after the building of the Royal Palm Hotel in 1898, attracting Thomas Edison, Henry Ford et al.
On June 19, 1886 the city of Pasadena, Calif. 10 mi. NE of downtown Los Angeles is incorporated (modern-day pop. 137K), becoming the home of the annual Tournament of Roses Parade and Rose Bowl football game, along with Caltech and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
In Sept. 1886 after gold is discovered in June 1884 in sedimentary rocks on Witwatersrand (Dutch "white waters range") on the Rand Ridge in the Transvaal between the Vaal and Limpopo Rivers, causing the Witwatersrand Gold Rush, the boom town of Johannesburg (elev. 5740 ft.) (modern-day pop. 957K/9.6M), named after deputy surveyor-gen. Johannes Rissik and mining commissioner Christiaan Johannes Joubert is founded 957 mi. NNE of Cape Town as a gold-mining camp, and zooms to a pop. of over 100K, with Cecil Rhodes' Consolidated Gold Fields setting up a microsoft, er, monopoly.
In Apr. 1887 Amarillo, Tex. (200K/276K) (Sp. "Yellow") (originally Oneida) ("the Yellow Rose of Tex.") in the Tex. Panhandle is founded by J.I. Berry along the Fort Worth and Denver City Railroad; on Aug. 30 it becomes the seat of Potter County; by the late 1890s the town becomes one of the busiest cattle-shipping points on Earth; in 1918 natural gas is discovered, followed by oil in 1921; in 1927 the U.S. govt. acquires the Cliffside Gas Field, and in 1929 the Federal Bureau of Mines begins operating the Amarillo Helum Plant, becoming the sole producer of helium on Earth, earning it the nickname "Helium Capital of the World"; it goes on to become a major meat-packing site, and the home of Pantex nuclear weapons assembly facility, giving it the nickname "Bomb City".
In 1887 the city of Whittier, Calif. near Los Angeles, named after Am. Quaker poet John Greenleaf Whittier (modern-day pop. 86K) is founded by Jonathan Bailey, whose Quaker meetings on his front porch attract Quaker settler, who build a meeting house along with Whittier College (originally Whittier Academy); it is incorporated at Feb. 25, 1898; the college is chartered by Calif. in 1901; sports teams are known as the Poets; alumni incl. U.S. pres. Richard M. Nixon.
In 1888 the "World's Largest Village" of Skokie, Ill. (Potawatomi "marsh") 15 mi. N of Chicago (modern-day pop. 65K) is incorporated as Niles Centre, changing to Niles Center in 1910, and Skokie on Nov. 15, 1940; it starts as a German-Luxembourger farming community, and hosts a large Jewish pop. after WWII; it goes on to become the scene of neo-Nazi protest marches in 1977-8 and the home of Olympic gymnast Bart Conner and barbershop quartet member Keyser Soze :)

On Apr. 22, 1889 (noon) the Oklahoma Land Rush (Run) ("Hoss Race") begins, opening the vacated Indian territory of Oklahoma to 50K eager "sooner" white settlers (Tom Cruise and Nicole Kidman?) waiting at the borders to claim 2M acres of land divided into 160-acre homesteads, while what's left of the Injuns go bonkers; Nannita Regina H. "Kentucky" Daisey (1855-) becomes the first person to claim a homestead tract; Guthrie City (new capital) (founded Apr. 22) and Oklahoma City (OKC) (founded Apr. 22) (modern pop 630K/1.46M) swell with Sooners, with the pop. of Guthrie and OKC starting at 10K, and OKC passing Guthrie up and becoming the state capital in 1910, causing the Okla. State Capitol to be built in 1914-17, becoming the only one in the U.S. with active oil rigs; the dome isn't completed until 2002 - everybody talks about how tough their truck is?

On Sept. 12, 1890 the city of Salisbury (originally Ft. Salisbury) in Mashonaland in NE Southern Rhodesia (modern-day pop. 1.6M) is founded by the Pioneer Column of the British South Africa Co., named after Conservative British PM (1885-92, 1895-1902) Robert Arthur Talbot Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury (1830-1903); in 1982 it is renamed Harare.
In 1893 the city of Novosibirsk ("New Siberia") on the Ob River in SW Siberia (original name Novonikolayevsk until Sept. 12, 1926) (modern-day pop. 1.4M7M/1.57M) is founded on the Trans-Siberian Railway, becoming known as "the Chicago of Russia" for its rapid growth and industralization under Joseph Stalin.

On July 28, 1896 after Standard Oil Co. co-founder Henry Morrison Flager (1830-1913) builds the Fla. East Coast Railway and finds out that the Great Orange Belt Freeze of 1894-5 spared the Miami River, and purchases the land from ("the Mother of Miami") Julia DeForest Tuttle (nee Sturtevant) (1849-98), then finances its development, the city of Miami, Fla. (modern-day pop. 450K/5.5M) in Dade County on Biscayne Bay (named after the Mayaimi (Maymi) (Maimi) people) is incorporated, Flagler graciously declining the honor of having it called Flagler - it would later have been nice to call it Fagler?
In 1896 the city of Harbin (Manchu "place for drying fishing nets") in Heilongjiang Province, NE China (modern-day pop. 10.6M) becomes the main construction center for the Chinese Eastern Railway through Manchuria, which by 1904 links the Trans-Siberian Railroad coming from E Lake Baikal, Siberia with the Russian port of Vladivostok on the Sea of Japan (East Sea); during the 1904-5 Russo-Japanese War it becomes a base for Russian military operations; after the 1917 Russian Rev. it becomes a haven for refugees, with the largest pop. of any Russian city outside the Soviet Union, gaining the nickname "Eastern Moscow"; in the 1920s it becomes China's fashion capital; in 1985 it begins hosting the annual winter ice sculpture festival in 2004 it is voted China's top tourist city.
In 1897 the city of Oxnard, Calif. on the Pacific coast of Southern Calif. 60 mi. W of downtown Los Angeles, Calif. (modern-day pop. 200K) starts as a $1M sugar beet factory operated by Henry Thomas Oxnard (1860-1922) of the Am. Crystal Sugar Co. in Minn.; it is incorporated as a city on June 30, 1903, becoming known for growing strawberries and lima beans, and as home to U.S. Navy bases at Point Mugu and Port Hueneme.
In 1899 the city of Nairobi (Maasai "enkare nyrobi" = cool water) on the Nairobi and Athi Rivers in SC Kenya (modern-day pop. 4M/6.5M) is founded by the authorities of British East Africa as a rail depot on the Uganda Railway, replacing Machakos as the capital of Kenya in 1907 and becoming a center for the coffee, tea, and sisal industry.

In 1904 after the town of Pacific City (formerly Shell Beach, Smeltzer, Gospel Swamp, and Fairview) cedes power to Oneonta, N.Y.-born Pacific Electric Railway magnate Henry Edwards Huntington (1850-1927) to secure access to the lines of the Pacific Electric Red Car from Los Angeles that stopped at Long Beach, the city of Huntington Beach, Calif. (modern-day pop. 200K) in Orange County builds a 1K-long pier on its 9.5-mi.long sandy beach that attracts beachgoers, and is incorporated on Feb. 17, 1909, becoming known for oil wells, sugar beets processed by Holly Sugar, and the defense contractor McDonnell Douglas Astronautics, known for the Apollo and Skylab space programs.

A giant grid with a city on top that shakes all the money out of people's pockets and funnels it to the lucky casino owners down below? On May 15, 1905 after 110 dusty acres in the Mojave Desert near the Union Pacific Railroad tracks are auctioned off, the city of Las Vegas, Nev. (Sp. "las vegas" = the meadows) (modern-day pop. 630K/2.4M) is founded; it is incorporated on Mar. 16, 1911; in 1931 Nev. legalizes casino gambling and reduces residency requirements for divorce to 6 weeks; in 1935 nearby Hoover Dam is completed; on Apr. 3, 1941 the Pair-o-Dice Club becomes the first casino built on the Las Vegas Strip (named after the Sunset Strip in Los Angeles), attracting New York City mobsters incl. Bugsy Siegel, who opens The Flamingo in 1946, causing the city to become known as "Sin City", "the City of Lights", and "The Gambling Capital of the World", going on to invite top entertainers incl. Wayne Newton, Dean Martin, Sammy Davis Jr., and Elvis Presley to perform, causing it to become known as "the Entertainment Capital of the World", combining it with quickie marriages, making it "the Marriage Capital of the World"; in 1955 the famous Welcome to Las Vegas Sign is located outside the city by Betty Willis; the mobsters later bow to corporate-funded mega-resorts, starting with The Mirage in 1989, making it "The Silver City", and "America's Playground"; in 1959 the Fremont Street Experience opens in a 5-block area of downtown known as Glitter Gulch, featuring 12.5M lights and 500MW shows held each hour from dusk until midnight; the town's ad slogan is: "What happens in Vegas stays in Vegas".
In 1906 the city of El Centro, Calif. (modern-day pop. 42.5K) in the Imperial Valley of S Calif. near San Diego (150 mi. SE of Los Angeles and 10 mi. N of Mexicali, Mexico) is founded by W.F. Holt and C.A. Barker, who purchase the land for $40//acre and put $100K into improvements; it starts out desert until irrigation from the Colorado River turns it into a major fruit-vegetable growing region of rubber and Chinese tung trees about 15 mi. to the SW.
In 1906 the city of Juneau, Alaska (formerly Harrisburg and Rockwell) at the base of Mount Juneau across from Douglas Island on the Gastineau Channel in the Alaskan Panhandle, named in 1881 after Quebec-born prospector Joseph "Joe" Juneau (1833-99) succeeds Sitka as capital of Alaska, becoming the most populous city in Alaska in 1920-50; on July 1, 1970 it merges with Douglas.
In 1910 the city of Elisabethville (Elizabethville) (Elisabethstad), capital of the Belgian Congo (modern-day pop. 1.79M) is founded in Katanga Province in modern-day SE Dem. Repub. of the Congo, becoming the mining capital; in 1966 it is renamed Lubumbashi, and in 1972 Katanga is renamed Shaba.
In Oct. 1912 the city of Torrance, Calif. on the Pacific Ocean in SW Los Angeles County (modern-day pop. 147K) is founded by real estate developers led by Gowanda, N.Y.-born Jared Sidney Torrance (1853-1921), who hire landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted Jr., and incorporate on May 12, 1921, becoming known for great climate and beaches, 30 city parks, 90K street trees, and the highest percentage of Japanese-descent residents in Calif. (9%).
On Aug. 4, 1914 - Nov. 11, 1918 the horrific World War I causes 15M deaths and 39M military casualties, and destroys the Old Order of white formerly Christian Europe. The U.S. played the Savior role, and lost a piddling number of troops compared to everybody else, and even after the horrific 1918 Spanish Influenza (Flu) Pandemic, you might call it lucky that it began to become the New Kid on the Block.
In 1914 the city of Anchorage, Alaska (originally Alaska City) in SC Alaska at the terminus of Cook Inlet near the mouth of Ship Creek (modern-day pop. 291K/401K) is founded by J.D. "Bud" Whitney, Jim St. Clair, Jack and Nellie Brown, and Frederick Mears as a railroad construction port for the Alaska Engineering Commission; it is incorporated on Nov. 23, 1920; the Alaska Railroad is completed in 1923, causing pop. growth, growing into Alaska's most populous city, with 40% of the state's pop.; in 1951 Anchorage Internat. Airport is built; in 2000 it is renamed for U.S. Sen. (R-Alaska) (1968-2009) Ted Stevens; located equidistant from Tokyo, Frankfurt, and New York City, and lying within 9.5 hours by air of 90% of the industrialized world, it becomes a major hub for FedEx.
In May 1927 Studio City (originally Laurelwood) is founded in the San Fernando Valley near Los Angeles, Calif. on a triangular lot bisected by the Los Angeles River by film producer Mack Sennett; in 1933 he declares bankruptcy and sells it to Mascot Pictures, which in 1935 merges with Monogram Pictures and Consolidated Film Corp. to form Republic Pictures, becoming Republic Studios, producing B-Westerns starring Gene Autry, Roy Rogers, John Wayne et al.; in the 1950s Republic leases space to Revue Productions (founded in 1943 by MCA), which produces "Leave It To Beaver" et al. before moving to Universal City; meanwhile Four Star Productions leases space to produce "The Rifleman", "Dick Powell's Zane Grey Theater", "The Big Valley" et al.; Republic Pictures ceases film production, leasing the lot to CBS-TV, producing "Gunsmoke", "Rawhide", "My Three Sons", "Gilligan's Island", and "The Wild Wild West"; in Feb. 1967 CBS-TV purchases the lot for $9.5M, renaming it CBS Studio Center; in 1970 it rents space to the new MTM Enterprises; meanwhile in 1927 the Sherman Oaks neighborhood in Los Angeles, Calif. is founded W of Studio City, which ends up bordered on the N by Valley Village, on the E by Universal City and Toluca Lake, on the S by Hollywood Hills West, and on the SW by Beverly Crest.



On Feb. 13, 1931 New Delhi S of Old Delhi (modern-day pop. 260K/27.9M) becomes the new capital of India, designed by English #1 architect Sir Edwin Landseer Lutyens (1869-1944), along with several monuments incl. the India Gate (1931) and the Rashtrapati Bhavan (Viceroy's House) (Presidential Residence) (1912).



On Sept. 1, 1939 - Sept. 2, 1945 the horrific $3.5T World War II results in 24M military and 49M civilian deaths, and features the low point of the Jewish Holocaust (Shoah) by the German Nazis - I guess it was the Jews' fault for not ransoming themselves to go to Israel before they could round them up for the camps? The whole experience turns Jews from lovers into fighters, ramping up the Zionist movement with full world sympathy and support by new world superpower U.S., which has its own guilt trip because on Nov. 24, 1942 Budapest-born Am. Zionist leader Rabbi Stephen Samuel Wise (1874-1949) announces in a press conference in Washington, D.C. that he was authorized by the U.S. State Dept. to confirm that the Nazis had murdered 2M Jews as part of a plan to exterminate all Jews in Europe; too bad, the nat. newspapers don't consider it front page news, and the U.S. govt. does nada. After the war ends and Americans toud the concentration camps in horror, Polish-born Jewish scholar Raphael Lemkin (1900-59), who single-handedly led an unsuccessful campaign to get the League of Nations to give internat. protections against genocide starting in 1933 finally gets what he wants after his own people got it, namely the Dec. 9, 1948 U.N. Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide (Gen. Assembly Resolution 260), which doesn't come in force until Jan. 12, 1951, and which the U.S. doesn't ratify until 1988. By the end of WWII the U.S. is the World's Policeman, with half the world's wealth, and a Baby Boom accompanied by an economic boom created a huge mass-market for novels and everything else.
On Oct. 12, 1939 Quezon City, Philippines N of Manila (modern-day pop. 2.9M), named for Pres. Manuel L. Quezon is incorporated as a city, becoming the capital of the Philippines in 1948-76, and the most populous city in the Philippines, with a pop. density of 46K/mi.
On Aug. 18, 1947 the municipality of Buayan (Dadiangas) in South Cotabato, Central Mindanao, S Philippines is created by order of Pres. Manuel Roxas; in June 1954 it is renamed General Santos City (modern-day pop. 594K); on July 8, 1968 it is chartered a a city, the southernmost in the Philippines; it becomes part of the admin. region of Soccskargen (Region XII) (South Cotabato, Catabato City, North Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, Sarangani, General Santos City).

On July 1, 1948 after years of experimental broadcasts, the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) approves commerical TV broadcasts; New York City station WNBT (later WNBC) becomes the first to make the changeover, hosting a 1-time episode of Truth of Consequences (which debuted on NBC Radio on Mar. 23, 1940), hosted by producer Ralph Livingstone Edwards (1913-2005), featuring impossible-to-answer trivia questions followed by Beulah the Buzzer, and the "consequences", a zany and embarrassing stunt, often involving reunion with a loved one; after a 1-time special on NBC-TV on July 1, 1948, it debuts again on Sept. 7, 1950 (until Dec. 31, 1987), becoming the first TV program with a live audience to be recorded on 35mm film with multiple cameras; in 1954 Edwards is replaced by Jack Bailey, followed in 1956 by Bob Barker, in 1977 by Bob Hilton, and in 1987 by Larry Anderson; on Jan. 22, 1957 it becomes the first TV program to be broadcast in all U.S. time zones from a videotape; in 1966 it becomes the first successful daily game show in first-run syndication (until 1978, then 1987-8); on Mar. 31, 1950 Hot Springs, N.M. (founded 1916) renames itself Truth or Consequences, N.M. (modern-day pop. 6K) to get Edwards to host the show there, after which he attends the annual fiesta the first weekend of every May until his death.


On Apr. 21, 1960 Brasilia (modern-day pop. 480K/2.9M), the new more accessible capital of Brazil, designed by Toulon, France-born architect Lucio Costa (1902-98) is inaugurated as the nat. govt. seat, replacing Rio de Janeiro; designed for a pop. of 500K, it zooms to 2M by the end of the cent.
In 1978 the Mission Viejo Co. purchases 24 sq. mi. of land in unincorporated Douglas County, Colo. 12 mi. S of Denver near Littleton, and in 1981 founds Highlands Ranch, Colo. (modern-day pop. 96K) becoming known for mazelike cul-de-sac streets and green belts, and houses that all look alike.
On Feb. 7, 2001 to prevent the city of Greenwood Village from annexing it, the city of Centennial, Colo. is formed from portions of unincorporated Arapahoe County, with its 100K pop. making it the largest incorporation in U.S. history (until ?); incorporated on a promise to keep city taxes at 1%, it grows to 2.5% by 2017.