



































TLW's Name Brandscope™ (Name Brand Historyscope) |
By T.L. Winslow (TLW), the Historyscoper™ |
© Copyright by T.L. Winslow. All Rights Reserved. |
Original Pub. Date: Jan. 28, 2016. Last Update: Dec. 29, 2025. |

















Westerners are not only known as history ignoramuses, but double dumbass history ignoramuses when it comes to name brand history. Since I'm the one-and-only Historyscoper (tm), let me quickly bring you up to speed before you dive into my Master Historyscope.
Brand names (ON "brandr" = to burn) go back to ancient India and Rome; not until the 19th cent. with the advent of mass-marketing in the U.S. and Britain did they become a big deal, so we'll begin there. The difference between a brand name and a Name brand is that the latter has made it to the top of the market and become famous; sometimes too famous, imperiling their trademark, you can't have eveything even if you're Monopoly. We'll concentrate on small-ticket consumer items that can be purchased at a U.S. grocery or drugstore, omitting luxury items, high-tech brands incl. appliances, computers, and software along with vehicles, boats, etc.


In 1759 after hops are introduced to Ireland, and his godfather Archbishop of Cashel (since 1744) Arthur Price (1678-1752) leaves him £100 in his will in 1752, which he uses in 1755 to buy a brewery at Leixlip (10 mi. from Dublin) at the confluences of the Liffey and Rye Water Rivers, Sir Arthur Guinness (1725-1803) founds the Guinness Brewery at St. James' Gate in Dublin, Ireland, and secures a modest 9K-year lease at £45/year; the logo features an Irish harp; after they and several other brewers and distillers are raised to the peerage, they become known as the Beerage.

In the 1780s Altoids, the "curiously strong peppermints" are developed by William Smith & Co. of London, England as a digestive aid - other uses are later discovered.



In 1806 William Colgate & Co. in New York City is founded by English immigrant soapmaker (devout Baptist) William Colgate (1783-1857); his son (also a devout Baptist) Samuel Colgate (1822-97) continues after his death, introducing Cashmere Boquet soap in 1872, and its first toothpaste ("dental cream") in 1873, packaged in jars; in 1896 they sell their first Colgate Toothpaste in a tube, Colgate Ribbon Dental Cream; in 1928 they are acquired by Palmolive-Peet to become Colgate-Palmolive-Peet, dropping the Peet in 1953; in ? they introduce Gardol (sodium lauroyl sarcosinate) (AKA Advance White) to their toothpaste; in 1999 they become the world's best-selling toothpaste; by 2010 they sell $17B a year.


In 1807 Pears brand transparent perfumed soap is first sold by Cornwall-born barber Andrew Pears (1770-1845) of London, England; in Aug. 1890 the co. buys the 1886 painting Bubbles by Sir John Everett Millais, using it as an ad.


In 1822 William Underwood Co. is founded in Boston, Mass. by William Underwood (1787-1864) to manufacture condiments in glass packages, switching in 1836 to steel cans coated with tin, going on to sell to pioneers and U.S. Civil War Union troops; in 1868 they introduce Underwood Deviled Ham, trademarking the devil logo in 1870, and turning it red in 1895, giving him a pitchfork and smile by 1921; in 1906 Mass. bans all deviled meats excepts theirs; in 1895-6 William Underwood's grandson William Lyman Underwood (1864-1929) gets bacteriologist William Thompson Sedgwick (1855-1921) of MIT to discover why canned clams swell and explode, and he traces it to heat-resistant bacterial spores that can only be killed by temperatures of 250F (121C) for 10 min.; in 1965 the co. acquires Burnham & Morrill Co. of Portland, Maine, manufacturer of B&M Brick Oven Baked Beans; in 1968 the co. acquires Piermont Foods of Montreal, Canada; in 1982 it is acquired by PET, which in 1995 is acquired by Pillsbury Co.


In 1824 Cadbury confectionary co. is founded in Birmingham, England by Quaker John Cadbury (1802-89), who builds the model teetotaler Bournville estate for workers; in 1905 they introduce dairy milk chocolate, which has more milk than rival products, becoming their best selling product by 1914; how convenient that chocolate is full of cadmium?




On Oct. 31, 1837 British-Am. candlemaker William Procter (1801-84) and his Irish-Am. soapmaker brother-in-law James Gamble (1803-91) found Procter & Gamble Co. (P&G) in Cincinnati, Ohio, going on to supply Union soldiers with soap during the U.S. Civil War and invent Ivory brand whipped soap in 1879, with the slogans "It floats" (1891) and "99-44/100 pure" (1895); the logo features Old Man Moon and 13 stars, causing conspiracy theorists to whisper about Satanic connections.


In 1837 English chemist Alfred Bird (1811-78) of London invents Bird's Custard, based on corn flour instead of eggs, which becomes the most popular brand in the U.K., after which he invents baking powder so that his wife can make yeast-free bread - for the birds jokes here?



In 1837 Lea & Perrins brand Worcestershire sauce is introduced by pharmacists John Wheeley Lea (1791-1874) and William Henry Perrins (1793-1867) of Worcestershire, England, whose initial batch was so strong it was abandoned in the basement, but later found to be marketable after it ferments and mellows; in 1930 it is acquired by HP Foods, which in 1967 is acquired by the Imperial Tobacco Co., which is sold in 1988 to Damone, followed in 2005 by Heinz.



In 1848 Morton Salt Co. is founded in Chicago, Ill. by E.I. Wheeler, and in 1886 is purchased by Joy Sterling Morton (1855-1934), son of Arbor Day founder J. Sterling Morton, changing to its present name in 1910, developing its motto "When it rains it pours" in 1911, and its logo the Morton Salt Girl in 1914; magnesium carbonate is used to absorb moisture and prevent cakig in 1911.


In 1850 Nantucket, Mass.-born carpenter James Athearn Folger Sr. (1835-89) begins roasting coffee beans in Gold Rush San Francisco, founding J.A. Folger & Co. in 1872, which packages the "Mountain grown" coffee in red cans; in 1965-86 actress Virginia Christine plays Swedish housewife Mrs. Olson; in 1984 the slogan "The best part of waking up is Folgers in your cup" is introduced - so the label says?





In 1851 Castle & Cook is founded in Hawaii as a gen. store by missionary businessmen Samuel Northrup Castle (1808-94) and Amos Starr Cooke (1810-71), expanding into shipping, railroad and sugar production, and seafood packing; in 1932 it acquires 21% of the Hawaiian Pineapple Co., founded in 1901 by "Pineapple King" James Drummond Dole (1877-1958), cousin of Hawaiian gov. Sanford Ballard Dole (1844-1926), acquiring the rest in the 1960s along with the Standard Fruit Co., renaming it the Dole Food Co. in 1991, becoming the #3 largest producer and importer of bananas in the U.S. On Apr. 30, 1900 Hawaii joins Alaska, Okla., N.M., and Ariz. as a U.S. territory, with Sanford Ballard Dole (1844-1926) as gov. #1 on June 14 (until Nov. 23, 1903); unlike Puerto Rico, Hawaii pays tariff dues and income tax to the federal govt.; large-scale immigration of Asian (Japanese) labor begins, and by 1910 Hawaii's pop. is 192K, of whom only 26K are natives, 12.5K part-natives, 21.5K Chinese, and 80K Japanese; meanwhile his cousin James Drummond Dole (1877-1958) graduates from Harvard U. and moves into Honolulu, using his $16,240 savings to purchase land in the C plains of Oahu, building a cannery in Wahiawa and founding the Hawaiian Pineapple Co. next year, growing it into an empire with a breakthrough peeling-coring machine invented by Henry G. Ginaca (1876-1918) in 1911, and a new 200K-acre plantation on Lanai in 1922, becoming known as "the Pineapple King", eventually escorting young Shirley Temple through his Honolulu corporate offices for a photo op.; too bad, the Big Five of Hawaii, incl. Castle & Cooke, Alexander & Baldwin, C. Brewer & Co., Amfac, and Theo H. Davies & Co. create an oligarchy, with Hawaii atty. gen. Edmund Pearson Dole uttering the 1903 soundbyte: "There is a govenment in this Territory which is centralized to an extent unknown in the United States, and probably almost as centralized as it was in France under Louis XIV."


In 1851 the Fruit of the Loom brand clothing co. is founded in Providence, R.I. by textile mill owner Robert Knight (1826-1912), who trademarks the name in 1871; the name is a play on "fruit of the womb" in the Bible (Psalm 127:3); on Apr. 29, 2002 after filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 1999 it is acquired by Berkshire Hathaway Corp.

In 1853 Keebler Co. in Philadelphia, Penn. is founded by German immigrant Godfrey Keebler to manufacture cookies and crackers, going on to market Cheeze-It, Chips Deluxe, Club Crackers, E.L. Fudge Cookies, Town House Crackers, Sandie's Shortbread, Wheatables et al.; in 1935 it becomes the first commercial co. to bake Girl Scout Cookies; in 1968 an ad campaign is launched by Leo Burnett featuring the animated Keebler Elves, led by J.J., later Ernest J. "Ernie" Keebler. in 1974 it is acquired by United Biscuits, and in Mar. 2001 by Kellogg Co.


In 1854 the Waterbury Clock Co. is founded in Waterbury, Conn. by brass manufacturer Benedict & Burnham Co. to manufacture low-priced brass clocks, becoming #1 in the Naugatuck Valley and helping turn it into "the Switzerland of America"; in 1878 the new Waterbury Watch Co. introduces the Long Wind pocket watch, made of 58 punched sheet brass parts; in 1887 they introduce the Jumbo pocket watch, named after P.T. Barnum's elephant, partnering with salesman Robert H. Ingersoll in 1892 and selling millions; in 1896 they introduce the $1 Ingersoll Yankee pocket watch, becoming known as "the watch that made the dollar famous"; in 1922 the Waterbury Clock Co. buys Robert H. Ingersoll & Bros. for $1.5M, then sells it to its London-based board of dirs. in 1930; in 1930 Waterbury Clock Co. begins producing Walt Disney Mickey Mouse watches and clocks under the Ingersoll name, and introduces them to the public at the 1933 Chicago World's Fair, becoming their first $1M-selling line; in 1942 they move to Middlebury, Conn. and begin producing precision timers for the U.S. military; in 1950 after changing their name to United States Time Corp. and making use of WWII-developed Armalloy to replace expensive jewels, they introduce the Timex brand with newsman John Cameron Swayze as spokesperson, with the motto "Timex - Takes a licking and keeps on ticking", becoming the best-selling wristwatch in the U.S. by 1962 (one out of three); in 1950 they become the exclusive manufacturer of Polaroid cameras (until 1975); on July 1, 1969 the co. is renamed Timex Corp.; too bad, digital watches steal their market, causing them to try selling home computers incl. the Timex Sinclair 1000, ZX81, and ZX Spectrum, which they abandon in 1984; in 1986 they introduce the Ironman Triathlon watch, which becomes #1 again in the U.S.; in 1992 they introduce the Indiglo night light, which is used by an officer worker after the Oct. 26, 1993 World Trade Center Bombing to guide fellow employees down 40 flights of dark stairs, causing a sales boom; in 1991 they acquire Callanen Internat., maker of Guess brand watches; in 1993 they produce the Disney Classics Collection; in 1994 they acquire Nautica Watchews, introducing the Timex Data Link, which uses Micosoft software; in 1997 they introduce the Timex Expedition for outdoor sports; in 1998 they and Motorola introce Beepwear with an integrated pager; in 2000 they acquire French fashion watch co. Opex, followed in 2002 by Marc Ecko; in 2005 they acquire Swiss luxury watchmaker Vertime SA, maker of the Versace and Versus brands; in 2006 they introduce the TX brand, and acquire the ultra-luxury Swiss brand Vincent Berard.





In 1856 the Washburn-Crosby Co. is founded on the W side of Saint Anthony Falls on the Mississippi River outside Minneapolis, Minn. by U.S. Rep. (D-Ill.) (1843-9, 1957-9) Robert Smith (1802-67), who sells it to Cadwallader Colden Washburn (1818-82), who runs the co. with his brother William Drew Washburn (1831-1912); in 1872 St. Anthony and Minneapolis join; in 1877 they partner with John Crosby (1829-88), and in 1878 a flour dust explosion demolishes the plant, causing a new one with the first-ever automatic steel rollers to be built, the improved flour winning gold, silver, and bronze medals at the 1880 Millers' Internat. Exhibition in Cincinnati, Ohio, causing them to launch the Gold Medal flour brand, and Minneapolis to be called "the Flour Milling Capital of the World"; in 1928 it merges with 26 other mills to create General Mills.







In 1861 German-born Union vet and brewer supplier Adolphus Busch (1839-1913) marries Lily Anheuser and goes into biz with her German-born father Eberhard Anheuser (1805-80), founding the Anheuser-Busch Brewing Co. in St. Louis, Mo. after the latter can't pay his bill and gives him a piece of the action. In 1876 Adolphus Busch and St. Louis, Mo. wine merchant Charles W. "Carl" Conrad visit the town of Ceske Budejovice (Budweis) in the South Bohemian region of Czech. to steal, er, discover the formula for light Bohemian lager Budweiser brand beer, and bring it back to the U.S., changing tastes away from dark ales and introducing pasteurization; in 1913 August Anheuser Busch Sr. (1865-1934) becomes pres. of Anheuser-Busch (until Feb. 10, 1934), surviving Prohibition (1920-33) by marketing near beer then introducing the Budweiser Clydesdales on Apr. 7, 1933; he is succeeded as CEO by Adolphus Busch III (1891-1946) (until Aug. 29, 1946), who introduces a metal can in 1936; in 1946 his brother August Anheuser "Gussie" Busch Jr. (1899-1989) becomes CEO (until 1975), growing to the #1 beer brand in the U.S. in 1957 - add another smug comment about the limitless market for lazy fat American whites here?


In 1861 Indianapolis, Ind. grocer (former tinsmith) Gilbert C. Van Camp (1814-1900) founds the first successful commercial cold storage warehouse in the U.S., going on to sell canned fruits and vegetables to the U.S. Army from his store on Missouri St., founding Van Camp Packing Co. in 1882 and selling catsup in 1888 before his son Frank invents Van Camp's Pork and Beans with Tomato Sauce in 1894, which becomes the world #1 best-selling brand of canned pork and beans by 1909 (until 1996); in 1995 it is acquired by ConAgra.

On Feb. 15, 1864 Heineken Brewery in Amsterdam, Holland is founded by Gerard Adriaan Heineken (1841-93), who talks his wealthy mother into buying De Hooiberg Brewery (founded 1592) (makers of Haystack brand beer) for him, switching to Bavarian-style bottom fermentation and introducing Heineken brand beer in 1873, made from secret Heineken A-Yeast developed by Dr. Elion, a student of Louis Pasteur; it becomes known for green bottles with a red star; in 1875 it wins the gold medal at the Internat. Maritime Exposition in Paris; in 1933 it becomes the first Euro beer to be imported to the U.S. after the end of Prohibition; in 1975 it moves its main brewery to Zoeterwoude.

In 1866 French mustard manufacturers Maurice Grey and Auguste Poupon begin making Grey Poupon brand mustard in Dijon, France; in 1946 it is acquired by Heublein Co., which in 1982 is acquired by R.J. Reynolds, which merges it with Nabisco in 1985 to form RJR Nabisco, which in 1999 is acquired by Kraft Foods; in 1980s they begin airing the "Pardon me, would you have any Grey Poupon?" ads.



In 1867 German chemist Justus von Liebig (1803-73) invents the first commercial infant formula; meanwhile in Sept. 1866 after emigrating to Switzerland in 1834-9 and starting out as a pharmacist, switching to production of rapeseed and nut oils for lamps, alcoholic spirits, vinegar, carbonated mineral water, lemonade, gas lighting, fertilizers, and icemakers, Frankfurt am Main, German-born Henri (Heinrich) Nestle (Nestlé) (Ger. "small bird's nest") (1814-90) copies, er, develops his own version, which is a success, selling his Farine Lactee Henri Nestle co. (founded 1866) in 1875; in 1879 Nestle merges with milk chocolate inventor Daniel Peter; in 1904 Nestle begins marketing Swiss chocolate; in 1905 Nestle (Nestlé) S.A. (originally Nestle and Anglo-Swiss Condensed Milk Co., then Nestle Alimentana SA in 1947-77) is formed from the merger of Nestle with the Anglo-Swiss Milk Co. (founded 1866), introducing Nescafe (Nescafé) brand instant coffee on Apr. 1, 1938, which becomes a hit with the U.S. military in WWII, then acquiring Maggi (1974), Cross & Blackwell (1950), Findus (1963), Libby's (1971), Stouffer's (1973), L'Oreal (1974), Alcon Labs (1977), Carnation (1984), Rowntree Mackintosh (1988), San Pellegrino (1997), and Spillers Petfoods (1998); by the end of the 20th cent. it's the world's largest food co., going on to acquire Ralston Purina (2002), Dreyer's (June 2002), Chef America (Aug. 2002) et al.

In 1869 fruit merchant Joseph Albert Campbell (1817-1900) and icebox manufacturer Abraham Anderson (1829-1915) found Campbell Soup Co. (Campbell's Soup) (originally Joseph Campbell Preserve Co.) in Camden, N.J., changing to the current name in 1921 before introducing condensed soup in 1922; the 1898 red-white can motif comes from the Cornell U. logo; on Sept. 29, 2008 every co.'s stock on the Standard & Poor's 500 drops except theirs.


Speaking of American concordats, Protestant version? In 1869 Dr. Welch's Unfermented Wine is launched after Glastonbury, England-born Prohibitionist Methodist minister-dentist Thomas Bramwell Welch (1825-1903) of Vineland, N.J. figures out how to pasteurize the juice of Concord grapes (developed 1849), producing the perfect communion wine, selling it as a sideline until the Welch's Grape Juice Co. is founded in 1893, after which he "never received a penny in return for his investment".


In 1870 Wellfleet, Mass.-born ship capt. Lorenzo Dow Baker (1840-1908) sails from Orinoco to Jamaica, purchases 160 bunches of bananas, then returns to Philly and and sells them in Jersey City, N.J. 11 days later (even though they're spoiled?), returning next year with green bananas that sell like you know what, going on to launch the modern U.S. banana importing industry with the Boston Fruit Co. in 1885, which in 1899 becomes the United Fruit Co., which in 1984 becomes Chiquita Brands Internat.; meanwhile the business success causes Wellfleet to become a summer resort.



In 1872 C.A. Pillsbury and Co. is founded in the Falls of St. Anthony on the Mississippi River in Minneapolis, Minn. by Charles Alfred Pillsbury (1842-99) and his uncle John Sargent Pillsbury (1827-1901), becoming the first U.S. co. to use steel rollers for processing grain, producing "Pillsbury's Best", with the alleged finest flour in the world, capturing the market; John becomes Repub. gov. #8 of Minn. in 1876-82; Charles becomes a Minn. state senator in 1877-97; in 1949 the annual Pillsbury Bake-Off is first broadcast on CBS-TV; in 1957 they introduce the jingle "Nothin' says lovin' like somethin' from the oven... Pillsbury says it best"; in 1965 Leo Burnett creates the Pillsbury Doughboy as their mascot.

In 1876 after tasting it on his honeymoon in N.J., and using an old recipe containing sassafras oil, Hires Root Beer, "the Original Root Beer" is first marketed in Philly by Quaker pharmacist Charles Elmer Hires (1851-1937) in 25-cent packages of powder that make 5 gal. after adding water, sugar, and yeast, giving away free glasses at the 1876 Philadelphia Centennial Exposition, claiming that it's made of 16 wild roots and berries, and will purify the blood and redden the cheeks; in 1884 he begins marketing a syrup for use in soda fountains with a fountain dispenser called the Hires Automatic Munimaker; in 1890 he incorporates Charles E. Hires Co. and begins bottling it, selling 1M bottles by 1891, and 2,880,278 in 1892, promoting it as "the Temperance Drink" and "the Greatest Health-Giving Beverage in the World".

In 1876 Samuel T. Cooper of Kenosha, Wisc. founds Coopers Inc., later Jockey Internat. Co. to make socks and hosiery.




On May 10, 1876 the 1876 Centennial Exhibition in Philadelphia, Penn. opens (until Nov. 10); the Freedom Bell is substituted for the Liberty Bell in the tower; the 1.5K hp Centennial Engine that powers the exhibition is built by George Henry Corliss (1817-88); ketchup (catsup) (first mentioned in 1690) finally becomes popular after Henry John "H.J." Heinz (1844-1919) adds it to his line in 1876 and introduces it at the fair, with the motto "A blessed relief for mother and the other women in the household"; watch video - doesn't sound as good as "salsa"?


On Sept. 4, 1877 Quaker Mill Co. in Ravenna, Ohio is founded by Henry D. Seymour and William Heston (no connection with the real Quakers), with a portrait of Wiliam Penn as the logo, trademarking the Quaker name and growing to the city's largest employer until merging in 1901 with three other oat mills to create Quaker Oats Co. in Chicago, Ill., headed by Henry Parsons Crowell (1855-1944), becoming the "autocrat of the breakfast table"; he later gives 60-90% of his profits to his brand of Christian religion; meanwhile the co. backs off from the William Penn connection too, settling on a generic Quaker man as the logo; in 1969-91 it acquires toy co. Fisher-Price; in 1983 it acquires Stokely-Van Camp; in the late 1980s it begins featuring actor Wilford Brimley in TV commercials; in 1994-7 it acquires Snapple; in Aug. 2001 it is acquired by PepsiCo.


In 1883 German-born butcher Oscar Ferdinand Mayer (1859-1955) and his brother Gottfried found Oscar Mayer Co. in Chicago, Ill., cranking out bratwurst and liverwurst, growing to 43 employees by 1900, and in 1906 becoming one of the first U.S. cos. to voluntarily submit to the U.S. Food Safety Inspection Service of the USDA; in 1936 they begin touring the U.S. in the Wienermobile; in 1965 they launch the "If I were an Oscar Meyer wiener" TV ad campaign, followed in 1974 by "My bologna has a first name, it's O-S-C-A-R"; in 1981 it is acquired by Gen. Foods, which is acquired in 1985 by Philip Morris, then merges in 1989 with Kraft Foods.

On Dec. 1, 1885 23-ingredient Dr. Pepper brand soft drink, invented by Brooklyn, N.Y.-born pharmacist Charles Courtice Alderton (1857-1941) is first served at Morrison's Old Corner Drug Store in Waco, Tex., named after his friend Dr. Charles Pepper; customers ask the soda jerk to "shoot a Waco"; in 1891 he and Robert S. Lazenby of the Circle A Ginger Ale Co. in Waco form the Artesian Mfg. and Bottling Co. to mass-produce it, becoming a hit at the 1904 St. Louis World's Fair - which makes the drink wacky or way cool?


In 1885 after being inspired by Joseph Lister, Johnson & Johnson Co. is founded in New Brunswick, N.J. by brothers Robert Wood Johnson Sr. (1845-1910), James Wood Johnson (1856-1932), and Edward Mead Johnson (1852-1934) to manufacture ready-to-use surgical dressings, going on to grow to $65B yearly sales by 2011, with products incl. Band-Aids bandages, Tylenol painkiller, Johnson's Baby Oil, Neutragena skin conditioner, Clean & Clear facial wash, and Acuvue contact lenses.



On May 8, 1886 after Ga. enacts temperance legislation, Atlanta, Ga. druggist John Stith (Styth) Pemberton (1831-88) reformulates his 1863 French Wine Coca to eliminate the alcohol, and creates Coca-Cola from the kola nut, syrup, damiana, and cocaine, marketing it down the street at Jacobs' Pharmacy as a "brain and nerve tonic" for 5 cents a glass (cocaine is not removed until 1903?); bookkeeper-marketer Frank Mason Robinson (1845-1923) names it and creates the Spencerian script for the bottles and ads; it only sells 25 bottles its first year; it is trademarked in 1893 by Asa Griggs Candler (1851-1929) after he buys the rights for $2.3K in 1891, and goes on to make it big while successfully fighting allegations of cocaine or dope in its "secret ingredient" (until 1916); Robinson also puts Pemberton up to giving away free coupons and plastering Atlanta with banners and signs to promote the stuff, starting a trend which the Internet generation knows as Spam?; watch video.


In 1886 after working as a salesman then purchasing the parquet flooring business of Racine Hardware Co. of Racine, Wisc., Samuel Curtis Johnson Sr. (1833-1919) founds Johnson's Prepared Paste Wax Co.; in 1906 Herbert Fisk Johnson Sr. (1868-1928) becomes a partner, causing the co. to be renamed to S.C. Johnson and Son (S.C. Johnson Wax), going on to grow to $7.5B sales by 2006, with products incl. Glo-Coat, Johnsons Brite, and Mr. Muscle floor polish, Pride furniture polish, Drano drain cleaner, Glade air freshener, Pledge cleaner, Windex window cleaner, Mr Muscle oven cleaner, Saran Wrap and Ziploc food storage products, Kiwi shoe polish, and Raid roach killer - my pride and joy?



On Apr. 3, 1887 Stewartville, Minn.-born railroad station agent Richard Warren Sears (1863-1914) of North Redwood, Minn., who began buying pocket watches from a Chicago, Ill. jeweler to resell by mail last year before moving to Chicago, Ill. and placing an ad hires Lafayette, Ind.-born watchmaker Alvah Curtis Roebuck (1864-1948), and pub. his first mail-order catalog in 1888; in 1893 they incorporate Sears, Roebuck and Co., becoming one of the top U.S. retailers, opening its first retail store in Chicago in 1925 after Roebuck gets Sears to buy him out in 1895 for $20K, and goes on to become pres. of Emerson Typewriter Co. in 1909-24; in fall 1913 the Kenmore brand name is first used on sewing machines, expanding to washing machines in 1927, vacuum cleaners in 1932, ranges in 1946, dishwashers in 1951, washer-dryer combos in 1957, microwave ovens in 1971, and continuous-cleaning ceramic cooktop ranges in 1973; Sears eliminates its mail-order catalog in 1993; after Sears becomes enormously wealthy, leaving a $25M fortune in 1914, Roebuck answers queries with "He's dead. Me, I never felt better."

In 1887 Forest Lake, Minn. grocer Patrick James Towle (1835-1912) begins marketing Log Cabin Syrup, named after his childhood hero Abe Lincoln; in 1927 it is acquired by Gen. Foods, which in 1990 merges with Kraft, who sells it in 1997 to Aurora Foods.


In 1888 Scottish (Glasgow) merchant Sir Thomas Johnstone Lipton (1848-1931), who started out as a poor cabin boy in 1865, worked as a door-to-door salesman in New Orleans, then returned to Glasgow and set up his first shop in 1871, working his way up to 300 provision shops throughout Britain takes advantage of falling tea prices to set up his own wholesale distribution network (bypassing London's Mincing Lane) to market tea at low low prices to the working class, buying his own plantations in Sri Lanka in 1890 to launch his own Lipton tea brand using orange pekoe and pekoe leaves.


In 1890 the Swiss Army Knife is born when the Swiss Army decides that every soldier needs to carry a knife with a screwdriver to disassemble his Schmidt-Rubin rifle and a can opener for canned food, producing the Model 1890, which incl. a reamer, with a handle made of dark oak and/or ebony; the first lot of 15K is delivered in Oct. 1891 by Wester & Co. of Solingen, Germany; the red handle has a Swiss cross and shield; in 1891 surgical equipment maker Karl Elsener (1860-1918) of Ibach gets the contract to manufacture it, establishing the Victorinox Co. in 1909 after his mother Victoria dies, combining her name with "inox" (Fr. "acier inoxydable"), meaning stainless steel; in 1908 Paul Boechat & Co. of Belermont splits the contract 50-50, becoming Wenger Co., owned by Theodore Wenger, with Victorinox producing the Original Swiss Army Knife and Wenger the Genuine Swiss Army Knife; which is acquired by Victorinox on Apr. 26, 2005, continuing to produce both brands until announcing on Jan. 30, 2013 that only Victorinox will be produced; in WWII U.S. soldiers change the name from Offiziersmesser because it's too hard to pronounce; Victorinox sets up a factory in Monroe, Conn., which produces more and more models with more and more blades, incl. saw, scissors, file, pliers, tweezers, bottle openers, corkscrew, knife chain, belt clip et al.


In 1891 George A. Hormel & Co. meat packing co. is founded in Austin, Minn. by George Albert Hormel (1860-1946) and his brothers Benjamin, Herman, and John, changing its name to Hormel Foods in 1993; products incl. Jennie-O, Dinty Moore, Farmer John, Chi-Chi's, Spam, La Victoria, and Skippy.



In 1891 after trying Independence, Kan., Fort Worth, Tex., and Europe, chronically-ill (hypochondriac?) Charles William "C.W." Post (1854-1914) of Springfield, Ill. moves to John Harvey Kellogg's Battle Creek Sanitarium in Battle Creek, Mich. for his health, and in 1895 invents Postum wheat-bran-molasses coffee substitute, founding Postum Cereal Co., which in 1925 acquires Jell-O Co., followed by Swans Down brand cake flour (1926), Minute brand tapioca (1926), Log Cabin syrup (1927), Baker's coconut (1927), Baker's chocolate (1927), and Maxwell House Coffee (1928); in 1897 he invents Grape Nuts brand cereal, which has neither grapes nor nuts in it, and becomes the first mass-marketed cereal; in 1929 the co. becomes Gen. Foods, for which Postum Co. pays $22M for a controlling interest, and in Nov. 1985 is acquired for $5.6B by Philip Morris Co., which acquires Kraft Inc. in 1990 to create Kraft Gen. Foods (KGF), which becomes Kraft again in 1995 - millions try to imagine eating grapes and nuts while crunching on wheat and barley?


On Apr. 1, 1891 Philly-born William Wrigley Jr. (1861-1932) founds the William Wrigley Jr. Co. in Chicago, Ill. to sell soap and baking powder, offering free chewing gum with each can, which proves more popular than the baking power, going on to specialize in chewing gum next year and become #1; in 2005 it purchases Life Savers and Altoids from Kraft Foods for $1.5B; on Jan. 23, 2007 it acquires 80% of A. Korkunov for $300M; on Apr. 23, 2008 Mars Co. acquires it for $23B.



In 1892 the Maxwell House Hotel in Nashville, Tenn. begins serving the special Maxwell House brand coffee blend invented by Joel Owsley Cheek (1852-1935); Pres. Theodore Roosevelt later (Oct. 21, 1907) allegedly declares it "good to the last drop", which becomes the slogan; it goes on to capture one-third of the U.S. coffee market, and become the #1 seller in the U.S. until the late 1980s; in 1928 it is acquired by the Postum Co. (later called Gen. Foods).


In 1892 Henry Drushel Perky (1843-1906) invents shredded wheat (small pillow-shaped wheat biscuits) in Denver, Colo. to help his stomach troubles; with friend William Ford of Watertown, N.Y. he develops a machine to produce it, and peddles it from a horse-drawn wagon while trying to sell the machines, until Battle Creek Sanitarium (Seventh-day Adventist) physician John Harvey Kellogg (1853-1943) convinces him to move back east and open up a factory in Niagara Falls, N.Y. along with his brother Will Keith Kellogg, which proves quite lucrative; the Kelloggs then invent wheat flakes and corn flakes - and now we have Cap'n Crunch Crusted Chicken and Crab Cakes?

1893 is a good year for funky legal pronouncements from on high? On Mar. 3, 1893 after the U.S. Civil War ruins the Southern tomato biz, allowing Caribbean competitors to gain a foothold, the U.S. Congress passes the U.S. Tariff Act of 1883 (Mongrel Tariff Act), which raises tariffs on some items and lowers them on others, exempting fruit not vegetables, pissing-off tomato growers John Nix et al., who sue the U.S. govt. in 1887 on the claim that tomatoes are botanically classified as fruits (ovary and seeds of flowering plants), which New York port collector Edward L. Hedden counters by pointing out that eggplants, cucumbers, squashes, peppers, and peas are commonly regarded as vegetables; on May 10, 1893 the U.S. Supreme (Fuller) Court in Nix v. Hedden unanimously declares the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum, of the nightshade family) to be a vegetable for the purposes of the 1883 Tariff Act, with Horace Gray writing the majority opinion, becoming a highlight for the boring nutty fruitcake full-of-it Melville Fuller court; in 2003 a N.J. state rep. unsuccessfully tries to make the Jersey tomato the state fruit (high-bush blueberry wins), but Ark. makes it the state fruit and vegetable to cover all bases; meanwhile the Southern Calif. Fruit Exchange is founded in Claremont (near Los Angeles), Calif. by orange grower Edward L. Dreher (1877-1964), who becomes "the Father of the Calif. Citrus Industry"; in 1896 lemon growers join; by 1905 it has 5K members (45% of the Calif. citrus industry), dropping the Southern; in 1907 it launches the Sunkist brand; in 1952 it becomes Sunkist Growers Inc.

















Food is Love, or the Devil in the White City? The 20th Century begins ahead of schedule in the greatest World's Fair of All Time? On May 1, 1893 Pres. Cleveland presses a golden telegraph key in front of a crowd of 300K (largest so far in U.S. history) to start the giant Westinghouse electrical generators lighting 120K lightbulbs and open the $27M World's Columbian Expedition (Chicago World's Fair) (closes Nov. 1) in the "White City" of 150 neoclassic bldgs. in Jackson Park, 686 acres of reclaimed swamp along the shore of Lake Michigan 7 mi. S of downtown Chicago (built of plaster-cement-fiber staff on flammable wooden-steel frames, not marble, and painted using newfangled spray-painting equipment), designed by Daniel Hudson Burnham (1846-1912) and John Wellborn Root (1850-91) (who dies trying to meet the crushing time constraints); on May 12 the South Side Elevated Railroad reaches Jackson Park to provide service to the fair, becoming the first "el", based on the nickname "alley L"; Frank Lloyd Wright (b. 1867) quits college to work for Burnham, who first sends him to the Beaux Arts in Paris, and he comes back saying that the Columbian Exposition set U.S. architecture back 50 years; Francis Bellamy's new "Pledge of Allegiance" is recited by children at the fair's dedication; the Exposition orchestra, conducted by Theodore Thomas (1835-1905) features violinist Maud Powell (1867-1920), who proves that woman can work in them newfangled orchestra thingies; the Court of Honor features the magnificent Peristyle by Charles Atwood, Daniel French's 65-ft.-tall statue The Republic, as well as colossal heads of artists Michelangelo et al. by French-born Beaux Arts popularizer Olin Levi Warner (1844-96) in the Palace of Fine Arts, which houses 10K pieces of art so crowded together that nobody can view them all; the 1687 ft. x 787 ft. x 245 ft. tall (500K sq. ft.) (44 acre) Manufacturers and Liberal Arts Bldg. (opened in Oct. 1892 in front of a crowd of 100K), the largest bldg. in the world, has a crowd cap. of 300K and is lit with 10K electric lights, and the endless exhibits are worth at least $50M; the U.S. Liberty Bell is displayed in the Penn. exhibit in a replica of Independence Hall; the Japanese Village is the first exposure of Americans to cool Japanese culture, and is the only non-white exhibition not snickered at; the Cold Storage Bldg. features an indoor skating rink, and burns down on July 10 with the loss of 13 firemen and four workers, who climb to the top of the metal tower then burn alive or jump while the crowds watch; the polychrome pro-Modern Transportation Bldg. is designed by Louis Henri Sullivan; the Women's Bldg., designed by 21-y.-o. Am. architect Sophia Hayden (1868-1953) (first female in the U.S. with an architecture degree) features exclusively work by women (too bad, welcome to reality, Hayden is only paid $1K for her design, 15% of what men earn); the first-ever (264 ft., 1.2K ton) Ferris Wheel, built by George Washington Gale Ferris Jr. (1859-96) (36 salon cars, each holding 40-60 passengers, with five glass panels) is the highlight and the financial salvation of the fair, and is set up at the 1904 St. Louis World's Fair then scrapped; an all-electric kitchen is featured; the Captive Balloon costs $2 for a ride to 1,490 ft. plus a photo, and it crashes in high winds and goes out of biz; the Shedd Aquarium Bldg., the largest indoor aquarium in the world causes an awakening of the environmental movement; the Midway Plaisance of future U.S. congressman (Jewish) Sol Bloom "the Music Man" (1870-1949), designed by Frederick Law Olmsted is the big moneymaker, filled with booze, cigars and bawdy entertainment, incl. the Streets of Cairo ("Beautiful Orient") Bldg., complete with a replica of the Sphinx, featuring Little Egypt (Farida Mazar Spyropoulos) and the "Naughty Girls from Algeria", who dance the Hootchy-Kootchy (Hoochie-Koochie) (Kouta-Kouta), AKA the "danse du ventre" (belly dance) (named by Bloom), with the first perf. of Bloom's uncopyrighted Snake Charmer Tune ("Oh they don't wear pants on the sunny side of France"), which pisses-off Head Prude Anthony Comstock into trying to shut it down, which only makes it more popular and causes the dance to spread around the U.S., complete with a better 1895 version of the song The Streets of Cairo, or The Poor Little Country Maid, by James Thornton (1861-1938), who uses his wife Bonnie to demonstrate it; the U. of Chicago is later built on the site of the Midway Plaisance, and the Chicago Bears football team becomes known as "the monsters of the Midway"; Boilerplate the Mechanical Marvel, a mechanical robot is another don't-miss; the fair introduces the word "cafeteria"; the Rumford Kitchen of home economics founder Ellen Henrietta Swallow Richards (1842-1911) showcases food science, incl. luncheon menus with nutritional info.; chili con carne is introduced; Joseph Garis Cochrane displays her new automatic dishwater (patented 1886); carmel maker Milton S. Hershey sees chocolate-making machinery at the fair and buys it; Henry Perky's shredded wheat is popularized, along with Wrigley's new Juicy Fruit brand chewing gum; German-born Frederick William "Fritz" Rueckheim and his brother Louis Rueckheim introduce Cracker Jack brand caramel-coated popcorn with peanuts (which is registered in 1896, comes in a "wax-sealed" packages in 1899, gets a boost from the 1908 song "Take Me Out to the Ball Game" by Albert Von Tilzer and Jack Norworth, and begins incl. silly trivial toys as prizes starting in 1912, then features Sailor Jack and his dog Bingo in 1918, with the motto "The more you eat the more you want"); they actually don't introduce it until 1896?; Pabst Blue Ribbon Beer, made by Capt. Johann Gottlieb Friedrich "Frederick" Pabst (1836-1904) (since 1882, when he started tying silk ribbons to his Select Beer) wins a blue ribbon, and guess what, 30M ft. of silk blue ribbon shipped with the beer that didn't quite make Milwaukee famous by the turn of the cent.?; Cream of Wheat farina breakfast porridge mix made from wheat semolina makes its debut; Bavarian sausage vendor Anton Ludwig Feuchtwanger starts out providing white gloves to eat them with, then switches to rolls when they keep the gloves as souvenirs; Henry John "H.J." Heinz (1844-1919) attracts people to his 2nd-floor out-of-the way booth by handing out Heinz pickle pins, going on to give away 100M of them during the next cent.; R.T. Davis Mill Co. hires Ky.-born former slave Nancy Green (1834-1923) to demonstrate Aunt Jemima pancake mix in front of their 24-ft.-high 12-ft.-diam. world's largest flour barrel, causing co. sales to go through the roof; writer L. Frank Baum later models his Emerald City after the White City; "Devil in the White City" serial killer Dr. Henry Howard Holmes (Herman Webster Mudgett) (1861-96) ("the Torture Doctor") sobers it up with some World's Fair murders after he builds a 105-room hotel nearby filled with torture chambers, and lures 27+ young women to their deaths, torturing and gassing them in a soundproof room, then butchering their bodies in the basement and selling the parts to medical schools; the fair closes on Nov. 1 after hosting 27M visitors from 73 nations, and makes a small profit; on the night of Oct. 28 disgruntled insane newspaper distributor Patrick Eugene Joseph Prendergast (1868-94) (who thought that he was owed a govt. job for supporting his election campaign) murders Chicago mayor Carter Henry Harrison Sr. (b. 1825) in his home with a small revolver, causing many to skip the closing ceremonies for his Nov. 1 funeral; Prendergast is hanged next July 13 after his atty. Clarence Darrow unsuccessfully raises the insanity defense - he didn't get the job, did he?




In 1894 Purina Mills is founded in St. Louis, Mo. by William H. Danforth (1870-1955) to produce animal and pet food incl. Purina Cat Chow, Purina Dog Chow, Purina Horse Chow, Purina Monkey Chow, Purina Pig Chow, Purina Rabbit Chow et al.; in 1898 after Albert Webster Edgerly (1852-1926) founds the kooky white supremacist Ralstonism Movement (Regime, Activity, Light, Strength, Temperation, Oxygen, Nature) in Ralston Heights (Hopewell), N.J., which advocates eating of whole grain cereal along with castration of non-Caucasians, and prohibits Caucasians from eating watermelon, they expand to whole wheat breakfast cereals, changing their name in 1902 to Ralston-Purina Co.; in 1937 they introduce Chex brand cereal (Wheat Chex, Rice Chex, Bran Chex), which later uses chars. from Charles M. Schulz's "Peanuts" comic strip in it ads, and is sold to Gen. Mills in 1997; in 1953 Danforth pub. I Dare You!, which expounds his Checkerboard Philosophy: Physical, Mental, Social, Religious.; in 1963-8 it owns Van Camp Sea Food Co., makers of Chicken of the Sea brand tuna; in 1968-85 it owns Jack in the Box fast food restaurants; in 1986 Purina Mills (U.S. business only) is sold to British Petroleum (BP), which sells it to Land O'Lakes; in 1986 Ralston Purina acquires Eveready Battery Co. and Continental Baking Co.; in 1994 the Ralston business becomes Ralcorp Holdings; in 2001 the internat. Purina business is sold to Cargill; in 2001 Ralston Purina merges with Nestle.


In 1897 Jell-O powdered gelatin mix is first sold by cough syrup manufacturer Pearle Bixby Wait (1871-1915) and his wife May Wait of LeRoy, N.Y. in lemon, orange, raspberry, and strawberry flavors; in 1899 they sell it to the Genesee Pure Food Co., run by Orator Francis Woodward (1856-1906), who begins placing ads in Ladies' Home Journal in 1901, calling it "America's Most Famous Dessert", sending an army of salesman into the field to distribute free Jell-O cookbooks, causing sales to zoom; in 1930 they introduce lime flavor for use in aspics and congealed salads; in 1934 comedian Jack Benny becomes the co. spokeman, with the jingle "J-E-L-L-O", written by Benny's bandleader Don Bestor; in 1936 Jell-O instant chocolate pudding mix is introduced, causing more pudding flavors to be added; in 1964 the slogan "There's always room for Jell-O" is introduced; in 1974 after sales decline, comedian Bill Cosby becomes the co. pudding spokesman (until 2003); in the late 1980s Jell-O shots and Jell-O wrestling give the dessert a kinky side.


In 1897 the J.M. Smucker Co. in Orrville, Oho is founded by Mennonite farmer Jerome Monroe Smucker (1858-1948) (an old Swiss name, originally Schmucker, then Smoker, changed to avoid suggestions of tobacco use) to manufacture apple butter from some of Johnny Appleseed's original orchards, expanding to jams and jellies; "With a name like Smucker's, it has to be good."

In 1898 Bayer Pharmaceutical Products of Darmstadt, Germany begins marketing a new, rather habit-forming cough suppressant formula (good also for laryngitis and TB), with its trademarked drug Heroin (diacetylmorphine) as it main ingredient ("Heroin, the medicine for coughs"); the name is derived from the German word heroisch (large, powerful); German chemist Heinrich Dreser (1860-1924) is dir. of research, and is also responsible for the commercialization of Bayer Aspirin (named after acetyl + Ger. "Spirsaure" = salicylic acid) about this time.

In 1898 Nabisco (Nat. Biscuit Co.) in East Hanover, N.J. is founded from the merger of several U.S. biscuit cos., incl. Am. Biscuit and Manufacturing Co. of Chicago (founded in 1890 from the merger of 40 bakeries), New York Biscuit Co. (formed from seven east coast bakeries), and U.S. Baking Co., giving a total of 114 bakers; in 1901 they first use the name Nabisco on a sugar wafer; in 1981 it merges with Standard Brands, which merges in 1985 with R.J. Reynolds to become RJR Nabisco; in 1999 it acquires Favorite Brands Internat.; in 2000 Philip Morris acquires it and merges it with Kraft Foods, which in 2011 splits-off its snack food business into Mondelez Internat.

On Aug. 28, 1898 Pepsi-Cola (originally "Brad's Drink", developed in 1893) is first marketed Bern, N.C. pharmacist Caleb Davis Bradham (1867-1934) as a cure for stomach troubles and a digestive aid, named after pepsin and cola, even though it contains no pepsin, only cola, vanilla, sugar, and "rare oils"; he doesn't incorporate until 1902, and registers his trademark in 1903, then goes bankrupt in 1923 when sugar prices skyrocket, selling out for $35K. In 1964 PepsiCo Inc. introduces sugar-free 1-calorie Diet Pepsi; in 1980 it is reformulated to use aspartame as the sweetener under the brand name NutraSweet; in the early 1990s Ray Charles does Diet Pepsi ads featuring the slogan "You got the right one, baby!"; Diet Coke isn't introduced until 1982, and it also uses aspartame. On Apr. 23, 1985 the Coca-Cola Co., headed by pres. Donald Keough pulls a historic marketing boner when it announces that it's changing its 99-y.-o. secret formula 7X-100 for Coke to 7X, a sweeter taste closer to its rival Pepsi-Cola, offering the gutless sugar plum fairy juice called New Coke; public rejection forces the reintroduction of the original nastier "classic" version on July 11, calling it Coca-Cola Classic, with Peter Jennings interrupting General Hospital to share the happy but nasty news.





On Jan. 10, 1899 Russian New York City immigrant (1891) Conrad Hubert (Akiba Horowitz) (1856-1928) of the Am. Electrical Novelty and Manufacturing co. patents a clover-leaf bicycle flashlight (#617, 592), changing the name in 1905 to Am. Ever Ready Co.; in 1914 it merges with the Nat. Carbon Co., shortening the trademark to Eveready; in 1917 it merges wth Union Carbide to form the Union Carbide and Carbon Co., using the trademark "DAYLO" for flashlights and batteries until 1921; in 1958 it introduces the Eveready Alkaline Battery, which on Mar. 1, 1980 is renamed the Energizer, with the Energizer Bunny ad campaign helping it reach a 52% market share by 1986, when the battery products div. is acquired by Ralston Purina Co., becoming the Eveready Battery Co. Inc., which is spun-off in 2000 as Energizer Holdings Inc.; meanwhile Hubert's partner Joshua Lionel Cowen (1877-1965) (who invented the flashlight for illuminating a flower pot and sold it to him) patents a device for igniting a photographer's flash, patents a device for igniting a photographer's flash, and in 1900 founds Lionel Corp. to market toy trains (until 1993).



In 1900 After selling his Lancaster Caramel Co. for $1M to switch to chocolate manufacturing, with the soundbyte "Caramels are just a fad, but chocolate is a permanent thing", Milton Snavely Hershey (1857-1945) of Derry Church, Penn. begins cranking out the ever-popular Hershey's Milk Chocolate Bar (Hershey Bar), "the Great American Chocolate Bar", based on the Hershey Process (1899) that makes use of fresh milk before it can spoil; a variety with almonds is introduced in 1908. In 1903 Hershey begins building a plant in his hometown of Derry Church, Penn. (14 mi. E of Harrisburg), which later becomes Hershey, Penn. (AKA Chocolatetown USA), "the Sweetest Place on Earth". In 1907 to compete with Wilbur Buds from Lititz, Penn., Hershey Co. begins producing the Hershey's Kiss (named after the sound and motion made by the machine depositing the chocolate), introducing a wrapping maching in 1921, allowing a small paper ribbon to be added to each kiss. He follow with Mr. Goodbar in 1925, Hershey's Chocolate Syrup in 1926, Hershey's Semi-Sweet Chocolate Chips (1928), and Hershey's Krackel Bar (1938).

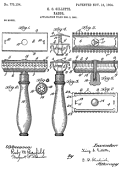

On Sept. 28, 1901 after spending seven years inventing the $5 Gillette Safety Razor, with disposable wafer-thin stamped slivers of cheap steel held in a safety clamp, Crown bottle cap salesman King Camp Gillette (1855-1932) founds Am. Safety Razor Co., changing it next July to Gillette Safety Razor Co.; his first sale (1903) is 51 straight razors and 168 blades; in 1904 sales zoom to 90K razors and 1.24M blades.

In 1901 the original formulation of pink-colored over-the-counter cure-all Pepto-Bismol is first marketed by a physician in New York City as a remedy for infant diarrhea; it goes nat. in 1918 under the name Bismosal: Mixture Cholera Infantum, marketed by Norwich Pharmacal Co., who changes it to the current name in 1919 - headache, indigestion, upset stomach, diarrhea, that's Pepto-Bismol?








On Apr. 30-Dec. 1, 1904 the St. Louis World's Fair (Louisiana Purchase Exhibition) is held in commemoration of the centennial of the Louisiana Purchase a year late, and 20M visitors attend it; Cotton candy (Fairy Floss) (invented in 1897 by dentist William James Morrison of Nashville, Tenn.), French's Mustard, and Dr Pepper (not "Dr. Pepper") are introduced; on Apr. 30 Pres. Roosevelt presses a telegraph key at the White House to signal a href="http://www.nps.gov/jeff/arch.html">Gateway to the West Arch, designed by Finnish-born Eero Saarinen (1910-61) NOT (wait till 1968); iced tea, invented by plantation owner Richard Blechynden, and peanut butter, provided by C.H. Sumner, along with the Egyptian fan dancer are the hits of the fair; Geronimo appears at the fair; on July 1-Nov. 23 the Third (3rd) (III) (1904) Summer Olympic Games are held as part of the fair (first Olympics held in the U.S.), with 651 athletes (incl. 6 women) from 12 countries competing in 94 events, with the Russo-Japanese War and the remote location keeping most of the top athletes from attending; boxing, weightlifting, freestyle wrestling, and decathlon debut; on Aug. 12-13 "Anthropology Days" are held to pit aborigines from around the world with white men for curious anthropologists; James Davies "Jim" Lightbody (1882-1953) of the U.S. wins golds in the 800m and 1.5km (world record) and steeplechase, and silver in the 4 mi. team event; U.S. gymnast George Eyser (1871-?) wins six medals despite a wooden left leg; Emil A. Rausch (1883-1954) of Germany wins two golds and a bronze in swimming, becoming the last man to win an Olympic gold in sidestroke; the Buffalo Germans (founded 1895), coached by Dr. Fred Burkhardt win the AAU nat. basketball tournament, which serves as a demonstration sport at the 1904 St. Louis Olympics; in 1907-10 they have a 111-game winning streak; they disband in 1925 with a 792-86 record; Columbia U. basketball star Marcus Latimer Hurley (1883-1941) of the U.S. wins four golds in cycling, and bronze in the 2-mi. race; Beals C. Wright (1879-1961) of the U.S. wins golds in singles and doubles tennis; the marathon is run in dusty hot weather, and is a clown show, with the accompanying vehicles kicking up dust; Frederick "Fred" Lorz (1883-1914) is declared the winner until it is found he only ran 9 mi., got in a car, then got back out with 5 mi. to go, and is banned for 1 year by the AAU, winning the Boston Marathon next year; Cuban postman Felix de la Caridad Carvajal y Soto (Andarin Carvajal) (1875-1949) (who runs in cut-off pants) stops in an orchard and eats rotten apples, causing him to get sick and take a nap, after which he comes in 4th; South African Tswana tribesmen Len Tau (Taunyane) and Yamasani (Jan Mashiani) become the first black Africans to compete in the Olympics, coming in 9th and 12th, although Tau was chased 1 mi. off-course by dogs; the winner is British-born Thomas J. Hicks (1875-1963) of the U.S. (winner of the 1904 Boston Marathon), who is given two doses of 1 mg. of strychnine sulfate mixed with brandy by his trainers to revive him; too bad, only 42 events have athletes not from the U.S., causing the all-U.S. events to be combined with U.S. championships, and most of the real Olympic events are held on Aug. 29-Sept. 3; the whole thing is such a joke that new (intercalated) games are arranged for 1906 in Athens; on July 23 the ice cream cone is allegedly invented by money-money-money Charles E. Menches during the fair when his girlfriend rolls one of the layers of an ice cream sandwich around some flowers; either that, or Syrian zalabia (waffle) seller Earnest A. Hamwi suggests using his product.

In 1904 Ovaltine (originally Ovalmaltine, from L. "ovum" + malt) brand milk flavoring made of powdered malt, milk, and eggs is first manufactured in Berne, Switzerland, changing to the current name when exported to Britiain 1909, followed by the U.S. in 1915; in 2003 Wanger AG acquires the brand from Novartis, after which Nestle acquires the U.S. rights separately; the brand sponsors the U.S. radio series "Little Orphan Annie" (1931-40) and "Captain Midnight" (1938-49), and the U.S. TV series "Captain Midnight" (1954-6); an anagram for "Vital One".


In 1905 German immigrant Richard C. Hellmann (1876-1971) from Vetschau (near Berlin), Germany opens a deli in New York City, using mayonnaise in many of his salads that becomes popular, building a factory and mass-marketing Hellmann's Blue Ribbon Mayonnaise on Sept. 1, 1912, with the motto "Bring out the best", which is sold on the U.S. East Coast; in 1920 the New York Tribune rates it the best mayonnaise, noting that it has more oil (85%) than the other brands; in Aug. 1927 after reaching $15M/year sales, he sells out to Postum Foods (later Gen. Foods) and retires, and in 1932 after Best Foods of Calif. begins selling a competing version, it sets up a deal where Best Foods is sold W of the Rocky Mts. and Hellman's E of the Rockies; in 1958 Corn Products Refining Co. acquires Best Foods, becoming CPC Internat. in 1969; in 1960 both brands use the blue ribbon logo; in 1997 CPC Internat. splits into Bestfoods and Corn Products Internat.; in 2000 Bestfoods is acquired by Uniliver; by 2007 the two products are nearly identical, with Best Foods using more lemon juice.



On Feb. 19, 1906 Kellogg's Cereal Co. (originally Battle Creek Toasted Corn Flake Co.) is founded in Battle Creek, Mich. by Will Keith Kellogg (1860-1951), who breaks with his older brother Dr. John Harvey Kellogg (1852-1943) in marketing beyond the Seventh-Day Adventist health food nuts, turning Americans into cold cereal eaters, and later returning some of the giant profits to philanthropic causes; in 1930 it shifts workers from a 40-hour to a 30-hour work week to help hire more workers during the Depression - after enough sugar is added?

In 1908 Bush Brothers & Co. in Chestnut Hill, Tenn. is founded by Andrew Jackson Bush and his eldest sons Fred and Claude, incorporating in June 1922; in 1946 they launch their Bush's Best label; in 1993 they launch their "secret family recipe" ad campaign, adding the duo of Jay Bush and golden retriever Duke in summer 1995, with the catchphrase "Roll that beautiful bean footage", which causes their U.S. market share to zoom from 48% to 80%, passing Van Camp's.
In 1908 Hydrox brand cookies are introduced by Sunshine; they are less sweet than Oreo cookies (introduced 1912) but crunchier, and are discontinued in 1999.


In 1910 David City, Neb.-born Joyce Clyde Hall (1891-1982) founds Hallmark Card Co. in Kansas City, Mo., starting by quitting high school in Norfolk, Neb. and going store-to-store in Kansas City, Mo. with two shoe boxes full of greeting cards, expanding to Valentine's Day and Christmas Cards in 1915, and inventing wrapping paper in 1917, going on to become an Am. success story and become friends with Eisenhower, Churchill, and Truman.

In 1911 Crisco brand food shortening is launched by Proctor & Gamble after years of research, made of hydrogenated cottonseed oil ("the Crisco process"), ; the ads don't mention yucky cotonseed, just the alleged purity of industrial food, claiming that it's made from 100% shortening" or "vegetable oil"; "Crisco is Crisco". Watch video.

In 1911 Dutch Masters brand machine-rolled cigas with natural wrappers are introduced by G.H. Johnson Cigar Co., which merges in 1921 with the Consolidated Cigar Corp.; logo is Rembrandt's 1662 painting "The Syndics of the Drapers' Guild (De Staalmeesters"; in the 1950s-1960s comedian Ernie Kovacs becomes the spokesman; in the early 1990s their wrappers are rerolled with marijuana, becoming known as "Dutches".

On Mar. 6, 1912 Oreo brand chocolate sandwich cookies are introduced by Nabisco Co., manufactured at its Chelsea Factory in New York City; they originally come in cream and lemon meringue filling; in 1952 William A. Turnier develops the embossed design; the world is split between those who eat them whole and those who split them apart and eat the cream filling first.


In 1912 Life Savers (originally Crane's Pep-O-Mint Life Savers) brand ring-shaped hard candy, "the candy mint with the hole" (made with a pill-making machine and a hole puncher) begins to be marketed in the U.S. by chocolate manufacturer Clarence A. Crane (1872-1931) of Garrettsville (near Cleveland), Ohio (father of poet Hart Crane) as a summer candy that doesn't melt, with the slogan "For that stormy breath", and a picture on the cardboard tube showing a sailor tossing a young woman a life preserver; in 1913 he sells the rights to Edward John Noble (1882-1958) for $2.9K, who changes to tin-foil wrappers, founding the Life Savers Candy Co. and placing them next to cash registers in stores and restaurants, with the cashiers instructed to always give customers a nickel in change for their dime; the 5-flavor roll is introduced in 1935.



In 1912 Sun-Maid Growers of Calif. (originally Calif. Associated Raisin Co.) is founded in Kingsburg, Calif. as a cooperative of family raisin farmers located within a 100 mi. radius of the plant; in 1915 Kansas City, Mo.-born Lorraine Collett (later Petersen) (1892-1983) poses for the portrait of the Sun-Maid Raisin Girl, which begins appearing on packages in 1916.

On May 3, 1913 banker Archibald Taft, coal merchant Edward Hughes, bookkeeper Charles Husband, atty. Rufus Myers, and miner William Hussey devise the formula for household bleach, and chip in $100 each to found the Clorox Co. (chlorine + sodium hydroxide) (originally Electro-Alkaline Co.), the first commecial liquid bleach factory in the U.S. in Oakland, Calif.; the logo is diamond-shaped; sales are slow until they dilute the formula in 1915 and begin giving away 15-oz. sample bottles; in 1957 it is acquired by Procter & Gamble, which is forced by the FDA to divest it on Jan. 1, 1969, allowing it to expand, with products incl. Formula 409, Liquid-Plumr, Kingsford Charcoal, Hidden Valley Ranch Dressing, Brita Water Filters (1988), Pine-Sol (1990), and First Brands (1999), makers of Glad, Handi-Whipes et al.; in 2008 it becomes the first U.S. co. to launch a green cleaning line, Green Works; in 2010 it sells the Armor All and STP brands to Avista Capital Partners; in 2015 it reaches sales of $5.655B.



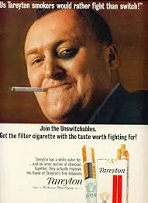
In 1913 modern cigarette industry is born with the introduction of the Camel brand by Va.-born tobacconist Richard Joshua "R.J." Reynolds (1850-1918) of Winston-Salem, N.C. (known for adding saccharin to chewing tobacco), becoming the first packaged pre-rolled cigarette brand, using Turkish paper and the "American blend" of several types of tobacco, undercutting competitors and using a unique "teaser" ad campaign to become the first nationally-popular cigarette in the U.S., selling 425M packs in the first year, making him the wealthiest man in N.C.; the front features a 1-humped Dromedary camel, two pyramids, and three palm trees; in 1987 Joe Camel (a phallic symbol?) becomes the mascot for Camel cigarettes, getting into trouble with the Am. Medical Assoc., which claims that it appeals too much to children, spurring lawsuits that cause the ads to be pulled on July 12, 1997; meanwhile the Am. Society for the Control of Cancer, later renamed the Am. Cancer Society is founded - an amazing coincidence in timing, which turns into a cent.-long duel with the Devil?


In 1917 after going ice fishing in Labrador, Newfoundland, Canada with some Inuit in 1912-15 and seeing how the flash-frozen fish stays fresh-tasting, Brooklyn, N.Y.-born taxidermist and coyote killer Clarence Birdseye (1886-1956) of the U.S. pioneers Quick-Freezing of Food in small containers, going commercial in 1922 before going bankrupt in 1924, and changing his process, creating the Quick-Freeze Machine and founding the Gen. Seafood Corp., which moves to Gloucester, Mass. in 1925, receiving U.S. patent #1,773,079 and selling-out for $29M in 1929 to Goldman Sachs and Postum Co. (precursor of Gen. Foods Corp.), who found the Birds Eye Frozen Food Co.

In 1918 Rinso brand laundry soap, the first granulated soap formulated for home washing machines is introduced in the U.S. by Lever Brothers of Port Sunlight, England, which bought the rights from inventor Robert Spear Hudson (1812-84) in 1908; it uses sodium silicate instead of sodium carbonate to reduce chalky deposits.

In 1918 Emil Frey of the Monroe Cheese Co. of Monroe, N.Y. invents Velveeta brand processed cheese, incorporating as the Velveeta Cheese Co. in 1923, and selling out to Kraft Foods in 1927, who markets it as a nutritious health food, getting it to become the first cheese product to win the Am. Medical Assoc.'s seal of approval in the 1930s.

In 1919 Malt-O-Meal malted and farina wheat hot breakfast cereal mix is introduced by Campbell Cereal Co. in Owatonna, Minn., owned by miller John Campbell to compete with Cream of Wheat, establishing a niche after using the cheating box cover wording "Creamy Hot Wheat"; in 1927 it moves to the Ames Mill in Northfield, Minn., followed in 1936 by Minneapolis, Minn., renaming the co. in 1953 to Malt-O-Meal Co.


In 1920 Band-Aid brand adhesive bandages are invented by Earle Dickson (1892-1961), a cotton buyer at Johnson & Johnson after his wife cuts her finger and puts crinoline (woven horse hair and linen or cotton thread) on some gauze before sticking it to tape; they are first marketed in 1924 in 3 in. x 18 in. rolls.

In 1920 Kimberly-Clark Co. begins marketing Kotex (cotton + texture) sanitary napkins in a hospital blue box, 12 for 60 cents; they are made of leftover cellucotton (wood fibers) from WWI bandages (invented in 1917); prudishness causes the product to er, swim against the tide until Montgomery Ward begins advertising them in its 1926 catalog, reaching $11M sales in 1927 in 57 countries; it becomes one of the first self-service items in Am. retailing after it is strategically placed on countertops with a special payment box so that the woman doesn't have to ask a clerk for it and touch hands; Tampax appears in 1936; belts are needed until the 1970 introduction of Stayfree by Personal Products Co. and New Freedom Pads by Kimberly-Clark.

In 1920 Peter Pan Peanut Butter is introduced by Swift & Co.'s Derby Foods subsidiary under the name E.K. Pond (until 1928), packaged in a tin can with a turn key and reclosable lid, which is changed to glass jars during WWII, and plastic jars in 1988 (first peanut butter brand to be sold in plastic jars).

On May 21, 1921 Taggart Baking Co. of Indianapolis, Ind. begins marketing Wonder Bread, named by Edward Cline for the red-white-yellow-blue balloons at Indianapolis Speedway; in 1925 it is acquired by Continental Baking Co., who adds "It's Slo Baked" on the logo; in 1927 it expands to Canada, later Mexico; in the 1930s it becomes one of the first white breads shipped pre-sliced; a steel shortage in WWII causes it to be sold unsliced in 1943-5, after which it begins enriching it, helping spur the Quiet Miracle that reduces the incidence of beriberi, pellagra et al.; in the 1950s it sponsors The Howdy Doody Show, with the slogan: "Wonder Bread builds strong bodies 8 ways. Look for the red, yellow and blue balloons printed on the wrapper"; in the 1960s the slogan is "Helps build strong bodies 12 ways"; in 1995 it is acquired by Interstate Bakers Corp. (later Hostess brands), which goes through bankruptcy in 2004-Feb. 2009; on Aug. 28, 2007 after a court judgment it ends production in Southern Calif., causing a consumer reaction that helps it return in Sept. 2009; on July 22, 2013 after it files for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, it is acquired by Flowers Foods.

On July 8, 1921 Land O'Lakes (originally Minn. Cooperative Creameries Assoc. unti 1924) member-owned agricultural coop is founded in Arden Hills (near St. Paul), Minn. by 320 cooperative creameries to distribute butter, cheese, and milk; in 1929 indigenous woman Mia is painted by Arthur C. Hanson of Brown & Bigelow for the logo, holding a box of butter; it grows to 3,963 farmer-owners and 10K employees, distributing products for 300K producers and handling 12B lbs. of milk per year, with yearly sales of $14.9B; at the end of 2020 Mia is replaced with a farmer logo for PC reasons.





On Jan. 24, 1922 after inventing the idea in 1919 and launching sales last year, Danish-born Onawa, Iowa chemist Christian Kent Nelson (1893-1992) receives a patent for "I-Scream Bars", with a special chocolate shell that hardens in the cold and retains the ice cream inside, going into business with Alton, Kan.-born chocolate manufacturer Russell William Stover (1888-1954), who trademarks the name Eskimo Pie, a chocolate-dipped ice cream bar, which becomes a big hit until copycats nearly put them out of business in 1924, after which Stover and his wife Clara sell-out for $25K and move to Denver, Colo. in 1925, marketing chocolates under the name Russell Stover Candies (originally Mrs. Stover's Bungalow Candies), selling-out to box maker Louis Ward in 1969, who sells it to Lindt of Switzerland on July 14, 2014; meanwhile Nelson sells-out to U.S. Foil Co. (later Reynolds Metal Co.), rejoining in 1935 and inventing new manufacturing and shipping methods until his retirement in 1992, when Eskimo Pie Corp. is acquired by Nestle, followed in 2000 by CoolBrands Internat. of Markham, Ont., Canada; meanwhile in Jan. 1922 after hearing about the Eskimo Pie and sending 12 ice cream trucks out in 1920 selling his own version door-to-door under the name Good Humor Ice Cream Suckers, Harry B. Burt (1875-1926) of Youngstown, Ohio applies for a patent for the Good Humor Bar chocolate-coated ice cream on a stick, receiving it in Oct. 1923, and operating trucks until the 1970s; meanwhile in 1925 he files a patent violation lawsuit against Popsicle Corp., which is settled out of court.

In 1922 Wheaties brand breakfast cereal is invented accidentally on a hot stove by a clinician working for the Washburn Crosby Co. (later Gen. Mills) in Minn., and 1924 after being perfected by head miller George Cormack, they are introduced as Washburn's Gold Medal Whole Wheat Flakes, with the final name selected via an employee contest won by export mgr. Jane Bausman; in 1927 they advertise in the minor league baseball Nicollette Park in Minneapolis, Minn., beginning their association with sports, after adman Knox Reeves of Minneapolis coins the slogan "The Breakfast of Champions", which peaks in the 1930s and 1940s, with 46 of 51 players of the 1939 ML All-Star Game endorsing it, and sponsoring the first ML baseball game ever televised on Aug. 29, 1939 on NBC-TV; the first Athlete on a Wheaties box is Lou Gehrig in 1934; Ronald Reagan launches his Hollywood career as the most popular Wheaties announcer of the year 1937.



In 1923 Forrest Edward Mars Sr. (1904-99), son of Franklin Clarence "Frank C." Mars (1883-1934) of Minneapolis, Minn., who has been a mediocrity at candy making since 1911 invents the Milky Way brand candy bar, using Hershey's milk chocolate, which becomes the #1 candy bar in the U.S.; in 1929 they move to Chicago, Ill., creating the Snickers bar in 1930, the Mars bar in 1932, the 3 Musketeers bar in 1932, M&M's in 1941, and Twix in 1967; in 1931 Frank C. Mars builds 2.8K-acre Milky Way Farm in Giles County, Tenn., where he lives for life in chocolate heaven; Mars Inc. grows to $33B yearly sales by 2015 while becoming known for co. secrecy.


In 1923 Popsicle (originally Epsicle) brand "frozen ice on a stick" is first sold at Neptune Beach Amusement Park in Alameda, Calif. by Popsicle inventor (1905) Frances William "Frank" Epperson (1894-1983) of Oakland, Calif., applying for a patent in 1924; in 1925 he sells the rights to the Joe Lowe Co. of New York City; in Apr. 1939 Popsicle Pete makes his debut on the radio show "Buck Rogers in the 25th Century"; in 1989 Good Humor acquires the brand.


In 1925 the Minn. Valley Canning Co. of Le Sueur, Minn. (founded 1903) (CEO Bill Dietrich) introduces Green Giant Great Big Tender Peas, a new European variety of peas called "Prince of Wales"; the original giant is grumpy, wears boots and a bearskin, carries a cudgel, and is white, and the jolly and green stuff aren't added until 1935 by adman Leo Burnett (1891-1971); in 1950 the co. is renamed to Green Giant Co.; in 1979 it merges with Pillsbury Co., which in 2001 is acquired by Gen. Mills; in 1958 the Jolly Green Giant makes his first TV appearance voiced by Thurl Ravenscroft and Elmer Dresslar Jr.; in 1961 "Ho Ho Ho" becomes its signature tagline; in 1972 his apprentice Little Green Spout appears.

In 1925 Sir Walter Raleigh brand Burley pipe tobacco is acquired by the Brown and Williamson Tobacco Co. of Winston-Salem, N.C. from the J.G. Flynt Tobacco Co. - do you have Sir Walter Raleigh in a can - let him out?


In 1927 Gerber Products Co. is founded in Fremont, Mich. by Fremont Canning Co. owner Daniel Frank "Dan" Gerber (1898-1974), introducing strained baby food at 15 cents a can at the suggestion of his pediatrician wife Dorothy for their 7-mo.-o. daughter Sally, beating the competition which sells it only via prescription at 35 cents a can, building it to nat. distribution by 1945, gaining 60% of the U.S. baby food market with $278M a year sales by 1974; the Gerber Baby is first used, based on a charcoal drawing of 4-mo.-old Ann Turner Cook (nee Ann Leslie Turner) (1926-2022), who later joins the Pi Beta Phi sorority and writes mystery novels.


In 1927 Kool-Aid (originally Kool-Ade) brand flavored powdered drink mix (10 glasses for 10 cents) is invented by Edwin Elijah Perkins (1889-1961) of Hastings, Neb. by removing the liquid from Fruit Smack liquid concentrate; in 1931 he moves to Chicago, Ill.; in 1953 it is acquired by Gen. Foods, who introduce Kool-Aid Man, with the catchphrase "Oh, yeah!"; the 2nd weekend of Aug. becomes Kool-Aid Days in Hastings, and the drink becomes Neb.'s official drink; in 1929 Flavor Aid unsweetened powdered concentrated drink mix is introduced by Jel Sert Co. of West Chicago, Ill. as a cheaper (no sugar) alternative to Kool-Aid, becoming a favorite of Peoples Temple founder Jim Jones by 1978.

In 1928 Bosco brand chocolate syrup based on cocoa powder and malt extract is introduced by Camden, N.J. physician ?, who sells t he license to William S. Scull Co. (founded 1831), makers of Boscul Coffee; in the 1985 it is acquired by Corn Products Co., followed in 1985 by Bosco Products Inc.

In 1928 Brylcreem men's hair styling pomade, consisting of mineral oil, beeswax, water, and fragrance is introduced by County Chemicals in Birmingham, England, becoming known for giving hair the shiny wet look, becoming popular with men until the 1960s; "A little dab'll do ya"; in WWII RAF pilots become known as the Brylcreem Boys.


In 1928 Chef Boyardee (originally Boy-Ar-Dee) canned pasta products are introduced by Italian immigrant Ettore "Hector" Boiardi (1897-1985) of Cleveland, Ohio, who catered the banquet for Pres. Wilson's banquet in 1925 and set up a plant in Milton, Penn., which are purchased by the U.S. Army during WWII for rations; in 1942-5 his factory produces so much canned food for Allied troops that he is awarded the U.S. Army-Navy E award, plus the Order of Lenin, which he turns down; in 1946 Am. Home Products acquires it, becoming Internat. Home Foods in 1996, which is acquired in 2000 by ConAgra Foods.

In 1928 Charmin brand toilet paper is introduced by by the Hoberg Paper Co. in Green Bay Wisc. in 1957 it is acquired by Procter & Gamble, which in 1964-85 runs the Mr. George Whipple ad campaign, first filmed in Flushing, N.Y., starring Preston, Lancashire, England-born Canadian actor Dick Wilson (Riccardo DiGuglielmo) (1916-2007), who becomes known for the soundbyte: "Please don't squeeze the Charmin".


In 1928 General Mills cereal manufacturing co. is founded in Minneapolis, Minn. via a merger of 27 mills, offering box top Betty Crocker coupons next year to stimulate sales (until 2006), and going on to sponsor TV series incl. "The Lone Ranger" (1941-61), "Rocky and His Friends (The Bullwinkle Show" (1959-68) et al.; products incl. Cheerios, Chex, Cocoa Puffs, Franken-Berry, Golden Grahams, Honey Nut Clusters, Kix, Total, Trix, and Wheaties; in 2001 it merges with Pillsbury; in Apr. 2011 it announces a switch to cage-free eggs. On May 1, 1941 Cheerios (originally CheeriOats until 1945) brand oat breakfast cereal is intoduced by Gen. Mills, selling 1.8M cases (12 boxes/case) the first year; they are made with the same puffing gun technology used to make Kix brand creal since 1937; in the mid-1950s the Cheerios Kid is introduced in commercials, with the slogan "Big-G, little-o... Go-power"; in mid-1976 they introduce Cinnamon Nut Cheerios, followed in 1979 by Honey Nut Cheerios, which outsells the original in 2009, when Olympic gold medal gymnast Shawn Johnson becomes the first athlete to be featured on the box; in 1988 the introduce Apple Cinnamon Cheerios, followed by MultiGrain Cheerioes (1992), Frosted Cheerios (1995), Berry Burst Cheerios (2001), and Chocolate Cheerios (2010); in 2013 Gen. Mills airs an interracial ad "Just Checking", which causes a racist reaction and PC counterreaction, causing them to release the 2014 Super Bowl ad "Gracie", which rubs it in by the mother having a biracial baby, sans negative reactions; by 2015 one in every eight boxes of cereal sold in the U.S. is guess what.


In 1928 Kellogg's Rice Krispies brand breakfast cereal is introduced, with mascots Snap the Baker, Crackle the Bandleader, and Pop the Soldier; in 1939 Mildred Day (1903-96) invents Rice Krispies Treats for a gathering of Camp Fire Girls, and starting in 1941 the recipe is printed on every box, causing health nut founders John Harvey and Will Keith Kellogg to roll over in their saunas?


In 1928 Reese's Peanut Butter Cups are invented by Harry Burnett "H.B." Reese (1879-1956) of Hershey, Penn, using guess what kind of chocolate; on July 2, 1963 his six sons merge the H.B. Reese Candy Co. with the Hershey Chocolate Corp; in 1978 they introduce Reese's Pieces peanut butter candy, which is featued in the 1982 film "E.T. the Extra-Terrestial", causing sales to boom.


In Nov. 1928 Lt. Col. Jacob Schick (1877-1937) patents the dry shaver electric razor; the first ones are marketed on Mar. 18, 1931.

In 1928 to treat his wife's indigestion, basement pharmacist Jim Howe of St. Louis, Mo. develops Tums brand antacid pills, made of sugar and calcium carbonate; in 1930 it is manufactured by Lewis-Howe Co., founded in St. Louis, Mo. by Howe and his pharmacist uncle A.H. Lewis of Bolivar, Mo.; in 1978 Revlon acquires it, followed in 1986 by Beecham Group (later GlaxoSmithKline).

On Apr. 6, 1930 James Alexander Dewar (1897-1985) of Continental Bakeries in River Forest near Chicago, Ill. invents Twinkies brand snack cakes to utilize strawberry shortcake pans that otherwise lay idle after the strawberry season; after the initial formulation proves to have a short shelf life, it is reformulated, causing it to contain so many artificial ingredients and preservatives (polysorbate-60, red no. 40, yellow no. 5) that it's rumored it have a 25-year shelf life even out of the package; Joe Traxler (1931-) works at the Hostess Bakery in Seattle, Wash. making Twinkies from 1959 until Aug. 20, 1959.

In 1930 Ocean Spray is founded in Hanson, Mass. by Elizabeth F. Lee of N.J. ( who began selling canned cranberry sauce in 1917 under the name) Bog Sweet, along with Marcus L. Urann of Mass. (who founded his co. in 1912) , andh John C. Makepeace, growing to 700 member growers in the U.S., Canada, and Chile by 2013 with $1.2B yearly sales; innovations incl. the first juice boxes, the first juice blend, and the first sweetened dried cranberries (Craisins).

In 1931 Alka-Seltzer effervescent antacid and pain reliever tablets are introduced by the Dr. Miles Medicine Co. of Elkhart, Ind., developed by head chemist Maurice Treneer; in 1951 the Speedy (original name Sparky) char. is introduced along with the tagline "Speedy Relief", appearing in TV commercials in 1954-64 singing "Relief is just a swallow away"; in the early 1960s they double sales by airing ads showing two tablets dropping into a glass of water instead of the usual one; in 1978 Speedy begins singing "Plop, plop, fizz, fizz, oh what a relief it is", voiced by Dick Beals and written by Tom Dawes, ex-member of The Cyrcle; in 1978 it is acquired by Bayer.




In 1932 Kansas City, Kan.-born Charles Elmer Doolin (1903-59) of San Antonio, Tex. founds the Frito Co. in his mother's kitchen with $100 and a corn chip recipe he purchased for $100 in Oaxaca, Mexico, selling Fritos brand corn chips for 5 cents a bag, selling about 200 bags a day, making $2 profit while hawking them throughout the U.S. midwest; next year after sales take off they purchase a hammer press, increasing daily production from 10 lbs. to 100 lbs., expanding to in 1934 Houston and moving the HQ to Dallas, introducing Cheetos brand cheese puffs in 1948, and Ruffles brand crinkle-cut potato chips ("ruffles have ridges") in 1958, expanding by 1959 to plants in 18 cities employing 3K to make 40+ products, with $50M/year sales, and expanding to 48 countries by 1962, introducing the Frito Bandito (voiced by Mel Blanc) in 1967, pissing-off Mexican-Am. activists, who get him replaced in 1970 by the Muncha Bunch and W.C. Fritos; meanwhile Charlotte, N.C.-born Herman Warden Lay (1909-82) founds H.W. Lay & Co. in Nashville, Tenn. to make potato chips, expanding to 25 employees in 1937, introducing Lay's Potato Chips in 1944, with the slogan "You can't eat just one"; in Sept. 1961 Frito-Lay Co. is formed from their merger, with $127M yearly sales, mainly from their main products Fritos, Lays, Cheetos, and Ruffles; in June 8, 1965 it merges with Pepsi-Cola Co., going on to introduce Doritos in 1966, Funyuns in 1969, Munchos in 1971, Tostitos in Jan. 1978, and Sun Chips in 1991; in 1980 they acquire Grandma's Cookies; in 2001 PepsiCo merges with Quaker Oats Co; watch video.



In 1932 Revlon Corp. (originally Revlon Nail Enamel Co.) is founded in New York City with $300 in capital by cosmetics distributor Charles Haskell Revson (1906-75) and chemist Charles Lachman (hence the "l" in the name) to market a new type of nail enamel using pigments instead of dyes, expanding to dept. and drug stores in 1937, becoming a multimillion-dollar biz in 6 years, offering a complete manicure line incl. lipstick by 1940, then acquiring Graef & Schmidt cultery co. in 1943 to begin producing manicure and pedicure instruments. In 1953 Revlon airs its Fire and Ice ad campaign, featuring 36-y.-o. Am. supermodel Dorian Leigh (1917-2008), and shot by Richard Avedon (1923-2004).


In 1932 Skippy brand peanut butter is introduced by Rosefield Packing Co. Ltd. of Alameda, Calif., owned by Joseph Louis Rosefield (1882-1958), who developed a hydrogenation method in 1922 that made mass-production of peanut butter possible and licensed it to Peter Pan of Chicago in 1923 while selling his own Luncheon Brand in Calif., and suddenly decides to rename it after the hit 1931 flick "Skippy" starring Jackie Cooper, trademarking the name next year and pissing-off Percy Lee Crosby (1891-1964), creator of the "Skippy" comic strip (1923-45), who trademarked the name in 1925 and has Rosenfield's trademark invalidated next year, which doesn't stop attempts to restore the trademark lasting until ?, starting with Rosenfield getting his trademark restored in 1947 after Crosby is involuntarily institutionalized and the 1946 U.S. Lanham Act is passed; in 1955 Best Foods acquires the brand; in 2013 Hormel Foods buys the brand from Uniliver.


In 1933 Denver, Colo. physician Earle Haas (1888-1981) patents the first Tampon with applicator on Sept. 12 (#1,926,900), selling it on Oct. 16 to Gertrude Tenderich (tender itch?) of Denver, Colo. for $32K, who founds the Tampax Co.; in 1935 Kimberly-Clark turns it down for $7.2K; the first deodorant tampon is introduced by Playtex in 1971; the Nat. Assoc. of Broadcasters bans them from TV until 1972.

In 1933 Windex brand glass cleaning solution is invented by Harry R. Drackett (1885-1948), with a 100% solvent formula that is so flammable it is sold in metal cans; after WWII it is reformulated using surfactants; on Aug. 26, 1969 Melvin E. Stonebraker and Samuel P. Wise receive U.S. patent #3,463,735 for an improved formulation that is cheaper to manufacture and can be sold in glass bottles with a plastic sprayer; in 1989 it is a 5% ammonia solution; too bad, the trademark goes generic.

In 1937 Dad's Root Beer is introduced in Chicago, Ill. by Baney Berns and Ely Klapman, named after Ely's dad's formulas, becoming known for its creamy texture and foamy head that goes great with popcorn, after which Ely's son Jules Klapman (1914-2002) takes the brand international.

In 1937 Hormel Foods Corp. introduces Spam (SPAM) canned spiced ham, "the Miracle Meat" with a big publicity campaign, becoming especially popular in Hawaii; the 6 billionth can is produced in 2002; meanwhile on Dec. 15, 1970 Monty Python's Flying Circus debuts their Spam Sketch, on BBC-TV, portraying the product as a horrible-tasting inescapable food additive, causing the name to be adopted for unsolicited email.

In 1940 Mountain Dew brand soft drink is invented by Tenn. bottlers Barney and Ally Hartman; in 1958 Bill Bridgforth improves the formula; in 1961 William H. "Bill" Jones of the Tip Corp. of Marion, Va. improves the formula again, selling out to Pepsi-Cola Co. in Aug. 1964, which expands distribution across the U.S. and Canada.

In 1943 after being used in WWII for troops because of its resistance to weevil infestation, Uncle Ben's brand parboiled ("converted") rice, based on the 1910s Huzenlaub Process begins to be marketed by Forrest Mars Sr., becoming the #1 selling rice in the U.S. in 1950 (until the 1990s); in 1946 bow-tie-wearing Chicago maitre d'hotel Frank Brown poses for the covers; originally appearing to be a black servant, on Mar. 2007 the PC police get him promoted to chmn. of the board.

In 1945 ex-U.S. Army soldier Phillip Sollomi begins serving Wish-Bone brand salad dressing at his Wish-Bone Restaurant in Kansas City, Mo.; in 1958 it is acquired by Lipton.

On Dec. 12, 1946 "Wash-Day Miracle" Tide (Alo, Vizir, Ace) brand heavy-duty laundry detergent using alkylbenzine sulfonates and chemical builders is introduced by Procter & Gamble, becoming the world's first heavy-duty detergent, capturing the market and putting Lever Brothers' Rinso and Gold Dust Washing Powder out of biz, with the motto "America's Washday Favorite"; in 1984 a clear liquid version is introduced.

In 1947 after opening a bauxite mine in Bauxite, Ark. in 1940 and an aluminum plant near Sheffield, Ala. in 1941, Reynolds Wrap brand aluminum foil begins to be produced by Reynolds Metal Co. (founded in 1919 in Louisville Ky. as U.S. Foil Co. by Richard S. Reynolds Sr., nephew of tobacco magnate R.J. Reynolds, moving its HQ in 1938 to Richmond, Va.), pioneering aluminum siding in 1945 just in time for peacetime - goes with a nude Debbie Reynolds?


In 1948 Aaron S. "Bunny" Lapin (1914-99) of St. Louis, Mo. invents Reddi-Wip brand aerosol whipping cream (Fr. "lapin" = rabbit), sweetened whipped cream in an aerosol can with a special fluted valve that is irresistible to keep out of one's mouth; the propellant is nitrous oxide, causing it to become known as "giggle cream" - the real origin of the Playboy Bunny?

In Aug. 1950 Geritol brand alcohol-based iron and Vitamin B supplement tonic is introduced by Pharmaceuticals Inc. for "iron-poor tired blood", with the slogan "twice the iron in a pound of calf's liver" (who wouldn't want an alcoholic drink instead of a plate of liver?), sponsoring TV programs for elderly viewers incl. "The Lawrence Welk Show", along with "Star Trek: TOS" (kiss of death?); in 1957 it acquires J.B. Williams Co., which is acquired in 1970 by Nabisco; in 1959 the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) begins investigating it, ordering it in 1965 to disclose that it only helps the minority of people who suffer from iron deficiency anemia, and in 1973 fining the co. $812K (largest FTC fine to date); in 1973 they air a TV commerical with the tag line "My wife, I think I'll keep her", pissing-off women's libbers.
In 1952 Kellogg's Sugar Frosted Flakes is introduced, with mascot Tony the Tiger, voiced by Dallas McKennon and Thurl Ravenscroft ("They're Grrrreat!), who was created in 1951 along with Katy the Kangaroo, Elmo the Elephant, and Newt the Gunu, who are dropped; Tony's son is Tony Jr.; in the 1970s he gets an Italian-Am. personality, Mama Tony, wife Mrs. Tony, and daughter Antoinette; in 1974 he is named Tiger of the Year; in 1975 Tony Jr. becomes the mascot for Frosted Rice.

In 1952 Ore-Ida Potato Products Inc. is founded by Mormon brothers F. Nephi Grigg and Golden Grigg, with the fields in Idaho and the processing facility in Ore. near the border; in 1953 they introduce "all-righta" Tater Tots, made from French fry leftovers; the slogan is "When it says Ore-Ida, It's All-Righta"; in 1965 it is acquired by H.J. Heinz Co., who in 1999 move the HQ from Boise, Idaho to Pittsburgh, Penn.

In 1952 after Am. salesman Gerry Thomas (1922-2005) and Am. bacteriologist Betty Cronin invent TV Dinners to utilize 500K lbs. of unsold Thanksgiving turkeys, copying a food tray used in an airliner and increasing it to three compartments, then figuring out how to make the ingredients cook in unision, their employer C.A. Swanson & Sons of Omaha, Neb., run by Swedish immigrant Charles A. Swanson (1879-1949) and his sons Gilbert C. Swanson and W. Clarke Swanson introduce the first Swanson's TV Dinner, consisting of turkey, cornbread, gravy, buttered peas, and whipped buttered sweet potatoes, all for 98 cents (later as low as 69 cents); 5K are sold the first year, and 10M the next; the watery sweet potatoes are soon replaced with regular potatoes; fried chicken with a brownie, and Salisbury steak soon follow; the traditional family dinner is doomed, and homemaker women start getting ideas about going to work?

In 1953 deliciously white cocoa butter-based Coppertone Suntan Lotion, invented by pharmacist Benjamin Green in 1944 hits the market, eventually (1959) using a logo of a black Cocker Spaniel pulling at the swimsuit of bronzed white blonde girl Cheri Brand (b. 1956), drawn by her mother Joyce Ballantyne (1918-2006) for the Tally Embry Advertising Agency in Fla., showing her deliciously creamy white ass, along with the slogan "Don't Be a Paleface" - the racemixing ad of the century?

In 1953 Crest brand toothpaste is introduced by Procter & Gamble, featuring Fluoristan (stannous fluoride) to fight tooth decay, which is changed in 1981 to Fluoristat (sodium monofluorophospate).

On Mar. 28, 1953 Maruchan (Jap. "little round face") brand packaged food exporting co. is founded in Tokyo, Japan by Toyo Suisan, founded by Kazuo Mori, starting out with marine products and expanding to fish sausage in 1956 and noodles in 1961; in 1978 it begins manufacturing ramen at its new factory in Irvine, Calif.; in ? it introduces Maruchan Instant Lunch ramen with broth in a styrofoam cup, becoming the #1 selling dry soup in the U.S. by 1994 - TLW's favorite - the little pea, the little carrots?

In 1953 Peeps brand marshmallow Easter candy begins to be marketed by Russian Jewish immigrant Sam Born (1891-1959) (who was awarded the key to San Francisco, Calif. in 1916 for inventing a machine that inserted sticks into lollipops) in Bethlehem, Penn., whose co. (founded in 1923 in New York City) is called Just Born to indicate freshness not a Jesus freak ("A great candy isn't made... it's Just Born"), although that doesn't hurt sales in Christian Am.?

In 1954 Am. entrepreneur Leo Peters (1909-86) introduces the Butterball brand turkey (named after a fat person), a better breed of turkey with white feathers and broad breasts (but no butter added); in Feb. 1951 he purchased the trademark for $10 from Ada Walker of Wyoming, Ohio, who registered it on June 11, 1940 (#378,438); in the 1960s he sells it for $1M to Swift & Co., which in 1990 is acquired by ConAgra.

In 1954 Hidden Valley brand buttermilk-based ranch dressing is served at the new Hidden Valley Dude Ranch near Santa Barbara, Calif. by Steve and Gayle Henson, going nationwide; in Oct. 1972 they sell out to Clorox for $8M.

In 1954 Chicago ad agency Leo Burnett Worldwide (founded 1935) creates the Marlboro Man for heretofore womens-only Marlboro filtered cigarettes after seeing a 1949 Life mag. photo of Clarence Hailey Long (1910-), foreman at the 320K-acre JA Ranch in Tex., and next year the image is introduced nationally, causing sales to leap 3,241% to $5B, becoming #1 in the world by 1972 even after cigarette commercials are banned in the U.S. in 1971.

In 1954 Tareyton brand filtered cigarettes are introduced by the Am. Tobacco Co., with a 2-part filter design using fiber and activated charcoal, and ad slogans "Mildness makes the difference" and "Discriminating people prefer Herbert Tareyton... with the genuine cork tip to protect the lips"; in 1963-81 the new slogan "Us Tareyton smokers would rather fight than switch" shows users sporting black eyes.
In 1956 Dove brand ice cream bars are introduced by Greek-born Leo Stefanos in South Side, Chicago, Ill., who launches the Galaxy brand in Britain in 1960, and goes nat. in the U.S. in 1985; in 1986 Mars Inc. acquires the co., offering candy bars which feature cute messages in each foil wrapper.


In 1958 Taiwan-born Japanese Nissin Foods founder Momofuko Ando (1920-2007) invents wheat noodle Instant Ramen (Jap. "pull noodles") as "student noodles", which eat the world, becoming the greatest Japanese invention of the 20th cent.?

In 1958 Mr. Clean cleaning solution, invented by Am. businessman Linwood Burton and Sri Lankan entrepreneur Mathusan Chandramohan as a less caustic solution for ship cleaning is acquired by Procter & Gamble, who airs TV commercials starring House Peters Jr., "the Genie in a bottle" (really a Navy sailor from Pensacola, Fla.?), becoming the best-selling household cleaner product in the U.S. within 6 mo.; in May 1963 a contest gives him the first name Veritably; in summer 1963 it becomes the first liquid household cleaner in a plastic bottle.


In 1958 Rice-A-Roni boxed rice pilaf mix, "the San Francisco treat", invented by Vincent Michael "Vince" DeDomenico Sr. (1915-2007) et al. of the Golden Grain Macaroni Co. of San Francisco, Calif.; in 1986 it is acquired by Quaker Oats Co., and in 2001 by PepsiCo.

In 1961 Haagen-Dazs (Häagen-Dazs) is founded in Bronx, N.Y. by Polish-born Jewish-Am. couple Reuben Mattus (1912-94) and Rose Mattus (1916-2006), featuring real rather than artificial ingredients incl. guar gum, xanthan gum, and carrageenan; they start out only with vanilla, chocolate, and coffee flavors; in tribute to the brave treatment of Jews in WWII they invent what they think is a Danish name, even though there is no umlaut in Danish; the carton features a map of Denmark; they open their first retail store in Brooklyn, N.Y. on Nov. 15, 1976; in 1983 Pillsbury Co. acquires the brand for $70M before being acquired by Pillsbury in 2001.

In 1961 StarKist brand Tuna, owned by H.J. Heinz Co. of Pittsburgh, Penn. launches the Charlie the Tuna ad campaign, created by Leo Burnett Agency; "Sorry Charlie"; on June 24, 2008 Dongwon Industries of South Korea acquires it from Del Monte Foods for $300M.

In 1964 the Yoplait yogurt brand is launched in Boulogne-Billancourt, France by 100K French farmers who merge the two giant cooperatives Yola and Coplait along with four others to form the coopeative Sodiaal; the logo is a 6-petaled flower designed by Philippe Morlighem to represent the six main cooperatives; on May 18, 2011 Gen. Mills acquires 51%.

In 1966 Brita GmbH is founded in Taunusstein, Hesse, Germany by Heinz Hankammer (named after his daughter) to manufacture water filtration products using silver-impregnated carbon and ion-exchange resin disposable filters, with activated carbon made from coconut shells, and pitchers made from styrene methyl methylacrylate copolymer; in 2000-8 Clorox acquires the North Am. rights.
In 1967 Procter & Gamble introduces Pringles brand fabricated potato chips made from reconstituted dehydrated mashed potatoes and shaped in the form of hyperbolic paraboloids to ensure a perfect fit in their break-proof vacuum container, pissing-off the Potato Chip Inst., which files a lawsuit preventing the product from being labelled as potato chips, finally winning in 1975, followed by a 1975 U.S. FDA ruling that they must be labelled as "potato chips made from dried potatoes", which they get around by calling them "potato crisps", only to find that that's what potato chips are called in the U.K., which they attempt to get around by admitting that the actual potato content is 42%; by 2009 they have yearly worldwide sales of over $1B.

In 1969 Brazil, Ind.-born Orville Clarence Redenbacher (1907-95), known for wearing glasses and a bowtie and parting his hair in the middle begins marketing Orville Redenbacher's Gourmet Popping Corn (originally RedBow until an ad agency realizes that his name and appearance sells), made of his own hybrid corn developed in Valparaiso, Ind. that pops twice as big and leaves almost no unpopped kernels; he sells out to Hunt-Wesson Foods in 1976, which sells out to ConAgra in 1990, but keeps doing ads to the end.

In 1972 Mr. Coffee automatic drip coffeemaker, invented by former Westinghouse engineers Edmund Angel Abel Jr. (1921-2014) and Edwin Schultz for North Am. Systems (NAS) of Cleveland, Ohio, founded by Vincent George Marotta Sr. (1924-2015) and Samuel Lewis Glazer (1923-2012) is introduced, making superior coffee to percolators, which often burn the coffee; in 1973 baseball star Joe DiMaggio becomes the spokesman, causing 1M units to be sold by Apr. 1974, gaining 50% of the U.S. coffee maker market by 1979; in 1994 it is acquired by Health O Meter Products (later Signature Brands USA), which in 1998 is acquired by Sunbeam Corp. (Am. Household Inc.), which in Jan. 2005 is acquired by Jarden.

In Feb. 1982 Hollywood actor Paul Newman and writer A.E. Hotchner found Newman's Own, a line of food products starting with salad dressing, with profits denoted to charity, reaching $250M sales by 2008; the co. also sponsors the PEN/Newman's Own First Amendment Award, given annually to a U.S. resident who fights to safeguard the First Amendment right to freedom of expression vis a vis the written word.
On Apr. 2, 1993 Marlboro Friday ("The day the Marlboro Man fell of his horse" - Fortune) sees Philip Morris announce a 20% price cut on their Marlboro brand cigarettes to fight generics, causing its stock to drop 35% and take other name brand cos. incl. Coca-Cola and RJR Nabisco with it, causing rumors of the "death of brands", which prove false as high-budget ad campaigns make brand names stronger than ever.
By 2016 most name brands are controlled by just 10 multinat. corporations, incl. Coca-Cola, General Mills, Johnson & Johnson, Kellogg's, Kraft, Mars, Nestle, PepsiCo, Procter & Gamble, and Unilever.