





































1780 Pop. of the Am. colonies: 2.7M; Catholic pop. of England: 70K. The Age of Heroic Medicine in Europe and the U.S. begins (ends 1850), in which the patient has to become a hero to endure bloodletting, forced vomiting, sweating, blistering, and intestinal purging via calomel. On Jan. 5 as his army at Morristown starves and freezes in log huts, mutinying and deserting in large numbers, Gen. Washington ("the man on his knees when the Congress goes to prayer") writes Congress complaining of the lack of supplies, but the weak Articles of Confederation make it impossible to raise taxes - so what can they do, I ask you? On Jan. 12 the German-language daily newspaper Neue Zuercher (Zürcher) Zeitung is founded in Zurich, Switzerland by Swiss painter-poet-bookseller Salomon Gessner (1730-88), raising the bar in journalistic objectivity and depth incl. coverage of music and theater as well as an advertising section, becoming the Swiss newspaper of record, with circ. reaching 18K in 1910, 47.5K in 1930, and 66.6K in 1950, peaking at 169K in 2000. On Feb. 15 a British force under Gen. Goddard and East India Co. officer James Hartley (1745-99) captures Ahmedabad, followed on Nov. 13-Dec. 11 by Ft. Bassein; on Nov. 13 another British force of 6K under Gen. Fraser defeats the Marathas and captures Deeg; on Aug. 3 another British force of 2K (mostly sepoys) under Capt. Popham surprises and captures Gwalior in C India. On Mar. 1 Penn. becomes the first U.S. state to make an abolition pledge with an Act for the Gradual Abolition of Slavery - have to get my money out of them first? On Mar. 2 Mass. adopts a 1780 Mass. Constitution written by John Adams (1735-1826), which becomes the model for the U.S. federal constitution. On Mar. 14 2K Spanish troops under La. gov. Bernardo de Galvez y Madrid capture Ft. Charlotte from 287 troops under Capt. Elias Durnford (1739-94), causing Mobile to surrender just as Gen. John Campbell of Strachur, slowed down by bad weather is about to arrive with reinforcements, causing him to return to Pensacola on Mar. 18, which is all that is left of the British province of West Fla. On Mar. 26 the E. Johnson's British Gazette and Sunday Monitor begins pub. in London (until Sept. 22, 1805), becoming the first Sunday newspaper in Britain - extra, extra, read all about it, we're not losing but not winning in America? In Mar. to counter hyperinflation Congress offers to exchange one of its new dollars for forty of the old ones, which wipes out the savings of many Americans, and gives rise to the saying "not worth a Continental". On May 4 the Am. Academy of Arts and Sciences is founded in Boston, Mass. by John Adams (1735-1826), James Bowdoin II et al. to encourage scientific work, with membership limited to 1500 Fellows and 190 Foreign Honorary Members elected for eminence; in 1955 it begins pub. the quarterly journal Daedalus and awards the Rumford Medal. Old English is the fastest way to clean down under? On May 12 after a 6-week siege, bringing new land and sea forces to join and bottle up Charleston Peninsula, the British under Lt. Gen. Sir Henry Clinton capture 5.5K Continental troops under Gen. Benjamin Lincoln (1733-1810) at the Battle (Siege) of Charleston (begun Mar. 29), becoming the largest Am. army to surrender since Saratoga, and the greatest single Am. loss of the war; former brig. gen. Christopher Gadsden (1724-1805), lt.-gov. of S.C. signs the surrender document, and is released on parole by Clinton, then a few weeks later is arrested by order of Lord Cornwallis and imprisoned for 10 mo. at Ft. Augustine; Brig. Gen. William Moultrie is captured, then exchanged in 1782 and promoted to Maj. Gen., going on to become gov. of S.C. after the war (1785-7, 1792-4); after Charleston falls, 25K blacks (25% of the total), plus a third of Ga. blacks seek their freedom with the Brits; S.C.-born Lt. Col. Francis Marion (1732-95) escapes and forms a band of guerrillas, and is nicknamed the Swamp Fox by British Gen. Banastre (Bannister) "Bloody Ban" "the Green Dragoon" "the Butcher" Tarleton (1754-1833), who becomes known for giving no quarter to the enemy ("Tarleton's quarter") after the May 29 Battle (Massacre) of Waxhaws, which begins when Tarleton's horse falls and traps him, and his troops go beserk; Congress goes against Gen. Washington's advice and dispatches Saratoga hero Horatio Gates from Hillsborough, N.C. to take command in the South. On May 19 a mysterious darkness envelops much of New England and part of Canada in the early afternoon; the cause has never been determined? - one drink ain't enough Jack, you better make it three? On June 2 after Irish MP Henry Grattan (1746-1820) demands Home Rule for Ireland, pissed-off London-born Scottish Gaelic-speaking, bagpipe-playing, highland reel-dancing Navy-reject fruitcake Lord George Gordon (1751-93) (son of Cosmo George Gordon, 3rd duke of Gordon) sets up the Protestant Assoc. to demand repeal of the 1778 Catholic Relief Act on the theory that Roman Catholic soldiers would be disloyal, and marches on the House of Commons from St. George's Fields with 50K supporters wearing blue cockades to present a petition with 100K names, shouting "No Popery!" and harassing House of Lords members, the situation degenerates into the savage anti-Catholic Gordon Riots, burning Newgate, Bridewell, Fleet and other prisons and liberating the prisoners, looting Langdale's distillery, leveling the Irish Catholic Moorfields section, and destroying the house of Lord Chief Justice Mansfield, causing aging retired Gen. Jeffrey Amherst to take the field again against the mob, killing over 800; after the riots are quelled on June 8, 25 ringleaders are hanged, but Gordon goes scot free; too bad, after being excommunicated by the archbishop of Canterbury in 1786, he is convicted in 1787 of defaming Marie Antoinette and other French officials, and given five years in Newgate Prison in Jan. 1788; meanwhile in 1787 he converts to Orthodox Judaism, grows a long beard and changes his name to Israel bar Abraham Gordon, associating only with other orthodox Jews in jail, causing them to call him the resurrected Moses - one Bourbon, one Scotch, and one Mogen David? On June 7 the HMS Enterprise (Enterprize) (commissioned Apr. 1775) is anchored in the Bay of Gibraltar when six drifting British vessels approach, and their crews set them on fire, causing Capt. Patrick Leslie to sink them before the waiting Spanish can get them. In June the British East India Co. ship Princess Royal lands at Bengkulu on Sumatra with Am. rebel POWs, who are sent to Ft. Marlboro to be trained as British soldiers to take Sumatra from the Dutch, which they do next year after Holland joins the armed neutrality against Britain. On July 10 French regulars under French marshal Jean Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur, Comte de Rochambeau (1725-1807) arrive in R.I. to help Gen. Washington at Yorktown, placing themselves wholly under his command - that must have been hard? On Aug. 16 after Congress ignores Gen. Washington's pleas that the so-called Hero of Saratoga is not up to snuff, the Battle of Camden 5 mi. N of Camden, S.C. is a V for the British under gen. Charles Earl Cornwallis (1738-1805) and Gen. Sir Banastre Tarleton (1754-1833), wh surprises Maj. Gen. Horatio Gates' force and routs them all the way back to Hillsborough, causing his "Northern laurels to turn to Southern willows" as Gates gallops 60 mi. to safety in Charlotte, N.C., stinking himself up and ending his career although he skirts a court martial; the patriots lose 900 casualties and 1K POWs, vs. 68 KIA, 245 wounded, and 11 missing for Cornwallis; Gates' Bavarian-born 2nd-in-command Gen. Johann von Robais, Baron de Kalb (b. 1721) is wounded and captured by the Brits, and dies on Aug. 19; Cornwallis then invades N.C., while Maj. Gen. Nathaniel Greene is given control over what is left of the rebel Southern army. On Aug. 24 Louis XVI of France abolishes the use of torture to obtain confessions. In Aug. after the exec. council of Penn., led by Penn. gov. (1781-81) Joseph Reed (1741-85) (known for his lusty prosecution of loyalists) has Gen. Benedict Arnold court-martialed for abuse of military authority and favoritism to Tories, and he is sentenced to be reprimanded by Gen. Washington, who takes his side and softens it as much as possible, Washington moves him out of Philly, appointing him as cmdr. of West Point; too bad, instead of making Arnold it breaks him, and he begins secret negotiations with the British to surrender his post, meeting with British Maj. John Andre at midnight on Sept. 21 and demanding Ł20K. On Sept. 9 the Brits, thinking they have control of Ga. and S.C. invade N.C. under Lord Cornwallis, reaching Charlotte on Sept. 26; meanwhile on Sept. 26 hundreds of feisty buckskin-clad sharpshooting backwoodsmen assemble at Ft. Watauga on the Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River in Tenn. and form a milita under Col. John Sevier (1745-1815) and Col. Isaac Shelby (1750-1826), then cross the Appalachians at Roan Mt. to join the regrouping Southern rebels under cols. Elijah Clarke (1742-99) and Charles McDowell (1743-1815), becoming known as the "overmountain men". On Sept. 22 the first recorded lynching, in Pittsylvania County, Va. is named for Capt. William Lynch (1742-1820), who terrorizes British loyalists with their own Anglo-Saxon Lex Talionis? Speaking of lynchings? On Sept. 23 West Point cmdr. Gen. Benedict Arnold (1741-1801), hero of Saratoga is discovered to be a traitor, with plans to surrender West Point to the British after his British contact Maj. John Andre (André) (b. 1750) (adjutant gen. of English forces in Am., and aide of Sir Henry Clinton since 1778) is captured by the Americans on Sept. 23 near Tarrytown in civilian clothes, with papers hidden in his boots (plans of West Point) implicating Arnold; British spy Ann Bates is found to be passing master-boots, er, messages between them; Arnold escapes on the British sloop Vulture off Teller's Point on the Hudson River after the news has to be sent directly to West Point because Washington has just arrived, tipping him off; Andre is taken to Washington's HQ at Tappan, N.Y. and hanged as a spy on Oct. 2 after unsuccessfully begging to be shot like a soldier rather than hanged like a dog, er, thief, his last words being, "It will be but a momentary pang"; Arnold's Tory half-his-age 2nd wife (since 1779) Margaret "Peggy" Shippen (1760-1804), who had been hoping to become part of the British aristocracy by making Benny Wenny live beyond his means put him up to it and is the real traitor? It's William Wallace Time? Feisty Scottish freedom fighters fight for their free-ee-ee-dom against the stankin' English again on the Am. side of the Pond? On Oct. 7 after 1K loyalist militia and 100 British provincial rangers under British cmdr. Maj. Patrick Ferguson (b. 1744) (who made the mistake of threatening the rebels to lay down their arms or he would "lay waste to their country with fire and sword") are chased by 900 pissed-off overmountain men towards Cornwallis' main body at Charlotte until they are forced to stand and fight, the Battle of Kings Mountain near Blacksburg, York County, S.C. (1.5 mi. S of the N.C. border) is a V for the rebels, becoming "the turning point of the American Revolution" (Theodore Roosevelt); Ferguson is KIA, and his Tory militiamen slaughtered, with 119 killed, 123 wounded, and 664 taken POW, vs. 28 rebels killed, incl. rebel cmdr. Col. James Williams (b. 1740), and 62 wounded; meanwhile Gen. Thomas "the Gamecock" Sumter (1734-1832) (later the last surviving officer of the Am. Rev. War) emboldens small farmers to join his guerrilla band - thank you very much, play ball? On Oct. 9-20 the 200 mph Great Hurricane (of the Antilles) of 1780 (Huracán San Calixto) kills 20K-27K in the Lesser Antilles and strip Barbados clean of vegatation, becoming the deadliest Atlantic hurricane (until ?); 40 French ships involved in the Am. Rev. War capsize. On Oct. 18 to celebrate the V over Benedict Arnold, Congress declares its 3rd nat. day of Thanksgiving. On Oct. 31 21-y.-o. Kingston upon Hull-born William Wilberforce (1759-1833) is elected to Parliament, becoming an evangelical Christian in 1785 , hooking up with anti-slave-trade activists Thomas Clarkson, Charles Middleton, Hannah More, Granville Sharp et al. in 1787 and silencing chuckles about his 4'11" hunchback frame with his deep religiousness and eloquent oratory, which makes him seem a giant. In Nov. Gen. Benjamin Lincoln is exchanged for British Maj. Gen. William Phillips (1731-81), and soon becomes Washington's 2nd in command. On Nov. 29 empress (since Oct. 20, 1740) Maria Theresa (b. 1717) dies after reigning 40 years and 40 days, and her son Joseph II (1741-90) succeeds to the imperial (Austrian) throne as HRE. On Dec. 4 at the Battle of Rugeley's Mills in Clermont, S.C., 6' Va.-born cavalry Col. William Washington (1752-1810) (2nd cousin of George Washington) attacks a fortified log barn with 107 loyalists led by Col. Henry Rugeley inside; when the patriots' small arms prove ineffective, Washington cuts "Quaker guns" (logs resembling cannon) and tricks the loyalists into giving up before he blows them to splinters. On Dec. 14 Alexander Hamilton marries fair maid Elizabeth Schuyler (1757-1854), daughter of wealthy patriot Gen. Philip Schuyler of Albany, N.Y.; he courted her in the 1760 home of Dr. Jabez Campfield (1737-1821) in Morristown, N.J. In Dec. after Congress chooses Gen. Nathanael Greene (1742-86), the "fighting Quaker" of R.I. as the new cmdr. of the Southern theater, he arrives in Charlotte, and soon moves the army E toward the Pee Dee River. Austria appropriates a great part of the bishoprics of Passau and Salzburg. The Brits under N.Y.-born loyalist leader Sir John Johnson, 2nd Baronet of New York (1741-1830), assisted by what's left of Capt. John Butler and his Butler's Rangers raid Mohawk River Valley settlements. Francis Dana (1743-1811) of Mass. is appointed U.S. minister to Russia, and after he fails to gain recognition he returns to the U.S. in 1783, ending up as the chief justice of the Mass. Supreme Court in 1791. The Second Anglo-Mysore War begins (ends 1784). Ngwane III dies, and his son Ndvungunye (Mavuso II) (Zikodze) (-1815) becomes king of Swaziland (until 1815). An army of 60K Peruvian (Incan) natives and Creoles under Inca (king) Tupac (Túpac) Amaru II (1742-81) (real name Jose Gabriel Condorcanqui) revolt from Spanish rule, but are crushed next year, and Tupac is tortured and executed along with thousands of his miserable chums. Siam unsuccessfully attacks the Tay Son army in Vietnam in support of Nguyen lord Phuc Anh - I can't go on? Serfdom is abolished in Bohemia and Hungary. About this time the Country Party (Old Whigs) (ends 1740) is formed as an unofficial coalition of Tories and disaffected Whigs who oppose the London-based Court Party for corruption, working for annual elections to Parliament, dissolution of standing armies, etc. Washington, Ga. becomes the first U.S. town named after George Washington. Settlers (13 families) brought by Col. George Rogers Clark in 1778 are joined by more settlers, founding a settlement at the "falls of the Ohio", which is named Louisville (Ky.) after Louis XVI of France (modern-day pop. 375K/850K); Thomas Jefferson signs the town charter. William Pitt the Younger (1759-1806) enters the House of Commons. Bookish James Madison of Va., son of the largest slaveholder in Orange County becomes the youngest member of the Continental Congress. Timothy Pickering (1745-1829) of Salem, Mass., who rose from army col. in 1776 to adjutant gen. in 1777 becomes Am. quartermaster gen. (until 1785) and member of the board of war. The English House of Commons affirms the principle of periodic scrutiny of the Civil List. The Continental Congress establishes a court of appeals. John Adams returns to France, but Benjamin Franklin helps get him dismissed as commissioner, telling Congress that Adams thinks "that America has been too free in expressions of gratitude to France; for that she is more obliged to us than we to her"; by the end of the year the U.S. is desperately in need of money to finance the war, and Adams travels alone and unannounced to Holland to seek a loan, pounding the streets knocking on doors for the next year. Maximilian de Lorraine (1756-1801), youngest son of Maria Theresa succeeds his uncle Charles de Lorraine as grandmaster of the Priory of Sion (until 1801) :). Baron Adolf von Knigge (1752-96) joins Adam Weishaupt's Bavarian Illuminati, and gives them mucho publicity, raising their membership to 2K, but quits in 1784 after Jesuit-hating Weishaput accuses him of working for the Jesuits. Dublin theater mgr. ? Daly makes a bet that within 24 hours he can introduce a new word into the English language, then spends all night chalking the word "quiz" on walls all over the city; the next day the new word is on everyone's lips, but since nobody knows what it means, they give it the meaning of a jokey puzzle. Transylvania U. (AKA Transy) in C Ky. is founded, becoming the first college W of the Allegheny Mts. Starting in this decade sexual habits in Europe began to loosen up, causing an increase in illegitimate births; Casanova's big decade was the 1750s, so think of something clever to say? In this decade pianist Johann Ludwig Dussek (1760-1812) becomes a hit in Germany and France, and a favorite of Marie Antonette, pleasing the ladies by becoming the first to sit sideways so that they can ogle him; after the French Rev. starts, he flees to London, where he becomes a hit again, working with John Broadwood (1732-1812) to develop the "English Action" piano to flaunt his powerful style, which is later used by Beethoven. In this decade wax artist (ceroplastician) Clemente Susini creates the beautiful nude lily white Medici Venus for anatomy students, inspired by Botticelli and Titian, who were inspired by ancient Greek painter Apelles. The Verlichting (Ger. "enlightenment") lit. movement in Holland begins, breaking from classicism. Early in this decade Olympian Dew begins to be marketed in England to improve female complexions; Mary Wollstonecraft Godwin is not a fan. In this decade Altoids, the "curiously strong peppermints" are developed by William Smith & Co. of London, England as a digestive aid - other uses are later discovered. Sports: The first Derby (Derby Stakes) (Epsom Derby) (AKA the Blue Riband) at Epsom Downs in England for 3-y.-o. colts (and later fillies) is run in June, becoming Britain's richest horse race; it is won by Diomed (1777-), owned by Sir Charles Bunbury; in 1787 Lord Derby's horse Sir Peter Teazle (1784-1811) wins. Architecture: The Federal Style of Architecture, a mix of Georgian, Roman classical, and Louis XVI French, attempting to repudiate Europe and its past by imitating Greek and Roman architecture becomes popular in the newfangled U.S., taking its cue from the works of Scottish architects Robert Adam and James Adam, peaking in 1785-1815 before fizzling in 1830; the Federal doorway has narrow sidelights and an elliptical overhead fanlight; architects incl. Thomas Jefferson, Charles Bulfinch, Pierre L'Enfant, and Alexander Parris. Barratt's Chapel is built in Del. by John Wesley's rep. Thomas Coke, becoming the first Methodist church in the U.S. In 1780-9 the Palladian Buxton Crescent in Buxton, Derbyshire is built for the 5th Duke of Devonshire by Horbury, West Riding of Yorkshire-born architect John Carr (1723-1807) (leading architect in N England), one-upping the Royal Crescent in Bath, containing a hotel, five lodging houses, and a grand assembly room. Inventions: Spanish dancer Sebastiano Carezo (Cerezo) of Cadiz invents the Spanish Bolero (3/4 time); the Modern Bolero is invented in Cuba in 1883. French printer Francois Ambroise Didot (1730-1804), son of Francois Didot (1689-1757) becomes the first to print on vellum paper. Italian scientist Felice Fontana (1730-1805) invents the Water Gas Shift (Water Splitting) Reaction, in which H2O and CO react at high temps to form CO2 and H2. The town of Paisley in Renfrewshire, Scotland on the White Court 7 mi. SW of Glasgow becomes famous for its Paisley Pattern and Paisley Shawls, which become fashionable until the 1870s. James Watt invents a Paper Copier, using a special ink that stays wet for 24 hours, thus allowing someone to press another paper over it and copy the ink. Science: Sir William Herschel first observes 95 Hercules, a double star in the Hercules constellation (between Lyra and Bootes) which changes its color, going from blue-white and white this year to orange and green in 1855 to double pale yellow in the 20th cent. Nonfiction: William Thomas Beckford (1760-1844), Memoirs of Extraordinary Painters. Johann Friedrich Blumbach (1752-1840), Handbuch der Naturgeschichte. John Burgoyne (1722-92), State of the Expedition from Canada. Gaetano Filangieri, Science of Legislation. Frederick II the Great (1712-86), De la Litterature Allemande. Gotthold Lessing (1729-81), Erziehung des Menschengeschlechts; plea for religious toleration. Thomas Sheridan (1719-88), General Dictionary of the English Language (2 vols.); written by an Irish stage actor (father of dramatist Richard Brinsley Sheridan); first to establish a simple standard of pronunciation. Samuel Auguste Tissot (1728-97), Traite des Nerfs et de Leurs Maladies (Treatise on the Nerves and Their Diseases); migraine headache research. Music: Karl Ditters von Dittersdorf (1739-99), Job (oratorio). Franz Joseph Haydn (1732-1809), "Toy" Symphony (Cassation in G major); really composed by Leopold Mozart in 1759? Symphony No. 34 in C major, K. 338; his farewell to Salzburg. Vicente Martin y Soler (1754-1806), I Ratti Sabini (ballet) (Naples); Ipermestra (opera). Giovanni Paisiello (1740-1816), Il Barbiere di Siviglia (The Barber of Seville) (opera) (St. Petersburg). Charles Wesley (1707-88), Hymns (about 480). Art: J.S. Copley, Death of Chatham. Alexander Nasmyth (1758-1840), Edinburgh Castle and Nor'Loch. Augustin Pajou (1730-1809), Mercury, God of Commerce (sculpture). Sir Joshua Reynolds (1723-92), Mary Robinson as Perdita. Plays: Hannah Cowley (1743-1809), The Belle's Stratagem (romantic comedy of manners) (Drury Lane Theatre, London) (Feb. 22); takes its title from George Farquhar's "The Beaux' Stratagem"; big hit of the season; makes a fan of Queen Charlotte, who decrees that it be performed by the royal season annually; Letitia Hardy (Harriet Smithson/Ellen Terry) and Doricourt; Sir George Touchwood and Lady Frances Touchwood. Poetry: Matthias Claudius (1740-1815), Lieder fur das Volk. Johann Kaspar Lavater (1741-1801), Jesus Messias (epic). Christoph Martin Wieland (1733-1813), Oberon (romantic epic); based on French medieval tale "Huon de Bordeaux"; final ed. pub. in 1796; nasty Charlot, Huon duke of Guienne, son of Karl the Great is sentenced to travel to Babylon (Baghdad) and demand four molars and a tuft of the beard of the caliph after kissing his daughter Rezia and killing her betrothed, using his magic horn and ring stolen from spirit world ruler Titania; too bad, he beds her before travelling to Rome to see the pope, causing Titania's hubby Oberon to put into captivity in Tunis, where they resist temptation to win their freedom. Novels: Thomas Holcroft (1745-1809), Alwayn; autobio. story of a strolling comedian. Nicolas-Edme Restif (1734-1805), Les Contemporaines (42 vols.) (short stories). Births: German physician-explorer-biologist Martin Hinrich Carl Lichtenstein (d. 1857) on Jan. 10 in Hamburg; educated at the U. of Jena, and U. of Helmstedt. French chemist Pierre-Jean Robiquet (d. 1840) on Jan. 13 in Rennes, Brittany. U.S. Supreme Court justice #22 (1830-44) Henry Baldwin (d. 1844) on Jan. 14 in New Haven, Conn.; educated at Yale U. U.S. commodore-diplomat David Porter (d. 1843) on Feb. 1 in Boston, Mass.; father of commodore William David Porter (1808-64) and adm. David Dixon Porter (1813-91); adopted father of adm. David Farragut (1801-70). Russian painter Alexei (Alexey) Gavrilovich Venetsianov (d. 1847) on Feb. 18 in Moscow; of Greek descent. English writer Frances Milton "Fanny" Trollope (d. 1863) on Mar. 10 in Heckfield, Hampshire; daughter of Rev. William Milton; mother of Thomas Adolphus Trollope (1810-92) and Anthony Trollope (1815-82). German mathematician August Leopold Crelle (d. 1855) on Mar. 11 in Eichwerder (near Wriezen). Serbian prince (1817-39, 1858-60) Milos Obrenovic I (d. 1860) on Mar. 18 (Mar. 7 Old Style) in Srednja Dobrna (Dobrinje); of peasant stock; father of Mihailo Obrenovic III (1823-68). Am. Unitarian minister William Ellery Channing (OF "church official") (d. 1842) on Apr. 7 in Newport, R.I. Am. Louisiana Purchase geologist-geographer George William Featherstonhaugh (d. 1866) on Apr. 9 in London; first geologist to the U.S. govt. French physician and naturalist (arachnologist) Leon Jean Marie Dufour (d. 1865) on Apr. 11 in Saint-Sever. French Romantic "Trilby" writer Charles Nodier (d. 1844) on Apr. 29 in Besancon; Freemason father. U.S. Supreme Court justice #27 (1837-52) John McKinley (d. 1852) on May 1 in Culpeper County, Va.; namesake of McKinley, Ala. Am. treasury secy. #11 (1833) William John Duane (d. 1865) on May 9 in Clonmel, Ireland; son of William Duane; emigrates to the U.S. in 1796. Argentine pres. (1826-7) Bernardino de la Trinidad Gonzalez Rivadavia y Rivadavia (d. 1845) on May 20 in Buenos Aires. French chemist Henri Braconnot (d. 1855) on May 29 in Commercy. German Prussian "On War" gen. and military historian Carl (Karl)Philipp Gottfried (Gottlieb) von Clausewitz (d. 1831) on June 1 in Burg bei Magdeburg; husband (1810-31) of Countess Marie von Bruhl (1779-1836). Am. reaper inventor Robert Hall McCormick Jr. (d. 1846) on June 8 in Walnut Grove, Rockbridge, Va.; son of Cyrus Hall McCormick (1809-84); father of Cyrus Hall McCormick (1809-84). British MP-statesman Henry Petty-Fitzmaurice, 3rd Marquess of Lansdowne (d. 1863) (AKA Lord Henry Petty) on July 2 in Mayfair, Middlesex. Mexican gen. and Conservative pres. (1830-32, 1837-9, 1939-41) Anastasio Bustamante y Oseguera (d. 1853) on July 27 in Jiquilpan, Michoacan. French "Le Roi d'Yvetot" lyric poet and republican chanson composer Pierre-Jean de Beranger (Béranger) (d. 1857) on Aug. 19 in Paris. French "Odalisque", "Turkish Bath" Neoclassicist painter-violinist Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres (d. 1867) on Aug. 29 in Montauban (near Toulouse), Languedoc; painter-violinist father. U.S. atty. gen. #8 (1814-7) Richard Rush (d. 1859) on Aug. 29 in Philadelphia, Penn.; 2nd son of Benjamin Rush (1745-1813); educated at Princeton U. British prince Alfred (d. 1782) on Sept. 22 in Windsor Castle; 14th child and 9th son of George III and Charlotte of Mecklenburg. U.S. Dem. vice-pres. #9 (1837-41) Richard Mentor Johnson (d. 1850) on Oct. 17 in Beargrass, Ky.; educated at Transylvania U. U.S. Dem.-Repub. secy. of state #13 (1834-41) John Forsyth (d. 1841) on Oct. 22 in Fredericksburg, Va.; son of U.S. marshal Robert Forsyth (1754-94); educated at Princeton U.; father of John Forsyth Jr. (1821-87). South African Boer leader Pieter Mauritz "Piet" Retief (d. 1838) on Nov. 12 in Soetendal. German chemist Johann Wolfgang Dobereiner (Döbereiner) (d. 1849) on Dec. 13 in Hof, Bayreuth. British Tory leader (founder of the Athenaeum Club) John Wilson Croker (d. 1857) on Dec. 20 in Galway, Ireland; educated at Trinity College, Dublin; basis of char. "Rigby" in Disraeli's "Coningsby". French Arc de Triomphe architect Jean-Nicholas Huyot (d. 1840) on Dec. 25 in Paris. Scottish physicist-writer Mary Somerville (d. 1872) on Dec. 26 in Jedburgh; wife (1812-) of William Somerville (1771-1860). Swaziland king (1815-36) (black) Sobhuza I (Ngwane IV) (Somhlolo = "the Wonder") (d. 1836); son of Ndvungunye (-1815) and Somnjalose Simelane. Sikh kingdom founder (maharja #1 of the Sikh Empire) Ranjit Singh (d. 1839)(AKA Sheri-e-Punjab "Lion of Punjab") on Nov. 2 in Gujranwala, Pakistan. Am. Old Three Hundred Tex. settler William Stafford (d. 1840) in Tenn. English prison reformer Elizabeth Gurney Fry (d. 1845) in Norfolk. Ecuadorian statesman-poet Jose Joaquin Olmedo (d. 1847). Am. celeb lt. col. Nathan Boone (d. 1856) (1780-1857?) on ? in Boone Station (modern-day Boonesboro) (near Athens), Fayette county, Ky.; youngest son of Daniel Boone (1734-1820); brother of Daniel Morgan Boone (1769-1839); first white child born in Ky.? Deaths: French salon host Madame du Deffand (b. 1697) on Sept. 23. English brewer Sir Benjamin Truman (b. 1699) on Mar. 20; "There's more hops in Ben Truman." English flying shuttle inventor John Kay (b. 1704). Am. explorer Jonathan Carver (b. 1710) on Jan. 31 in London; dies in poverty when the profits from his bestselling book are slow in arriving. Am. colonial Mass. gov. (1769-74) Thomas Hutchinson (b. 1711) on June 3 in Brompton, Middlesex, England. French-born Austrian field marshal prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine (b. 1712) on July 4 in Tervuren, Flanders. English diphtheria physician John Fothergill (b. 1712) on Dec. 26 in London. German prince Charles I of Brunswick-Wolfenbuttel (b. 1713) on Mar. 26 in Braunschweig. French architect Jacques Germain Soufflot (b. 1713) on Aug. 29 in Paris. Scottish economist Sir James Steuart (b. 1713) on Nov. 26 in Coltness, Lanarkshire. French sensationalist philosopher Etienne Bonnot de Condillac (b. 1715) on Aug. 3. Austrian HRE (1745-65) Maria Theresa (b. 1717) on Nov. 29 in Hofburg Palace, Vienna. Italian painter Bernardo Canaletto (Bellotto) (b. 1720). German Gen. Baron Johann De Kalb (b. 1721) on Aug. 19 in Camden, S.C. English jurist Sir William Blackstone (b. 1723) on Feb. 14 in Wallingford, Berkshire. Spanish dramatist Nicolas Fernandez de Moratin (b. 1737). British army maj. Patrick Ferguson (b. 1744) on Oct. 7 in King's Mountain, N.C.; buried with his mistress Virginia Sal. British spy maj. John Andre (b. 1750) on Oct. 2 in Tappan, N.Y. (hanged); buried in the Poet's Corner of Westminster Abbey by order of George III, with a memorial tablet; John Andre's Journal, his military journal from June 1777 to Nov. 1778 is discovered in England in 1902. Canadian-born Am. diarist Anna Green Winslow (b. 1759) on July 19 in Hingham, Mass. (consumption); leaves Diary of Anna Green Winslow, A Boston School Girl of 1771, pub. in 1894.



































1781 On Jan. 1 after another harsh winter and supply shortages, the Penn. Line of the Continental Army, believing its enlistments have been fulfilled riots, kills three officers, and marches to Morristown, N.J., causing Congress to send loyalist-persecuting Penn. gov. Joseph Reed to negotiate with them, getting 1,250 of them discharged by the end of the mo.; too bad, the troops in N.J. see their chance and follow suit later in Jan., but this time Gen. Washington steps in, puts down the revolt and executes some leaders by early Feb.; the whole affair causes some states to allocate more funds to pay troops. The original "I'll be baaack" Arnold? On Jan. 5 a British naval expedition led by British brig. gen. Benedict Arnold (commissioned by Sir Henry Clinton) burns Richmond, Va., almost capturing Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826), who virtually abdicates as gov. of Va. and returns to Monticello. On Jan. 5 the British surrender Ft. San Juan in Nicaragua to the Spanish. On Jan. 17 after Gen. Nathanael Greene sends Col. Daniel Morgan (1736-1802) with 700 men on a sweep W of Cornwallis' HQ at Winnsboro, S.C., and the British under Gen. Banastre Tarleton catch him and force a fight, but Tarleton sends his men in prematurely, the Battle of Cowpens sees Tarleton lose 110 KIA and 700 POWs; the British under Cornwallis advance back into N.C. as Col. Daniel Morgan's army links up with Gen. Nathanael Greene's army at Guilford Courthouse (now Greensboro) and then retreats; on Feb. 1 at the Battle of Cowan's Ford sees N.C. militia commander Gen. William Lee Davidson KIA; after the rebels lead the Brits on a wild goose chase up to the Dan River, Cornwallis draws back to Hillsborough for supplies. On Jan. 24 British man-of-war Culloden goes aground on Culloden Point on Long Island Sound. In Jan. a 500-man British force under Col. Von Hanxleden sent by gen. John Campbell of Strachur unsuccessfully try to recapture Mobile from the Spanish, and Leden is KIA. On Feb. 3 3K British troops from Saint Lucia under Adm. George Rodney and Gen. John Vaughan capture the Dutch colony of St. Eustatius, causing people back home to accuse themselves of trying to enrich themselves and neglect more important military duties; it is retaken by French forces late in the year. On Feb. 16 pissed-off at being passed over for promotion, Alexander Hamilton breaks with his boss Washington at his HQ at New Windsor on the Hudson River, accusing the latter of falsely claiming he had shown disrespect, but keeps it under wraps to preserve the old man's popularity; they part company in early Mar., and Washington is without his brilliant French translator, letter writer and virtual adopted son; but not quite, as Hamilton soon moves with his wife to De Peyster's Point opposite Washington's New Windsor HQ, pestering him with letters for an artillery command. On Feb. 25 Am. Gen. Nathanael Greene, having received reinforcements from Va. and the Carolinas, crosses the Dan River on his way S to a final confrontation with Charles Lord Cornwallis at Guilford Court House. On Feb. 27 after N.Y., Va. and Conn. cede their claims to the Ohio Country to pacify it, the last state, Md., finally adopts the Articles of Confederation, in which "each state retains its sovereignty, freedom and independence", and on Mar. 1 the Continental Congress formally adopts them; Conn.-born jurist Samuel Huntington (1731-96) of Conn., who has been pres. of the Continental Congress since Sept. 28, 1779 grandfathers in and becomes pres. #1 of the United States under the Articles of Confederation (really the pres. of Congress), then resigns due to bad health on July 9, and on July 10 Penn.-born Del. jurist (chief justice of Penn. since 1777) Thomas McKean (1734-1817) becomes pres. #2 (until Nov. 4). In Feb. Benjamin Franklin pleads the govt. of France for 25 livres, and they give him 6M, just enough to keep America going; Franklin then pleads old age and tenders his resignation to Congress, but they refuse and instead appoint him to a 5-man commission (with John Adams, Thomas Jefferson, S.C. planter-merchant Henry Laurens and John Jay) to negotiate peace with Britain when and if, with instructions to take no steps without France's approval; Laurens is captured by the British and put in the Tower of London. In Feb. a new British force sent by Bengal gov. Warren Hastings led by Gen. Carmac defeats Gwalior Maratha chief Madhav Rao II (1774-95) in Sipri, and the Marathas are all-but kaput. On Mar. 11 a force of 11 Spanish ships under Bernardo de Galvez y Madrid captures Santa Rosa Island and enters Pensacola Bay, causing British gen. John Campbell of Strachur to attempt to capitulate on favorable terms to save the town and garrison; too bad, a renegade British officer burns some houses, causing the Spanish to attack, and after a heroic defense Campbell surrenders Ft. George on May 10, and his troops are allowed to return to New York, where he moves into a house at the corner of Trinity Place and Thames St. off Wall St., giving the Am. rebels a free hand to go after Yorktown; the Brits have no bases left in the Gulf of Mexico except Jamaica. The pesky Am. rebels finally sink to the winning formula? On Mar. 15 2.1K redcoats under Gen. Charles Cornwallis rout 4.5K rebels under Gen. Nathanael Greene at the 5-hour Battle of Guilford Courthouse, 5 mi. NW of Greensboro, N.C., with 260 Am. and 600 British casualties, incl. 91 British KIA, becoming a Pyrrhic victory depleting Cornwallis' troops so much that he is forced to abandon the Carolinas and move to the Va. coast to get protection from the royal navy and get reinforcements; English parliamentary leader Charles James Fox utters the soundbyte "Another such victory and we are undone"; Cornwallis evacuates to Wilmington to resupply while Greene heads into S.C. to link up with guerrillas and draw Cornwallis after him into a war of endless attrition: "We fight, get beat, rise, and fight again." On Apr. 30 British forces under Brig. Gen. Benedict Arnold are prevented from capturing Richmond, Va. by Gen. Lafayette and his 1.2K men; Gen. William Phillips links up with Arnold and assumes overall command, but dies on May 13 of typhoid fever. On May 13 (May 14?) 1st Rhode Island Regiment cmdr. Col. Christopher Greene (b. 1737) is ambushed by a group of loyalists in his HQ on the Croton River in Westchester County, N.Y., and his body mutilated as a reprisal for leading black soldiers in combat against whites? In May Gen. Cornwallis ignores Gen. Greene's bait and marches N into Va. to link up at Petersburg with Gen. Benedict Arnold and 6K British troops sent by Gen. Clinton in New York, and aids Arnold in his war of maneuver with American forces under Lafayette and von Steuben; the combined British force numbers 7.2K, far outnumbering the American force. In May the Continental Congress appoints Liverpool-born Robert Morris (1734-1806), the richest man in Philly (who this year founds the Bank of Penn., the oldest financial institution in the U.S.) as the new supt. of finance, and he asks Gouverneur Morris (1752-1816) of N.Y. (a relative?), who wrote a series of Essays on the Proposed Financial System of the U.S. in 1780 to be his asst.; Alexander Hamilton is passed over again, but he writes Robert Morris a long letter telling him how to do his job, which he praises; in May Congress approves Morris' plan for the Bank of North Am., a merchant bank to help finance the war, which is chartered by Congress by a narrow margin on Dec. 31, and opens next Jan. 7; meanwhile Polish Jewish immigrant (since 1775) Haym (Chaim) Salomon (Solomon) (1740-85) aids Morris, brokering bills of exchange for federal govt. expenses and personally financing members of the Continental Congress incl. James Madison at low interest rates, becoming known as "the Financial Hero of the Am. Rev."; in May Gen. Philip John Schuyler (1733-1804) laments in a letter written to his son-in-law Alexander Hamilton that the New York frontier around Albany, which had been plundered repeatedly by Tory and Indian raids, is "one general scene of ruin and desolation"; the success of his spy network causes about 20 Tories and Indians to try to kidnap him on Aug. 7 at his mansion. On June 4 after Gen. Cornwallis's army ravages the Richmond area, one sortie led by Tarleton almost capturing Gov. Thomas Jefferson and his Virginia Legislature at Charlottesville, the finally flee; Cornwallis then occupies Yorktown and Gloucester on Aug. 1-2; Yorktown, on the peninsula between the York and James Rivers, surrounded on three sides by water is equally a perfect fortress and a perfect trap?; Am. Gen. Thomas Nelson Jr. (1738-89) of Va., a DOI signer who succeeded Thomas Jefferson as gov. of Va., who had already raised $2M for the rebel cause by using his property as collateral urges Gen. Washington to shell his Nelson House home in Yorktown (HQ of Cornwallis), offering 5 guineas to the first man to hit it, and ends up bankrupt ("he gave all for liberty"); Lafayette occupies Williamsburg (12 mi. S of Yorktown) with a small force; in Aug. Cornwallis begins defensive earthworks around Yorktown with 8.3K regulars and 2K escaped slaves promised their freedom; the British army numbers 8.7K; in mid-Aug. French Adm. of the West Indies Francois Joseph Paul, Comte de Grasse (1722-88) informs Gen. Washington that his fleet is sailing for the Chesapeake, causing Washington and French Gen. Comte de Rochambeau to cancel plans to attack New York and support Comte de Grasse and Lafayette, crossing the Hudson River in late Aug. with 2K patriot and 5K French troops, arriving on Aug. 30 and winning the Battle of the Chesapeake on Sept. 5, trapping Cornwallis; explorer Louis Antoine de Bougainville commands a ship under de Grasse; the naval Battle of the Virginia Capes (Capes Charles and Henry) starting on Aug. 30 is won by de Grasse on Sept. 15, after first sealing off Cornwallis' army from sea evacuation, and landing 3K French troops; on Sept. 5 the British fleet arrives off the Virginia Capes and finds 26 French warships in three straggling lines; rear adm. Thomas Graves waits for the French to form their battle lines farther out to sea and then fights for five days, finally withdrawing to New York City; the French have 37 ships and 29K soldiers and sailors at Yorktown while Washington has 16K men (half French; 75% of his Am. troops are Irish). On June 11 a Congressional peace commission, composed of John Adams (1735-1826), John Jay (1745-1829), Benjamin Franklin (1706-90), Henry Laurens and Thomas Jefferson is formed; on June 15 CoThey may be losing in America, but the Brits make up for it in India? On July 1 Irish-born British Lt. Gen. Sir Eyre Coote (1726-83), British CIC in India beats 5-1 odds to defeat Hyder Ali of Mysore, an ally of the French at the Battle of Porto Novo (Parangipettai) ("place of foreigners") in Tamil Nadu on the E coast, then defeats them again on Aug. 27 at the Battle of Pollilur, and mops them up on Sept. 27 at the Battle of Sholingarh; meanwhile Warren Hastings deposes the Rajah of Benares and plunders the treasure of the Nabob of Oudh, and the Dutch settlement at Negapatam, Madras is captured by the British, along with Padang, Sumatra. Congress modifies the 1779 peace instructions to include only as essential the independence and sovereignty of the U.S. On July 31 Alexander Hamilton finally succeeds in obtaining command of a New York light infantry battalion, his big chance for battlefield glory; meanwhile, in July-Aug. he pub. four essays in The New-York Packet titled The Continentalist under the alias A.B., calling for a strong nat. govt. that could swing large foreign loans to win the war. In Aug. the case of Brom and Bett v. Ashley is heard in Great Barrington, Mass., granting freedom to slave Mum Bett (Mumbet), who takes the name Elizabeth Freeman (1744-1829), ending slavery in Mass. as incompatible with the 1780 Mass. Constitution. The fox becomes the hound and the war is no longer in doubt as the fighting generals put their best foot forward and fight with true gallantry like gen gen gentlemen to a final conflict? In June in Bolivia Aymara take-another-shot-at-courage Indian leader Tupac (Tupak) Katari (Julian Apasa) (b. 1750) lays siege to La Paz for 200 days with an army of 40K, then regroups and does it again in Aug. with the help of Andres Tupac Amaru, nephew of Tupac Amaru II; too bad, Spanish royalist forces led by Josef Reseguin break the siege in Oct. 17, then get him betrayed, and capture and execute Katari on Nov. 13 by quartering him, after which former rebel Miguel Bastidas Tupac Amaru switch sides and helps crush the remaining rebels in return for an every-night-when-the-sun-goes-down pardon. On Sept. 8 the Continentals under Gen. Nathanael Greene attack a British force in the Battle of Eutaw Springs in S.C., driving the British back, becoming the last major Am. Rev. War battle in the lower South; the patriots enter the British camp and begin enjoying captured rum, giving the Brits time to reform, counterattack and drive them from the field; both sides suffer high casualties, with the Brits suffering the highest of any force in the war; the Brits return to Charleston, leaving Greene in control of the rest of the state; George Washington's 2nd cousin Col. William Washington is captured, and remains a POW for the rest of the war, then is promoted to brig. gen. after the war. The original Doo-Wah-Diddy-Diddy walking down the street? On Sept. 16 British Gen. Lord Charles Earl Cornwallis (1738-1805) directs the sinking of a fleet of ships at Yorktown to block a French landing and keep them out of enemy hands; on Sept. 28 the Battle of Yorktown (staged from Williamsburg, Va.) begins with the siege of Yorktown Heights, during which Gen. Washington and his staff come under fire while observing the action; when an aide suggests to GW that he "step back a little", he replies, "Col. Cobb, if you are afraid, you have the liberty to step back"; on Oct. 6 French engineers begin to dig two parallel trenches around the British lines, trapping them; on Oct. 9 the shelling of the trapped British begins with Washington himself touching off the first volley of cannon fire; on Oct. 14 the trenches are almost complete, and a night bayonet raid on the last two British redoubts led by Alexander Hamilton's patriots on one side and the French on the other allows them to be finished; attacks begin with two 400-man columns, one Am. and one French, and continue day and night; desperate Cornwallis tries infecting black slaves with smallpox and letting them wander to the other side; an attempt at a sea escape on the night of Oct. 16 is foiled by a storm; Cornwallis offers surrender on the morning of Oct. 17 via a red-coated drummer boy and an officer waving a white handkerchief on the parapet, which takes awhile to get noticed amid all the fury; the surrender is signed on Oct. 18, and on Oct. 19 the troops formally surrender to Maj. Gen. Benjamin Lincoln (who had surrendered his sword to Clinton at Charleston 17 mo. earlier) and 17.6K handsomely-dressed French and raggedly-dressed Am. troops to the sound of the old English ballad The World Turned Upside Down, while the Yankees play "Yankee Doodle"; Cornwallis has a subordinate surrender his sword, becoming the last major battle of the Am. Rev. War, which drags on for 2 more years, 4 years since Saratoga and 6.5 since Lexington and Concord; Gen. Lafayette later writes "The play is over... the fifth act has just ended"; Gen. Layfayette's Virginia Campaign helped set it up and end it?; on Oct. 23 Gen. Henry Clinton arrives off Chesapeake Bay with 7K relief troops, and then returns to New York after finding that he is too late; Washington's army returns to positions N of New York City; by Oct. the Continental army has 5K black regulars (25%), plus 10K working as servants, laborers, and cartmen. On Sept. 4 Spanish gov. of Calif. (1777-82) Felipe de Neve (1724-84) along with the Franciscans found El Pueblo de la Reina de Los Angeles (Town of the Queen of the Angels) (modern-day pop. 3.8M/18.6M) from an Indian village named Yangma; 29 of the first 44 Spanish settlers (Los Pobladores) are of African ancestry. In Sept. British gen. Benedict Arnold leads marauding raids into Conn.; in Dec. Arnold and his babe Peggy Shippen move to England, where he ends up a miserable businessman after he can't get an army commission. In Sept. Dutch patriotic leader Baron Joan Derk van der Capellen tot den Pol (1741-84) pub. a pamphlet titled To the People of the Netherlands (Aan het Volk van Nederland), attempting to spark an Am.-style govt. there. On Nov. 5 John Hanson (1715-83) of Md. becomes pres. #3 of the United States under the Articles of Confederation (unti Nov. 3, 1782). On Nov. 15 Gen. George Washington writes a letter to Thomas McKean, pres. of the Continental Congress patting himself on the back about Yorktown, saying, "I take particular pleasure in acknowledging that the interposing Hand of Heaven... has been most conspicuous and remarkable". On Nov. 19 word of the big V at Yorktown reaches France. In Nov. the New York legislature bars Tory lawyers from state courts, causing a boom for patriot lawyers (repealed in 1786); Aaron Burr opens an Albany law office next July, followed by Alexander Hamilton 6 mo. later. The secret Treaty of Alliance between Catherine II the Great and HRE Joseph II contemplates a gen. partition of the Ottoman Empire, and ignites the explosive Eastern Question. The Nguyen army loses Saigon (captured 1778) to the Tay Son brothers, and retreats to the island of Phu Quoc. N.H. abolishes slavery, joining R.I., Penn. and Mass. HRE Joseph II grants a patent of religious tolerance and freedom of the press in Austria, and abolishes serfdom in his domains; a zealous reformer, he prohibits the pub. of any religious decrees originating outside of his realm, and suppresses 700 convents while reducing the number of clergy from 63K to 27K. Spanish gov. #44 of the Philippines (1778-87) Jose Basco y Vargos establishes a basco, er, tobacco monopoly in the Philippines which becomes so exploitative that it ends up causing native uprisings. 14-y.-o. Andy Jackson is captured in ? The 9 coral Lagoon (Ellice) Islands (total of 14 sq. mi.) in the Pacific Ocean are discovered; the become a British protectorate in 1892. John Quincy Adams serves as secy. to the U.S. ambassador to Russia. Comtess de Genlis (1746-1830) becomes governess of the sons of Duke Louis Philippe I of Orleans, incl. future king (1830-48) Louis-Philippe, going on to invent new teaching methods, incl. the use of the magic lantern. In Charlestown, S.C. William Collings sells his wife to Thomas Schooler with her bed and clothing for $2 and a half dozen bowls of gross. John Paul Jones, "father of the American Navy" returns to the U.S. and supervises the construction of USS America (American ship), the largest vesssel in the U.S. Navy, uttering the immortal soundbyte "In time of peace prepare for war"; too bad they give it to France instead; after the war ends he goes to Paris as agent of the U.S. to collect money for all the prizes taken and delivered to France. Badder than old King Kong? Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart breaks with his patron Archbishop Colloredo of Salzburg, who gives him a literal boot in the rump, and he strikes off on his own, moves to Munich, composes the opera seria Idomeneo, King of Crete (Jan. 29) for elector Karl Theodor, then settles in Vienna in the summer in a house rented for him by friends, where he tries teaching; Mozart's favorite horn player Joseph Leutgeb (Leitgeb) (1732-1811), who moved in 1777 fom Salzburg to Vienna, making his living as a cheesemonger inspires him to compose a set of Horn Concertos, incl. Horn Concerto No. 1, K.412 (1791), Horn Concerto No. 2, K.417 (1783), Horn Concerto No. 3, K.447 (1784-7), and Horn Concerto No. 4 (K. 495) (1786) (most famous). Dr. John Phillips (1719-95), uncle of Phillips Academy of Andover founder Samuel Phillips (1752-1802) founds Phillips Exeter Academy in nearby Exeter, Mass. to inculcate more Calvinism, with the motto "Youth from Every Quarter", becoming rivals with Phillips Exeter Academy and going on to gain famous Exonians Daniel Webster (1782-1852), Pres. Franklin Pierce, the sons of presidents Abe Lincoln and Ulysses Grant, Amos Alonzo Stagg, and Booth Tarkington. The Royal Toxophilite Society (Gr. "bow-loving") is founded in England to advance the sport of archery by Sir Ashton Lever. The original No-Tell Motel? Medical sex therapist (quack?) Dr. James Graham (1745-94) of Edinburgh opens a Temple of Health in the Royal Terrace of the Adelphi in London, and sells nights in his electromagnetic musical Grand State Celestial Bed for Ł500, attended by the tight, beautiful, scantily-clad it-feels-like-the-first-time Rosy Goddess of Health" Emma Hart (daughter of a Cheshire blacksmith who slept her way up), who later becomes the-woman-in-you-brings-out-the-man-in-me Lady Emma Hamilton (1761-1815), Adm. Lord Nelson's mistress (1793); Graham is later imprisoned in Scotland as a lunatic. Correspondence with the Continental Congress leads to the establishment of the U.S. Mint in 1792. The 6.8K-mi. Trans-Siberian Highway begins construction, going on to become the longest nat. highway on Earth. The first Building Society is founded in Birmingham, England. Asprey of London, the royal jewelry and tea party co. is founded. Clarendon Press is founded in Oxford, England. Johann Adam Hiller (1728-1804), creator of the Singspiel founds the Gewandhaus Concerts in Leipzig. Inventions: Benjamin Franklin allegedly invents Speed-Reading after visiting the Congregation Mikveh Israel in Philly and seeing them use a yad (ritual pointer for reading the Torah). ? Scheller of Leipzig invents the fountain pen; steel pen points begin to replace quill feathers. In Oct. James Watt patents the Sun-and-Planet Gear that makes it possible to give rotary motion to machinery via a steam engine - bringing the power of the sky down to Earth? Science: German-born English amateur astronomer Frederick William (Friedrich Wilhelm) Herschel (1738-1822) discovers a new comet on Mar. 13, sending An Account of a Comet to the Royal Society; when it turns out to be a new planet, Uranus, he names it Georgium Sidus in honor of George III, and gets knighted in return; in 1850 "the Georgian" is renamed Uranus - Your Anus would suggest itself later quite naturally when thinking about him? French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb verifies Guillaume Amontons' 1699 rediscovery of the laws of friction first proposed by Leonardo da Vinci. Spanish (Basque) brother chemists Don Fausto Fermin de Elhuyar (Delhuyar) y De Lubice (1755-1833) and Juan Jose de Elhuyar (1754-96) discover the mineral element Tungsten (Swedish "heavy stone") (W) (#74) in wolframite and scheelite, and Karl Wilhelm Scheele determines its composition; because of the wolframite connection it receives the German symbol W and is also called wolfram; it has the highest melting point of any metal (3380 C, 6116 F). Music: Franz Joseph Haydn (1732-1809), The Russian Quartets, Nos. 29-34, Op. 33; incl. How Do You Do?, The Joke, The Bird. Francis Hopkinson (1737-91), Temple of Minerva (opera); the first U.S. opera ("oratorical entertainment"). Vicente Martin y Soler (1754-1806), La Bella Arsene (ballet) (Milan); Tamas Kouli-Kan (ballet) (Milan); based on a libretto by Vittorio Amedeo Cigna-Santi; La Barbiere di Siviglia; based on the play by Beaumarchais. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756-91), Idomeneo, King of Crete (Munich) (Residenz Theatre, Jan. 29); composed for elector Karl Theodor after moving to Munich. Art: Jacques-Louis David (1748-1825), Belisarius. Henry Fuseli (1741-1825), The Nightmare; his first hit. Jean-Antoine Houdon (1741-1828), Moliere (sculpture); Voltaire (sculpture). Nonfiction: Peter Beckford (1740-1811), Thoughts on Hunting. Etienne Bonnot de Condillac (1715-80), Logique (posth.). Christian Wilhelm von Dohm (1751-1820), Concerning the Improvement of the Civil Status of the Jews (2 vols.); friend of Moses Mendlessohn argues for giving Jews civil rights, causing HRE Joseph II to issue an Act of Toleration (Toleranzpatent) this year for Jews in the Austrian Empire, on the condition of compulsory military service, leading to riots in Galicia. Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826), Notes on the State of Virginia; his only full-length book pub. during his lifetime; pub. anon. in Paris in 1785; the most important Am. book pub. before 1800?; praises Va. for its natural resources economy, as well as its ideal society, which incl. constitutional govt. with checks and balances, individual liberty, and separation of church and state; espouses his view on the races, slavery, and miscegenation, claiming that whites must be supreme and cannot live together with blacks in a free society, calling for science to prove the obvious inferiority "in the endowments both of body and mind" of blacks, speculating that blackness might come from "the color of the blood"; "They seem to require less sleep. A black, after hard labor through the day, will be induced by the slightest amusements to sit up till midnight, or later, though knowing he must be out with the first dawn of the morning. They are at least as brave, and more adventuresome. But this may perhaps proceed from a want of forethought, which prevents their seeing a danger till it be present. When present, they do not go through it with more coolness or steadiness than the whites. They are more ardent after their female: but love seems with them to be more an eager desire, than a tender delicate mixture of sentiment and sensation. Their griefs are transient. Those numberless afflictions, which render it doubtful whether heaven has given life to us in mercy or in wrath, are less felt, and sooner forgotten with them. In general, their existence appears to participate more of sensation than reflection... Comparing them by their faculties of memory, reason, and imagination, it appears to me, that in memory they are equal to the whites; in reason much inferior, as I think one [black] could scarcely be found capable of tracing and comprehending the investigations of Euclid; and that in imagination they are dull, tasteless, and anomalous... I advance it therefore as a suspicion only, that the blacks, whether originally a distinct race, or made distinct by time and circumstances, are inferior to the whites in the endowments both of body and mind"; contains observations of the climate in Williamsburgh, Va. in 1772-7, with the soundbyte: "A change in our climate however is taking place very sensibly. Both heats and colds are become much more moderate within the memory even of the middle-aged. Snows are less frequent and less deep. They do not often lie, below the mountains, more than one, two, or three days, and very rarely a week. They are remembered to have been formerly frequent, deep, and of long continuance. The elderly inform me the earth used to be covered with snow about three months in every year. The rivers, which then seldom failed to freeze over in the course of the winter, scarcely ever do so now. This change has produced an unfortunate fluctuation between heat and cold, in the spring of the year, which is very fatal to fruits. From the year 1741 to 1769, an interval of twenty-eight years, there was no instance of fruit killed by the frost in the neighbourhood of Monticello. An intense cold, produced by constant snows, kept the buds locked up till the sun could obtain, in the spring of the year, so fixed an ascendency as to dissolve those snows, and protect the buds, during their developement, from every danger of returning cold. The accumulated snows of the winter remaining to be dissolved all together in the spring, produced those overflowings of our rivers, so frequent then, and so rare now"; "Those who labor in the Earth are the chosen people of God." Immanuel Kant (1724-1804), Critique of Pure Reason (Kritik der Reinen Vernunft) (July) (Riga); 2nd ed. 1787; rejects David Hume's extreme empiricism, proposing that there is more to knowledge than bare sense experience, distinguishing between "a posteriori" and "a priori" knowledge, the former derived from perception, hence occurring after it, and the latter a property of thought, independent of experience and existing before it, founding the Idealist School of Philosophy, which promotes Transcendental Idealism and the Transcendental Aesthetic, dividing knowledge into sensible (based on the senses) and logical (based on reason), reversing the assumption that experience is shaped by reality with the assumption that reality is shaped by experience, blowing the bubble of theists by ruling out the possibility of acquiring knowledge of his existence and nature along with the soul's; he ends up turning ontological questions into epistemological ones - I know what I want to say but it takes so many pages to say it? Charles Messier (1730-1817), Star Catalog; 110 galaxies, star clusters and nebulae. Rev. Samuel Andrew Peters (1735-1826), General History of Connecticut; by a Tory clergymen who fled to England during the Am. Rev.; satirizes the Blue Laws of the Colony of New Haven. Plays: Jean-Francois de La Harpe (1739-1803), Jeanne de Naples. Poetry: George Crabbe (1754-1832), The Library. Novels: Johann Pestalozzi (1746-1827), Leonard and Gertrude; Romantic social novel about his educational aims. Nicolas-Edme Restif (1734-1805), La Découverte Australe par un Homme-Volant, proto-science-fiction notorious for its prophetic inventions. Births: Am. jurist Lemuel Shaw (d. 1861) on Jan. 9 in Barnstable, Mass.; chief justice of the Mass. Supreme Court (1830-). French PM #18 (1836-9) and PM #23 (1848) Louis-Mathieu Mole (Molé) (d. 1855) on Jan. 24 in Paris. German Romantic poet-botanist Adelbert von Chamisso (Louis Charles Adelaide de Chamissot) (d. 1838) on Jan. 30 in Champagne; grows up in Berlin. English portraitist George Dawe (d. 1829) on Feb. 6 in Westminster, London; paints 329 portraits of Russian gens. during Napoleon's 1812 invasion of Russia for the Military Gallery of the Winter Palace. German zoologist Johann Baptist von Spix (d. 1826) on Feb. 9 in Hochstadt an der Aisch, Bamberg, Middle Franconia; educated at the Bavarian Academy of Sciences. French physician (inventor of the stethoscope) Rene Theophile Hyacinthe Laennec (d. 1826) on Feb. 17 in Quimper, Brittany. English Christian missionary Henry Martyn (d. 1812) on Feb. 18 in Truro, Cornwall; educated at St. John's College, Cambridge. German Neoclassical architect-painter Karl Friedrich Schinkel (d. 1841) on Mar. 13 in Neuruppin, Brandenburg; student of Friedrich Gilly and David Gilly. German pantheist philosopher (Freemason) Karl Christian Friedrich Krause (d. 1832) on May 6 in Eisenberg, Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg; student of Schelling, Hegel and Fichte. English engineer and railroad inventor ("Father of Railways") George Stephenson (d. 1848) on June 9 in Wylam, Northumberland; inventor of the 4' 8-1/2" Stephenson gauge. French mathematician-physicist Simeon (Siméon) Denis Poisson (d. 1840) on June 21 in Pithiviers, Orleanais. English colonial admin. Sir Thomas Stamford Bingley Raffles (d. 1826) on July 6 at sea off the island of Jamaica on a ship commanded by his father. Am. businessman (Tufts U. founder) Charles Tufts (d. 1876) on July 16 in Medford, Mass. Am. Washington Monument architect Robert Mills (d. 1855) on Aug. 12 in Charleston, S.C.; student of Benjamin Latrobe; first prof.-trained native-born Am. architect? U.S. atty. gen. #10 (1829-31) John MacPherson Berrien (d. 1856) on Aug. 23 in Rocky Hill, N.J.; grows up in Savannah, Ga.; educated at Princeton U. French gen. Eugene Rose de Beauharnais, Prince Francais, Prince of Venice, Viceroy of the Kingdom of Italy, Grand Duke of Frankfurt, 1st Duke of Leuchtenberg, 1st Prince of Eichstatt (d. 1824) on Sept. 3 in Paris; eldest child and only son of Vicomte Alexandre de Beauharnais (1760-94) and Josephine de Beauharnais (1763-1814); Napoleon's adopted stepson. Austrian composer-publisher Anton Diabelli (d. 1858) on Sept. 6 in Mattsee (near Salzburg). English composer-conductor-musician and music publisher Vincent Novello (d. 1861) on Sept. 6 in London. Czech (Austrian) mathematician-philosopher and Roman Catholic priest Bernhard (Bernard) Bolzano (d. 1848) on Oct. 5 in Prague; educated at the U. of Prague. Venezuelan-Chilean humanist writer-statesman Andres Bello (Andres de Jesus Maria y Jose Bello Lopez) (d. 1865) on Nov. 29 in Caracas; #1 intellectual figure of 19th cent. Latin Am. English Kaspar Hauser case aristocrat Philip Henry Stanhope, 4th Earl Stanhope (d. 1855) on Dec. 7; eldest son of Charles Stanhope, 3rd earl Stanhope (1753-1816) and Louisa Grenville (1758-1829), daughter of Barbados gov. Henry Grenville; father of Philip Stanhope, 5th earl Stanhope (1805-75). Scottish physicist (inventor of the kaleidoscope) Sir David Brewster (d. 1868) on Dec. 11 in Jedburgh. Am. "don't give up the ship" naval Capt. James Scott Lawrence (d. 1813) in Burlington, N.J. Italian guitar composer Mauro Giuliani (d. 1829). English "Chantrey Bequest" sculptor Sir Francis Chantrey (d. 1841). English Pyramidology founder John Taylor (d. 1864) in East Retford, Nottinghamshire. Scottish minister Alexander Keith (d. 1880); educated at Marischal College. Deaths: Russian "Black Knight" Gen. Abraham Petrovich Gannibal (b. 1696). Italian soprano Faustina Bordoni (b. 1697) on Nov. 4 in Venice. Kazakh khan Ablai (b. 1711). Spanish Franciscan missionary Padre Francisco Garces (b. 1712) on July 18; killed at the Mission San Pedro y San Pablo di Bucuner on the Colorado River along with fellow missionaries by an uprising of Quechan Indians. English naturalist John Needham (1713). English poet Richard Jago (b. 1715). Irish-born Am. Rev. leader (DOI signer) George Taylor (b. 1716) on Feb. 23 in Penn. French economist A.R.J. Turgot (b. 1727) on Mar. 18: "To suppose all consumers to be dupes, and all merchants and manufacturers to be cheats, has the effect of authorizing them to be so, and of degrading all the working members of the community." German dramatist-critic Gotthold Ephraim Lessing (b. 1729) on Feb. 15 in Braunschweig. Japanese painter Soga Shohaku (b. 1730). Am. DOI signer Richard Stockton (b. 1730) on Feb. 28 in Princeton, N.J. British gen. William Phillips (b. 1731) on May 13 in Petersburg, Va. (typhus). U.S. col. Christopher Greene (b. 1737) on May 13 (May 14?) in Westchester County, N.Y. (KIA). Danish poet Johannes Ewald (b. 1743) on Mar. 17.






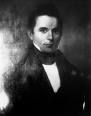



























1782 The Great Tenmei Famine in Japan begins (ends 1788), killing 1M of 30M. On Feb. 27 the British House of Commons votes against waging further war on the pesky rebels in Am.; on Mar. 5 it authorizes the crown to make peace, causing Lord North's ministry to crumble; French foreign minister Comte de Vergennes entrusts Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours with peace negotiations with the British. On Mar. 8 the Gnadenhutten (Moravian) Massacre in Ohio sees 96 unarmed Christianized Indians slain by militiamen in retaliation for raids carried out by other Indians. On Mar. 17 Italian violinist Giovanni Battista Viotti (1755-1824) debuts in Paris, becoming an instant hit, going on to found the Theatre de Monsieur in 1788 under the patronage of the king's brother the comte d'Artois; too bad, after the French Rev. his royal connections backfire, causing him to flee to London in 1792, where he is also a hit, but after Britain goes to war with France he is expelled, ending up in Paris again; he owns a 1709 violin by Antonio Stradivari called the Viotti Stradivarius, given to him as a love gift by Catherine II the Great. The original chipping golf balls in Rockingham while somebody else does it at Gretna Green? On Mar. 20 British PM (since Jan. 28, 1770) Lord North resigns, and on Mar. 27 Whig Charles Watson-Wentworth, 2nd Marquess of Rockingham (b. 1730) (who helped repeal the Stamp Act) becomes British PM for the 2nd time (until July 1); his first act in office is to acknowledge the existence of the new country in America; on Mar. 27 pro-American Whig orator Charles James Fox (1749-1806) is appointed secy. of state for foreign affairs over the king's opposition; on July 1 Rockingham dies, and on July 4 William Petty-Fitzmaurice, 2nd Earl of Shelburne, 1st Marquesse of Lansdowne (1737-1805) (friend of Benjamin Franklin) becomes home (colonial) secy. (PM) (until Mar. 26, 1783), with both being sent to begin negotiations in Paris with Benjamin Franklin (1706-90), the only one of the five commissioners present for the next few mo.; Franklin suggests that the British cede control of Canada to help pay reparations, then makes a mistake by giving British peace commissioner Richard Oswald (1705-84) some notes that hint at compensating British loyalists in America, and covers it up by printing a fake newspaper about British atrocities making such compensation out of the question and sending it to John Adams; meanwhile Fox and Lord Shelburne disagree on the Am. peace terms and become enemies. On Mar. 26 maj. gen. Guy Carleton, 1st Baron Dorchester (1724-1808) replaces Henry Clinton as CIC of the crumbling British army in the birthing U.S. (until 1783); Gen. Lord Amherst is dismissed, and replaced as lt. gen. of the ordnance, causing the king to appoint him col. of the Second Troop of Life Guards to keep him close. On Mar. 31 Father Junipero Serra founds San Buenaventura (Ventura) Mission in modern-day Ventura, Calif., becoming Spanish Calif. mission #9 (last founded by Serra). On Apr. 6 mad king (since Dec. 28, 1767) Taksin the Great (b. 1734) is executed by a coup after they reject his offer to become a monk; on Apr. 6 after defeating the rebels, gen. Chao Phraya Chakri becomes king Rama I (Phra Phutthayotfa Chukalok) (Thongduang) (1737-1809) of Siam (until Sept. 7, 1809), founding the Chakri (Thai "chakra" = discus") Dynasty in Siam (Thailand) (ends ?) on Apr. 21 at 54 min. after sunrise by placing the City Pillar for the new capital city of Bangkok (originally Rattanakosin) on the Chao Phraya ("River of Kings") River (modern-day pop. 8.3M/14.6M). On Apr. 9-12 the British Navy under Adm. Sir George Rodney wins its only naval engagement against the rebel colonists in the Am. Rev. at the Battle of Saints' Passage (the Saintes) (Dominica) off Dominica, taking advantage of a shift in the wind to break the French line unnder French Adm. Comte de Grasse not once but twice, saving Jamaica and ruining French naval prestige, after which Rodney writes "Within two little years I have taken two Spanish, one French and one Dutch admirals."; the French fleet was the same one that blockaded the British army during the Siege of Yorktown. On Apr. 19 the Netherlands recognizes U.S. independence. In Apr. Russia bans secret societies. On May 17 the Treaty of Salbai between the Maratha Empire and the British East India Co. ends the First Anglo-Maratha War (begun 1773), recognizing Madhav Rao II (1774-95) as the ruler (peshwa), granting Rabhundath Rao a pension, and returning all territories W of the Jumna (Yamuna) River to Shinde, bringing peace for the next 20 years. In May 27-y.-o. Thomas Grenville, son of George "Stamp Act" Grenville arrives in Paris as British envoy for Charles James Fox, and Benjamin Franklin soon discovers that he is authorized only to negotiate with France because the English king still won't recognize American independence, but French minister Vergennes helps Franky Baby out by insisting that England deal directly with America "consistent with the dignity of your state". In May Alexander Hamilton finally becomes a citizen of New York State. On June 11 on the strength of the V at Saratoga, John Adams finally arranges a large loan for the Continental Congress from Holland, allowing the rebels to keep the pressure on the way and hammer the last stake in their hearts; as he returns to France peace talks are already underway, and he sends for lonely Abigail, who brings her children and is wowed by Paris nightlife. On June 20 the U.S. Congress approves the Great Seal of the United States, originally designed by Irish-born Continental Congress secy. (1774-89) (DOI signer) Charles Thomson (1729-1824) and Penn. lawyer William Barton (1754-1817), with the motto "E Pluribus Unum" (out of many, one), with a coat of arms derived from the Belcher Coat of Arms, used by Jonathan Belcher (1682-1757), founder of Princeton U. and friend of Benjamin Franklin; on Sept. 16 the design of the Great Seal is adopted: 13 stars, 13 stripes, 13 clouds, 13 arrows, 13 laurel leaves, 13 berries, 13 feathers in each wing and tail of the American Bald Eagle, 13 rows in pyramid, 13 letters in each motto (E pluribus unum and Annuit coeptis); the colors red, white and blue stand for courage, justice and innocence - and the Wheel of Fortune? Plenty of Freemason and Illuminati symbology to keep any conspiracy theorist happy? In June British foreign secy. Charles James Fox obtains a grant of complete legislative independence for Ireland. In the summer the Continental Army's sets up its last cantonment at New Windsor, N.Y., 60 mi. N of New York City (until next summer); Gen. Washington's HQ is in nearby Newburgh. In summer King Kalani'opu'u (b. 1729) dies, after which Kamehameha I defeats his cousin Keoua Kuahu'ula (Hawaiian "rain cloud of the red cloak") (son of Kalani'opu'u) and the latter's half-brother Keawemauhili (1710-90) (half-brother of Kalani'opu'u) at the Battle of Mokuohai S of Kealakekua Bay with help from Keeaumoku Papa'iahiahi (1736-1804), father of Ka'ahumanu (1768-1832) (Hawaiian "feathered mantle") (Kamehameha I's favorite wife) and Kuakini (1789-1844), taking control of Kona and Kohala (W and N sides) in the Big Island of Hawaii, leaving Keoua with the E side. On July 1 the Marquis of Rockingham (b. 1730) unexpectedly dies after 14 weeks as British PM (since Mar. 27), and the king offers the job to Lord Shelburne, causing rival minister (no favorite of the king) Charles James Fox to resign, and his envoy Thomas Grenville to be recalled from Paris, prompting Benjamin Franklin to make an informal peace offer on July 10, divided into "necessary" provisions (recognition of independence, removal of British troops, secure boundaries, secure fishing rights off Canada), and "advisable" ones (reparations, acknowledgement of British guilt, a free trade agreement, ceding Canada to the U.S.); Franklin then suffers a gout attack lasting until late Sept., keeping him at Passy, causing John Jay to take over as lead negotiator. On July 11 the British evacuate Savannah, Ga. On Aug. 7 Gen. George Washington creates the Order of the Purple Heart (originally the Badge of Military Merit) to recognize merit in enlisted men and noncommissioned officers wounded in combat; in May 1783 the first recipients are Elijah Churchill and William Brown; only one more is awarded to Rev. War soldiers; it is not revived until George Washington's 200th birthday on Feb. 22, 1932. On Aug. 19 the Battle of Blue Licks near modern-day Mount Olivet, Ky. sees 50 British rangers plus 300 Indians ambush and rout 182 Kentucky militiamen, incl. Daniel Boone, becoming their worst D of the Am. Rev. War; Boone's son Israel Boone (b. 1759) is killed. On Aug. 27 the Battle of the Combahee River in Beaufort County, S.C., a skirmish as British troops are foraging for rice becomes the last fighting between Americans and British in the Am. Rev. War; Alexander Hamilton's friend (lover?) John Laurens is killed. In Aug. Ben Franklin's son William flees to London after his ordering of a raid on rebel forces results in the lynching of an Am. captain. On Oct. 5 after John Jay sends secret envoy Benjamin Vaughan to ask for it, Lord Shelburne sends a note to commissioner Richard Oswald changing his commission to negotiate with "the said colonies and plantations" to "the colonies under the title of 13 united states", and formal peace negotiations begin in Paris between the formally recognized U.S. and Britain; fearing that the French are angling for a separate peace with the British, John Jay persuades Franklin to do the same; the new U.S. offer allows Britain free navigation rights on the Mississippi; John Jay arrives in Paris, along with Adm. Howe's secy. Henry Strachey, fresh from the British V at Gibraltar, and negotiations get serious starting on Oct. 30 (Adams' 47th birthday), haggling over fishing rights off Newfoundland ("New England's ancient stake in the sacred codfish" - Adams), prewar debts, the western boundary, and compensation for British loyalists in America. On Nov. 1 after the V at Yorktown, the Continental Congress issues a Thanksgiving Proclamation for Nov. 28. On Nov. 3 Philly-born Elias Boudinot Jr. (1740-1821) becomes pres. #4 of the United States under the Articles of Confederation (until Nov. 2, 1783); Alexander Hamilton takes a seat in the Congress, which suffers from many members staying home in preference to state seats, and meets James Madison (1751-1836), who has the record for most attendance; they become friends and allies in the struggle to strengthen the federal govt. On Nov. 10 an Am. retaliatory attack against loyalist and Indian forces at a Shawnee village in Ohio territory is the last battle of the Am. Rev. War. On Nov. 18 the British evacuate Wilmington, N.C. On Nov. 30 Preliminary Peace Articles are signed at the British suite at the Grand Hotel Muscovite in Paris (the U.S. secy. is Ben Franklin's grandson Temple Franklin), acknowledging the U.S. as "free, sovereign and independent", and ending the Am. War of Independence, but with final agreement depending on a Franco-British settlement, which takes 9 mo.; the Northwest Territory (S and W of the Great Lakes, NW of the Ohio River, and E of the Mississippi River, incl. the future states of Ohio, Ind., Ill., Mich., Wisc. and part of Minn.) is ceded by Britain to the U.S., becoming its first possession; meanwhile Franklin tries to fix things up with the French for acting without consulting them, on Dec. 25 writing "one of the most famous of all diplomatic letters", implying that making the "little misunderstanding" public would help Britain divide them, even drive the U.S. into an alliance with Britain, which causes stunned French minister Vergennes to crumble, commenting "We shall be but poorly paid for all that we have done for the United States and for securing to them a national existence" - no wonder the French have a love-hate relationship with Yankees? In Nov. the Patriots faction in the Dutch Repub., led by Joan Derk, Baron van der Capellen tot den Pol (1741-84) gains power, wishing to create a U.S.-style govt. and remove Prince William V of Orange and end the corrupt Stadtholder regime, recognizing the U.S. govt.; too bad, by summer 1785 more and more repubs. back the prince despite his refusal to carry out reforms, fleeing to France in Sept. 1787, settling around Dunkirk, with leaders Francis Adrian Vanderkemp and Adam Gerard Mappa moving to the U.S. in 1789 at the invitation of George Washington. On Dec. 14 Charleston, S.C. becomes the last British outpost in the U.S. to be evacuated.; 5K blacks are evacuated, incl. 2.5K slaves owned by loyalists, who are sent to the West Indies; 500 black slaves are sent to E Fla. In Dec. the Russians under Adm. Potemkin easily conquer and annex the Crimea, causing many Tatars to flee to Ottoman territory. In Dec. Washington's officers complain to Congress about the lack of back pay and pensions, without satisfaction. In Dec. Hyder Ali (b. 1722) dies in Chittoor, and his learned multilingual Muslim lets-talk-about-the-army soldier-poet son Tipu (Tippu) Sultan (1750-99), "the Tiger of Mysore" succeeds him as sultan of Mysore, attacking Mangalore (400 mi. SSE of Bombay on the Arabian Sea), the British 42nd regiment under Col. John Campbell valiantly defending it (ends Jan. 30, 1784). The Battle of Zubarah is a V for the Bani Utbah tribal confederation over resident Persian gov. Nasr Al-Madhkur; by 1800 the sheikdom of Bahrain (ancient name Dilmun) passes from the Shiite Persians to the Sunni al-Khalifa family from Kuwait under "the Conqueror" Shaykh Ahmad bin Khalifa (-1795), and the minority Sunnis begin ruling the country (until ?); under them the independent Arab Ali Bin Ali tribe become the pirate kings of the Persian Gulf until the early 20th cent. The Spanish capture Minorca from the British. The Spanish under Bernardo de Galvez y Madrid capture New Providence in the Bahamas from the British. Nguyen Anh and his Roman Catholic priest buddy Pigneau de Behaine are defeated by the Tay Son brothers. The Highland Dress Proscription Act is repealed after 136 years (1646), and kilts and tartans are back in - along with Playlamb mag.? After 80K Irish Protestants form volunteer militias under a pretext of defending Ireland from the French, they demand legislative independence for Ireland, and on a motion of Charles Fox the British Grattan's Parliament passes the Constitution of 1782), freeing the Irish Parliament of legal restrictions imposed by the anti-Catholic Poyning's Laws of 1494-5; too bad, the Irish Parliament is still all Protestant, and refuses to extend suffrage to Catholics, and after the 1798 United Irishmen Uprising the Parliament of Ireland is abolished and the kingdom of Ireland is absorbed into Britain. The Patent of Settlement encourages settlement in beautiful Bukovina. The last witch-burning in Europe takes place in Canton Glarus in Switzerland - do you believe in magic, then just close your mind? Pope Pius VI goes to Vienna to unsuccessfully persuade HRE Joseph II to rescind his program of religious tolerance - you'll regret it in the morning? Saratoga loser Gen. John Burgoyne becomes British CIC in Ireland, where he mainly spends his time writing dramas. Christopher Gadsen is elected gov. of S.C., but refuses to accept the office because of ill health from his long imprisonment by the Brits, although he continues to be active politically, becoming a member of the S.C. conventions which ratify the U.S. Constitution and draft the S.C. state constitution. 24-y.-o. James Monroe is elected to the Va. legislature and becomes a member of the executive council. Oh-baby-I'm-ready-for-love Aaron Burr marries Mrs. Theodosia Prevost (-1794), widow of a British officer; they have one daughter, Theodosia. English Arctic explorer Samuel Hearne is captured by French explorer La Perouse, and returns to England in 1787. The Royal Irish Academy is founded in Dublin to examine "the ancient state of arts and literature". Washington College in Chestertown, Md. is founded, named in honor of George Washington, becoming the first college chartered after U.S. independence, becoming known for celebrating May Day in the nude by the flagpole. Louis XVIII's triple-chinned ex-chef (of the Prince of Conde and the Count of Provence) Antoine B. Beauvilliers (1754-1817) opens the Taverne Anglaise Restaurant in the Palais Royale in Paris, becoming the first luxury restaurant in Paris, catering to aristocratic clientele with mahogany tables and fine linen tablecloths, crystal chandeliers, elegantly-dressed waiters, fine cuisine, and an extensive wine cellar; in 1788 he moves to the Gallery de Valois near the Cafe de Chartres, calling it Restaurant Beauvillers Le Magnifique; after being forced to close in 1795, he opens another restaurant in Paris that closes in 1825. Welsh-born actress Sarah Kemble Siddons (1755-1831) returns to Drury Lane, and finally becomes a star in David Garrick's version of Thomas Southerne's "The Fatal Marriage", going on to do a great Lady Macbeth. The first English language Bibles are printed in North Am. - copyright pirates? Inventions: Oliver Evans (1755-1819) constructs the Hopper-Boy, the first automated flour mill in Wilmington, Del. James Watt develops the double-acting rotary steam engine, coining the term "horsepower", finding that a mine pony can lift 22K ft.-lb./min., increasing it by 50% for horses (33K). Josiah Wedgwood (1730-95) of England invents a pyrometer for pottery furnaces. Science: The sulfur-like element Tellurium (#52) (Te) (Lat. "tellus" = earth) is discovered combined with gold in Transylvania by Austrian mineralogist Franz=Joseph Muller (Müller) von Reichenstein (1740-1826). Nonfiction: Jacques Pierre Brissot (1754-93), Bibliotheque Philosophique du Legislateur. J. Hector St. Jean De Crevecoeur, Letters from an American Farmer; "What then is the American, this new man?" August Friedrich Wilhelm Crome (1753-1833), Producten-Karte von Europa; contains the first known example of a cartogram, a geographic distribution of 56 European commodities. Rev. William Gilpin (1724-1804), Observations on the River Wye and Several Parts of Wales, etc. Relative Chiefly to Picturesque Beauty; Made in the Summer of the Year 1770; originates the idea of the picturesque, which becomes part of the Romantic sensibility. Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826), Commerce Between Master and Slave. Johann Kaspar Lavater (1741-1801), Pontius Pilate. Comte de Mirabeau (1749-91), Essai sur les Lettres de Cachet et les Prisons d'Etat; written in Vincennes Castle, where his daddy confined him from 1777-80 for debts and naughtiness. Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours (1739-1817), Memoires sur la Vie et les Ouvrages de Turgot. Joseph Priestley (1733-1804), A History of the Corruptions of Christianity. Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-78), Confessions (autobio.) (12 vols.); covers his life up to 1765; completed in 1769-70; vols. 7-12 pub. in 1789; known for the quote: "I recalled the makeshift of a great princess who was told that the peasants had no bread and who replied: 'Let them eat brioche'", although Marie Antoinette probably never said it. Louis Claude de Saint-Martin, Natural Table of the Correspondences between God, Man and the Universe. Dugald Stewart, Elements of the Philosophy of the Human Mind. Girolamo Tiraboschi (1731-94), History of Italian Literature (Storia della Letteratura Italiana) (13 vols.) (Modena); first history of Italian lit.; written in 1771-82 using the library of Duke Francis III of Modena; 2nd ed. (16 vols.) pub. in 1787-94. Music: Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756-91), Abduction from the Seraglio (Die Entfuhrung aus den Serail) (opera) (Vienna) (July 16); a young man in love with two Spanish women; requested by HRE Joseph II; no longer a bum, on Aug. 4 he marries foxy German soprano and musician Konstanze (Constanze) Weber (1762-1842), one of the four Weber sisters (daughters of composer Carl Maria von Weber's brother Fridolin) after giving up on her older sister Aloysia Weber (1760-1839), one of the leading singers of the day, who appears later as Donna Anna in the first Viennese production of "Don Giovanni". Art: Francesco Guardi (1712-93), Fetes for the Grand Duke Paul of Russia (Venice). Gilbert Stuart (1755-1828), The Skater; atty. William Grant skating on ice, showing him in motion; Stuart has to let cruddy skater Grant grab his coattails to guide him off the ice; a big hit, he becomes a star, commanding top prices for portraits and coming in #3 after Joshua Reynolds and Thomas Gainsborough; too bad, he mismanages his finances and flees his creditors to Dublin in 1787 before returning to the U.S. in 1793, settling in Germantown (near Philly), Penn., where his portraits of George Washington supply him with a good income. Plays: George Colman the Younger (1762-1836)), The Female Dramatist (first play) (Little Theatre, Haymarket, London); based on Tobias Smollett's "Roderick Random"; a flop. Hannah More (1745-1833), Sacred Dramas: Chiefly Intended for Young Persons, the Subjects Taken from the Bible. Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (1759-1805), The Robbers (Die Rauber) (Die Räuber) (Mannheim) (Jan. 13) (first play); a Gothic drama that makes him an instant star. Poetry: William Cowper (1731-1800), Poems. Novels: Aagje Deken (1741-1804) and Betje Wolff (1738-1804), Historie van Mejuffrouw Sara Burgerhart; two lit. friends move in together in 1781 in Beverwijk and begin cranking them out, moving to Treoux, Burgundy from 1788-97. Fanny Burney (1752-1840), Cecilia, or Memoirs of an Heiress. Tomas de Iriarte y Oropesa (1750-91), Fabulas Literarias. Pierre Choderlos de Laclos (1741-1803), Dangerous Liaisons (Les Liaisons Dangereuses) (Mar. 23) (4 vols.); an epistolary novel about Marquis de Merteuil and Vicomte de Valmont, who love perverted cruel sex and seduction games and use sex as a weapon in their rivalry, becoming a giant hit and a favorite of Marie Antoinette; too bad, after the French Rev. starts, it becomes a condemnation of the Ancien Regime; "Vengeance is a dish best served cold" (La vengeance est un plat qui se mange froid). Helen Maria Williams (1761-1827), Edwin and Eltruda: A Legendary Tale (first novel). Births: Am. Whig statesman-lawyer-orator and U.S. secy. of state #14, 19 (1841-3, 1850-2) ("Black Dan") ("the Cicero of America") Daniel Webster (d. 1852) on Jan. 18 in Salisbury, N.H.; educated at Phillips Exeter Academy, and Dartmouth College. Am. celeb Philip Schuyler Hamilton (d. 1801) on Jan. 22 in Albany County, N.J.; eldest son of Alexander Hamilton (1755-1804) and Elizabeth Schuyler Hamilton; educated at Columbia U. French "La Muette de Portici", "Fra Diavolo" opera composer Daniel Francois Esprit Auber (d. 1871) on Jan. 29 in Caen, Normandy. Am. Baptist preacher (ex-Freemason) William Miller (d. 1849) on Feb. 15 in Pittsfield, Mass. Am. pro-Manifest Destiny politician Thomas Hart "Old Bullion" Benton (d. 1858) on Mar. 14 in Hart's Mill (near Hillsboro), N.C.; opposed to paper currency and nullification; father of Jessie Benton Fremont (1824-1902); granduncle of artist Thomas Hart Benton (1889-1975); first 5-term U.S. Sen. (D-Mo.) (1821-50). Am. Dem.-Repub. pro-slavery politician and U.S. vice-pres. #7 (1825-33) John Caldwell Calhoun (d. 1850) on Mar. 18 near Calhoun Mills (Abbeville), S.C.; educated at Yale U.; husband (1811-) of Floride Bonneau Calhoun (1782-1866). Corsican queen of Naples-Sicily Maria Annunziata Carolina (Marie Annonciade Caroline) Bonaparte Murat (d. 1839) on Mar. 25 in Ajaccio; sister of Napoleon Bonaparte (1769-1821). Am. Detroit, Mich. mayor #1 (1924-5, 1830, 1844-7) (co-founder of the Detroit Free Press) John R. Williams (d 1854) on May 4 in Detroit, Mich.; nephew of Joseph Campau (1769-1863). English "Greta Bridge" landscape painter John Sell Cotman (d. 1842) on May 16 in Norwich; friend of Joseph Turner. Russian field marshal Prince Mikhail Semyonovich Vorontsov (d. 1856) on May 30. Russian gen. Pyotr Stepanovich Kotlyarevsky (d. 1852) on June 21 in Olkhovatka (near Kharkiv). French geologist Pierre Berthier (d. 1861) on July 3. Mexican pres. #2 (1829) gen. Vicento Ramon Guerrero Saldana (Saldańa) (d. 1831) on Aug. 10 in Tixtla. British gen. (CIC in India) Gen. Sir Charles James Napier (d. 1853) on Aug. 10 in Whitehall, London; eldest son of Col. George Napier (1751-1804); brother of Sir George Napier (1784-1855), Sir William Napier (1785-1860), and Capt. Henry Napier (1789-1855); knighted in 1843. Scottish "Marriage", "The Inheritance", "Destiny" novelist Susan Edmonstoune Ferrier (d. 1854) on Sept. 7 in Edinburgh; friend of Sir Walter Scott (1771-1832), who works with her daddy James Ferrier in the Court of Session. Chinese Manchu Qing emperor #6 (1820-50) Dao Guang (real name Mianning) (d. 1850) on Sept. 16 in Beijing; 2nd son of Yong Yan. German ethnologist-naturalist-explorer Prince Alexander Philipp Maximilian zu Wied-Neuwied (d. 1867) on Sept. 23 in Neuwied. Irish "Melmoth the Wanderer" novelist-playwright Charles Robert Maturin (AKA Dennis Jasper Murphy) (d. 1824) on Sept. 25 in Dublin; educated at Trinity College, Dublin. Am. gov. #2 of Mich. Territory (1813-31), U.S. secy. of war #14 (1831-6), U.S. Sen. (D-Mich.) (1849-57), and U.S. secy. of state #22 (1857-60) (Freemason) Lewis Cass (d. 1866) on Oct. 9 in Exeter, N.H.; educated at Phillips Exeter Academy; gov. of Mich. (1813-31); helps open up the Middle West to whites. Danish poet-novelist Steen Steensen Blicher (d. 1848) on Oct. 11 in Vium (near Viborg), Jutland. Am. Indian fighter, gov. #1 of Wisc. Territory (1836-41) and U.S. Sen. (1848-1854) Henry Dodge (d. 1867) on Oct. 12 near Vincennes, Ind. English PM (1827-8) Frederick John Robinson, 1st Earl of Ripon, Viscount Goderich (d. 1859) on Nov. 1 in Newby Hall, Yorkshire; educated at Harrow Schol, and St. John's College, Cambridge U. Am. gov. #14 of N.C. (1817-20), U.S. Sen. (D-N.C.) (1823-9), and U.S. navy secy. #8 (1829-31) John Branch Jr. (d. 1863) on Nov. 4 in Halifax County, N.C.; educated at the U. of N.C.; uncle of Lawrence O'Bryan Branch (1820-62). U.S. Dem. pres. #8 (1837-41) and vice-pres. #8 (1833-7) Martin Van Buren (d. 1862) on Dec. 5 in Kinderhook, N.Y.; son of Dutch farmer Abraham Van Buren and Mary Hoes; husband (1807-19) of Hannah Hoes. Irish pianist-composer John Field (d. 1837) in Dublin; pupil of Muzio Clementi in London; inventor of the nocturne (musical composition evocative of the night), which influences Chopin. Italian #1 violinist and composer Nicolo (Nicolň) Paganini (d. 1840) in Genoa; makes his debut at age 9 playing his own set of variations on a French air; makes his first tour of Italy at age 13. English Liberal Whig statesman John Charles Spencer, 3rd Earl Spencer, Viscount Althorp (d. 1845); son of John Spencer, 2nd earl Spencer (1758-1834); educated at Trinity College, Cambridge U. Am. chemist (inventor of chloroform) Samuel Guthrie (d. 1848) in Brimfield, Mass. Scottish painter Sir William Allen (d. 1850) in Edinburgh. German pedophile, er, pedagogue and educational reformer Friedrich Froebel (Fröbel) (d. 1852) in Oberweissbach, Thuringia; uncle of Julius Froebel (1805-93); inventor of the kindergarten (1816). French political writer Abbe Hugues Felicite Robert de Lamennais (d. 1854). Russian-French writer Anne Sophie Swetchine (d. 1857) in Moscow. English consul-gen. to Madeira Henry Veitch (d. 1857); husband of Margaret Harrison, sister of treasury secy. Sir George Harrison; father of Henry Gordon Veitch (1814-63), father of Violet Agnes Veitch (1863-1954), mother of Noel Coward (1899-1973). Deaths: Scottish noble Thomas Fairfax, 6th lord Fairfax of Cameron (b. 1693) on Dec. 9 in Greenway Court, Va. Scottish philosopher Henry Home, lord Kames (b. 1696) on Dec. 27 in Edinburgh. French geographer Jean d'Anville (b. 1697) in Jan. French architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel (b. 1698) on Jan. 4. Italian poet-librettist Metastasio (b. 1698) on Apr. 12 in Vienna. Italian architect Ferdinando Fuga (b. 1699) on Feb. 7 in Naples. Portuguese statesman Marquis de Pombal (b. 1699) on Aug. 8. Swiss mathematician Daniel Bernoulli (b. 1700) on Mar. 17. Italian castrato singer Carlo Broschi (Farinelli) (b. 1705); retired at the Spanish court of Philip V. German chemist Andreas Sigismund Marggraf (b. 1709) on Aug. 7 in Berlin. French inventor Jacques de Vaucanson (b. 1709) on Nov. 21 in Paris. German Goethe's father Johann Caspar Goethe (b. 1710) on May 25 in Frankfurt am Main. Welsh painter Richard Wilson (b. 1714) on May 15 in Colomendy, Denbighshire. German banker Simon Moritz Bethmann (b. 1721) in Frankfurt am Main. British gen. Robert Monckton (b. 1726) on May 21 in London. English PM (1765-6, 1782) Charles Watson-Wentworth, 2nd marquess of Rockingham (b. 1730) on July 1 in Wimbledon, London - hitting tennis balls with O.J.? Am. Rev. War gen. Charles Lee (b. 1731) on Oct. 28 in Philadelphia, Penn. (TB). Swedish botanist Daniel Solander (b. 1733) on May 16 in Soho Square, London (stroke); dies at the home of Sir Joseph Banks. Thai king (1768-82) Taksin the Great (b. 1734) on Apr. 7 (executed). German composer (piano sonata specialist) Johann Christian Bach (b. 1735) on Jan. 1. U.S. First Lady-not Martha Wayles Skelton Jefferson (b. 1748) on Sept. 6; wife of Thomas Jefferson. British prince Alfred (b. 1780) on Aug. 20 in Windsor Castle; dies of a smallpox inoculation.






























1783 The pop. of New York City doubles over the next two years to 24K. The creation of the U.S. leaves Britain without a place to dump its convicts, causing them to end up sending them Down Under. You can find me on Monster.com? On Jan. 6 the officer corps presents Congress with a petition airing their many grievances, incl. being owed up to six years of back pay, and being in danger of being put in debtors' prisons at war's end; on Mar. 10 as the Continental Army bivouacks in Newburgh, N.Y., two anon. letters by Maj. John Armstrong Jr. (aide to Gen. Horatio Gates) call on them to mutiny; after learning of them, Gen. George Washington calls for a meeting of 500 officers on Mar. 15, where he urges them to wait until Congress satisfies their claims, urging "more moderation and longer forbearance"; after they begin to tune him out, he pulls out a pair of glasses and utters the soundbyte: "You must pardon me, for I have grown not only gray but blind in the service of my country", causing a three-hanky moment, ending the mutiny, allowing Washington to lobby Congress on their behalf; after Penn. militiamen march on Philly and force Congress to flee to Princeton, N.J., they are finally promised a pension equal to five years' back pay. On Jan. 20 Britain signs a preliminary peace treaty with France and Spain after the latter give up on Gibraltar - but not really? In Jan. Comte de Rochambeau and his troops return to France, and the U..S. Congress votes the thanks of the nation to them; on May 24, 1902 a Statue of Comte Rochembeau is unveiled in Washington, D.C. by Pres. Theodore Roosevelt. On Feb. 3 Spain recognizes U.S. independence. On Feb. 4 Britain officially declares an end to hostilities in former British Am. On Feb. 4 a series of earthquakes begins in Calabria, Italy killing 50K, becoming the first earthquake to be investigated scientifically. On Feb. 5 Sweden recognizes the U.S. On Feb. 6 the Spanish-French siege of Gibraltar (begun 1779) is lifted after 3 years 7 mo. 12 days. On Apr. 2 after Lord North and Charles James Fox make up and help defeat British PM (since July 4, 1782) Lord Shelburne Mar. 26, aristocratic Whig (lord lt. of Ireland in 1782) William Cavendish Bentinck, 3rd Duke of Portland (1738-1809) becomes PM (until Dec. 18) of a coalition govt., with Fox as secy. of state, and Fox and North calling the real shots; too bad, after Fox introduces the India Bill, proposing that the govt. of India be vested in an India Board appointed by Parliament, the pissed-off king personally intervenes, causing Portland's ministry to come unglued (uncemented?), and on Dec. 19 American-woman-get-away-from-me "independent Tory" (not a Whig) William Pitt the Younger (1759-1806) becomes English PM (until Mar. 14, 1801), the youngest in history pip pip bloody bloody and all that rot; for one reason or another Fox is kept out of the ministry until 1806, becoming content with being the you-really-got-me hot lips orator of Parliament; meanwhile conservative Whig William Wentworth-FitzWilliam, 2nd and 4th Earl FitzWilliam (1748-1833) (a descendant of William I the Conqueror, who inherited his uncle the Marquess of Rockingham's vast Yorkshire estates in 1782, making him a player, and who was slated to become head of the India Board but now is out of that job) becomes head of the opposition. On Apr. 11 the Continental Congress officially declares an end to the little ole warry war war war with the hated Brits, but now their own constitutional weakness leads to a near breakdown; Alexander Hamilton is chmn. of the committee in charge of peace arrangements; they enact a new system of import duties in an attempt to pay the soldiers, who are clamoring for their pay, but they prove to be too little too late; in mid-June rebellious troops in Philly send Congress a petition demanding their pay, followed by 80 armed soldiers marching from Lancaster to get it by force, entering Philly on June 20, seizing several arsenals; on June 24 400 drunken soldiers circle the State House, where Congress was in a special Saturday afternoon session, causing them to exit and flee to Princeton after Pennsylvania refues to send out the state militia; a month later they move to Annapolis; a year later to Trenton and Princeton (sitting in Nassau Hall), then to New York City in 1785; the whole affair gives rise to the resolve to house the national capital in a special federal district not at the mercy of state govts. On Apr. 17 the Battle of Ark. Post (Colbert Raid) (Colbert Incident) sees British partisans under James Colbert siege the fort for six hours before being repelled by Spanish defenders; too bad, they didn't get the news of the Jan. 20 peace treaty between Britain and Spain, becoming the only Am. Rev. War battle fought in Ark. On Apr. 19 Thomas Paine pub. the last issue of The Crisis, with the soundbyte "These are the times that tried men's souls, and they are over". On Apr. 23 U.S. supt. of finance Robert Morris (1734-1806) writes a Letter to Congress proposing the idea of his asst. Gouverneur Morris of decimalizing U.S. coinage, and Thomas Jefferson takes up the idea based on the Spanish dollar. On Apr. 26 7K loyalist businessmen set sail for Nova Scotia, Canada from New York City, bringing the total to 100K; New York's economy suffers as the businessmen take their capital with them. On Apr. 28 despite being an old fart, Guatemalan gov. Matias de Galvez y Gallardo gets his dream job, becoming the last viceroy of New Spain to make a formal entry into Mexico City on horseback, then goes on to drain the lake surrounding the city, build bridges and a sewer system, divide the city into four quarters, and found the San Carlos Academy of Fine Arts, becoming the first major art academy and art museum in the Americas; he also orders the reconstruction of the Palace of Chapultepec, founds the Banco Nacional de San Carlos plus a pawn shop, and arranges to trade Chinese mercury for his silver mines in exchange for furs; on Nov. 13 he gives permission to Manual Antonio Valdes Murguia y Saldana to begin pub. the Mexican nat. newspaper "Gaceta de Mexico", which was originally founded in 1722 then suspended in 1742, but limits him to official govt.-approved news; he takes a census which finds that there are 637 coaches in Mexico City. On May 31 the French Academie Royale of Painting and Sculpture accepts Elisabeth Vigee-Lebrun (1755-1842) (Marie Antoinette's court painter) and Adelaide Labille-Guiard (1749-1803) as members in order to let their works be compared, leaving men out of it? In May the Black Sea port city of Sevastopol (modern-day pop. 418K) is founded, becoming the main base of the Russian Black Sea fleet. In May Gen. Henry Knox, Alexander Hamilton et al. hold the first meeting of the Society of the Cincinnati in Fishkill (modern-day Beacon), N.Y. for Continental officers who served with honor for at least three years, named after Roman Gen. Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus (-519 to -430), dictator of Rome in -458 and -439, who resisted the urge to becoming a dictator for life or king and went back to his humble farm (what a man, guess who Washington is the reincarnation of, it's not just beautiful, it's just another ordinary miracle today?); too bad, it pisses-off Samuel Adams, who calls it "a stride towards a hereditary military nobility"; after they do it anyway when the war ends, it becomes the oldest military hereditary society in the U.S. to survive to modern times. Do you know the way to Hot Air Bay? On June 4 the French papermaker Montgolfier Brothers incl. Joseph-Michel Montgolfier (1740-1810) and Jacques-Etienne (Étienne) Montgolfier (1745-99) of Annonay (near Lyons), France test their first small unmanned smoke-filled paper-lined linen hot air balloon, which rises to a height of 3K ft. at Annonay, France in a 10-min. 1-mi. flight; on Aug. 27 Parisian physicist Jacques Alexandre Cesar (César) Charles (1746-1823) launches a 13-ft.-dia. silk balloon (constructed under his supervision by A.J. and M.N. Robert) filled with hydrogen in Paris in front of 50K spectators; it floats at 3K ft. for more than 45 min. and lands in a village 16 mi. away, where the spooked villagers attack it with stones and knives; on Sept. 19 the Montgolfier Brothers conduct another demo in Versailles, witnessed by Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette, where a duck, rooster, and sheep become the first living passengers, traveling 2 mi. in 8 min., with max. alt. of 1.5K ft, pissing-off the king with the dense smoke they deliberately generate in the belief that it's what causes the buoyancy, later learning that it's heat; on Oct. 15 French daredevil physician Jean Francois Pilatre de Rozier (1754-85) makes the first tethered balloon ascension, repeating the demo on Oct. 17 before a group of scientists, then reaching 324 ft. on Oct. 19; on Nov. 21 (2 p.m.) champagne-toting de Rozier and army officer Marquis Francois Laurent le Vieux d'Arlandes (1742-1809) make the first untethered human flight, reaching a peak alt. of 500 ft. and traveling 5.5 mi. in 25 min. from the Bois de Boulogne in Paris in the presence of Louis XVI and a huge crowd, across the Seine River to the Butte-aux-Cailles; the next day Benjamin Franklin et al. sign the official certification at Passy; on Nov. 31 Jacques Charles (financed by Franklin) flies in his hydrogen balloon, while gouty Franklin watches from his carriage near the Tuileries Gardens; balloon exhibition flights soon become the rage in Paris; when asked what was the practical use of these balloon thingies, Franklin replies "What is the use of a newborn baby?"; the power of a mere individual to go over the king's head and attract large crowds is a giant leap for popular democracy, making the French Rev. inevitable, and, combined with the success of the U.S., it coulda gone better if only they hadn't dabbled with the powder keg of godless atheism? In June Laki Volcano in SE Iceland begins erupting for the next 8 mo. (until Feb.), killing 50%+ of the cattle and most of the crops, leading to a famine that kills 25% of the human pop., becoming the worst in Icelandic history (until ?); after 120M tons of sulfur dioxide is spewed into the atmosphere of the Northern Hemisphere, global temps drop, causing crop failures in Alaska and droughts in North Africa and India. On July 8 the Supreme Court of Mass. finalizes the 1781 abolition of slavery in Mass. On Aug. 4 after small eruptions on May 9 and a larger eruption on July 26, Mt. Asama 85 mi. N of Tokyo, Japan erupts bigtime, destroying four villages plus an 18 sq. km primeval forest and killing thousands, worsening the Great Tenmei Famine; in 1820 Dutch ambassdor Isaac Titsingh (1745-1812) pub. an account of the eruption. On Aug. 17 a UFO is sighted over the North Sea between Ostend and Edinburgh. On Sept. 3 the Treaty of Paris (drafted Nov. 30, 1782) is signed by the U.S. and Great Britain, along with the Treaties of Versailles by France and Spain, formalizing U.S. independence and defining its borders, with Britain recognizing U.S. independence and agreeing to a W boundary at the Mississippi River, while the N and S boundaries are left for future definition; Spain regains East and West Florida and Minorca in exchange for the Bahamas; Illinois is formally ceded by Britain, and the U.S. is granted the liberty of fishing off Newfoundland the St. Lawrence Gulf, along with the right to dry their catches on the unsettled Atlantic coast of Canada, causing a shipbuilding boom in New England; there is also some mumbo jumbo about restoration of confiscated Tory property and removal of legal impediments to British merchants seeking to collect debts; following this treaty, the British withdraw from the U.S., taking thousands of freed slaves with them and settling them in Nova Scotia (until 1791); British adm. George Rodney (d. 1792), who destroyed or captured 15 of the 21 U.S. ships in the war, and accepted the surrender of four adms. during his super career, and who was made vice-adm. of Great Britain (the top job) in 1781, goes into retirement; La. gov. Bernardo de Galvez y Madrid, who helped draft the Treaty of Paris to make sure the Spanish got Fla. returns to Spain as a hero, and the towns of Galveston, Tex. and St. Bernard Paris, La. are later named after him; Green Bay, Wisc. (founded 1634) becomes the first U.S. town in Wisc.; in Sept. on their way home Algerian pirates harass Am. ships, causing Americans to claim that Britain paid them to attack them; Joseph Calve is sent from Mackinac to notify the Indians of the Upper Mississippi River of the cessation of hostilities; the 120-sq.-mi. island of Grenada in the E Caribbean is ceded by the French, becoming a British possession, along with the 133-sq.-mi. island of St. Vincent between Grenada and Saint Lucia, where the Black Caribs (Garifuna) fight the British under paramount chief Joseph Chatoyer (Satuye) (-1795). On Sept. 9 Dickinson College in Carlisle, Penn. becomes the first college chartered in the U.S., founded by DOI signer Benjamin Rush and named in honor of DOI signer-not John Dickinson. On Oct. 7 the Va. House of Burgesses grants freedom to slaves who served in the Continental Army. On Nov. 3 Washington-lookalike Quaker maj. gen. Thomas Mifflin (1744-1800) (who miffled fellow Quakers by fighting in the Am. Rev. War) becomes pres. #5 of the United States under the Articles of Confederation (until Oct. 31, 1784); Thomas Jefferson is sent to Congress from Va. On Nov. 6 the last public hanging in Britain takes place at Tyburn Hill. On Nov. 8 Mass. gov. John Hancock proclaims a day of Thanksgiving for Dec. 11. On Nov. 25 (Evacuation Day) the last British troops leave New York City, greasing the flagpole so that the U.S. flag can't be raised without pitching another pole; Gov. George Clinton and George Washington ride side-by-side into the city, guarded by Westchester light cavalry, amid cheering crowds; during his week stay in New York City, Gen. Washington salvages the reps of suspected Tories who really are patriot spies, incl. Hercules Mulligan and James Rivington, who helped steal the British fleet's signal book and transmit it to Admiral de Grasse; former Pensacola gov. gen. John Campbell of Strachur succeeds Sir Guy Carleton as CIC of British North Am. based in Canada until 1787, after which he returns to Scotland and pouts about his big D in West Fla., uttering the soundbyte "It has been my Misfortune... to be employed in an ill fated Corner of his Majesty's Dominions... My Endeavours have unremittingly been exerted for West Florida's preservation to the British Empire since I took upon me the military command, and if my Labours and Exertions to that End shall but find favour with my sovereign, I shall forget the Frowns of Fortune and be happy in the Royal Approbation." On Nov. 26 the brig Philadelphia Packet runs ashore on Sinepuxent Bar, and about 70 passengers hire a schooner to go ashore, but it overturns, killing them all. On Dec. 2 Gen. George Washington writes a letter to a group of recent Irish immigrants, with the soundbyte: "The bosom of America is open to receive not only the Opulent and respectable Stranger, but the oppressed and persecuted of all Nations And Religions; whom we shall wellcome to a participation of all our rights and previleges, if by decency and propriety of conduct they appear to merit the enjoyment." On Dec. 4 the British evacuate Staten Island and Long Island; the same day Gen. Washington delivers his tearful farewell address to his army at Fraunces Tavern at the corner of Broad and Pearl Sts. run by his West Indian steward Samuel "Black Sam" Fraunces, resisting all calls to become a king; Alexander Hamilton, who a few days earlier had rented a house at 57 Wall Street close by, pointedly fails to attend; the troops are discharged the next day; Washington strolls down Whitehall St., trailed by speechless admirers, and boards a barge for New Jersey; the last vestiges of British rule are gone, capping eight years of fighting, with 25K Am. military deaths (1% of the entire pop.); New York City (pop. 12K) is in ruins, its trees having been used as firewood by British troops. On Dec. 23 George Washington resigns as CIC of the Continental Army and retires to his home in Mount Vernon, Va. On Dec. 26 French physicist Louis Sebastien Lenormand (1757-1837) gives the first public demonstration of a parachute (a term he coined from Fr. "parasol + chute" = sunshield + fall) as a way to save people jumping from burning bldgs., jumping from the tower of the Montpellier Observatory after first testing it on animals; in 1797 he jumps 3K ft. from a balloon. On Dec. 23 Gen. George Washington appears before Congress in Annapolis and resigns his commission, refusing offers of a crown, saying that he didn't fight the war to create an American throne; a superior act in the entire history of humanity, even topping Roman gen. Cincinnatus? On Dec. 24 Washington arrives back home at Mount Vernon, Va. in time for Xmas. Erekle II of Kakheti and Kartli in E Georgia places his precarious kingdom under Russian protection. Nguyen Anh and his Roman Catholic priest buddy Pigneau de Behaine are defeated again by the Tay Son brothers, and return to Phu Quoc, then are chased to Siam, causing Behaine to leave in Dec. with Anh's son Canh to appeal to the French govt., arriving in Pondicherry in Feb. 1785. Luis de Unzaga becomes gov. of Cuba (until ?), ordering a halt to the unrestrained cutting of cedars. A U.S. Congressional apportionment of taxes counts a slave as three-fifths of a white person, which great idea is later used in the sugar-free U.S. Constitution. Livonia on the Gulf of Riga becomes a province of Russia (until 1918). Nguyen leader Nguyen Anh and his army are driven out of Vietnam by the Tay Son army. Hamburg, devastated by the Thirty Years' War establishes trade ties with the U.S., reviving its fortunes until the Napoleonic Wars (1806). New Brunswick on the St. John River in Canada is settled by 14K refugee loyalists (out of 35K in Novia Scotia) from the U.S., led by Harvard-educated Edward Winslow (1746-1815); the British approve it as a new colony next June. The Bank of Ireland is founded, issuing the first Irish-only notes. Civil marriage and divorce are legalized in the Austrian dominions, and HRE Joseph II enforces the use of the German language in Bohemia. Tory leader Capt. John Butler settles in Canada, and becomes an agent for Indian affairs. Charles Simeon (1759-1836) begins an evangelical movement in Cambridge, England, going on to pub. hundreds of "sermon skeletons" - so what if the Stones are 60, they're still 20 here? The first German brass band is founded in Philadelphia; 3K-5K Hessians remain in the U.S. after the war ends; the Hessian fly (Mayetiola destructor), which ravages wheat, rye, and barley crops appears in Long Island, N.Y. about this time, causing rumors that it was imported in Hessian military bedding straw. The Spanish crown sponsors a botanical expedition to South Am.; too bad, it doesn't accomplish much, and it takes until the early 1800s for Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt to make it happen. The first African-Am. benevolent society is founded in New Orleans. Aaron Burr enters New York politics, working up to state atty. gen. in 1789, then U.S. Sen. from 1791-7. James Monroe is elected to the U.S. Congress from Va. (until 1786), working for Western development. Josiah Flagg (1763-1816) of Boston, Mass., a silversmith trained by Paul Revere becomes the first native-born Am. dentist, going on to invent the dental chair in 1790 by adding an armrest and handrest to a Windsor chair. The Kirov Ballet begins performing on the stage of the St. Petersburg Bolshoi Theater. George III of England creates the Most Illustrious Order of St. Patrick for Irish knights; the last knight is created in 1936, and the last surviving one is Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester (1900-74). Evan Williams of Louisville, Ky. begins distilling Bourbon Whiskey, becoming the first in Ky.?; in the mid-1900s the brand is resurrected; it is first distilled and aged in the U.S. on the banks of the Ohio River in Louisville, Scott County, Ky. by Baptist Rev. Elijah Craig?; in 1785 Bourbon County (named after the French royal family) becomes part of Va. until 1792, when it becomes part of the new Commonwealthy of Ky., becoming known as Old Bourbon and becoming famous for corn-based Bourbon whiskey, which is shipped from Limestone, Ky. (modern-day Maysville, Mason County, Ky.) down the Ohio River, where it is sold in the port of New Orleans on Bourbon St. Waterford, Ireland begins manufacturing crystal, which becomes world famous. Inventions: Henry Bell invents a copper cylinder for calico printing. English pianoforte maker John Broadwood (1732-1812) patents piano pedals. Claude Francois Dorothee, Marquis de Jouffroy d'Abbans (1751-1832) sails a paddle wheel steamboat on the Saone River, making him its inventor? George Matthews of England makes the first malleable cast steel chains for ships; they are not used again until WWI. Taking advantage of the lengthening of human hair with humidity, Swiss geologist Horace-Benedict de Saussure (1740-99) invents the Hair Hygrometer, which is so reliable it is not replaced by an electrical version until the 1960s. German-born Geneva jeweler Johann Jacob Schweppe (1740-1821) uses a pump to carbonate mineral water, moving to London in 1792 to manufacture Schweppes Tonic Water, going on to introduce a ginger ale in 1870 and a bitter lemon in 1957. Science: French physicist Jacques Alexandre Cesar (César) Charles (1746-1823) makes and tests the first hydrogen-filled balloon, which is witnessed by Ben Franklin. Dutch-born deaf English amateur astronomer John Goodricke (1764-86) suggests that the variable star Algol (Beta Persei) (the Demon Star) is an eclipsing binary. About this time English natural philosopher (known for his black complexion) Rev. John Michell (1724-93) proposes the Cavendish Experiment to measure the gravitational constant, and first pub. the Schwarzschild Radius for a star, where gravity causes it become a "dark star" from which light cannot escape, later called a black hole; the experiment is performed in 1797-8 by British scientist Henry Cavendish. Danish naturalist Otto Friedrich Mueller (Müller) (1730-84) becomes the first to describe Diatoms. Nonfiction: William Thomas Beckford (1760-1844), Dreams, Waking Thoughts and Incidents; written in exile in Italy after his seduction of William Courtenay, 9th earl of Devon makes him a pariah in England; suppresses it prior to its public release. Phillippe Buache, History of the Saints (Paris). Benjamin Bell (1749-1806), A System of Surgery (6 vols.) (1783-8); bestseller in Europe and the U.S., going through 7 eds. by 1801; gives the advice "save skin" in mastectomy and limb amputation operations, recommending the routine use of opium to relieve post-operative pain, causing him to become known as the first Scottish scientific surgeon. Felice Fontana (1730-1805), Principi Generali della Solidita e della Fluidita de Corpi; his theory of matter as subject to an attractive and an expansive force. William Herschel (1738-1822), Motion of the Solar System in Space. Immanuel Kant (1724-1804), Prolegomena to Any Possible Metaphysics. Moses Mendelssohn (1729-86), Jerusalem; or On Religious Power and Judaism; the "little hunchback" of Berlin makes a plea for freedom of conscience for I-really-love-you-oh-you're-my-best-friends Jews; ancestor of composer Felix Mendelssohn argues against the stern Jewish god, saying that on Mt. Sinai Jehovah never commanded Jews to action, only appealed to them; helps found the Haskalah (Jewish Enlightenment); too bad, after he goes too secular, all of his grandchildren convert to Christianity? Ezra Stiles (1727-95), The United States Elevated to Glory and Honor. Noah Webster (1758-1843), A New and Accurate Standard of Pronunciation ("Webster's Spelling Book"), Pt. 1 of A Grammatical Institute of the English Language; Comprising An Easy, Concise, and Systematic Method of Education, Designed for the Use of English Schools in America (3 vols.) (1783-5); known as the "blue-backed speller"; it simplifies English, soon becoming the most popular book in the U.S. Hugh Blair (1718-1800), Lectures on Rhetoric and Belles Lettres. Comte de Mirabeau (1749-91), Erotica Biblion; a love manual and history of sex; "If all men's penises become as hard as oak trees, then the world will turn into a forest where it would be impossible to move." Music: Ludwig van Beethoven's first works are printed. Carl Michael Bellman (1740-95), The Temple of Bacchus; songs about drinking and sex, becoming a hit in sweet little Sweden. Robert Burns (1759-96), Scots Musical Museum (6 vols.) (1783-1803); printed by who's-in-your-family-tree right-right-you're-bloody-well-right-to-say James Johnson (1750-1811) of Ettrick. Luigi Cherubini (1760-1842), Lo Sposo di Tre e Marito di Nessuna (The Betrothed of Three and Husband of None) (comic opera) (Venice) (Nov.); his first comic opera, after which he heads to London then France in 1785, spending the rest of his life producing serious stuff but really blurring the lines, making friends with fellow child prodigy Frederic Chopin, and getting admired by Beethoven, who calls him his greatest contemporary. Andre Gretry (1741-1813), La Caravane du Caire (opera-ballet) (Oct. 30) (Fontainebleau); libretto by Etienne Morel de Chedeville. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756-91), Mass in C minor ("Kyrie"), K.427 (Oct. 26) (Salzburg); composed as the result of a vow in relation to his wife Constanze and father Leopold to ease their strained relationship. Art: Antonio Canova (1757-1822), Theseus Vanquishing the Minotaur (sculpture). John Singleton Copley (1738-1815), The Defeat of the Floating Batteries at Gibraltar, Sept. 13, 1782. Jacques-Louis David (1748-1825), Grief of Andromache. William Dunlap (1766-1839), Portrait of George Washington; his earliest known painting. Benjamin West (1738-1820, Apotheosis of Prince Octavius. Plays: Vittorio Alfieri (1749-1803), Antigone. Jean-Francois de La Harpe (1739-1803), Les Brames. Frederick Howard, 5th Earl of Carlisle (1748-1825), The Father's Revenge (tragedy) (London). Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (1759-1805), Fiesco (Fiesko) (Die Verschworung des Fiesco zu Genua) (Hoftheater, Bonn). Poetry: William Blake (1757-1827), Poetical Sketches (debut); all written before age 21. William Cowper (1731-1800), The Diverting History of John Gilpin. George Crabbe (1754-1832), The Village (Suffolk). Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749-1832), Das Gottliche (Göttliche); mentions the "great eternal iron laws". Sir William Jones (1746-94) (tr.), Mu'allqat (7 Arabic poems). Novels: Thomas Day (1748-89), The History of Sandford and Merton (3 vols.) (1783-9); popular children's books emphasizing Rousseau's educational ideals. August von Kotzebue (1761-1819), Die Jungsten Kinder Meiner Laune (6 vols.) (1783-96). Willem Leevend (1724-85) and Rhijnvis Feith (1753-1824), Julia; clone of Goethe's "Werther". Births: Swedish historian-poet-hymn composer Erik Gustaf Geijer (d. 1847) on Jan. 12 in Ransater, Varmland; collaborator of Arvid Azfelius (1785-1871). French "The Charterhouse of Parma", "The Red and the Black" realist novelist Stendhal (Marie-Henri Beyle) (d. 1842) on Jan. 23 in Grenoble; his alias comes from Stendal, Germany, home of his hero Johann Joachim Winckelmann; dedicates his works to "the Happy Few". Am. Colgate Co. founder (Presbyterian) William Colgate (d. 1857) on Jan. 25 in Hollingbourne, Kent; starts out as a soap and candle maker; emigrates to the U.S. in 1798; father of Robert Colgate (1812-85), James Boorman Colgate (1818-1904), and Samuel Colgate (1822-97). German grand duke (1828-53) Karl Friedrich (Charles Frederick) of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (d. 1853) on Feb. 2 in Weimar; eldest son of Grand Duke Karl August (1757-1828) and Luise Auguste of Hesse-Darmstadt. Belgian geologist Jean Baptiste Julien d'Omalius d'Halloy (d. 1875) on Feb. 16 in Liege. Am. First Lady-not Hannah Hoes Van Buren (d. 1819) on Mar. 8 in Kinderhook, N.Y.; wife (1807-19) of U.S. pres. Martin Van Buren. Am. "The Legend of Sleepy Hollow", "Rip Van Winkle" writer Washington Irving (OE "sea friend") (d. 1859) on Apr. 3 in New York City; uses the alias Jonathan Oldstyle. Dutch queen (1806-10) Hortense Eugenie Cecile Bonaparte (nee de Beauharnais) (d. 1837) on Apr. 10; wife of Louis Bonaparte (1778-1846); mother of Napoleon III (1808-73). Am. Mormon witness Martin Harris (d. 1875) on May 18 in Easton, N.Y. Swiss historian Johann Konrad Hottinger (d. 1860) on May 18 in Zurich; great-grandson of Johann Heinrich Hottinger (1620-67). English physicist (inventor of the electromagnet, galvanometer, and DC motor with commutator) William Sturgeon (d. 1850) on May 22 in Whittington, Lancashire. U.S. Supreme Court justice #24 (1836-41) Philip Pendleton Barbour (d. 1841) on May 25 in Frascati (near Gordonsville), Va.; brother of James Barbour (1775-1842). Am. "Washington Crossing the Delaware" portraitist Thomas Sully (d. 1872) on June 8 in Horncastle, Lincolnshire, England; emigrates to Charleston, S.C. in 1792. German economist (founder of economic geography) Johann Heinrich von Thunen (Thünen) (d. 1850) on June 24 in Canarienhausen, Wangerland, Friesland. South American soldier-statesman ("the Liberator of South America") (El Libertador) (Freemason) Simon Bolivar (Simón Bolívar) (Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar Palacios Ponte y Blanco) (d. 1830) on July 24 in Caracas; raised as a wealthy orphan in Venezuela, then moves to Europe during the time of the French Rev. and Napoleon before moving back to South Am. and becoming a cream-rises-to-the-top unflappable native-born Spanish liberator from did-I-say Caracas. British princess Amelia "Emily" (d. 1810) on Aug. 7 in the Royal Lodge, Windsor; 15th child and youngest daughter of George III and Charlotte of Mecklenburg. Italian Neoclassical sculptor Pompeo Marchesi (d. 1858) on Aug. 7 in Saltrio (near Milan); student of Antonio Canova (1757-1822); teacher of Giosue Argenti (1819-1901). Am. celeb Theodosia Burr Alston (d. 1813) on June 21; daughter of Aaron Burr and Theodosia Bartow Prevost; wife (1801-) of S.C. gov. Joseph Alston; mother of Aaron Burr Alston (1802-12). Am. War of 1812 naval officer Samuel Chester Reid (d. 1861) on Aug. 24 in Norwich, Conn. Am. businessman ("the Ice King of Boston") Frederic Tudor (d. 1864) on Sept. 4 in Boston, Mass.; 3rd son of William Tudor; brother of William Tudor (1779-1830). Mexican emperor (1822-3) Agustin (Agustín) de Iturbide (Agustin Cosme Damian de Iturbide y Aramburu) (d. 1824) on Sept. 27 in Valladolid (Morelia), Michoacan; noble Spanish father, Mexican mother; designer of the Mexican flag. English Birmingham School economist-reformer Thomas Attwood (d. 1856) on Oct. 6 in Hawne House, Halesowen, Shropshire; not to be confused with composer Thomas Attwood (1765-1838). French Bell-Magendie Law physiologist Francois Magendie (d. 1855) on Oct. 6 in Bordeaux; a notorious vivisector; describes the foramen of Magendie, the Magendie sign, and the concept of empty calories; rival of Sir Charles Bell (1774-1842). German Orientalist-traveler Julius Heinrich Klaproth (d. 1835) on Oct. 11 in Berlin; son of Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1743-1817). Am. gen. Henry Leavenworth (d. 1834) on Dec. 10 in New Haven, Conn.; grows up in Danville, Vt.; father of Jesse Henry Leavenworth (1807-85). Italian patriot poet Giovanni Berchet (d. 1851) on Dec. 23 in Milan. U.S. Navy Capt. (Episcopalian) Thomas Macdonough Jr. (d. 1825) on Dec. 31 in The Trap, MacDonough (near Odessa), New Castle County, Del.; son of Maj. Thomas McDonough Sr. Swedish liberal leader Carl Henrik, Greve Anckarsvard (Anckarsvärd) (d. 1865). Deaths: Swiss writer Johann Jakob Bodmer (b. 1698) on Jan. 2 in Zurich. German composer Johann Adolph Hasse (b. 1699) on Dec. 16 in Venice. Japanese poet Yokai Yagu (b. 1702). Swiss #1 mathematician Leonhard Euler (b. 1707) on Sept. 18 (Sept. 7 Old Style) in St. Petersburg, Russia (brain hemorrhage); last words: "I am dying"; died blind but still productive; his complete works total 92 vols., most in history (until ?). Irish-born Am. historian-trader James Adair (b. 1709). Italian castrato opera singer Caffarelli (b. 1710) on Jan. 31 in Naples. English #1 landscape designer Lancelot "Capability" Brown (b. 1716) on Feb. 6. French encyclopedist Jean le Rond d'Alembert (b. 1717) on Oct. 29; buried in a common unmarked grave since he was an unbeliever. Am. Boston pastor Samuel Cooper (b. 1725) on Dec. 29. Am. Rev. statesman James Otis Jr. (b. 1725) on May 23 in Andover, Mass.; killed by lightning while standing in an interior doorway of a farmhouse - the original Otis elevator? Am. Rev. War. maj.-gen. William Alexander, Lord Stirling (b. 1726). Irish-born British lt. gen. Sir Eyre Coote (b. 1726) on Apr. 28 in Madras, India; a monument to him is erected in Westminster Abbey. French author Louis Florence d'Epinay (b. 1726) on Apr. 17 in Paris. Spanish Catalan composer Antonio Soler (b. 1729). French mathematician Etienne Bezout (b. 1730) on Sept. 27 in Basses-Loges (near Fontainebleau). Russian statesman Count Grigory Orlov (b. 1734); dies insane. English statesman John Spencer, 1st Earl Spencer (b. 1734) on Oct. 31. English giant Charles Byrne (b. 1761); he requests that his body be put in a lead coffin and buried in the English Channel, but surgeon Dr. John Hunter pays off the undertaker and steals it, and his 7'7" skeleton of charled byrnes ends up housed in the Museum of the College of Surgeons. British prince Octavius (b. 1779) on May 3 in Windsor; dies of a smallpox inoculation; last British royal to suffer from smallpox (until ?); his death combined with that of Prince Alfred in 1780 freaks out George III, who begins hallucinating about them.


































1784 On Jan. 6 Turkey and Russia sign the Treaty of Constantinople, annexing the Crimea to Russia; from now until the 2nd Balkan War in 1913 5M-7M Muslims are forcibly displaced into the Ottoman Empire. On Jan. 14 the (Second) Treaty of Paris, "In the name of the most holy and undivided Trinity, Amen" (signed Sept. 3, 1783) is ratified by the U.S. Congress, effective May 12 after the British ratify it on Apr. 9, ending the Am. Rev. War (begun Apr. 19, 1775) (9 years, 23 days); total Am. war deaths: 6.8K KIA, 17K killed by disease, 25K-70K total killed; total British daths: 9,372 KIA, 27K killed by disease, 43,833 total killed; France: 7K KIA; Spain: 5K KIA; Germany: 1.8K KIA, 4,888 deserted, 7,774 total killed; Netherlands: 37K-82.5K KIA, 500 civilians killed; British loyalists: 1.7K KIA, 5,300 killed by disease, 7K total killed; total soldiers KIA: 78.2K. On Jan. 15 Sir William Jones (1746-94), a supreme court judge in Ft. William, Bengal founds the Asiatic (Asiatick) Society to study Sanskrit and further research on Asia, going on to pub. the journal Asiatick Researches. In Jan. Benjamin Franklin pub. the pamphlet Information to Those Who Would Remove to America (written in Passy, France) in English and French, telling Europeans that America wants "mediocre" (middle-class) immigrants. On Feb. 28 John Wesley (1703-91) (picking a good time for it, since what American would want to continue with the church headed by King George III?) issues the Deed of Declaration in Baltimore, Md., establishing Methodism as a separate denomination from the Anglicans under the name Methodist Episcopal Church (until 1939), with leaders designated by Wesley, incl. bishop Francis Asbury (1745-1816) and itinerant evangelist Charles Atmore (1759-1826); freed slave Richard Allen (1760-1831) is ordained at the first conference of the church, but after experiencing racial prejudice he decides to form a separate Methodist Free African Society in Apr. 1787, followed in 1792 by the African Episcopal Church of St. Thomas in Philly, the first black Episcopal church in the U.S., which in 1816 becomes the African Methodist Episcopal Church; on Nov. 24 Samuel Seabury (1729-96) of Conn. becomes the first Am. Anglican (Episcopal) bishop consecrated by Scottish bishops; meanwhile Britain appoints the first Anglican bishop for the British colonies. On Mar. 1 the R.I. Emancipation Act declares all children born in R.I. from this date henceforth free, but doesn't prohibit the slave trade; later this year Conn. joins Penn., Mass., and N.H. in abolishing slavery. . On Mar. 11 the Second Anglo-Mysore War (begun 1782) ends with the Treaty of Mangalore, with both sides agreeing to restore the others' territories to the pre-war status quo. On Apr. 14 after being declared of legal age, and staging a coup involving a fistfight with his half-uncle Prince Frederick (regent since Jan. 1772), Frederick VI (1768-1839) takes the regency over his insane father Christian VII until his Mar. 13, 1808 death, instituting liberal and agricultural reforms. On Apr. 15 Maximilian Frederick of Konigsegg-Rothenfels (b. 1708) dies, and Austrian archduke Maximilian Franz (1756-1801), 16th and last child of Empress Maria Theresa and HRE Francis I, and brother of Marie Antoinette is appointed archbishop-elector of Cologne (until 1794), with seat in Bonn, helping elect his brother Leopold II in 1790, and giving young Ludwig van Beethoven his musical ed.; in 1791 because his daddy Ludwig Sr. is kappelmeister, he is rumored to be a grandmaster of the mysterious Priory of Sion too, woo woo woo. On June 22 after Adam Weishaupt sends plans for a French Rev. to Maximilien Robespierre in Paris, but the courier is intercepted by the Bavarian authorities, freaking them out, Bavarian elector Karl Theodor suppresses the Order of the Illuminati, along with Freemasonry, imprisoning members and forcing the rest to flee, incl. Adam Weishaupt, causing the Illuminati Order to spread to the U.S., where Thomas Jefferson defends Weishaupt as an "enthusiastic philanthropist"; secret financier Mayer Amschel Rothschild buys off the authorities to avoid prosecution; the flood of anti-Illuminati lit. spawns the modern Conspiracy Theory Movement? In Apr. N.C. votes to give the Confed. Congress 29M acres between the Allegheny (Appalachian) Mts. and the Mississippi River; on Aug. 23 the pissed-off Watauga settlers declare the state of Franklin (Frankland) in modern-day Tenn. (ends Dec. 1788) on lands W of the Appalachians ceded by N.C. to the U.S. govt., with Jean Sevier (1745-1815) (veteran of the 1780 Battle of King's Mountain) as gov. #1 (last) (1785-8), and William Cocke (1747-1828) as its rep. to Congress; after being forced to abandon his claims to Boonesboro because of faulty titles, Daniel Boone explores the Appalachian and Ozark areas, and helps found the state - you must have a dirty mind? On June 4 French opera singer Madame Marie Elisabeth Thible of Lyon becomes the first woman to fly in a hot-air balloon, the Gustave, rising to 8.5K ft. (2,591m) (45 min.) - how cool is that? On Aug. 13 William Pitt's India Act gives the British crown the power to guide Indian politics - who's the biggest celebrity in the world, but is he ready to leave? In Aug. Thomas Jefferson (appointed in May) joins Benjamin Franklin and John Adams in Paris; to rumors that he arrived to replace Franklin, Jefferson replies, "No one can replace him, Sir; I am only his successor." On Sept. 15 crowd-pleasing "daredevil aeronaut" Vincenzo Lunardi (-1806) of Lucca, Tuscany makes the first balloon ascent in England in front of a crowd incl. the Prince of Wales, taking a dog, cat, and pigeon with him as he travels 24 mi.; on Nov. 23, 1785 he wows Glasgow, Scotland. On Sept. 21 the Penn. Packet and Gen. Advertiser, founded by Irish-born John Dunlap (1747-1812) begins pub. in Philly, becoming the first successful daily newspaper in the U.S. On Sept. 22 the Russians under Grigori Shelekov settle Kodiak (Kikhtak) Island in Alaska. In Oct. the 300-ton Boston, Mass. ship Betsy is attacked 100 mi. off the W coast of Africa by Muslims, and the sailors are sent to slave markets in Morocco. On Nov. 30 Richard Henry Lee (1732-94) becomes pres. #6 of the United States Congress under the Articles of Confederation (until Nov. 6, 1785). Thomas Jefferson's land ordinance is passed. HRE Joseph II abrogates the Hungarian constitution, suppressing feudal rights; Buda becomes the capital of Hungary, replacing Bratislava, capital since 1541. Serfdom is abolished in Denmark. A hat tax for hat sellers of 5 shillings is imposed in England, rising to Ł2 in London, with the death penalty for forging a hat tax license; it is abolished in 1811. Benjamin Franklin is appointed by Louis XVI to a commission to investigate the theories of Friedrich Anton Mesmer, who is a big fad in Paris, replacing ballooning as #1; the commission concludes that Mesmer is a fraud. 26-y.-o. Capt. Horatio Nelson, who saw battle service in the West Indies in 1780, then was chosen to instruct the Prince of Wales in naval tactics and sent to France to study naval strategy is given command of the British frigate HMS Boreas, stationed in Antigua, West Indies. Am. surveyors David Rittenhouse (1732-96) and Andrew Ellicott (1754-1820) finish surveying the Mason-Dixon Line to SW Penn., 5 deg. of longitude from the Delaware River; the 1769 Mason-Dixon line is extended to settle the boundary between Penn. and Va. (later W. Va.). After meeting Great White Fathers Washington and Jefferson, wowed chief Cornplanter (1750-1836) of the Iroquois Confederation signs the Treaty of Ft. Stanwix, handing over all their land W of the Niagara River to the U.S. - plant in peace, palefaces? Loyalist gen. Sir John Johnson is assigned by the British govt. to distribute crown lands along the St. Lawrence River and N shore of Lake Ontario to loyalists, going on to settle 3,776 of the loyal pluckers. To reward them for siding with the British in the Am. Rev. War, Mohawk Chief Joseph Brant and the Six Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy settle in the Six Nations of the Grand River Reservation 12 mi. from Brantford (modern-day pop. 97K/134K) (founded May 31, 1877), the seat of Brant County, Ont., 26 mi. SW of Hamilton on the Grand River; it later becomes famous as the location of the first successful test of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell at his father's home Melville House, causing it to become known as "the Telephone City", later becoming the birthplace of NHL hockey star Wayne Gretzky. French philosopher-Orientalist Constantin Francois de Chasseboeuf, Comte de Volney (1757-1820) (born Boisgiras, thenchanging his name to Volney = Voltaire + Ferney) visits Palestine, and after leaving Nablus arrived "at a town, which... presents a striking example of the vicissitudes of human affairs, when we behold its walls levelled, its ditches filled up, and all its buildings embarrassed by ruins, we scarcely can believe we view that celebrated metropolis, which, formely, withstood the efforts of the most powerful empires... In a word, we with difficulty recognize Jerusalem"; he goes on to conduct the first scientific survey of Jerusalem, noting the huge profits made by the Ottomans from the stupidity of the Christian factions by playing them off against each other, and how few pilgrims come to the city from Europe. Robert Burns' father dies bankrupt, and Robert and his brother Gilbert rent Mossgiel Farm near Mauchline; meanwhile he discovers the vernacular works of Scottish poet Robert Fergusson, and starts churning out his own poems, producing most of his best-known ones in the next two years. Japanese seaman Chunosuke Matsuyama is wrecked with 44 shipmates (who all die of starvation) on a Pacific coral reef; before dying, he carves an account of their tragedy on a piece of wood, seals it in a bottle, and throws it into the sea, and it is found in 1935 at the seaside village where he was born? The Boston Society of New Jerusalem is founded after members hear a lecture on Emanuel Swedenborg; after moving to Beacon Hill in 1845, it becomes known as the Church on the Hill (Swedenborgian). Valentin Hauy (Haüy) (1745-1822) is given the job of interpreter to the blind for Louis XVI, and with Austrian pianist Maria Theresa von Paradis (1759-1824) founds the first school for the blind in Paris. Madame Necker opens Necker Hospital in Paris, which survives to modern times as a children's hospital. The North-West Co. is formed by French fur merchants from Montreal, led by Isaac Todd to compete with Hudson's Bay Co. German immigrant John (Johann) Jacob Astor (1763-1848) arrives in New York City with $25 in cash and seven flutes, and enters the fur trade, dealing directly with Indians, accumulating a $200K fortune from the ignorant red suckas in six years, then going on to become America's richest man - I'll tell you the story when the kiddies retire? The Boston Sentinel is founded in Boston, Mass. by Maj. Bursell. English artist Thomas Rowlandson (1756-1827) draws the first political cartoons, when he isn't cranking out erotica. Italian composer Giovanni Paisiello (d. 1816) becomes court conductor to Ferdinand IV of Naples (until 1802), where he cranks out even more good operas than in freezing Russia. The French musical society Les Concerts de la Loge Olympique requests Franz Joseph Haydn to compose six symphonies, which become so popular that three more are requested. The earliest recorded mention of Merlot (Fr. "young blackbird") wine is made by an official in Bordeaux, France. The Le Grand Vefour (Véfour) restaurant is opened in the Palais-Royal in Paris by Antoine Aubertot, becoming the first grand restaurant in Paris; in 1820 it is purchased by Jean Vefour, who retires in 1823, selling it to Jean Boissier; it goes on to become the #1 Paris restaurant, introducing Mornay Sauce, closing in 1905. The Ailanthus altissima AKA the Tree of Heaven (Chin. "chouchun" = stinking tree), first imported to Europe from N and C China in the 1740s is brought to the U.S., turning into an invasive species, gaining the nicknames Tree of Hell, Stink Tree, and Ghetto Palm. Architecture: Pope Pius VI builds a new Appian Way from Rome to Albano, parallel to the old. The Sacristy of St. Peter's Basilica, by Carlo Marchionni is added, and the work originally planned by Pope Nicholas V in the 15th cent. is finally complete after nearly 350 years? John Nash begins the Brighton Pavilion for the Prince Regent (Prinny of the ever-expanding waistline) (finished 1827). The Emerald Buddha Chapel in Bangkok is officially opened on Mar. 22 by Rama I of Thailand to house the Emerald Buddha. Inventions: Aime (Aimé) Argand (1755-1803) of Switzerland designs the oil-burning Argand Lamp, whose single circular wick in a hollow cylinder emits as much light as seven candles; a reflector is later placed behind it. On Aug. 21 Joseph Bramah (1748-1814) of England patents a pickproof barrel-shaped safety lock with 494M possible combinations, which is not picked until 1851, despite a 200 guinea prize, by Am. locksmith Alfred Charles Hobbes, who takes a month to do it; in 1773 Bramah, a Yorkshire farmer's son walked 170 mi. to London to seek his fortune. The Puddling Pocess of ironmaking, invented by Henry Cort (1740-1800) of England goes into production; rolled rods and bars are now being produced. Benjamin Franklin announces the invention of bifocal eyeglasses ("double spectacles") in Aug.; "I have only to move my eyes up or down.... to see distinctly far or near." Robert March invents a rope-spinning machine. Scottish millwright Andrew Meikle (1719-1811) invents a threshing machine. French mathematician-engineer Gen. Jean Baptiste Marie Charles Meusnier (1754-93), known for his 1776 Meusnier's Theorem develops the first propeller-driven and elliptically-shaped balloon; the crew cranks three propellers on a common shaft, and the craft reaches a speed of 3 mph, and can be kinda maneuvered. Scottish-born William Murdock (Murdoch) (1754-1839), foreman of James Watt's and Matthew Boulton's Soho Engineering Works constructs a small working model of a steam road locomotive, but is not encouraged to build a full-size model; he switches to gas lighting in the 1790s, and invents the term "gasometer" for large ambient pressure containers of natural gas. James Ramsey invents a steam-driven motorboat, and demonstrates it on the Potomac River, witnessed by George Washington - hand me a silver dollar? English artillery officer Maj.-Gen. Henry Shrapnel (1761-1842) invents the Shrapnel Shell. Josiah Spode Sr. (1733-97) of Stoke-on-Trent, England perfects the blue glaze underprinting (transfer printing) process for china. The first Model Helicopter is flown in France by naturalist Christian de Launoy and mechanic ? Bienvenu, powered by a tightly-wound cord. Science: London-born English mathematician George Atwood (1745-1807) accurately determines the acceleration of a free-falling body; he also invents a machine to illustrate the effects of Newton's First Law of Motion. Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749-1832) of Germany discovers that the human intermaxillary bone has a similar structure to that in apes, foreshadowing comparative morphology - while who was giving whom head? On Sept. 10 English astronomer Edward Pigott (1753-1825) detects the variability of Eta Aquilae, becoming the first known Cepheid Variable; in Dec. his neighbor and friend John Goodricke (1764-86) discovers the variability of star Delta Cephei in the Cepheus ("king") constellation; too bad, he contracts pneumonia from the effort, and soon dies. French mineralogist Abbe Rene Just Hauy (Haüy) (1743-1822) of the U. of Paris proposes the Law of Rational Indices, that the regular form of crystals is caused by a regular internal arrangement of tiny cubes or polyhedra ("molecules integrantes"); 174 years later (1958) an electron microscope confirms his model. Nonfiction: Miss Hannah Adams (1755-1831), Alphabetical Compendium of the Various Sects Which Have Appeared in the World from the Beginning of the Christian Era to the Present Day; launches her career as the first prof. female writer in the U.S. Rene Just Hauy (1743-1822), Essai d'une Theorie sur la Structure des Crystaux. Johann Gottfried von Herder (1744-1803), Ideas for a Philosophy of History of Mankind (Ideen zur Philosophie der Geschichte der Menschheit) (4 vols.) (1784-91); explores the central ideas of nationalism, starting with the existence of a nation that has a unique claim to be considered a legitimate political basis for sovereignty, concluding that they must speak the same language; "Has a people anything dearer than the speech of its fathers? In its speech resides its whole thought-domain, its tradition, history, religion, and basis of life, all its heart and soul. To deprive a people of its speech is to deprive it of its one eternal good... As God tolerates all the different languages in the world, so also should a ruler not only tolerate but honor the various languages of his peoples... The best culture of a people cannot be expressed through a foreign language; it thrives on the soil of a nation most beautifully, and, I may say, it thrives only by means of the nation's inherited and inheritable dialect. With language is created the heart of a people; and is it not a high concern, amongst so many peoples—Hungarians, Slavs, Rumanians, etc to plant seeds of well-being for the far future and in the way hat is dearest and most appropriate to them?" - get to Golden Pond before the lake dries up? Immanuel Kant (1724-1804), Idea for a Universal History from a Cosmopolitan Point of View. William Mitford (1744-1827), The History of Greece (5 vols.) (1784-1810); by a friend of Edward Gibbon in the South Hampshire Militia, who suggested the idea; he never visits Greece. Jacques-Henri Bernardin de Saint-Pierre (1737-1814), Etudes de la Nature. Antonio de Ulloa (1716-95), Relacion Historica del Viaje a la America Meridional; scientific description of South Am. Music: Andre Gretry (1741-1813), Richard Coeur de Lion (opera comique) (Paris) (Oct. 21); libretto by Michel-Jean Sedaine; his masterpiece?; Richard I of England is rescued from captivity by his troubadour Blondel de Nesle. Antonio Salieri (1750-1825), Les Danaides (opera) (Paris). Art: Francisco de Goya (1746-1828), Don Manuel de Zuniga. Sir Joshua Reynolds (1723-92), Mrs. Siddons as the Tragic Muse. Plays: Pierre-Augustin Caron de Beaumarchais (1732-99), Le Mariage de Figaro (The Marriage of Figaro); plebeians and aristocrats unite against an oversexed nobleman. George Colman the Younger (1762-1836), Two to One; his first hit. Rhyijnvis Feith (1753-1824), Thirsci (tragedy); The Patriots. Jean-Francois de La Harpe (1739-1803), Coriolan. Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (1759-1805), Intrigue and Love (Kabale und Liebe) (Mannheim). Novels: Aagje Deken (1741-1804) and Betje Wolff (1738-1804), Historie van den Heer Willem Leevend. Births: French sculptor Francois Rude (d. 1855) on Jan. 4 in Dijon; step-father of Paul Cabet (1815-76); teacher of Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux (1827-75). Am. "The Old Oaken Bucket" poet-playwright Samuel T. Woodworth (d. 1842) on Jan. 13 in Scituate, Mass. English Peelite PM (1852-5) George Hamilton-Gordon, 4th Earl of Aberdeen (d. 1860 (AKA Lord Haddo) on Jan. 28 Edinburgh, Scotland; educated at St. John's College, Cambridge U. Am. Mormon leader John Alpheus Cutler (d. 1864) on Feb. 29 in Plainfield, N.H. German neoclassical Greek revival architect-painter-writer Franz Karl Leopold (Leo) von Klenze (d. 1864) on Feb. 29 in Buchladen (near Schladen). English scientist-mathematician (inventor of the Wheatstone Bridge) Samuel Hunter Christie (d. 1865) on Mar. 22; educated at Trinity College, Cambridge U. Hungarian philologist-orientalist Alexander Csoma de Koros (Sandor Korosi Csoma) (d. 1842) on Mar. 27 in Kodos, Transylvania (Chiurus, Romania). Spanish rev. gen. Rafael del Riego Nunez (Nuńez) (d. 1823) on Apr. 2 in Santa Maria de Tuna, Asturias. German "Jessonda" composer-violinist-conductor (Freemason) Louis (Ludwig) Spohr (d. 1859) on Apr. 5 in Braunschweig; inventor of the baton for conducting, the violin chin rest, and rehearsal letters on sheet music. German Prussian field marshal (1856-) Count Friedrich Heinrich Ernst "Papa" von Wrangel (d. 1877) on Apr. 13 in Stettin, Pomerania. U.S. Supreme Court justice #27 (1841-60) Peter Vivian Daniel (d. 1860) on Apr. 24 in Stafford Count, Va.; educated at Princeton U. British Chartist leader John Frost (d. 1877) on May 25 in Newport, Monmouthshire. French chef ("King of Chefs and Chef of Kings") (inventor of haute cuisine, the chef's hat or toque blanche) Marie-Antoine (Antonin) Careme (Caręme) (d. 1833) on June 8 in Paris. French Canadian trapper Jacques La Ramie (Ramee) (Ramée) (d. 1821) on June 8 in Quebec, British Canada; brother of Joseph La Ramie; namesake of the Laramie River and Laramie, Wyo. German mathematician-astronomer (inventor of Bessel Functions) Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (d. 1846) on July 22 in Minden, Prussia. Am. "Dictionary of the English Language" lexicographer Joseph Emerson Worcester (d. 1865) on Aug. 24 in Bedford, N.H.; educated at Yale U.; main competitor of Webster's Dictionary. British gov.-gen. of India (1836-42) George Eden, 1st Earl of Auckland (d. 1849) on Aug. 25 in Beckenham, Kent; son of William Eden, 1st baron Auckland (1745-1814); brother of William Eden (1782-1810); created earl in 1838. German Nazarene painter Peter von Cornelius (d. 1867) on Sept. 23 in Dusseldorf. French mathematician (Roman Catholic) Baron Pierre Charles Francois Dupin (d. 1873) on Oct. 6 in Varzy; created baron in 1824. Am. Unitarian clergyman (leader in bringing German Higher Criticism to the U.S.) Joseph Stevens Buckminster (d. 1812) on Oct. 14 in Portsmouth, N.H.; educated at Harvard U.; teacher at Phillips Exeter Academy until 1804, then pastor of Brattle Street Church in Boston, finishing up as lecturer in Biblical criticism at Harvard U. in 1811 - and after that don't ask? Spanish Bourbon king #5 (1808, 1813-33) Ferdinand VII (d. 1833) on Oct. 14 in San Lorenzo de El Escorial; brother of pretender Don Carlos Maria (1788-1855); father of Isabella II (1830-1914). Am. "Toplady" hymn tune writer Thomas Hastings (d. 1872) on Oct. 15 in Washington, Conn. Uruguayan gen. Jose Fructuoso Rivera y Toscana (d. 1854) on Oct. 17 in Durazno. English "Story of Rimini" poet-writer James Henry Leigh Hunt (d. 1859) on Oct. 19 in Southgate, London; Am. Loyalist parents. Am. Hudson's Bay Co. dir. (1824-46) John (Jean-Baptiste) McLoughlin (d. 1857) on Oct. 19 in Riviere-du-Loup, Quebec, Canada. English fashionplate poet PM (1855-65) Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston (d. 1865) (AKA Pam) on Oct. 20 in Broadlands, Hampshire near Romsey, Hants, England; educated at Harrow School, and St. John's College, Cambridge U.; known for flip-flopping between Whig and Tory sentiments - the Bill Clinton of 19th cent. England? British 6'3" Zionist financier-philanthropist (Jewish) Sir Moses Haim Montefiore, 1st Baronet (d. 1885) on Oct. 24 in Leghorn (Livorno), Italy; knighted in 1938; created baronet in 1846. Am. printer Robert Hoe (d. 1833) on Oct. 29 in Leicestershire, England; emigrates to the U.S. in 1803; inventor of the Hoe press; first to use steam as motive power in a U.S. plant; father of Richard March Hoe (1812-86). U.S. pres. #12 (1849-50) and brig. gen. ("Old Rough and Ready") Zachary Taylor (d. 1850) on Nov. 24 in Montebello, Orange County, Va.; first pres. born after the Am. Rev.; son of Richard Taylor, later collector of the port of Louisville, Ky., and Sarah Strother; 2nd cousin of pres. #4 James Madison - and great-great-great grandfather of Sheriff Andy Taylor of Mayberry? Scottish poet-writer Allan Cunningham (Gael. "village of the milk pail") (d. 1842) on Dec. 7 in Keir Parish (near Dalwsinton), Dumfriesshire, Scotland; father is a neighbor of Robert Burns; moves to London as a journalist in 1810. German actor Ludwig Devrient (d. 1832) on Dec. 15 in Berlin; most popular actor of his time, noted for playing Shakespeare and Schiller. Am. explorer Stephen Harriman Long (d. 1864) on Dec. 30 in Hopkinton, N.H.; educated at artmouth College. Spanish royalist gen. Joaquin Ibanez (Joaquín Ibáńez), Baron de Eroles (d. 1825) in Tlarn, Catalonia. Italian physicist Leopoldo Nobili (d. 1835) in Trassilico, Garfagnana. English-born Am. stage actor-mgr. Edmund Simpson (d. 1848). British army col. Michael Childers (d. 1854); great-uncle of Hugh Childers (1827-96). Am. warden Capt. Elam Lynds (d. 1855) in Litchfield, Conn.; grows up in Troy, N.Y. Am. Restoration Movement leader John "Raccoon" Smith (d. 1868) in Sullivan, Tenn.; grows up in Clinton County, Ky. Deaths: English writer Dr. Samuel Johnson (b. 1709) on Dec. 13 in London; buried in Westminster Abbey; a monument to him is later placed in St. Paul's Cathedral; last words: "I am about to die." Am. Rev. War gen. Josiah Quincy Sr. (b. 1710) on Mar. 3 in Quincy, Mass. German composer Wilhelm Friedemann Bach (b. 1710) on July 1 in Berlin; dies in poverty. Euro mystery man Comte de Saint Germain (b. 1712) on Feb. 27 in Altona, Schleswig; Theosophists later claim that he is the immortal Wandering Jew and an Ascended Master, the resurrected Sir Francis Bacon et al. French "Encyclopedie" philosopher Denis Diderot (b. 1713) on July 31 in Paris (emphysema and dropsy); leaves Lettres sur les Sourds et Muets; "Man will never be free until the last king is strangled with the entrails of the last priest"; "There are little testicles at the bottom of our most subline feelings and our purest tenderness." Scottish painter Allan Ramsay (b. 1713). Spanish missionary Father Junipero Serra (b. 1713) on Aug. 28 in Mission San Carlos Borromeo de Carmelo (Carme-by-the-Seal), Calif. Japanese poet-painter Yosa Buson (b. 1716) on Dec. 25 in Kyoto. Spanish gov. of Guatemala (1779-83) and New Spain viceroy (since Apr. 29, 1783) Matias de Galvez y Gallardo (b. 1717) on Nov. 3 in Mexico City, Mexico. Spanish gov. of Calif. (1775-82) Felipe de Neve (b. 1724) in Coahuila, Mexico. Am. Rev. leader (DOI signer) Caesar Rodney (b. 1728) on June 26 in St. Jones Hundred, Kent County, Del. Danish naturalist Otto Friedrich Mueller (b. 1730) on Dec. 26. Am. loyalist "Considerations on the Present State of Virginia" loyalist John Randolph (b. 1733) on Jan. 31 in Brompton, London; buried at the College of William and Mary. Swedish chemist Torbern Olaf Bergman (b. 1735) on July 8 in Medevi. English-born Am. Shaker founder Mother Ann Lee (b. 1736). Dutch Patriots leader Baron Joan van der Capellen tot den Pol (b. 1741) on June 6 in Zwolle.




































1785 On Jan. 1 John Walter (1739-1812) founds The Daily Universal Register in London, England, concentrating on ads in competition with eight other newspapers; on Jan. 1, 1788 he changes its name to The Times, and branches into scandals and gossip whiile striving to record the views of the London elite, launching a trend of naming newspapers some variant of Times; Times Roman typeface is developed to be legible despite low-tech printing, switching in Nov. 2006 to Times Modern; in 2004 it switches from broadsheet to compact formats, escept The Sunday Times; in Dec. 2016 it has a daily circ. of 446K, 792K for The Sunday Times; on June 6, 2006 it launches a U.S. ed.; it becomes a favorite of libraries, with its detailed index insuring popularity with researchers. On Jan. 7 the English Channel is first crossed (Dover to Calais) in a hot air balloon by Dr. John Jeffries (1745-1819) of Boston, Mass. and Jean-Pierre Francois Blanchard (1753-1809) of France (who made his first successful ascent on Mar. 2, 1784, a few mo. after Rozier on Nov. 21, 1783), entering the 18th cent. space race); Blanchard latter gives the first successful demonstration of a parachute by dropping a dog in a basket hooked to one; they have to ditch their ballast equipment and clothing to keep from landing in the water. On Jan. 21 the U.S. signs the Treaty of Fort McIntosh with the Cherokee, Wyandot, Chippewa (Ojibwe), Delaware (Lenape), and Ottawa (Odawa) at Ft. McIntosh, ceding modern-day Ohio to the U.S. and other Indians in exchange for fair payment (what color baubles do you prefer?); the Continental Congress passes the Land Ordinance of 1785 for the orderly settling of the Northwest Territory (Ohio, Ind., Mich., Ill., Wisc.); it divides all land won during the war into 640-acre (1 sq. mi.) sections and offers it for sale for $1 an acre; 36 sections comprise a township, and within each township one section is set aside to support public schools; Mass. delegate Rufus King (1755-1827) introduces a resolution prohibiting slavery in the Northwest Territory, which is incorporated in the Ordinance of 1787. In Jan. the New York Manumission Society in Long Island, N.Y. is founded by white mainly wealthy Quaker men to promote abolition (until 1849), with John Jay as pres. and Alexander Hamilton as secy. In Jan. U.S. ships Dauphin and Maria are captured by Muslim Algerian pirates, who parade the 21 crewman to their leader the dey, who spits on them and says "Now I have you, you Christian dogs - you shall eat stones"; this action becomes one of the driving reasons for adopting the U.S. Constitution on Mar. 4, 1789, according to Thomas Bailey. In Feb. the Diamond Necklace Affair in Versailles, France causes Cardinal (French Marshal) (Grand Almoner) Charles de Rohan, Prince de Soubise (1715-87) to be arrested for conspiring to steal a 2,842-carat diamond necklace once ordered by Louis XV for Madame du Barry (he dies before its completion); you see, Rohan's mistress Countess de La Motte has a smart hubby, and after Rohan fell into disfavor with the royal court and Queen Marie Antoinette refused to buy the necklace, he put his wife up to telling Rohan that the queen is secretly in love with him and feed him fake letters; after he bites, she dressed Mme. Olivia (a whore who resembles her) up as her and arranged a meeting with him last July in the Versailles Palace garden to make him think they have a thing, and the ho asks him to buy the necklace for her on a promise to pay him later; on Feb. 1 the dope signs a note for 1.6M livres with Parisian jewelers Boehmer and Bassenge, and is then duped into giving it to a man claiming to be the queen's valet, after which Count de la Motte and the necklace disappear, leaving Rohan and the Countess holding the bag and unable to pay the jewelers, who take his note to the police, getting them arrested two weeks later; on May 31, 1786 Rohan is acquitted, the Countess sentenced to be scourged, branded and imprisoned for life, and her hubby sentenced to death in absentia; she later blows, er, escapes from prison and flees to England; even though Marie Antoinette is innocent of any knowledge of the swindle, the numerous porno drawings of her having sex with famous handsome lothario Count Hans Axel von Fersen the Younger (1755-1810) (son of Count Axel von Fersen the Elder), herself and other women that the left has been circulating, combined with her extravagant lifestyle makes everyone think that "Madame Deficit" really did screw the Cardinal to lose his money, and contributes to her becoming "the most hated woman in France". On Mar. 10 Thomas Jefferson is appointed minister to France, succeeding Benjamin Franklin (1706-90), who prepares to return from France, where he has resided since 1776; "I succeed him, but can never replace him"; John Adams becomes U.S. envoy to London (resigns 1788); in Mar. Jefferson and Adams visit Tripoli's ambassador to London Sidi Haji Abdrahaman (Abdul Rahman) Adja, and ask him by what right the Barbary states prey upon American shipping, enslaving both crews and passengers, and next Mar. 28 they write a letter to U.S. foreign affairs minister John Jay, with the soundbyte: "We took the liberty to make some enquiries concerning the ground of their pretensions to make war upon nations who had done them no injury, and observed that we considered all mankind as our friends who had done us no wrong, nor had given us any provocation. The Ambassador answered us that it was founded on the laws of their prophet [Mohammed]; that it was written in their Koran; that all nations who should not have acknowledged their authority were sinners; that it was their right and duty to make war upon them wherever they could be found, and to make slaves of all they could take as prisoners; and that every Mussulman [Muslims] who was slain in battle was sure to go to Paradise." "We took the liberty to make some inquiries concerning the Grounds of their pretensions to make war upon a Nation who had done them no Injury, and observed that we considered all mankind as our Friends who had done us no wrong, nor had given us any provocation. The Ambassador answered us that it was founded on the Laws of their Prophet, that it was written in their Koran, that all nations who should not have acknowledged their authority were sinners, that it was their right and duty to make war upon them wherever they could be found, and to make slaves of all they could take as Prisoners, and that every Musselman who should be slain in Battle was sure to go to Paradise. He said, also, that the man who was the first to board a vessel had one slave over and above his share, and that when they sprang to the deck of an enemy's ship, every sailor held a dagger in each hand and a third in his mouth; which usually struck such terror into the foe that they cried out for quarter at once"; Barbary pirates seize U.S. ships and imprison their crews in Algiers for 11 years while the U.S. negotiates for their release - the Muslim World gave the U.S. fair warning of the treachery of U.S. presidents Obama et al., and they didn't take it? In Mar. commissioners from Va. and Md. meet at the Mount Vernon Conference to settle differences about the navigation of the Potomac River and Chesapeake Bay, which leads to plans for all thirteen states to send delegates to a yearly convention in Annapolis beginning next Sept. On Apr. 14 William Whitehead (b. 1715) dies, and Thomas Wain Warton (1728-90) becomes poet laureate of England. On May 26 former La. gov. Bernardo de Galvez y Madrid arrives in Veracruz, Mexico as new viceroy of Spain to replace his father Matias de Galvez y Gallardo, who died last Nov. 3; too bad, on Aug. 27 a great freeze occurs, leading to a famine, followed by a plague next year, for which he donates 12K pesos from his inheritance and raises 100K more; he goes on to install street lights in Mexico City and build a highway to Acapulco while curbing abuses of Indian labor, then dedicates 16% of income from the Mexican lottery to charity; too bad, the audiencia grows jealous of his popularity, believing that he wants to declare independence of New Spain, but he solves their problems by dying on Nov. 8, 1786 after they get the crown to rebuke him, causing him to grow despondent (poisoned?). On June 1 farmer's son and former hanging list header John Adams meets with George III, telling him how they should now be friends because they share a common language and blood - sugar sugar lip balm? On June 15 Jean Francois Pilatre de Rozier, dying to be elected to the Academie des Sciences attempts to duplicate Blanchard's and Jeffries' feat of flying in a balloon across the English Channel, but unfortunately decides to use two balloons, one containing hot air and the other hydrogen; at 1.7K ft. the hydrogen bag ignites, and Rozier and his assistant drop to their deaths - welcome to now? On June 20 James Madison (1751-1836) delivers the speech Memorial and Remonstrance Against Religious Assessments to the Va. legislature against a bill "establishing a provision of teachers of the Christian religion", giving eight reasons incl. "1. Because we hold it for a fundamental and undeniable truth, that religion or the duty which we owe to our Creator and the manner of discharging it, can be directed only by reason and conviction, not by force or violence"; "5. Because the Bill implies either that the Civil Magistrate is a competent Judge of Religious Truth; or that he may employ Religion as an engine of Civil policy. The first is an arrogant pretension falsified by the contradictory opinions of Rulers in all ages, and throughout the world: the second an unhallowed perversion of the means of salvation"; "15. Because finally, the equal right of every citizen to the free exercise of his religion according to the dictates of conscience is held by the same tenure with all our other rights. If we recur to its origin, it is equally the gift of nature; if we weigh its importance, it cannot be less dear to us; if we consult the Declaration of Rights which pertain to the good people of Virginia, as the basic and foundation of government, it is enumerated with equal solemnity, or rather studied emphasis." On July 4 the first Fourth of July Parade (a prayerful walk) is held in Bristol, R.I. by Am. Rev. War veteran Rev. Henry Wright of the First Congregational Church; by the next cent. festivities begin on June 14 (Flag Day) and end on July 4 with a 2.5-mi. parade; John Adams gets pissed-off when all his work to get the independence movement going is upstaged by a single document written at his request by slaveholding Johnny-come-lately Thomas Jefferson? - you have no idea I'm down here, you can't even hear me can ya, oh I pulled a muscle, it's probably in my neck? On July 6 the Continental (Confederation) Congress adopts the name Dollar for the "money unit of the United States of America", to be divided on the decimal system into smaller units; next year Congress specifies the definition of the cent and the dime (from the French dixieme); the U.S. becomes the 1st country to use decimal currency. On July 12 Benjamin Franklin leaves Passy, then travels to the port of Le Havre, France in Queen Marie Antoinette's personal enclosed litter borne by Spanish mules; leaving Southampton on July 27, he uses his ocean voyage to do scientific experiments, arriving in Philly in Sept. to hunker down in gouty retirement. On July 17 France limits the importation of goods from Britain. On July 23 Frederick II the Great of Prussia forms Die Furstenbund (League of German Princes) against HRE Joseph II. On Aug. 9 the first recorded Chinese on the East Coast of the U.S. are brought by the ship Pallas. On Sept. 10 Prussia and the U.S. sign a Treaty of Amity and Commerce. On Nov. 23 John Hancock is elected pres. #7 of the U.S. Congress under the Articles of Confederation (2nd time); Penn.-born historian David Ramsay (1749-1815) becomes acting pres. (until May 12, 1786). On Dec. 15 Prince George of Wales (later George IV) marries twice-widowed Roman Catholic sweet cheeks Maria Anne Fitzherbert (1756-1837); lucky for him, the marriage is invalid under the 1772 Royal Marriages Act, else he would be disinherited from the crown, so she is officially treated like merde by the snob establishment, and he goes on to marry bluebood Protestant 1st cousin Caroline of Brunswick in 1795, but still hooks up with sweet cheeks now and then; after he gets Caroline to to marry him by presenting her with a miniature painting of his right, er, eye, she gets Richard Coway to paint her right eye for him around Xmas, starting the Lover's Eyes Fad in London, which spreads through Europe, peaking in the 1810s; meanwhile English actress Dorothea "Dorothy" Jordan (1761-1819) hooks up with him, bearing at least 10 illegitimate children by him with the surname FitzClarence; he also hooks up with Mrs. Robinson, an actress who made her name playing Perdita in Shakespeare's "A Winter's Tale", causing him to be called Prince Florizel. Wilhelm I of Kassel becomes King Wilhelm IX. Warren Hastings resigns as gov.-gen. of India and returns to England. HRE Joseph II unsucessfully tries to add Bavaria to his Austrian dominions by diplomacy. The Charter of the Nobility (Cities) is issued in Russia by Catherine II the Great, becoming the Magna Charta of the nobles, guaranteeing the nobles the right to trial by their peers, freedom from corporal punishment, compulsory military duty, poll tax et al. The Russians settle the Aleutian Islands. French naval officer Jean-Francois de Galoup, Comte de La Perouse (Pérouse) (1741-88) leads a royal French expedition to the Pacific in the ships Bustamove and Asshole, er, Astrolabe and Boussole, carrying specialists in the sciences, and visits the Hawaiian islands, Macao, Philippines, Japan, Kamchatka, and Korea, discovering the La Perouse (Soya) Strait between S Sakhalin Island and Yezo (Ezo) (Yesso) (Hokkaido); in Samoa they encounter hostile natives, losing the capt. and 11 crew of the Astrolabe; they then head for the Solomons (ends 1788); in 1786 La Perouse lands near Makena Beach on the S end of the Hawaiian island of Maui and discovers and maps La Perouse Bay, during which time Haleakala erupts for the last time in modern history. Up-and-coming Corsican-born Napoleon Bonaparte (b. 1769) joins the French army. Harvard grad. James Bowdoin II (1726-90), son of rich merchant James Bowdoin I (1676-1747), and pres. #1 of the Am. Academy of Arts and Sciences becomes gov. #2 of Mass. (until 1787), with becoming the U.S. pres. in his sights; too bad, his heavy-handed quashing of Shays' Rebellion causes him to lose his reelection, and his TB soon kills him - I knew Jack Kennedy, senator, and you're no Jack Kennedy? "Hill town" Bristol, Conn., 18 mi. SW of Hartford splits off from Farmington. Thomas Paine receives $3K from Congress and a confiscated royalist farm in New Rochelle from the state of N.Y. in return for his services to the Am. Rev. cause - Congress gives him nada? The Dukhobors (Dukhobortsy) (Russ. "spirit wrestlers") peasant religious sect in Russia is kicked out of the Russian Orthodox Church; named disparagingly by priests to describe them as fighting against the spirit of God, they at first take to the name, then later call themselves Christians of the Universal Brotherhood, teaching that all humans are equal brothers, and refusing to acknowledge any wordly ruler or participate in military service - Russian Jehovah's Witnesses? The pietist Harmony Society is founded in Iptigen, Germany, experiencing persecution by the Lutheran Church and causing them to emigrates to the U.S. in 1804. Greenville County, S.C. is founded in honor of Gen. Nathanael Greene, who goes on to live on his own plantation near Savannah, Ga. until he dies of heat stroke in 1786. Scottish philanthropist Thomas Douglas, 4th Earl of Selkirk (1771-1820) receives a 116K-sq.-mi. grant on the Red River from the Hudson's Bay Co., and goes on to establish posts at Ft. Carlton, Ft. Cumberland, and Edmonton House on the Saskatchewan River. Galveston, Tex. is founded by Spanish explorer Jose Antonio de Evia (1740-?) in honor of La. gov. Bernardo de Galvez y Madrid; the first Euro settlement is begun in 1816 by pirate Louis-Michel Aury (1788-1821) as a base to support the Mexican rebellion against Spain, after which pirate Jean Lafitte takes it over in 1817. The Royal Philippine Co. is established, and required to invest 4% of its earnings in the development of the Philippine economy in return for internat. trading rights that are so extensive that its ships seldom visit the Philippines after 1789, concentrating on Latin Am. trade. Robinson Crusoe translator Joachim Heinrich Campe (1746-1818) launches educational reforms in Brunswick, Germany. Queen Mary U. of London is founded as London Hospital Medical College, renamed after Queen consort Mary of Teck (1867-1953) and admitted to the U. of London in 1915, going on to merge in 1989 with Westfield College, and marge again in 1995 with St. Bartholomew's Hospital Medical College and London Hospital Medical College. Seven immigrant loyalist graduates of Harvard and King's College found the U. of New Brunswick in Saint John, New Brunswick, becoming the oldest English-language univ. in Canada. It is decided to move the stinking Cemetery of the Innocents in Paris to the limestone quarries S of the city, taking two stinking years. In Sweden the first Illis Quorum Meruere Labores (For Those Whose Works Have Deserved It) gold medal is awarded by Gustavus III; Greta Garbo later receives one. French Jansenist-educated mainly porno writer Nicolas-Edme Restif (Rétif) (1734-1806) coins the word "communism" in a review of a book by Joseph-Alexandre Hupay de Fuveau, announcing his Project for a Philosophical Community. The Augusta Chronicle weekly newspaper is founded in Augusta, Ga., becoming known for coverage of the Masters Tournament, reaching a modern-day circ. of 55K daily and 71K Sun.; on Aug. 9, 2017 it is announced that it will be sold to GateHouse Media along with 10 other daily newspapers for $120M. The Poughkeepsie Journal is founded in Dutchess County, Poughkeepsie, N.Y.; in 1788 its ed. becomes the official reporter of the ratification of the U.S. Constitution; during the Franklin D. Roosevelt admin. it serves as the launchpoint for stories by FDR from his estate in nearby Hyde Park; it goes on to become the oldest paper in N.Y. James Watt and Matthew Boulton install a rotary steam engine in a cotton-spinning factory in Papplewick, Nottinghamshire, England. Noah Webster sums up the weakness of the current confederate U.S. govt.: "Our pretended union is but a name, and our confederation is a cobweb." Aging skirt-chaser Jacques (Giacomo) Casanova (1725-98) becomes a semi-retired librarian working for Count Ferdinand Ernst Joseph Gabriel von Waldstein und Wartenberg (1762-1823), (Beethoven's first patron in Bonn) in the Chateau de Dux until death, dying quietly at the job - while doing things in the library stacks? Rev. James Wilmot (1726-1808) of Warwickshire, England claims that well-situated Francis Bacon (1561-1626) was the real author of Shakespeare's plays - the original lone gunman theory? Robert Burns gives his mother's domestic helper Betty (Elizabeth) Paton a daughter, and his mother takes it in; meanwhile he courts and impregnates Jean Armour (1765-1834), daughter of a local building contractor - do you like music, that sweet soul music? Budweiser Budvar Brewery is founded in Ceske Budejovice, S Bohemia, producing a beer that makes the town famous. Architecture: Wadsworth House is built by U.S. Gen. Peleg Wadsworth (1748-1829) with bricks shipped from Philadelphia by his grandfather, becoming the first brick house in Portland, Maine (487 Congress St.); his grandson poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow later lives there. Inventions: On May 9 Joseph Bramah of England patents the hydraulic beer pump handle (beer engine), allowing kegs to be stored beneath the bar in the cool cool basement. Oliver Evans (1755-1819) of the U.S. invents an automatic grist mill. Dutch scientist Martinus Von Marum (1750-1837) discovers ozone in electrical discharges. David Rittenhouse of Penn. makes the first diffraction grating using 50 hairs at a spacing of 100 lines per in. The first practical sewing machine is invented by Thomas Saint in England. George Washington's dentist (former Am. Rev. scout) John Greenwood (1760-1819) helps raise public awareness about porcelain teeth; George Washington's teeth, which he makes in 1798 are made from hippo tusks, animal, and human teeth, but no wooden teeth, although other people at the time wear them? - I wouldn't want to go to a dentist with bad wooden teeth? English philosopher Jeremy Bentham proposes the Panopticon, a prison designed to allow one guard to see all the prisoners without being seen; after talking Parliament into it, the king refuses to pay for it in 1811, and in 1813 he is awarded Ł23K in damages. Science: Comte Claude Louis Berthollet (1748-1822), who was appointed supt. of dyeing processes for the French govt. the year before discovers methane and ethylene, and invents chemical bleaching using chlorine, joining the ranks of those backing Antoine Lavoisier's anti-phlogiston theory, although not going for his idea that oxygen is the fundamental acidifying principle. French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb (1736-1806) discovers Coulomb's Law of electrical forces. D. Domenico Salsano of Naples develops a seismograph for detecting earthquakes. English physician William Withering (1741-99) introduces the use of digitalis (obtained from the seeds and leaves of the purple foxglove, Digitalis purpurea) in heart therapy. Nonfiction: James Boswell (1740-95), Journal of a Tour to the Hebrides; his 1773 trip with Dr. Johnson. James Hutton (1726-97), Theory of the Earth; or An Investigation of the Laws Observable in the Composition, Dissolution, and Restoration of Land Upon the Globe; incl. "Theory of Rain"; founds the modern science of geology with its presentation of the Bible-bashing principle of uniformitarianism, an Earth with "no vestige of a beginning - no prospect for an end"; too bad, it's too technical to obtain gen. acceptance until John Playfair popularizes it in 1802 - no end maybe, but it could have been created and had a beginning? Immanuel Kant (1724-1804), Foundations (Groundwork) (First Principles) of the Metaphysics of Morals (Ethics); presents the concept of the Categorical Imperative, which tells us which actions are obligatory and which forbidden, all without mean old Jehovah and his Bible? August von Kotzebue (1761-1819), Die Leiden der Ortenbergischen Familie. White racism starts out as white colorism? Christoph Meiners (1747-1810), Outline of the History of Mankind (Grundriß der Geschichte der Menschheit ); divices humanity according to beauty, from the "beautiful white race" to the "ugly black race", praising the Celts as the noblest race, and Slavs and Native Ams. as inferior races. William Paley (1743-1805), Principles of Moral and Political Philosophy; utilitarian ethical theory. David Ramsay (1749-1815), The History of the Revolution of South Carolina, from a British Province to an Independent State (2 vols.). Thomas Reid (1710-96), Essays on the Intellectual Powers of Man; big hit with Arthur Schopenhauer. Nicolas-Edme Restif (1734-1806), Les Nuits de Paris (1786-92); reports of events in Paris incl. the September Massacres of 1792. Sir Charles Wilkins (1749-1836) (tr.), The Bhagavat-Geeta, or Dialogues of Kreeshna and Arjoon; first English trans., wowing Westerners and spreading Orientalism Fever. Music: Franz Joseph Haydn (1732-1809), Quartet No. 35 in D minor, Op. 42. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756-91), Piano Concerto No. 21 in C major, K.467 (Mar. 9); the 2nd movement is featured in the 1967 Swedish film Elvira Madigan, and gains that name; Six Haydn String Quartets, Op. 10; incl. String Quartet in G major, K.387, String Quartet in D minor, K421, String Quartet in E flat major, K.428, String Quartet in B flat major ("Hunt"), K.458, String Quartet in A major, K.464, String Quartet in C major ("Dissonances"), K.465; composed after hearing Franz Josef Haydn's quartets for the first time and getting turned on, then spending two years figuring out how to do it, causing Haydn to tell Mozart's daddy Leopold "I tell you before God as an honest man that your son is the greatest composer known to man either in person or by reputation. He has taste and, what is more, the most profound knowledge of composition." Art: Jacques-Louis David (1748-1825), The Oath of the Horatii. Thomas Gainsborough (1727-88), Mrs. Sarah Siddons. Jean-Antoine Houdon (1741-1828), George Washington (sculpture) (1785-8); made after being invited to visit Mount Vernon by Benjamin Franklin; his clay life models and plaster life mask are reused for years by Am. artists; his family thinks it's his best likeness - looks like Hollywood actor Karl Malden (1912-)? Charles Wilsson Peale (1741-1827), Benjamin Franklin; shows him wearing his new "double spectacles". Sir Joshua Reynolds (1723-92), The Infant Hercules. Poetry: William Blake (1757-1827), An Island in the Moon (unpub.). William Cowper (1731-1800), The Task. George Crabbe (1754-1832), The Newspaper. Rev. Timothy Dwight (1752-1817), The Conquest of Canaan; first Am. epic poem. Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart (1739-91), Complete Poems (2 vols.) (1785-6); Sturm und Drang; incl. "Die Forelle", set to music by Franz Schubert in 1817; composed while imprisoned in Hohenasperg Fortress near Stuttgart (1777-87). Ann Yearsley (1753-1806), Poems on Several Occasions; pub. under the name Lactilia after Hannah More raises money for her, earning her Ł600, but More tries to put it in a trust for her to keep it from Ann's husband, causing her to accuse her of stealing, after which she releases the money and leaves London and its nutcase lit. set, settling in Cowslip Green in Somerset and going into Puritanical religious writing, enjoying a big readership of women who let her get away with her anything-goes style. Novels: Willem Leevend and Rhyijnvis Feith (1753-1824), Ferdinand en Constantia; another Werther novel. August von Kotzebue (1761-1819), Die Leiden der Ortenbergischen Familie. Nicolas-Edme Restif (1734-1806), Ingenue Saxancour. Marquis de Sade (1740-1814), The 120 Days of Sodom; or, The School of Libertinism; four wealthy male libertines are into orgies in an inaccessible castle in Saint-Martin-de-Belleville with a harem of male and female victims along with four female brother keepers, who tell X-rates stories while they sexually abuse and torture the victims, ending with their murders; not pub. until the 20th cent. Births: German "Grimm's Fairy Tales" philologist-folklorist Jacob Ludwig Carl Grimm (d. 1863) on Jan. 4 in Hanau, Hesse-Kassel; brother of Wilhelm Grimm (1786-1859); educated at the U. of Marburg. German electrolysis chemist Christian Johann Dietrich Theodor von Grotthuss (d. 1822) on Jan. 20 in Leipzig. English physician-chemist William Prout (d. 1850) on Jan. 15 in Horton, Gloucestershire; educated at Edinburgh U.; coiner of the term "convection"; author of Prout's Hypothesis that all atoms are made of hydrogen and their weights are exact multiples of its weight; namesake of the proton and the Prout unit of nuclear binding energy - close but no seegar? French Law of Dulong and Petit chemist-physicist Pierre Louis Dulong (d. 1838) on Feb. 12 in Rouen. Italian "The Betrothed" Romantic poet-dramatist-novelist Alessandro Francesco Tommaso Antonio Manzoni (d. 1873) (whose portrait bears a striking resemblance to Hollywood actor Sylvester Stallone (1946-)?) on Mar. 7 in Milan; starts out as a rationalist skeptic then in 1809-10 flops into a devout Roman Catholic patriot along with his Calvinist wife. U.S. Supreme Court Justice #21 (1829-61) (Methodist) John McLean (d. 1861) on Mar. 11 in Morris County, N.J.; grows up in Ridgeville, Warren County, Ohio; educated at Harvard U. English geologist Adam Sedgwick (d. 1873) on Mar. 22. French king (1793-5) (in title only) Louis XVII (Charles de Bourbon) (d. 1795) on Mar. 27 in Versailles; 2nd son of Louis XVI (1754-93) and Marie Antoinette (1755-93). Am. naturalist, bird watcher and artist ("the American Woodsman") John James Audubon (d. 1851) on Apr. 26 in Les Cayes (Santo Domingo), Haiti; illegitimate son of a French sea captain and a Creole servant girl, his mother dies shortly after giving birth, and he is taken to France and raised by his stepmother, where he tryies to hide his swarthy origins by claiming to be born on May 4, 1780 in New Orleans; at 18 he is sent to a family-owned estate in Penn. German Draisienne inventor Karl Freiherr von Drais (Karl Friedrich Christian Ludwig Freiherr Drais von Sauerbronn) (d. 1851) on Apr. 29 in Karlsruhe. Scottish poet-writer-critic John Wilson (d. 1854) (AKA Christopher North) on May 18 in Paisley; lives in an estate on Lake Windermere, associating with the Lake Poets. English botanist Sir William Jackson Hooker (d. 1865) on July 6 in Norwich; knighted in 1836. Am. writer-diplomat-activist (Jewish) Mordecai Manuel Noah (d. 1851) on July 14 in Philadelphia, Penn. Scottish "Journal of a Residence in India" writer Maria Graham (nee Dundas) (Maria, Lady Callcott) (d. 1842) on July 19 near Cockermouth, Cumberland; daughter of Adm. George Dundas (1756-1814). Ottoman sultan #30 (1808-39) Mahmud (Mahmoud) II (d. 1839) on July 20; son of Abdul Hamid I (1725-89); father of Abdul Mecid I (1823-61). English opium-eating writer Thomas de Quincey (d. 1859) on Aug. 15 in Manchester, Lancashire; educated at Worcester College, Oxford U., where he picks up the habit. Am. clock manufacturer Seth Thomas (d. 1859) on Aug. 19 in Wolcott, Conn. Am. surgeon Valentine Mott (d. 1865) on Aug. 20 in Glen Cove, N.Y.; educated at Columbia U.; founder of New York U. Medical College. Am. "We have met the enemy and they are ours" naval commodore Oliver Hazard Perry (d. 1819) on Aug. 23; son of Capt. Christopher Raymond Perry (1760-1818); brother of Matthew Calbraith Perry (1794-1858). Peruvian pres #10 (1829-33) and #14 (1838-41) Agustin (Agustín) Gamarra Messia (d. 1841) on Aug. 27 in Cusco; mixed Spanish-Quechua ancestry. Italian Romantic painter Giovanni Migliari (d. 1837) on Oct. 5 in Alessandria. Swedish writer-pastor Arvid August Afzelius (d. 1871) on Oct. 8 in Enkoping (Enköping). English "Nightmare Abbey" novelist-poet Thomas Love Peacock (d. 1866) on Oct. 18 in Weymouth, Dorset; collaborator of Erik Gustaf Geijer (1783-1847); friend of Percy Bysshe Shelley. German Biedermeier painter Georg Friedrich Kersting (d. 1847) on Oct. 31 in Gustrow, Mecklenburg-Schwerin. English novelist Lady Caroline Lamb (nee Ponsonby) (d. 1828) on Nov. 13; wife of William Lamb, 2nd viscount Melbourne (1779-1848); has famous love affair with Lord Byron in 1812. Scottish genre painter Sir David Wilkie (d. 1841) on Nov. 18 in Fifeshire; godfather of Wilkie Collins (1824-89). German classical scholar-antiquarian Philipp August Bockh (d. 1867) on Nov. 24 in Karlsruhe. Irish "History of the War in the Peninsula" historian Gen. Sir William Francis Patrick Napier (d. 1860) on Dec. 7 in Celbridge (near Dublin); 3rd son of Col. George Napier (1751-1804); brother of Sir Charles Napier (1782-1853), Sir George Napier (1784-1855), and Capt. Henry Napier (1789-1855); grandfather of Philip Napier Miles (1865-1935); knighted in 1848. Zulu chief (1816-28) (black) Shaka Zulu (d. 1828); son of chief Senzangakona (-1816) and Nandi of the Langeni (-1827); half-brother of Singukana. French-Canadian fur trapper Etienne (Étienne) Provost (Provot) (Proveau) (d. 1850) in Chambly, Quebec, Canada. English chemist Edmund Davy (d. 1857). English civil engineer Sir William Cubitt (d. 1861) in Norfolk. Deaths: English Georgia founder Gen. James Oglethorpe (b. 1696) on June 30 in Cranham, Essex. Viennese painter Pietro Longhi (b. 1701) on May 8. Viennese composer Baldassare Galuppi (b. 1706) on Jan. 3. Am. Rev. leader (DOI signer) Stephen Hopkins (b. 1707) on July 13 in Providence, R.I. Am. Rev. patriot "Brother" Jonathan Trumbull Sr. (b. 1710) on Aug. 17 in Lebanon, Conn. French philosopher-historian-diplomat Abbe de Mably (b. 1709) on Apr. 2 in Paris; leaves Des Droits et des Devoirs du Citoyen (The Rights and Duties of a Citizen) (1789) (written in 1758); advocates the abolition of private property, and argues for the equality of needs not just legal rights, criticizing idless and claiming that virtue is more important than acquisition of wealth, helping launch Socialism and Communism. English actress Kitty Clive (b. 1711) on Dec. 6 in Twickenham; dies in a villa donated by her friend Horace Walpole. French statesman Cesar Gabriel de Choiseul, duc de Praslin (b. 1712) on Nov. 15. French mathematician Jean Paul de Gua de Malves (b. 1713) on June 2. French sculptor Jean Baptiste Pigalle (b. 1714) on Aug. 28. English aristocrat Margaret Cavendish Bentinck, duchess of Portland (b. 1715) on July 17 in Bulstrode Park, Buckinghamshire; leaves the largest natural history collection in Britain. English poet laureate (1757-85) William Whitehead (b. 1715) on Apr. 14; "In short, 'twas that provoking charm/ Of Caelia altogether". English politician-soldier George Germain, 1st Viscount Sackville (b. 1716) on Aug. 26. French statesman Etienne Francois, Duke of Choiseul (b. 1719) on May 8 in Paris. Dutch novelist Willem Leevend (b. 1724). French duke Louis Philippe I of Orleans (b. 1725) on Nov. 18. Italian artist Giovanni Battista Cipriani (b. 1727). Swiss-born English Methodist leader John Fletcher (b. 1729) on Aug. 14; dies before he can succeed John Wesley (d. 1791), who delivers a sermon on his death: "The error of rigid Calvinists centers in the denial of that ecclesiastical liberty, whereby all men, under various dispensations of grace, may without necessity choose life... The error of rigid Arminians consists in not paying a cheerful homage to redeeming grace, for all the liberty and power which we have to choose life, and to work righteousness since the fall.... To avoid these two extremes, we need only follow the Scripture-doctrine of free-will restored and assisted by free-grace." Am. DOI signer William Whipple Jr. (b. 1730) on Nov. 28 in Portsmouth, N.H. Jamaican-born British traveller-writer Elizabeth Marsh (b. 1735) in India (breast cancer). Polish-born Am. Rev. War financier Haym Salomon (b. 1740) in Philadelphia, Penn. Am. statesman Joseph Reed (b. 1741) on Mar. 5. Corsican atty.-politician Carlo Maria Buonaparte (b. 1746) on Feb. 24 in Montpellier, France (stomach cancer); father of Napoleon I, whom he leaves penniless. French balloonist Jean Francois Pilatre de Rozier (b. 1754) on June 15 near Wimereux, Pas-de-Calais (balloon crash).



























1786 On Jan. 16 the Religious Freedom Act of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison becomes law in Va., abolishing the state church and all religious tests; too bad, most other states keep their state churches, tests and all. On Jan. 3 the U.S. signs a treaty with the Chocktaw, on Jan. 10 with the Chickasaw, and on Jan. 31 with the Shawnee - who can say no to Great White Father Washington? On June 6 Mass.-born Nathaniel Gorham (1738-96) becomes pres. #8 of the United States under the Articles of Confederation (until Nov. 13, 1786). On June 8 Mr. Hall runs the first ads for commercially made ice cream in the U.S. in New York City. On July 4 Vermont (Vt.) adopts a constitution. On July 11 Morocco agrees to stop attacking U.S. ships in the Mediterranean for a jizya payment of $10K; on Aug. 18 after a debate about whether the U.S. should have a permanent navy to fight Muslim piracy instead of paying tribute, Thomas Jefferson writes to James Monroe: "The states must see the rod; perhaps it must be felt by some one of them... Every national citizen must wish to see an effective instrument of coercion, and should fear to see it on any other element than the water. A naval force can never endanger our liberties, nor occasion bloodshed; a land force would do both"; on Dec. 26 Jefferson writes to Ezra Stiles: "It will be more easy to raise ships and men to fight these pirates into reason, than money to bribe them." On July 29 the Pittsburgh Post-Gazette (originally the "Pittsburgh Gazette") is founded in Pittsburgh, Penn. by Joseph Hall and John Scull (1765-1828), becoming the first U.S. newspaper pub. W of the Allegheny Mts., starting out by pub. the new U.S. Constitution; in 1829-41 Neville Burgoyne Craig (1787-1863) becomes ed., backing the Anti-Masonic movement, turning it into an afternoon daily on July 30, 1833, then switching to morning in 1844 ater merging with the "Pittsburgh Post" (founded Sept. 10, 1842), backing the Whig Party before switching in the 1850s to the new Repub. Party., becoming one of the first papers to suggest that a civil war is coming; it goes on to win four Pulitzer Prizes, reaching a modern-day circ. of 173K daily and 317K on Sun. On Aug. 8 after a reward is offered by Swiss mountaineer Horace-Benedict de Saussure, 4,808m (15,774 ft.) Mont Blanc ("white mountain") near the French-Italian border, highest mountain in the Alps and W Europe is first ascended by Savoyards Jacques Balmat (1762-1834) and 3-time loser Michel-Gabriel Paccard (1757-1827), causing the king of Sardinia to give Balmat the title "le Mount Blanc", and the nearby town of Chamonix in E France to boom, launching modern mountaineering; on July 14, 1808 Marie Paradis (1778-1839) of Chamonix becomes the first female to reach the summit, along with Balmat, getting so sick that she begs to be thrown into a crevasse, but later becoming rich and famous, known as Mmaria de Mont Blanc; in 1838 Henriette d'Angeville (1794-1871) of Geneva becomes the 2nd woman to reach the summit, receiving congratulations from Paradis; by modern times it is ascended by 20K people/year. On Aug. 17 Prussian king (since 1740) Frederick II the Great (b. 1712) dies after uttering the famous last words: "I am tired of ruling over slaves"; he is succeeded by his handsome unmilitaristic artsy-fartsy nephew Frederick William II (1744-97), who ends his uncle's oppressive French system of taxation, lowers custom duties, removes his uncle's ban on the German language, admits German writers to the Prussian Academy, and other things that make him popular, but then appoints Rosicrucian Freemason mystic Johann Christof von Wollner (Wöllner) (1732-1800) (a professed orthodox Roman Catholic) as finance minister and de facto PM on Aug. 26, who gets kingy to begin a war against "enlighteners" and modernists. On Aug. 29 Capt. Daniel Shays (1747-1825) starts Shays' Rebellion in Mass. (ends June 1787) among disgruntled farmers, many of them Am. Rev. War vets, who were getting shafted economically by the merchant class when they had to pay a war tax in cash, and want to force the debtors' courts to close; as Thomas Jefferson puts it, "A little rebellion now and then is a good thing". In Aug. Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826), lonely since his wife (since 1772) Martha Wayles Skelton Jefferson (b. 1748) died in Sept. 1782 meets gorgeous married-to-a-twerp Italian-English artist-musician Maria Luisa Caterina Cecilia Cosway (nee Hadfield) (1760-1838), and they fall in love; one day he tries to impress her by jumping over a fence or a pool, and fractures his right wrist so badly that he has to learn to write with his left hand; too bad, he has to part with her on Oct. 4 as she leaves with her twerp hubby for Antwerp, after which he writes her a string of weird Jeffersonian love letters until he returns to Va. on Nov. 23, 1789 aboard the Clermont from Norfolk, Va. - all she can say is, he's not her kind? On Sept. 6 the Daily Hampshire Gazette is founded in Northampton, Mass. starting out with coverage of Shays' Rebellion. On Sept. 11-14 the Annapolis Convention in Md. at Mann's Tavern, called to develop uniform commercial regs among the states starts out limping when only five states send a total of 12 delegates, but Alexander Hamilton turns it into a success by getting a resolution passed to hold a constitutional convention in Philly next May to rewrite the Articles of Confederation "to render the constitution of the Federal Government adequate to the exigencies of the Union"; George Washington puts in his two cents regarding the confederate form of govt.: "We have, probably, had too good an opinion of human nature in forming our confederation." On Sept. 9 George Washington calls for the abolition of slavery. On Sept. 12 Lord Cornwallis is appointed gov.-gen. of India. On Sept. 24 he delivers his Am. black slave Jupiter Hammon (1711-1805) delivers Hammon's Address to the Negroes in the State of New York to the inaugural meeting of the African Society of New Yoork City, arguing for black slaves to be good Christians, with the soundbyte: "If we should ever get to Heaven, we shall find nobody to reproach us for being black, or for being slaves", and hoping for gradual emancipation, wishing that "the young negroes were free." On Sept. 26 France and Britain sign the Eden Treaty (a trade agreement) in London, negotiated by Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours, based on the principles of Adam Smith's "Wealth of Nations", ending the cent.-long economic war between the countries and substituting a system to reduce tariffs on both sides; too bad, it is so lopsided on the British side that it hurts the French economy, fomenting the French Rev.? Prussia recognizes the U.S. 300 former slaves are finally defeated at their fortified settlement in the Savannah River marshes. British Gen. Sir Guy Carleton (created 1st Baron Dorchester for his Am. Rev. War services) becomes gov. of Quebec (1786-91, 1793-96). Shogun (since 1760) Tokugawa Iyeharu (b. 1744) dies, and Tokugawa Iyenari (Ienari) (1773-1841) becomes shogun #11 of Japan (until 1837). The Tay Son army of Vietnam finally defeats the pesky Trinh army of N Vietnam, which flees to China, causing emperor Le Hien Tong to flee to China also, seeking aid to stage a comeback against the romantic never-slow-down-never-grow-old Tay Son brothers. The British East India Co. acquires Penang Island in the Malay Peninsula from the Rajah of Kedah; too bad it proves useless as a base. Sail away, sail away, sail away? The U.S. no longer welcoming British undesirables, the British govt. announces its plans to make Australia a penal colony. The King of England's Soldiers, The capital of Ga. is moved from Savannah to Augusta. The city of Dearborn, Mich. (modern-day pop. 98K) is settled by Europeans, named after U.S. Am. Rev. War. gen. Henry Dearborn (1751-1829); it becomes Dearborn Township in 1833, and Dearbornville village in 1836; in 1893 it is incorporated as a village, and in 1927 as a city, becoming the world HQ of the Ford Motor Co. The city of Knoxville, Tenn. (modern-day pop. 179K/868K) in the Tennessee Valley is settled by Rowan County, N.C.-born Am. Rev. War brig. gen. James White and James Connor, who build White's Fort; the city is incorporated in 1815; the arrival of the railroad in 1855 causes an economic boom. Mennonites from C Europe settle in Canada. Wool workers in Leeds complain about automation taking away their jobs. Marie-Augustin Marquis de Pelier of Brittany is arrested for whistling at Queen Marie Antoinette as she enters a theater, and spends the next 50 years in prison? Mohawk Chief Joseph Brant visits England, meeting prominent people and collecting funds which he uses to build the first Episcopal church in Upper Canada. Young Va. atty. John Marshall (b. 1755) distinguishes himself in the case of Hite v. Fairfax, in which he gets the claim of Lord Fairfax to the N neck of Va. upheld. James Wilkinson (1757-1825) purchases a 260-acre tract of land at Frank's Ford on the N side of the Kentucky River, which becomes Frankfort, Ky. Va. politician James Monroe (b. 1758) marries Elizabeth (Eliza) Kortright (1768-1830); they have no children. Francisco de Goya becomes a court painter for Charles III, working his way up to head painter by 1799, producing tapestry cartoons with candid views of everyday Spanish life, revolutionizing the tapestry industry, which up till then cloned Flemish scenes created by 17th cent. artist David Teniers. After outgrowing the Sturm und Drang stuff, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749-1832) begins a journey of Italy in a search for new principles, visiting several cities in N Italy then settling in Rome, remaining until 1788 while visiting Naples and Sicily on the side, discovering the classic spirit of balance and perfection which trumps emotion, and changing his style. Future U.S. presidents Thomas Jefferson and John Adams visit Stratford-upon-Avon, England, and chip off a piece of Shakespeare's chair as a souvenir. Internal gas lighting is attempted in Germany and England. Molson Brewery is founded outside Montreal, Canada by English-born Unitarian Freemason John Molson (1763-1836), going on to become the oldest brewery in North Am., and the 7th largest brewery in the world by 2005, when it merges with Coors to become the Molson Coors Brewing Co. Sports: The First Golf Club in Am. is founded in Charleston, S.C. Architecture: The Berlin Court Theater opens. The Paris Catacombs underneath Paris (created in 1738 when limestone is quarried) have their roofs strengthened after some parts of Paris begin to sink, and begin to be filled with bodies removed from other burial grounds incl. recently closed (1780) Saints-Innocents in nightly processions, eventually housing 6M, the bones arranged in varied designs along the sides of the galleries. Am. Renaissance man Charles Willson [two ls] Peale (1741-1827) founds the American Museum, the first museum of nat. history open to the gen. public in the U.S. in Philadelphia, Penn. next door to Independence Hall, opening on July 18. The rebuilt neoclassical Somerset House in The Strand, London overlooking the Thames River (begun 1776) is completed after 20 years by Scottish-born Chinese-traveled Sir William Chambers (1723-96) and his pupil Thomas Hardwick Jr. (1752-1825) - who will get a rose and who will leave broken-hearted, find out when The Bachelor continues? Inventions: Am. inventor John Fitch (1743-98) develops the first Screw-Propeller Steamboat, which he launches on the Delaware River next Aug. 22 for delegates of the Continental Congress. Am. inventor Ezekiel Reed of Bridgewater, Mass. invents a nail-making machine, but it doesn't lower nail costs enough to replace wooden pegs. Am. inventor James Rumsey (1743-92) invents the first mechanically-driven boat. Science: On Feb. 2 Westminster, London-born Anglo-Welsh hyperpolyglot linguist Sir William Jones (1746-94) delivers a famous speech in Calcutta to the Asiatic Society, claiming a common source for the Sanskrit, Persian, Greek, Latin, Celtic, and German languages, with the soundbyte: "The Sanskrit language, whatever be its antiquity, is of a wonderful structure; more perfect than the Greek, more copious than the Latin, and more exquisitely refined than either, yet bearing to both of them a stronger affinity, both in the roots of verbs and the forms of grammar, than could possibly have been produced by accident; so strong indeed, that no philologer could examine them all three, without believing them to have sprung from a common source, which, perhaps, no longer exists; there is a similar reason, though not quite so forcible, for supposing that both the Gothic and the Celtic, though blended with a very different idiom, had the same origin with the Sanskrit; and the old Persian might be added to the same family." Italian scientist Luigi Galvani (1737-98) discovers that nerves transmit electricity, and goes on in 1789 to experiment on the muscular contraction of dead frogs. Swiss mountaineer and French lt. gen. Franz Ludwig Pfyffer (1716-1802) constructs the first Relief Map, a 3-D model of the Lake Lucerne area after working on it for 24 years. German scientist Karl Wilhelm Scheele (1742-86) discovers hydrocyanic acid; he dies on May 21, and it's no surprise, since he tasted or sniffed all his chemical discoveries, most of which others get credit for, causing Isaac Asimov to call him "hard-luck Scheele"; he actually dies from long-term mercury poisoning? Nonfiction: Georges Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (1707-88), Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux. Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749-1832), Italian Journeys; "See Naples and die!" William Herschel (1738-1822), Catalogue of Nebulae. John Hunter (1728-93), A Treatise on Venereal Disease; describes chancre and lymphogranuloma venereum. William Playfair, Commercial and Political Atlas (London); contains the first Bar Chart. Henry Thrale (1724-81), Anecdotes of the Late Samuel Johnson (Mar. 26); based on the diary "Thraliana" of his wife Hester (1741-1821). Adam Weishaupt (1748-1830), Apologie der Illuminaten. Music: Charles Dibdin (1745-1814), Liberty Hall (opera) (Feb. 8) (Drury Lane Theatre, London); incl. "Jock Ratlin'", "The Highmettled Racer", "The Bells of Aberdovey". Ditters von Dittersdorf (1739-99), Doctor und Apotheker (comic opera) (Vienna). Franz Joseph Haydn (1732-1809), The "Bear" Symphony in C major, Op. 82. Sir William Jones (1746-94), The Sanscrit Language; Greek, Latin, and Sanskrit have a common root, and that goes ditto for Gothic, Celtic, and Persian. Vicente Martin y Soler (1754-1806), Una Cosa Rara (comic opera); libretto by Lorrenzo Da Ponte; based on Luis Velez de Guevara's play "La Luna de la Sierra"; introduces the waltz to Vienna; Il Burbero di Buon Cuore (comic opera); based on a play by Carlo Goldoni. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756-91), The Marriage of Figaro (K492) (opera) (Vienna) (May 1); teams with Jew-turned-Catholic librettist Abbe Lorenzo Da Ponte (1749-1838) for this, plus Don Giovanni and Cosi Fan Tutte; Cherubino sings "Non So Piu" to explain why he goes for maidens, although it is a "breeches" role, played by women. Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart (1739-91), Musikalische Rhapsodien (3 vols.). Art: Henry Fuseli (1741-1825), Titania and Bottom. Francisco de Goya (1746-1828), The Seasons (tapestries). John Hoppner (1758-1810), A Lady. Sir Joshua Reynolds (1723-92), The Duchess of Devonshire. Plays: John Burgoyne (1722-92), The Heiress; his greatest hit. Catherine II the Great (1729-96)), This It Is to Have Linen and Buck-Baskets; (Hermitage Theater, St. Petersburg); an adaptation of Shakespeare's "The Merry Wives of Windsor", written after reading Eschenburg's German translations of Shakespeare, becoming the first Russian play to credit Shakespeare's influence; she ends up writing four plays "in imitation of Shakespeare", incl. "Timon of Athens". George Colman the Younger (1762-1836) and Samuel Arnold (1740-1802), Turk and No Turk (musical comedy) (Little Theatre, Haymarket, London). Jean-Francois de La Harpe (1739-1803), Virginie. August von Kotzebue (1761-1819), Adelheid von Wulfingen. Poetry: Anon., The Anarchiad: A New England Poem (1786-7); by the Connecticut Wits. Gottfried Burger, Gedichte. Now I'm gonna love ya till the stars fall from the what? Robert Burns (1759-96) gives Jean Armour a marriage contract along with twins, but her father won't approve it, and Robert's mother takes in the babies; burdened with debt he resolves to emigrate to Jamaica as a bookkeeper, and to pay for his passage he pub. Poems Chiefly in the Scottish Dialect in Kilmarnock, Ayrshire on July 31, and its 612 copies sell out within a month, giving him instant fame, Edinburgh literati calling him the "Heavens-taught Ploughman", which pisses him off since he's not an untutored bard but just as good as them?; incl. To a Louse, To a Mouse ("The best laid schemes o'Mice an'Men/ Gang aft agley/ An' lea'e us nought but grief an' pain,/ For promis'd joy!"), To a Mountain Daisy, Hallowe'en, The Cotter's Saturday Night ("From scenes like these old Scotia's grandeur springs"), Holy Willie's Prayer; he adds 22 pieces for a new 1787 Edinburgh ed. by William Creech, which earns him Ł600, and he goes back to hooking up with with Jean Amour, who gives him another set of twins in the spring of 1787; he also fathers a couple more illegitimate children in Edinburgh. Hannah Cowley (1743-1809), The Scottish Village, or Pitcairne Green. Philip Morin Freneau (1752-1832), The Wild Honey Suckle; forerunner of the Transcendentalist movement. Hannah More (1745-1833), Bas-Bleu; Florio. Novels: William Thomas Beckford (1760-1844), Vathek; claims to write it in French in 3 days and 2 nights. Johann Musaus, Volksmarchen der Deutschen (fairy tales). John Trumbull (1750-1831), The Anarchiad (1786-7). Christoph Martin Wieland (1733-1813), Dschinnistan (1786-9); fairy tales, showing the triumph of rationalism over mysticism. Births: U.S. Supreme Court justice #26 (1837-65) John Catron (d. 1865) on Jan. 7 in Wythe County, Va. Am. financier (Quaker?) Nicholas Biddle (d. 1844) on Jan. 8 in Philadelphia, Penn.; ancestors immigrated with William Penn. French explorer rear adm. Louis Francois Marie Nicolas Le Goarant de Tromelin (d. 1867) on Jan. 11 in Morbihan, Gavrin. English historical painter-writer Benjamin Robert Haydon (d. 1846) on Jan. 26 in Plymouth. French mathematician-physicist-astronomer Jacques Philippe Marie Binet (d. 1856) on Feb. 2 in Rennes. German "Grimm's Fairy Tales" folklorist Wilhelm Carl Grimm (d. 1859) on Feb. 24 in Hanau, Hesse-Kassel; brother of Jakob Grimm (1785-1863); educated at the U. of Marburg. French physicist-astronomer and politician Francois Jean Dominique Arago (d. 1853) on Feb. 26 near Perpignan, Catalan. Polish nationalist historian Joachim Lelewel (d. 1861) on Mar. 22 in Warsaw; of Prussian descent. Italian astronomer-botanist-inventor Giovanni Battista Amici (d. 1863) on Mar. 25 in Modena; inventor of the direct vision prism. British brewer and MP (1818-37) (abolitionist) Sir Thomas Foxwell Buxton, 1st Baronet (d. 1845) on Apr. 1 in Castle Hedingham, Essex; Quaker mother; created baronet in 1840. U.S. Dem. vice-pres. #13 (1853) and U.S. Sen. (D-Ala.) (1819-44, 1848-52) William Rufus de Vane King (d. 1853) on Apr. 7 in Sampson County, N.C.; U.S. Sen. 1819-44, 1848-53; educated at the U. of N.C. English naturalist-explorer Rear Adm. Sir John Franklin (d. 1847) on Apr. 16 in Spilsby, Lincolnshire; knighted in 1829. Am. Pabst Brewing Co. founder Jacob Best Sr. (d. 1861) on May 1 in Mettenheim, Hesse-Darmstadt, Germany. German "Briefe aus Paris" Young Germany writer (Jewish-turned-Lutheran) Karl Ludwig Borne (Börne) (Loeb Baruch) (d. 1837) on May 6 in Frankfort-am-Main. Am. vulcanization and masticator inventor Thomas Hancock (d. 1865) on May 8 in Marlborough; brother of Walter Hancock (1799-1852). English actor-mgr. William Farren (d. 1861) on May 13 in London; son of William Farren (1725-). French liberal utilitarian economist Cahrles Dunoyer Barthelemy Charles Pierre Joseph Dunoyer de Segonzac (d. 1862) on May 20 in Carennac, Quercy (Lot); colleague of Auguste Comte. Am. abolitionist Arthur Tappan (d. 1865) on May 22 in Northampton, Mass.; brother of Lewis Tappan (1788-1873) and Benjamin Tappan (1773-1857). Am. statesman-diplomat Louis McLane (d. 1857) on May 28 in Smyrna, Del.; educated at the U. of Del. Am. gen. (Freemason) ("Fuss and Feathers") Winfield Scott (d. 1866) on June 13 near Petersburg, Va.; educated at the College of William and Mary. British Whig MP John Cam Hobhouse, 1st Baron Broughton (d. 1869) on June 27 in Redland (near Bristol); son of Sir Benjamin Hobhouse; educated at Westminster School and Cambridge U.; friend of Lord Byron (1788-1824); coiner of the phrase "His Majesty's Loyal Opposition" (1826). Am. frontiersman-politician David "Davy" Crockett (d. 1836) on Aug. 17 in Limestone, Greene County, N.C.; of French Huguenot (de Crocketagne) and Irish descent. Bavarian king (1825-48) Ludwig I (d. 1868) on Aug. 25 in Strasbourg; named after his godfather Louis XVI of France; son of Maximilian I (1756-1825) and Wilhelmine of Hesse-Darmstadt (1765-96); father of Maximilian II (1811-64). French fatty acid chemist Michel Eugene (Eugčne) Chevreul (d. 1889) on Aug. 31 in Angers. Danish Classical-Romantic Danish Golden Age composer Friedrich Daniel Rudolf Kuhlau (d. 1832) on Sept. 11 S of Luneburg, Lower Saxony, Gerany; loses right ice at age 7 from a slip on ice; emigrates to Denmark in 1810. French embryologist Antoine Etienne (Étienne) Renaud Augustin Serres (d. 1868) on Sept. 12 in Clairac. Danish king (1839-48) and Norwegian king (1814) Christian VIII (d. 1848) on Sept. 18 in Copenhagen; son of Prince Frederick of Denmark (1753-1805) and Sophia Frederica of Mecklenburg-Schwerin (1758-94). French-Canadian leader Louis Joseph Papineau (d. 1871) on Oct. 7 in Montreal, Quebec; son of Joseph Papineau (1752-1841); grandfather of Hneri Bourassa (1868-1952). Austrian Hapsburg gen. ("the Hapsburg Tiger") ("the Hyena of Brescia") ("the Hangman of Arad") Julius Jacob von Haynau (d. 1853) on Oct. 14 in Kassel; illegitimate son of elector William I of Hesse-Kassel (1743-1821) and Rosa Dorothea Ritter. English adventurer (blind) ("the Blind traveller") James Holman (d. 1857) on Oct. 15 in Exeter; becomes blind at age 25. Am. gunsmith Henry Deringer (d. 1868) on Oct. 26 in Easton, Penn.; invents John Wilkes Booth's weapon of choice. Am. "To the victor belong the spoils" statesman William Learned Marcy (d. 1857) on Dec. 12 in Sturbridge (Southbridge), Mass.; educated at Brown U. German Romantic composer-pianist Carl (Karl) Maria Friedrich Ernst von Weber (d. 1826) on Nov. 18/19 in Eutin, Holstein; brother of Fridolin Weber, father of Josepha Weber, Aloysia Weber, Constanze Weber, and Sophie Weber. Russian "Orthodoxy, Autocracy and Nationality" statesman-writer (atheist) Count Serge Sergeyevich Uvarov (d. 1855); a total hypocrite? Japanese #1 woodblock artist Utagawa Kunisada (d. 1865). Am. Suquamish-Duwamish chief Seattle (Sealth) (Si'ahi) (d. 1866) in Blake Island, Wash. English adm. Sir Fairfax Moresby (d. 1877) in Calcutta, India; father of John Moresby (1830-1922). Am. "Life of a Slave" ex-slave writer (black) Moses Grandy (d. ?) in Camden County, N.C. Deaths: English-born Am. Rev. leader William Peters (b. 1702) in Philadelphia, Penn. French explorer Jean-Baptiste Charles Bouvet de Lozier (b. 1705). Portuguese architect Mateus Vicente de Oliveira (b. 1706). Prussian king (1740-86) Frederick II the Great (b. 1712) on Aug. 17 in Potsdam: "God is always with the strongest battalions"; "He who tries to defend everything, defends nothing." English composer John Stanley (b. 1712) on May 19. English astronomer Thomas Wright (b. 1712) on Feb. 25. Spanish gov. #1 of Alta Calif. (1767-70) Gaspar de Portola (b. 1716) in Lleida. Portuguese king (1777-86) Pedro III (b. 1717) on May 25 in Queluz. British adm. Augustus Keppel, 1st viscount Keppel (b. 1725) on Oct. 2. Am. Rev. War brig. gen. John Alexander Lillington (b. 1725) in N.C. English cabinetmaker George Hepplewhite (b. 1727) on June 21; his wife pub. a book with 300 of his designs in 1788, making him famous, even though until then he's a bum and none of his furniture survives to modern times? English writer-clergyman John Duncombe (b. 1729) on Jan. 19. German Jewish philosopher Moses Mendelssohn (b. 1729) on Jan. 4. Am. Rev. War Gen. Alexander McDougall (b. 1731). Am. Rev. War Gen. Nathanael Greene (b. 1742) on June 19 near Savannah, Ga. (heat stroke); Greenville, S.C. and Greensoboro, N.C. are named after him; his Mulberry Cove plantation near Savannah, Ga. (given to him in appreciation for his Rev. War service) later becomes the site of Eli Whitney's cotton gin invention. Swedish chemist Karl Wilhelm Scheele (b. 1742) on May 21 (chemical poisoning). Spanish military leader Bernardo de Galvez y Madrid (b. 1746) on Nov. 30 in Tacubaya, Mexico City, Mexico (poisoned?). Dutch-born English astronomer John Goodricke (b. 1764) on Apr. 20 (pneumonia) - the good die young?















































1787 Pop. of the U.S.: 3.894M. There is a famine in Md. this year, and another in Russia. On Jan. 25 Shays' Rebellion (begun Aug. 1786) is quashed after Capt. Daniel Shays and his ragtag army of 1.2K debt-ridden farmers try to seize a federal weapons arsenal in Springfield, Mass., and a small militia scatters them with a single volley that kills four, followed by Gen. Benjamin Lincoln mopping them up with reinforcements from Boston on Feb. 4 at Petersham, Mass.; the reactionaries in several state govts. suddenly become convinced federalists, seeing commie mobs under every bush, although the state legislature makes concessions to Shayites next year that pacify them; on Nov. 13 from Paris Jefferson writes a Letter to William S. Smith (son-in-law of John Adams), containing the soundbyte: "The tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time with the blood of patriots and tyrants"; this attitude causes Abigail Adams to snub him for months? On Feb. 2 Scottish-born George Washington lookalike Arthur St. Clair (1736-1818) becomes pres. #9 of the United States under the Articles of Confederation (until Nov. 4, 1787). On Feb. 21 Congress approves a Constitutional Convention to meet on May 25 in Philadelphia, Penn. "for the sole and express purpose of revising the Articles of Confederation". On Feb. 28 (10 weeks before the Constitutional Convention in Philly opens) the U. of Pittsburgh (originally the Pittsburgh Academy until 1819, then Western U. of Penn. until 1908) in Pittsburgh, Penn. is founded in a log cabin by lawyer Hugh Henry Brackenridge (1748-1816), 1786 founder of the Pittsburgh Gazette, first newspaper W of the Appalachian Mts., becoming the oldest higher ed. inst. in the U.S. W of the Allegheny Mts. to survive to modern times; in 1966 it goes public. In Feb. after the Spanish Franciscans in Rome try in vain to stop him, French priest Pigneau de Behaine reaches Versailles, France, and talks Louis XVI into how he can "dominate the seas of China and the archipelago" by backing Nguyen Anh's comeback to the Vietnamese throne, and in Nov. a treaty of alliance is concluded in which France promises four frigates and 1.65K soldiers plus 250 Indian sepoys in return for concessions; too bad, the French gov. of Pondicherry refuses to carry out the deal, forcing Pigneau to get backing from French mechants, who equip two ships for him, and he's soon on the sea highway - seven rivers to cross, sometimes you get lost? In Mar. up-and-coming British Navy capt. Horatio Nelson (b. 1758) marries physician's widow Frances Nisbet (1761-1831) in Nevis, West Indies; she already has a 5-y.-o. son Josiah. In Apr. a Vice Admiralty Court is created in New South Wales, Australia, which continues till 1911; on May 13 the First Fleet leaves Portsmouth, England with 750 convicts bound for Australia's Botany Bay. On May 15 a group of "Black Poor" from London (incl. some African-Am. slaves freed by the British for fighting for their side in the Am. Rev.) accompanied by some English tradesmen financed by the St. George's Bay Co. arrive off the coast of Sierra Leone ("Lion Mountains") in Africa, and in Aug. found Freetown on the coast after British Anti-Slavery Society leader Granville Sharp (1735-1813) leases some land from a local tribal chief; too bad, disease and hostile natives virtually wipe the group out, causing former African-Am. N.C. slave Thomas Peters (Potters) (1738-92) to found the Sierre Leone Co. to recruit another group to try it again in 1792, after which the 1807 abolition of the slave trade by Britain causes British ships to start delivering thousands of African "recaptives" to Freetown after liberating them from illegal slave ships. The Constitution Solution at long last shows how white men with big blue eyes and a heart of gold can think about us? On May 25 the U.S. Constitutional Convention opens in Independence Hall in Philadelphia, Penn. with 29 delegates from nine states (average age 42) (swells to 55 from 12 states by the end, avg. age 44 - all except R.I.) (27 college grads) (34 lawyers) (over half Am. Rev. War vets), originally intending to rewrite the Articles of Confederation but deciding to write a new constitution instead; John Adams and Thomas Jefferson are absent because they are serving abroad; George Washington (nominated by Robert Morris and unanimously chosen pres.) stays in Philly as a guest of delegate Robert Morris, and doesn't take part in debates, although he consults in private; Alexander Hamilton, a prime mover in getting the convention called, attends irregularly and makes unpersuasive arguments?; James Madison's voice is so weak that no one can hear him?; Ben Franklin is too weak to stand and make a speech, asking other delegates to read for him?; Patrick Henry of Va. "smelt a rat" and refuses to attend (along with three other delegates), gets James Monroe to make several lengthy arguments against ratification, and later demands that it be investigated as a conspiracy, but then changes his mind and supports both the Constitution and the Bill of Rights; the windows are kept shut allegedly to keep out horseflies but actually to preserve secrecy?; Ben Franklin (81) is the oldest delegate, and he travels in a sedan chair brought from Paris?; the youngest delegate is Jonathan Dayton (1760-1824) of N.J.; the convention delgates are divided between federalists (strong "energetic" central govt.), inc. George Washington and James Madison of Va., Alexander Hamilton and Gouverneur Morris of N.Y., James Wilson (1742-98) of Penn., Rufus King (1755-1827) of Mass., and indigo grower Charles Cotesworth Pinckney (1746-1825) of S.C., and states' rightsers, incl. William Paterson (1745-1806) of N.J., John Dickinson (1732-1808) of Del. (the dude who refused to sign the DOI but came around late after being appointed brig.-gen. in the Continental Army as a joke, resigning, then moping around for two years), Luther Martin (1748-1826) of Md., and John Ten Eyck Lansing Jr. (1754-1829) and Robert Yates (1738-1801) of N.Y. (who pull N.Y. out of the convention and never sign the constitution); on May 29 big-state men Edmund Jennings Randolph (1753-1813) and James Madison (1751-1836) of Va. introduce the Virginia Plan of proportional representation in Congress; on June 15 small-state man William Paterson (1745-1806) of N.J. counters with the New Jersey Plan of equal numbers of members for each state; Hugh Williamson (1735-1819) of N.C. plays a key role in the large vs. small state debate; on June 18 Alexander Hamilton introduces a plan for a strong executive elected for life, but it is rejected, and he walks out with the New York delegation because of their states' rights principles; on June 28 Benjamin Franklin rises to his feet and leads a prayer, which causes the members to quit stonewalling and begin making progress, causing Washington to call it a miracle (if it weren't for the Christian faith, there would have been no U.S. Constitution?); too bad for blacks, on July 12 very Christian James Madison introduces the Three-Fifths Compromise, counting three-fifths of a state's slave pop. in apportioning representation; on July 16 self-taught lawyer Roger Sherman (1721-93) and state superior court judge Oliver Ellsworth (1745-1807) of medium-state Conn. introduce the Great (Connecticut) Compromise, setting up the House of Representatives and the Senate based on the Va. and N.J. plans, respectively, and incorporating the three-fifths plan; Randolph acts like the big man and stubbornly opposes a compromise; Madison's Notes of the Debates in the Federal Convention cause him to become known as the Father of the Constitution, and he observes that the decision to make the chief executive a single person causes "considerable pause", with Va. planter ("the gentleman revolutionary") ("the reluctant statesman") George Mason (1725-92), who worries about it becoming a "fetus of monarchy". Angels with dirty faces, English style? On June 1 King George III issues a Proclamation for the Encouragement of Piety and Virtue and for the Preventing of Vice, Profaneness, and Immorality, drafted by William Wilberforce (1759-1833), decrying "every kind of vice which, to the scandal of our holy religion, and to the evil example of our loving subjects, have broken upon this nation"; Whig Lord FitzWilliam scoffs at it, saying "The only way to reform morals is to ruin purses." On June 6 Franklin College in Lancaster, Penn. is founded by four members of the German Lutheran and Reformed Churches after Benjamin Franklin donates Ł200; in 1836 Marshall College in Mercersburg, Penn. is founded, named after U.S. Chief Justice John Marshall; on June 7, 1853 they merge as Franklin and Marshall College, with future U.S. pres. James Buchanan as pres. #1. On June 20 Conn. atty. Oliver Ellsworth (1745-1807) moves the Federal Convention to strike the word "National" from "National Government of the United States" and substitute "United States Government". In June English Unitarian MP William Smith (1756-1835) (grandfather of Florence Nightingale) becomes one of the first to advocate an end to the slave trade, becoming friends with 4'11" William Wilberforce (1759-1833), MP since 1780 (a shrimp who becomes a whale when giving speeches, according to James Boswell), who is converted to Christianity by "evangelical Dr. Johnson" abolitionist mathematician (7th Lucasian prof. of mathematics and pres. of Queens' College, Cambridge U.) Isaac Milner (1750-1820), then meets former slave trader and clergyman John Newton (1725-1807), author of "Amazing Grace", and makes a tour of England reading the Bible regularly, becoming convinced that slavery is wrong and devoting his life to ending it, even though virtually every businessman in England makes some income from it; his cause of "the abolition of the slave trade and the reformation of manners" attracts Grenville Sharp, Zachary Macaulay, Thomas Clarkson, Sir William Dolben et al., and they research the necessary legislation; each year Wilberforce makes a motion to abolish slavery, which is handily defeated despite his eloquent and moving speeches, and he decides to go directly to the people with his case, causing Josiah Wedgewood to design the black-yellow Jasper Wedgewood Slave Medallion, a cameo depicting a slave kneeling and crying "Am I not a man and a brother?", and poet William Cowper next year to write The Negro's Complaint; a boycott of slave-produced sugar gains a following of 300K across England; 519 petitions are brought to Congress, and in 1792 it finally relents and passes Wilberforce's motion, after adding the word "gradually"; too bad, the French Rev. and the West Indies slave revolts turn Parliament against him, and they flip-flop, and final victory takes until 1807 - may the force be with you? Angels with dirty faces, American style? On July 13 the U.S. Northwest Ordinance of 1787 creates the Northwest Territory (Ohio River Valley) (future U.S. states of Ohio, Ind., Ill., Mich. and Wisc.) as an area free of slavery; on Aug. 23 Congress forbids itself from ending the Atlantic slave trade until 1808, and requires fugitive slaves to be returned to their owners; it is approved in Federal Hall in 1789. On July 23 delegates from New Hampshire finally arrive at the Constitutional Convention after the action's all but over, but get to sign it first as they are the most northern? On July 30 the French parliament refuses to approve a more equitable land tax and demands that the king summon the Estates-General; on Sept. 4 Louis XVI recalls Parliament and declares that the Estates-General will be summoned in July 1792. On Aug. 6 the first draft of the U.S. Constitution is submitted to the Constitutional Convention in Philly after 87 days of drafting. On Aug. 10 the Seventh Russo-Turkish War (ends 1792) begins after Turkey declares war on Russia; Austria joins Russia next year, while Sweden and Prussia side with Turkey but provide no assistance. On Aug. 11 George III of England creates the diocese of Nova Scotia, with loyalist Charles Inglis (1734-1816), former rector of Trinity Church in New York City as its first bishop, becoming the first Church of England bishop in North Am. The most momentous event in human history since Eden, and the genius of compromise is enshrined in a monarchy (president), oligarchy (Senate), and democracy (House of Reps.) wedded into a menage a trois? On Sept. 15 after Gouverneur Morris makes the final revision of the draft and writes the Preamble, the U.S. Constitution is approved by the Constitutional Convention in Philly; that evening the 55 delegates party at a tavern, drinking 54 bottles of Madeira, 60 bottles of claret, eight bottles of whiskey, 22 bottles of porter, eight bottles of hard cider, 12 bottles of berr,and seven bowls of alcoholic punch"; on Sept. 17 "an assembly of demi-gods" (Jefferson), presided over by George Washington assembles, and 12 of 13 states (R.I.) sign it (a total of 39 signers, not incl. John Hancock, who only signed the DOI), with Washington going first, followed by the states going from N to S; George Reed signs for John Dickinson of Del., who is sick; Maj. William Jackson (1759-1828) of S.C., secy. of the convention (later Pres. Washington's 1st term private secy.) is the 40th signer; George Mason of Va. refuses to sign because it doesn't have a bill of rights, like he drafted for Va. in 1776, and which he later becomes the father of; Edmund Randolph of Va. refuses because it gives the pres. too much power; Elbridge Gerry of Mass. refuses because it gives the federal govt. too much power and has insufficient protection for the liberties of the people (to gerrymander?); Howard Chandler Christy (1873-1952) paints a famous Portrait of the Signing of the U.S. Constitution; in 1936 Barry Faulkner (1881-1966) paints a 14 ft. x 35 ft. Mural of the Signers of the U.S. Constitution for the rotunda of the Nat. Archives in Washington, D.C.; Ben Franklin weeps after he signs it, then delivers a moving address, saying, "I have happiness to know that it is a rising and not a setting sun"; the delegates celebrate at the City Tavern; it is pub. on Sept. 19, delivered to the Congress in New York City on Sept. 20 as part of a 6-page report along with a letter from Washington, and submitted to the states for ratification on Sept. 28 after efforts to censure the convention for exceeding its authority are defeated; after the convention adjourns, Washington predicts that the Constitution won't last for more than twenty years; the words "federal" and "democracy" are not mentioned in the final version, as the govt. is assumed to be a republic with qualified electors appointing officials, and everybody knows that the new constitution's aim is to correct the defects of the old one by strengthening the federal govt.?; the federal govt. is given 20 different powers, not jillions like it comes to believe by the 20th cent.?; Penn. State Assembly asst. clerk and calligrapher Jacob Shallus (1750-96) is hired for $30 to "engross" (write out in large letters on a parchment with ink using a turkey feather quill) the actual document, four pages measuring 29" x 24" (check out that cool "We the People") (page two has 1,054 words); the U.S. Constitution has seven articles and a total of 24 sections, and doesn't mention God, Christ or the Bible, although it is dated "In the year of our Lord"; I: the Congress (10 sections) (a rep. must be 25-y.-o. and a U.S. citizen for 7 years, a senator must be 30-y.-o. and a citizen for 9 years); II: the President (4); III: the Courts (3); IV: Interrelation between state and federal govt., Full Faith and Credit (Sect. 1), "Privileges and Immunities" (Sect. 2), Admission of New States (Sect. 3), "Republican form of govt." guaranteed for each state (Sect. 4); V: Amendment Process (1), VI: Supreme Law of the Land et al. (1), VII: Manner of Establishment (ratification by 9 of the 13 original states) (1); the Preamble uses eight key verbs (form, establish, insure, provide, promote, secure, ordain, establish) and six key goals (Union, Justice, Tranquility, Defence, Welfare, Liberty); originally it listed the states ("We the People of the United States of New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, etc."): "We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America"; the Am. Founding Founders score a 5K Year Leap, making possible more human progress in the next 200 years than in the last 5K? - feel a little bit dance schooley? On Sept. 30 Am. fur-trading ship Lady Washington, captained by Robert Gray (1755-1806), and fur-trading ship Columbia Rediviva, captained by John Kendrick (Kenrick) (1740-94) are sent by a group of Boston merchants incl. Charles Bulfinch from Boston, Mass. to trade pelts on the Pacific Northwest coast and take them to China, based on Capt. Cook's success in selling otter pelts in Canton; on Aug. 9, 1790 Gray arrives in Canton, trading his cargo for tea, continuing on a round-the-world voyage and arriving in Boston on Aug. 9, 1790 with a Hawaiian islander he parades through Boston, becoming the first Am. vessel to circumnavigate the globe. On Oct. 1 an Ottoman fleet lands troops on the Kinburn Spit in the Crimea, but after heroic actions by wounded gen. Count Alexander Vasilievich Suvorov (1729-1800) (who is rescued by Russian grenadier Novikov then stays on the battlefield commanding the troops), they are finally thrown back into the sea; on Dec. 17 the Russians take Ochakov in S Ukraine and ochakov, er, massacre the pop. On Oct. 5 Arthur St. Clair is voted gov. of the new Northwest Territory. On Oct. 27 The Federalist Papers, a series of 85 2K-word political essays promoting the proposed new Constitution begin to be pub. in New York City newspapers under the alias Publius over the next two years (last in July 1788); the authors are Alexander Hamilton (51 of 85: 1, 6-9, 11-13, 15-17, 21-36, 59-61, 65-85), James Madison (26: 10, 14, 37-58, 62-3), and John Jay (5: 2-5, 64) (nos. 18-20 are written jointly by Madison and Hamilton); Jay would have written more but he takes sick in the fall, and Madison likewise but he has to leave the Congress in New York and return to Virginia in Mar. 1788; No. 10 (Madison) features the argument that republics work better in large inhomogeneous nations because no single faction can succeed in dominating; No. 51 (Madison) contains the quote, "Ambition must be made to counteract ambition"; No. 70 (Hamilton) argues that a single energetic executive unhampered by a council is needed; No. 78 (Hamilton) is a brilliant defense of judicial review; No. 85 (Hamilton) brings the series to a close with an appeal to get the Constitution passed now and let amendments be made later, saying, "A nation without a national govt. is, in my view, an awful spectacle. The establishment of a Constitution, in time of profound peace, by the voluntary consent of a whole people, is a prodigy, to the completion of which I look forward with trembling anxiety." On Nov. 29 Louis XVI promulgates an edict of tolerance giving civil status to Protestants. On Dec. 7 after letters and speeches by John Dickinson, "Blue Hen State" Delaware (Del.) becomes the first state to ratify the U.S. Constitution and be admitted, followed by #2 "Keystone State", "Coal State", "Birthplace of the U.S. State" Pennsylvania (Penn.) on Dec. 12, and #3 "Garden State" New Jersey (N.J.) on Dec. 18 - quick, hand me dela pen? I don't wanna be thoid? On Dec. 20 a revival breaks out among the Shakers of New Lebanon, Ind., spreading to Ky. and other frontier regions; the first Shaker song is written by Father James Whittaker, titled "In Yonder Valley". The New York Assembly imposes duties on foreign goods. Amar Singh (1774-98) becomes ruler of S India; during his reign Three Brahmin musicians, Thyagaraja (1767-1847), Muthuswami Dikshitar (1775-1835), and Syama Sastri (1762-1827) begin reforming the art of Carnatic (Karnatic) music. Catherine II the Great visits the Crimea and tours Potemkin's artificial villages - see the adult video? Nguyen Angh signs a treaty with the French giving them the city of Da Nang (Tourane). Lord Dunmore, former colonial gov. of Va. becomes gov. of the Bahamas (until 1796). Louis XVI revokes a 1752 edict of Louis XV and declares Protestant marriages legal. Victor Marie du Pont de Nemours (1767-1827), son of economist Pierre Samuel enters the French diplomatic service as attache to the French legation in the U.S., going on to become first secy. of the legation in 1795 and French consul in Charleston, S.C., where he talks his daddy into emigrating. Alexander Hamilton forms the Federalist Party, backed by urban bankers and businessmen (ends 1816); John Adams becomes the only Federalist U.S. pres. Thomas Paine returns via Paris to England, where he nourishes ambitions of rabble-rousing on the Continent? Horace-Benedict de Saussure (1740-99) reaches the summit of Mont Blanc, where he makes scientific weather observations - it's colder than a witch's teat? The city of Dnepropetrovsk (Ekaterinoslav until 1925, Dnipro since May 2016) is founded on the Dnieper River 243 mi. SE of Kiev in SC Ukraine by the Cossacks (modern-day pop. 980K/1.4M)). The Society for the Abolition of the Slave Trade is founded in Britain; Benjamin Franklin becomes pres. of the Penn. Society for Promoting the Abolition of Slavery, saying, "When you're finished changing, you're finished." William Samuel Johnson (1727-1819) of Conn. becomes pres. #1 (until 1800) of Columbia College (formerly King's College) in New York City. The term "Americanism" is coined for the emerging new vocabulary of American English (lot, caucus, bluff, swamp, et al.), as well as the American habit of speaking with a twang or nasal drawl; Thomas Jefferson coins the word "belittle" in a work pub. this year. I love making Tylenol, I put love into this product? French king Louis XVI has a nervous breakdown; meanwhile his queen Marie Antoinette begins to wake up and smell the bread baking, and sits for a portrait with her children while wearing single earrings and no necklace as a desperate attempt to counter all the propaganda about her being a spendthrift self-absorbed sexually aggressive slut with a voracious uterus. Benjamin Franklin allegedly delivers the Franklin Prophecy to the Constitutional Convention, warning that the pesky Jews are going to infiltrate and take over the U.S. within a cent.; it actually never appears until 1934 in the pro-Nazi weekly Liberation, ed. by William Dudley Pelley? The Fugio Cent becomes the first official U.S. coin, meant to displace coins struck by individual states in the 1780s; the Brasher Doubloon becomes the rarest and most valuable U.S. coin by the 20th cent. The Merovingian Order of the Holy Grail is founded. Violoncello-loving Luigi Boccherini (1743-1805) becomes court composer in Berlin. Thomas Jefferson sends a letter from Paris, noting that he can't find any corn (maize) in Europe, mentioning his corn garden in Va. and how likes it boiled on the cob and eaten with salt. Sports: The Marylebone Cricket Club in Dorset Square, London is founded by Thomas Lord (1755-1832), who plays his first game on May 31 for Middlesex against Essex, and moves to Lord's cricket ground; co-founders incl. Charles Lennox, 4th Duke of Richmond (1764-1819); the club pub. the 42 Laws of Cricket next May 30, and copyrights them - changing them laws ain't cricket? Inventions: On Aug. 22 John Fitch (1743-98) demonstrates his steamboat for delegates of the Continental Congress on the Delaware River. William Blake's brother Robert dies, causing him to slip into a deep sleep for three days and nights, awakening to tell of seeing Robert's soul rising from his body "clapping his hands for joy"; he then claims that his bro' gave him the idea for Relief Etching (Illumined Printing), using an engraved copper plate for printing both text and illustrations, thus bypassing a commercial printer, although limiting the number of copies since each has to be hand-painted with watercolors? Edmund Cartwright (1743-1823) of England invents the Power Loom, featuring driving shafts driven by water; too bad, pissed-off weavers burn down a cotton mill using it, and it works poorly, taking until 1813 for William Horrocks to perfect it, adapting it to steam by 1822; in 1813 there are 2.4K power looms in use, followed by 12,150 in 1820, 45.5K in 1829, 85K in 1833, and 250K in 1850; British cotton exports zoom from Ł355K in 1781 to Ł7M in 1801, and Ł23.4M in 1841; meanwhile, the woolen industry lags behind in automation, with many hand looms still in use in 1850. Tribologist John Garnett invents the first roller bearings. At the Constitutional Convention, George Washington sees a Fan Chair (worked by pedals) and orders one, using it until his death; Ben Franklin and artist Charles Willson Peale also use them. Science: French physicist Jacques Alexandre Cesar (César) Charles (1746-1823) discovers Charles' Law, describing the relationship between gas volume and temperature. Ernst Chladni (1756-1827) experiments with sound patterns on vibrating plates. On Jan. 11 William Herschel discovers Uranus' moons Titania and Oberon, naming them after Shakespeare's "A Midsummer Night's Dream". Nonfiction: John Adams (1735-1826), A Defence of the Constitutions of Government of the United States. Jean-Sylvain Bailly (1736-93), A Treatise on Indian and Oriental Astronomy. Jeremy Bentham (1748-1832), Defense of Usury. Jonathan Edwards Jr. (1745-1801), A Study of the Mohegan Language; claims that Algonquin is distinct from Iroquoian. Carlo Goldoni (1707-93), Memoirs (Paris). Imperial Russian Dictionary (initiated by Catherine II the Great); 285 words in 200 languages. Antoine Lavoisier (1743-94), Methode de Nomenclature Chimique; his brainy wife Mariane is the real head of the team, and helps him devise the modern system of nomenclature in collaboration with Claude Louis Berthollet, Louis B. Guyton de Morveau, and Anton de Fourcroy. James Madison (1751-1836), Vices of the Political System of the United States. Comte de Mirabeau (1749-91), Sur la Monarchie Prussienne sous Frederic le Grand (4 vols.); based on materials given to him by Maj. Mauvillon on a secret 1786 French govt. mission to Berlin. Count de Volney (1757-1820), Voyage en Egypte et en Syrie; his trip to Egypt and Syria (incl. Lebanon and Palestine) in 1782-5; "Palestine is a ruined and desolate land"; "The peasants are incessantly making inroads on each other's lands, destroying their corn, durra, sesame and olive-trees, and carrying off their sheep, goats and camels. The Turks, who are everywhere negligent in repressing similar disorders, are attentive to them here, since their authority is very precarious. The Bedouin, whose camps occupy the level country, are continually at open hostility." Music: Franz Joseph Haydn (1732-1809), The Prussian Quartets, Nos. 36-41, Op. 50; The Seven Last Words of Christ, Op. 51. Vicente Martin y Soler (1754-1806), L'Arbore di Diana (comic opera). Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756-91), Don Giovanni, Il Dissoluto Punito (opera) (greatest ever?) (Estates Theatre, Prague) (Oct. 29) (conducted personally); starts with serial rapist Don Giovanni pursuing Donna Anna, and ends with a Statue from Hell taking him down; incl. Vedrai Carino; A Little Night Music (Eine Kleine Nachtmusik) (Serenade No. 13 for strings in G major) (K.525). Art: Thomas Barker of Bath (1769-1847), Woodman and His Dog in a Storm. William Blake (1757-1827), The Approach of Doom; his first attempts at relief etchings sans text. Antonio Canova (1757-1822), Pope Clement XIV (sculpture); makes him a star; Psyche Revived by Love's Kiss. Jacques-Louis David (1748-1825), The Death of Socrates. Alexander Nasmyth (1758-1840), Robert Burns. Henry Raeburn (1756-1823), Portrait of the Second Lord President Dundas (Edinburg). Sir Joshua Reynolds (1723-92), Lady Heathfield. Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Tischbein (1751-1829), Goethe on the Roman Ruins in Campagna. Plays: Samuel Arnold (1740-1802) and George Colman the Younger (1762-1836), Inkle and Yarico (opera) (London) (Aug.); London-bred Inkle and his servant Trudge are left on a cannibal island, and he falls in love with Yarico, then must choose between her and his betrothed Narcissa in Barbados. Pierre-Augustin Caron de Beaumarchais (1732-99), Tarare (comedy). Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749-1832), Egmont (poetic drama); Flemish martyr Lamoral, Count of Egmont (1522-68); in 1810 an overture based on it by Beethoven debuts. Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (1759-1805), Don Carlos (Mannheim); unlucky Spanish prince Don Carlos de Austria (1545-68). Novels: Aagje Deken (1741-1804) and Betje Wolff (1738-1804), Abraham Blankaart. Wilhelm Heinse (1749-1803), Ardinghello und die Gluckseligen Inseln; his biggest hit; set in 16th cent. Italy. Births: U.S. Mass. gov. #14 and #17 (1834-5) and U.S. Sen. (Whig-Mass.) (1835-41) John Davis (d. 1854) on Jan. 13 in Northborough, Mass.; educated at Yale U.; husband (1822-) of Eliza Bancroft, sister of George Bancroft; father of John Chandler Bancroft Davis, Hasbrouck Davis, and Horace Davis; ancestor of Gherardi Davis (1858-1941), Henry Cabot Lodge Jr., and John Davis Long. French archeologist Jean Antoine Letronne (d. 1848) on Jan. 25 in Paris. English "Elements of Logic" logician-economist-theologian and Anglican archbishop of Dublin (1831-) Richard Whately (d. 1863) on Feb. 1 in London; educated at Oriel College, Oxford U. Am. DeWitt Colony founder Green DeWitt (d. 1835) on Feb. 12 in Lincoln County, Kan.; grows up in Mo. Am. educator and women's rights activist Emma Hart Willard (d. 1870) on Feb. 23 in Berlin, Conn. James Davis (d. 1862) on Mar. 6; first black Am. born in the state of Ohio. German physicist Joseph (Josef) Ritter von Fraunhofer (d. 1826) on Mar. 6 in Straubing (near Munich), Bavaria; father is a glazier, and the large family is too poor to pay for his education, so he ends up apprenticed at age 11 to a mirror maker in Munich, rising to foreman at 20 and dir. at 22. German surgeon Karl Ferdinand von Grafe (Gräfe) on Mar. 8 in Warsaw. English artist William Etty (d. 1849) on Mar. 10 in York; student of Sir Thomas Lawrence (1769-1830); first significant British painter of nudes and still lifes. English #1 stage actor Edmund Kean (d. 1833) on Mar. 17 in London; son of actress Anne Carey. English traveller-scholar Claudius James Rich (d. 1821) on Mar. 28 near Dijon, France; grows up in Bristol. Am. journalist-politician Neville Burgoyne Craig (d. 1863) on Mar. 29 in Pittsburgh, Penn.; educated at Princeton U. Am. frontiersman Erastus "Deaf" (pr. DEEF) Smith (d. 1837) on Apr. 19 in Dutchess County, N.Y.; grows up in Port Gibson (near Natchez), Miss.; one of Sam Houston's most reliable scouts. English clergyman (of carriage fame) FitzRoy Henry Richard Stanhope (d. 1864) on Apr. 24. Austrian field marshal Alfred I (Alfred Candidus Ferdinand), Prince of Windisch-Graetz (Windisch-Grätz) (d. 1862) on May 11 in Brussels. Swedish chemist Nils Gabriel Sefstrom (Sefström) (d. 1845) on June 2 in Ilsbo, Halsingland; student of Jakob Berzelius. English geologist Rev. William Daniel Conybeare (d. 1857) on June 7 in London; educated at Westminster School, and Christ Church, Oxford U. U.S. Navy secy. #7 (1823-9) Samuel Lewis Southard (d. 1842) on June 9 in Basking Ridge, N.J. Am. naturalist (Quaker) Thomas Say (d. 1834) on June 27 in Philadelphia, Penn. English lt. gen. Sir Harry Smith (Henry George Wakelyn Smith), 1st Baronet of Aliwal (d. 1860) on June 28 in Whittlesey, Cambridgeshire. Italian statesman and utilitarian philosopher Pellegrino Rossi (Luigi Edoardo Pellegrino, Count Rossi) (d. 1848) on July 13 in Carrara, Tuscany; educated at the U. of Pisa, and U. of Bologna. German ironmaster Friedrich Krupp (d. 1826) on July 17 in Essen; founder of the Krupp family of munitions makers. U.S. Sen. (R-Conn.) (1843-9) and U.S. postmaster gen. #9 (1840-1) John Milton Niles (d. 1856) on Aug. 20 in Windsor, Conn. English Weddell Sea seal hunter-explorer James Weddell (d. 1834) on Aug. 24 in Ostend. Russian statesman-gen.-adm. prince Alexander Sergeyevich Menshikov (d. 1869) on Aug. 26. German "Das Schloss am Meer", "Der Gute Kamerad" Romntic poet Johann Ludwig Uhland (d. 1862) on Aug. 26 in Tubingen. U.S. atty. gen. #15, #22 (1841, 1850-3) and Ky. gov. #17 (1848-50) John Jordan Crittenden (d. 1863) on Sept. 10 near Versailles, Ky.; educated at the College of William and Mary. English Buckingham Palace, Lambeth Palace architect Edward Blore (d. 1879) on Sept. 13 in Derby; son of Thomas Blore (1754-1818). French historian and liberal PM #22 (1847-8) Francois Pierre Guillaume Guizot (d. 1874) on Oct. 4 in Nimes; Protestant parents. English "Home Sweet Home" composer Sir Henry Rowley Bishop (d. 1856) on Nov. 18 in London. French photography pioneer Louis Jacques Mande (Mandé) Daguerre (d. 1851) on Nov. 18 in Cormeilles-en-Parisis, Val-d'Oise. British shipping magnate Sir Samuel Cunard, 1st Baronet (d. 1865) on Nov. 21 in Nova Scotia, Canada. Danish philologist Rasmus Christian Rask (d. 1832) on Nov. 22 in Braendekilde, Funen Island; co-founder of the science of comparative linguistics. Austrian schoolteacher and "Silent Night" lyricist Franz Xaver Gruber (d. 1863) on Nov. 25 in Hochburg-Ach, Upper Austria. Am. maj. gen. Bennet C. Riley (d. 1853) on Nov. 27 in St. Mary's County, Md.; 6th and last military gov. of Calif. (1849). Am. Am. School for the Deaf founder Rev. Thomas Hopkins Gallaudet (d. 1851) on Dec. 10 in Philadelphia, Penn.; son of Peter Wallace Gallaudet (1756-1843); grows up in Hartford, Conn.; educated at Yale U., and Andover Theological Seminary; father of Thomas H. Gallaudet (1922-1902) and Edward Miner Gallaudet (1837-1917). English Socialist political economist Thomas Hodgskin (d. 1869) on Dec. 12 in Chatham, Kent; educated at Edinburgh U. English "Our Village" writer Mary Russell Mitford (d. 1855) on Dec. 16. Czech Purkinje Effect physiologist Jan Evangelista Purkinje (Purkyne) (d. 1869) on Dec. 17 in Libochovice, Bohemia. Russian explorer Capt. Otto von Kotzebue (d. 1846) on Dec. 30 in Reval (Tallinn), Estonia. Am. politician-atty. Barnard Elliot Bee Sr. (d. 1853) in Charleston, S.C.; son of Thomas Bee (1739-1812); father of Barnard E. Bee Jr. (1824-61) and Hamilton Prioleau Bee (1822-97); grandfather of Carlos Bee (1867-1932). Serbian rebel Toma Vucic-Perisic (d. 1859) in Baric. Am. Santa Fe Trail pioneer trader William Becknell (d. 1865) in Amherst County, Va. Belgian Neoclassical painter Francois Joseph Navez (d. 1869) in Cherleroi; pupil of Jacques-Louis David; teacher of Jean-Francois Portaels. Deaths: Italian Catholic theologian St. Alphonsus di (Alfonso de) Liguori (b. 1696) on Aug. 1 in Nocera de' Pagani; canonized in 1839; created Doctor of the Church in 1871. Italian painter Pompeo Batoni (b. 1708) on Feb. 4 in Rome; bequeaths his palette and brushes to Jacques-Louis David. English bishop Robert Lowth (b. 1710) on Nov. 3. Croatian scientist Roger Boscovich (b. 1711) on Feb. 13 in Milan, Italy. German-born Am. Lutheran clergyman Henry Melchior Muhlenberg (b. 1711) on Oct. 7 in Trappe, Penn. English portraitist Arthur Devis (b. 1712) on July 25 in Brighton. German organist Christoph Gluck (b. 1714) on Nov. 15 in Vienna. French Marshal Charles de Rohan, prince de Soubise (b. 1715). English brewer William Bass Jr. (b. 1717) on Mar. 2 in Burton-on-Trent. French diplomat-statesman Charles Gravier, comte de Vergennes (b. 1717) on Feb. 13. French marshal Francois-Gaston de Levis (b. 1719) on Nov. 26 in Arras. Austrian violinist-composer (Wolfy's dad) Leopold Mozart (b. 1719) on May 28. Spanish miniser Jose de Galvez (b. 1720) on June 17 in Aranjuez. English type-founder and chocolatier Joseph Fry (b. 1728) on Mar. 27 in Bristol.





























1788 France begins sinking into an economic depression just as the independent U.S. is taking off, and George III's hereditary metabolic disorder of porphyria is causing him to begin periodically losing his mind; this year he is spotted having a conversation with an oak tree - he was in good mental condition when he lost the American colonies? 11 of the original 13 states join the U.S. in seven months, but it's a tough fight (D-P-NJ-G-C-MA-MD-SC-NH-VA-NY-R-NC)? On Jan. 2 "Peach State" Georgia is admitted as the 4th U.S. (slave) state; "Nutmeg State" Conn. on Jan. 9 as the 5th (free); "Bay State" "Old Colony State" Mass. on Feb. 7 as the 6th (free) by a 187-168 vote; "Old Line State" "Free State" Maryland on Apr. 28 as the 7th (slave); "Palmetto State" S.C. on May 23 as the 8th (slave); "Granite State" New Hampshire on June 21 as the 9th (free); on July 2 the Constitution is legally ratified in Augusta, Ga., but without the approval of Va. (the largest state) and New York (3rd largest), it won't fly; luckily, after Edmund Randolph flip-flops when he hears about a proposed Bill of Rights (17 amendments) by James Madison (1751-1836), Patrick Henry can't hold the state back, and on June 25 "Old Dominion" (later "Birthplace of Seven Presidents") Va. votes 89-79 to ratify, being admitted as the 10th (slave) state; on July 26 after DeWitt Clinton composes the opposition prayer: "From the insolence of great men - from the tyranny of the rich - from the unfeeling rapacity of the excise-men and tax-gatherers - from the misery of despotism - from the expense of supporting standing armies, navies, placemen, sinecures, federal cities, senators, presidents, and a long train of etceteras, Good Lord deliver us" "Empire State" New York ratifies by a 30-27 vote after Alexander Hamilton and his Federalists tell them that the caravan will leave with or without them, and comes in as the 11th (free) state; "Ocean State" "Little Rhody" Rhode Island rejects ratification on Mar. 24 (until May 29, 1790); "Tar Heel State" N.C. votes to postpone ratification on Aug. 2 until a Bill of Rights is submitted to Congress (Nov. 21, 1789); "Green Mountain State" Vermont proves to be a slow as molasses in January and takes until Mar. 4, 1791 (gotcha, it wasn't one of the original 13). Is there any continent on Earth not being taken over by whitey? On Jan. 18 (8 mo. after setting sail on May 13, 1787) the 11-ship First Fleet containing the first white English (European) settlers (732 convicts), led by British Navy Capt. (later Adm.) Arthur Phillip (1738-1814) of the Sirius arrive in Botany Bay in SE Australia (New Holland), and on Jan. 26 after realizing there's no water or secure anchorage they move to Port Jackson, and land the marines and convicts at Sydney Cove, which Phillip names in honor of British home secy. (1783-9) catch-the-mystery-of-white (well-meaning angel or devil?) Thomas Townshend, 1st Viscount Sydney (1732-1800), who appointed him gov. #1 of New South Wales (until 1792), which he rules from Port Jackson, while his marines guard the farmer-prisoners, who become Australia's first settlers; the first horses in Australia arrive with the First Fleet from Cape Town, South Africa; on Feb. 15 Capt. Phillip sends men to establish a 2nd colony in Norfolk Island, and claims Australia E of 135 E longitude for Britain, establishing Botany Bay Penal Colony as a place to dump English undesirables a good safe 13K mi. from London; Sydney (modern-day pop. 5M) becomes the first British settlement in Australia, with Sydney Hospital established on George St. on The Rocks as a tent hospital before being moved to Macquarie St. in 1811; the newcomers (who are watched by the indigenous Eora Tribe, which Phillip makes a hanging offense for his men to kill) have virtually no clothes or equipment, are covered with vermin and riddled with disease, are not farmers, and the seed brought on the journey is spoiled by sea-damp and fails to germinate; they do bring along 100 Bibles and 100 copies of the bestseller "Exhortation to Chastity", but who can read, and since there aren't enough women for the men, Capt. Phillip writes back to England to send women of childbearing age, and of course they send whores; finding the marines also undisciplined slackers, Phillip, uttering the soundbyte "In a new country there will be no slavery and hence no slaves" sets some convicts up as overseers, and also sets up two civil courts where prisoners can get around the usual laws against felons being able to sue, beginning the gradual process of emancipation, which is helped by the little fact that after the convicts serve their sentences they find it too expensive to leave, causing Australia to become known as "the country where people got stuck", and their usually illegimate children to become known as cornstalks. On Jan. 22 Va.-born Cyrus Griffin (1749-1810) becomes the 10th and last pres. of the United States under the Articles of Confederation (till Nov. 2). On Jan. 31 "Young Pretender" Bonnie Prince Charlie (b. 1720) dies in Rome, leaving his brother Cardinal (since 1747) Henry Benedict Stuart (1725-1807), bishop of Frascati as the sole surviving heir to the Jacobite claim, and he begins calling himself Henry IX of England and Henry I of Scotland; when he dies he leaves the crown Jewels to the Church, and George IV (still prince regent) is sent a few. Win some, laperouse some? In Jan. La Perouse's ships reach Botany Bay, and he writes a letter dated Feb. 7; his ships are both wrecked at Alpha Ceti 6, er, Alpha Ceti 5, er, Vanikoro Island in the Solomon Islands N of the New Hebrides, and he is never seen again; the wreckage is discovered in 1826. On Feb. 15 one of the biggest assemblies in English history in the House of Commons is addressed by Edward Burke, who gives the opening speech in the impeachment of Warren Hastings (1732-1818), England's first gov.-gen. of India on charges of corruption and abuse of office; the speech lasts through four sittings, and Hastings is acquitted after an 8-year trial, where Charles James Fox backs impeachment; Gen. John Burgoyne participates in the proceedings. On Feb. 19 after being imprisoned in the Bastille for 4 mo. for anti-govt. propaganda and fleeing to England, French rev. journalist Jacques Pierre Brissot (alias de Warville) (1754-93) founds the Societe des Amis des Noirs (Society of the Friends of the Blacks) to promote abolition. On Mar. 4 the first U.S. land patent is issued to John Martin (1789-1854), reserving one-third of all gold, silver, lead and copper. On Apr. 13 the 1788 Doctors' Riot sees a mob storm Columbia College medical school in New York City to protest the practice of grave robbing for human dissection practice, and 6-20 die in the ensuing riot, while the medical students are locked in jail to protect them; next year New York passes a strict statute against grave robbing. In Apr. ailing Benjamin Franklin donates Ł5 to the Congregation Mikveh Israel (founded 1740) for its new synagogue in Philadelphia; during the July 4 celebrations as per arrangements made by Franklin, "the clergy of different Christian denominations, with the rabbi of the Jews, walked arm in arm" in the parade past his window. In June John Adams finally returns to the U.S. and his Abigail for good, and they settle on Richmond Hill (modern Greenwich Village), with a nice view of the Hudson River, along with sons Charles, John Quincy and Thomas, and daughter Nabby. In June after several MPs visit a slave ship in London to see the terrible conditions, and Richard Pennant, Baron Penrhyn, representing the West Indian lobby (an owner of 8K acres in Jamaica, with 600 slaves) gives a speech about how happy Africans are to be shipped away as slaves, causing angry PM William Pitt to threaten to resign, Parliament passes a bill sponsored by Sir William Dolben (1726-1814) regulating the number of slaves that can be transported per ship for one year, which only mobilizes the pro-slave lobby more, causing them to gain the upper hand until 1792; "Things have come to a pretty pass when religion is allowed to invade public life" (Lord Melbourne); the slave trade employs 3.5K sailors and 160+ ships, with a human cargo worth Ł800K a year. In June Robert Burns, after finally collecting his fee from printer William Creech, the only money he makes from his poems, leases a farm in Ellisland, which is a loser, forcing him to take up tax collecting next year as his health deteriorates; in Nov. 1791 he is assigned to service in Dumfries, and gives up the farm. On July 2 the United States (U.S.) Constitution is ratified (per Article VII) by the required nine states after New Hampshire takes it over the top and becomes the 9th state to ratify it on June 21. On July 6 10K troops are called out in Paris to control unruly crowds protesting poverty and lack of food; on July 15 Louis XVI jails 12 deputies who protest new judicial reforms; on Sept. 23 Louis XVI declares the Parliament restored, and it meets in triumph the next day. On July 9 Frederick William II of Prussia issues the Wollner (Wöllner) Edict, proclaiming the need to protect Christianity from modernists, and prohibiting ministers from preaching anything not contained in their official pubs.; on Dec. 18 a censorship law is enacted. On Aug. 25 after Riverhead, N.J.-born John Cleves Symmes (1742-1814) of N.J. (father-in-law of Pres. William Henry Harrison) negotiates the 330K-acre Symmes (Miami) Purchase (Ohio River to Great Miami River to Little Miami River) from Congress for $225K, and Morristown, N.J.-born surveyor Israel Ludlow (1765-1804) surveys the 1.5M-acre Ludlow Survey (Scioto River to Little Miami River) for the Ohio Co. of Associates, separated from the Symmes Purchase by the disputed Ludlow Line, the city of Cincinnati, Ohio at the N side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio Rivers (modern pop. 296K/2.1M) is founded by Col. Robert Patterson (1753-1827), surveyor John Filson (1747-88), and Mathias Denman, settled on Dec. 28 by 26 more people, and named Losantville ("city opposite the mouth of the Licking River") by Filson, then renamed in 1790 by Arthur St. Clair after the 1783 Society of the Cincinnati, becoming the first U.S. boomtown; it is incorporated as a village in 1802, and as a city in in 1819; as settlers from N.J. and other mideastern U.S. states purchase 1M acres along the Ohio River and establish several settlements, Cincinnati becomes the Gateway to the South for steamboats on the Ohio, which are introduced in 1811, with its pop. zooming from 9,642 in 1910 to 24,831 in 1830 and 115K in 1850; in 1827 the Miami and Erie Canal opens, connecting Cincinnati with Middletown and Toledo. On Sept. 13 the Congress of the Confederation authorizes the first U.S. nat. election, and declares New York City the temporary nat. capital after Kingston, N.Y. (90 mi. to the N) is considered and rejected; on Oct. 10 the Confederation Congress holds its last session; on Nov. 2 the position of Cyrus Griffin as pres. of the U.S. "in Congress assembled" is eliminated, and next year he is appointed commissioner of the Creek nation, the judge of the U.S. Court for the district of Va. in Dec. 1789 until his death on Dec. 14, 1810. On Sept. 17 the Battle of Karansebes (Karánsebes) (Caransebes) in Romania sees an Austrian army of 100K go crazy after soldiers buy schnapps from some gypsies, causing a fight which ends up being mistaken for a Turkish attack by multi-nat. troops unable to understand each other's speech, causing the whole army to flee and HRE Joseph II to be pushed off his horse into a creek; the real Turks arrive on Sept. 19, finding 10K dead or wounded, winning without firing a shot. On Dec. 14 Spanish king (since 1759) Charles III (b. 1716) dies, and his 2nd son Charles IV (1748-1819) becomes Bourbon king #4 of Spain (until Mar. 19, 1808). On Dec. 23 the state of Md. cedes an area "not exceeding ten miles square" for the seat of the federal govt.; about two-thirds becomes the District of Columbia. HRE Joseph II enters the Sixth Russo-Turkish War on Catherine II's side; Sweden declares war on Russia. George III has his 2nd bout of madness (1765) when he gets out of a coach in Windsor Park and addresses an oak tree as his talented cousin Frederick II the Great of Prussia; he then begins to talk ever faster, once talking for 24 straight hours; when his wastrel son the Prince of Wales tries to console him, he tries to throttle him, and is put in a straightjacket, causing Prinny to dress up in expectation of becoming king for two days and nights, but the old fart doesn't die, even though he is never quite sane again, and drives through the streets to a service of Thanksgiving amid a loud cheering parade? Yussef Chehab abdicates, and Bashir Chehab (Shihab) II (1767-1850) is elected as emir #6 of Lebanon and wali of Mt. Lebanon, the Beqaa Valley, and Jabal Amel under Ottoman suzerainty (until 1840); he and his family convert from Sunni Muslim to Marionite Christianity at the end of the cent. The Qajar Dynasty rulers of Iran make Tehran their capital; they rule Iran until the 1920s. Ohio ("good river") and Iowa ("beautiful land") are settled; Marietta, Ohio, the first settlement in Ohio is named for Marie Antoinette. After the pesky Iroquois are forced into Canada, where Britain gives them a large land grant on the Grand River, the city of Rochester, N.Y. (modern-day pop. 210K/1.1M) is first settled by English Puritans from New England, it is incorporated as a village on Mar. 21, 1817, and as a city on Apr. 28, 1834 after reaching a pop. of 9.2K, becoming the largest flour-producing city in the U.S. by 1838, known as "the Flour City", and "the Young Lion of the West" for doubling its pop. in 10 years, becoming the first U.S. boomtown; by 1850 it becomes known as "the Flower City" for its nurseries; it goes on to become the home of revivalist Charles Finney, Frederick Douglass, Susan B. Anthony, John Jacob Bausch and Henry Lomb, George Eastman, and Emma Goldman. Mass. rep. Rufus King helps procure ratification of the U.S. Constitution by the Mass. Convention, then moves to New York City, and in 1789 is elected to the U.S. Senate as a Federalist. The 1788 Mass. Immigration Law requires foreigners to register, and prohibits those likely to seek public relief; in 1794 it is amended to authorize forcible removal of poor people. The Chimney Sweepers Act of Britain is passed in Britain, limiting child workers to age eight, with parental consent required, suitable clothing and living conditions supplied by the master sweep, and time off for church services on Sundays. The Marshall Islands in the W Pacific, E of the Caroline Islands are discovered by British explorer Capt. John William Marshall. John Paul Jones enters the Russian navy to fight the Turks (until 1790). The city of Charleston, W. Va. at the confluence of the Elk and Kanawha Rivers (modern-day pop. 51K/222K) is founded as Ft. Lee, becoming the seat of Kanawha County, and the state capital of W. Va.; members of the Kanawha County Assembly incl. Daniel Boone. After settling in 1785 on the Mississippi River opposite the modern-day Wisc.-Ill. boundary on the site of modern-day Dubuque, Iowa (modern-day pop. 57K/96K), French-Canadian Quebecois pioneer Julien Dubuque (1762-1810) receives permission from the local Meskwaki tribe and the Spanish govt. to mine lead; after the Meskwaki are forced out of the region in 1830, the first permanent settlement is founded in 1833. After the N.C. assembly chooses it as the site of the new capital to replace New Bern (1743), the city of Raleigh, N.C. (modern-day pop. 403K/2.2M), located on land owned by Wakefield mansion owner Joel Lane is named in honor of Sir Walter Raleigh; it is chartered on Dec. 31, 1792. British explorer Capt. Thomas Gilbert discovers the atoll of Tarawa, capital of the 33-island C Pacific Ocean nation of Kiribati (pr. "KEE-REE-bahs"). Daniel Boone settles near Point Pleasant, Va. (W. Va.) (until 1798). The flowering plants Hortensia (Hydrangea) and Fuchsia are imported to Europe from Peru. The Linnean Society, named after Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus (1707-78) is founded in England to pub. works on botany and zoology. After Floyer Sydenham, translator of Plato's Dialogues dies in a debtors' prison, Welsh philosopher David Williams (1738-1816) founds the Royal Lit. Fund to help published British writers out of financial difficulties. Goethe returns to Weimar and inaugurates the classical period of German lit. despite some initial opposition, dumping stale Frau von Stein for voluptuous young Christiane Vulpius (1765-1816), who bears him a son in 1789, and whom he marries in 1806 after the brat grows up, apparently because she lets him have affairs with novelist Bettina Brentano von Arnim (1785-1859) (daughter of a former mistress), publisher Christiane Friederike Wilhelmine "Minna" "Minchen" Herzlieb (1789-1865) (foster daughter of Jena publisher Karl Ernst Friedrich Frommann) et al. After King (1760-1820) George III begins suffering from bouts of insanity, Shakespeare's "King Lear" is banned from the British stage (until 1820). The first German cigar factory opens in Hamburg. Joel Barlow of Conn. travels to France as agent for the Scioto Land Co., and induces French settlers to settle Gallipolis, Ohio (Fr. "city of the Gauls"), and they arrive next Oct. 17; too bad, his exposure to France makes him a Freethinking Rationalist, later becoming a friend of Thomas Paine. Spanish composer Vicente Martin y Soler (d. 1806), in Vienna since 1785 is invited to become the Russian court composer at St. Petersburg, where he stays for the rest of his life, turning on Catherine the Great. Architecture: Prussian architect Carl (Karl) Gotthard Langhans (1732-1808) begins the Neoclassical Brandenburg Gate (Brandenburger Tor) (originally the Friedenstor or Peace Gate, dedicated to Eirene, goddess of peace) in Berlin (finished 1791), commissioned by Friedrich Wilhelm II to represent peace, based on the Propylaea in Athens, becoming the first structure in Langhans' "Athens on the River Spree"; it features six Doric columns and five passageways on each side, of which the public is only allowed to use the outermost two; a Quadriga (chariot pulled by four horses) sits atop the gate, sculpted by Berlin-born sculptor Johann Gottfried Schadow (1764-1850); it is built on the site of a a former city gate that marked the start of the road from Berlin to Brandenburg an der Havel, capital of the margaviate of Brandenburg; after the fall of Hitler in 1945, it ends up incorporated into the Berlin Wall by the Commies. Giacomo Quarenghi (1744-1817), Hermitage Theatre (1783-7); built on the Palace Embankment of the Neva River in St. Petersburg in place of the Third Winter Palace of Peter II the Great to replace the Russian Imperial Theatre; inspired by Andrea Palladio's Teatro Olimpico in Vicenza. The Richmond, Va. State Capitol, designed by Thomas Jefferson is finished, modeled on the ancient Maison Caree Roman temple in Nimes, France, becoming the first example of Neoclassical architecture in the U.S. Inventions: James Watt invents the centrifugal governor for steam engines. Nonfiction: William Blake (1757-1827), There Is No Natural Religion; All Religions Are One; his first experiments with combining text with relief etchings to create cool illuminated mss. George Hepplewhite (1727-86), The Cabinet Maker and Upholsterer's Guide; or Repository of Designs for Every Article of Household Furniture, in the Newest and Most Approved Taste (posth.); his 300 best designs, incl. shield-back chairs, making him a star. Immanuel Kant (1724-1804), Critique of Practical Reason; claims that pure practical reason must not be restrained like pure theoretical reason, but cultivated, founding deontological moral philosophy, making a fan of Johann Gottlieb Fichte. Thomas a Kempis (1380-1471), Imitatio Christi (folio ed.) (posth.); pub. by Pierre Francois Didot (1732-93). Baron Adolph Knigge (1752-96), On Human Relations (Uber den Umgang mit Menschen); the philosophical basis of good manners, causing the term "Knigge" to be coined for good manners. Bernard Germain de Lacepede (1756-1825), Histoire des Quadrupedes, Ovipares et des Serpents (2 vols.) (1788-9). Pierre Simon de Laplace (1749-1827), Laws of the Planetary System; tries to prove that the Solar System is stable, but leaves some terms out to make the equations manageable, which later turn out to prove that it isn't? John Lempriere (1765-1824), Bibliotheca Classica (Classical Dictionary Containing a Full Account of All the Proper Names Mentioned in Ancient Authors) (Nov.); becomes a std. work for dramatists, poets, teachers, and journalists for the next 200 years; makes a fan of John Keats. Gaspard Monge (1746-1818), Traite Elementaire de la Statique. Hannah More (1745-1833), Thoughts on the Importance of the Manners of the Great to General Society. Rev. Dr. John Trusler, The Honours of The Table or Rules For Behavior During Meals; with the Whole Art of Carving Illustrated by a Variety of Cuts. Thomas Reid (1710-96), Essays on the Active Powers of Man. Mercy Otis Warren (1728-1814), Observations on the New Constitution; pub. under the alias "A Columbian Patriot"; claims that a powerful central govt. will trample the rights of the states and people and argues for pure republicanism, later backing anti-Federalist Thomas Jefferson. Music: Luigi Cherubini (1760-1842), Demophoon (Démophoon) (opera) (Grand Opera, Paris); libretto by Jean-Francois Marmontel; his first tragedy; a success, getting him a job as dir. of the Theatre de Monsieur in the Tuileries next year, followed by the Theatre Feydeau in Paris in 1792; incl. Dirce Duet. Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756-91), Symphony No. 39 in E flat major, K.543 (June 26); "Great" Symphony No. 40 in G minor, K.550 (July 25) (his 2nd and last minor key symphony); Piano Sonato No. 16 in C major, K.545; Symphony No. 41 in C major ("Jupiter"), K.551 (Aug. 10) (his last symphony, by Jove?); his three great symphonies, all composed in the summer of 1788, none ever performed under his direction; Divertimento for String Trio in E flat major, K.563; and The Trios, K.496, K.548, K.564. Giovanni Paisiello (1740-1816), La Molinara (opera) (Naples); incl. Nel Cor Piu Non Mi Sento. Art: Thomas Banks (1735-1805), Shakespeare Attended by Painting and Poetry; commissioned by John Boydell for 500 guineas for his Shakespeare Gallery in Pall Mall, which opens in May 1789; the pedestal reads: "He was a Man, take him for all in all, I shall not look upon his like again"; moved in 1871 to the garden in Shakespeare's home of New Place, Stratford-upon-Avon. Jacques-Louis David (1748-1825), Love of Paris and Helena. Francisco de Goya (1746-1828), The Duke and Duchess of Osuna with Their Children. Sir Joshua Reynolds (1723-92), Death of Cardinal Beaufort in 1447; based on Shakespeare's "Henry VI, Pt. II". Plays: George Colman the Younger (1762-1836), Ways and Means. Poetry: William Collins (1721-59), Ode on the Popular Superstitions of the Highlands of Scotland (posth.). William Cowper (1731-1800), The Negro's Complaint; "Still in thought as free as ever,/ What are England's rights, I ask,/ Me from my delights to sever,/ Me to torture, me to task?/ Fleecy locks and black complexion/ Cannot forfeit nature's claim;/ Skins may differ, but affection/ Dwells in white and black the same." Hannah More (1745-1833), Slavery; a Bluestocking who is friends with William Wilberforce and Zachary Macaulay lets slavers have it; "If heaven has into being deign'd to call/ Thy light, O LIBERTY! to shine on all;/ Bright intellectual Sun! why does thy ray/ To earth distribute only partial day?"; "While the chill North with thy bright ray is blest,/ Why should fell darkness half the South invest?/ Was it decreed, fair Freedom! at thy birth,/ That thou shou'd'st ne'er irradiate all the earth?/ While Britain basks in thy full blaze of light,/ Why lies sad Africa quench'd in total night?" Novels: Thomas Day (1748-89), History of Little Jack, a Foundling; another children's book. August von Kotzebue (1761-1819), Geschichte Meines Vaters. Bernardin de Saint-Pierre (1737-1814), Jacques-Henri Bernardin de Saint-Pierre (1737-1814), Paul and Virginia (Paul et Virginie); about young friends-since-birth lovers on Mauritius who live harmoniously with Nature on the eve of the French Rev., becoming a popular children's novel; "She had read Paul et Virginie, and she had fantasized about the little bamboo cottage, the Negro Domingo, the dog Fidčle, but even more the sweet friendship of some good little brother who would go and gather ripe fruits for you from great trees taller than spires, or who would run barefoot in the sand, bringing you a bird's nest." Births: French utopian Socialist writer (founder of the Icarian Movement) Etienne (Étienne) Cabet (d. 1856) on Jan. 1 in Dijon. U.S. war secy. #17 (1841-3) and treasury secy. #16 (1843-4) John Canfield Spencer (d. 1855) on Jan. 8 in Hudson, N.Y.; son of Ambrose Spencer (1765-1848); educated at Union College. British hydrographer-astronomer-numismatist Adm. William Henry Smyth (d. 1865) on Jan. 21 in Westminter, London. English "Don Juan", "She Walks in Beauty" high-living free-loving water-loving flamboyant Romantic poet (first modern celeb, launching Byromania) George Gordon Byron (Noel), 6th Baron Byron (OE "cow barn") (d. 1824) on Jan. 22 in London; son of army Capt. "Mad Jack" Byron (a notorious libertine) and Catherine Gordon (half-mad); grandson of adm. "Foulweather Jack"; grandnewphew of William, Lord Byron (1788-1824), from whom he inherits title and estates; educated at Harrow College (1801-5) and Trinity College, Cambridge U. (1805-18); husband (1815-16) of Anne Isabelle Noel Byron (nee Milbanke) (1792-1860); father of Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace (1815-52); born with a malformed (club) foot, which doesn't keep him out of sports, and ends up as his trademark, getting copied by would-be poets; spends his young (pre-30) adulthood in an alcoholic fog; wears curlers in bed. British Conservative PM (1834-5, 1841-6) Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet (d. 1850) on Feb. 5 in Chamber Hall, Bury, Lancashire; son of Sir Robert Peel, 1st baronet (1750-1830); father of the English Bobbies. German Odic Force naturalist-industrialist Baron Karl (Carl) Ludwig von Reichenbach (d. 1869) on Feb. 12 in Stuttgart; educated at the U. of Tubingen; discoverer of paraffin, phenol, eupione, pittacal, etc., all from tar; coins the term "od" for the force in Nature that manifests itself in hypnotism, magnetism, and light. erman "The World as Will and Representation" pessimistic The-Universe-Isn't-Rational philosopher (atheist) Arthur Schopenhauer (d. 1860) on Feb. 22 in Danzig (Gdansk); educated at the U. of Gottingen - he didn't need to see the U.S. Civil War or the World Wars to know he was right? South Am. rev. liberator Jose Francisco San Martin y Matorras (d. 1850) on Feb. 25 in Yapeyu, Corrientes. French physicist Antoine Cesar (César) Becquerel (d. 1878) on Mar. 7 in Chatillon sur Le Crea (Chatillon-Coligny); father of physicist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel (1820-91); grandfather of physicist Antoine Henri Becquerel (1852-1908). German "Life of a Good-for-Nothing" poet-novelist Baron Joseph Karl Benedikt von Eichendorff (d. 1857) on Mar. 10 near Ratibor, Upper Silesia. French chemist Pierre Joseph Pelletier (d. 1842) on Mar. 22; discoverer of caffeine, quinine, and strychine - the ultimate cocktail? Spanish pretender Don Carlos Maria Isidro de Borbon (Borbón), Conde de Molina (d. 1855) on Mar. 29 in Madrid; son of Charles IV of Spain (1748-1819); brother of Ferdinand VII (1784-1833). Thai Chakri king #3 (1824-51) Rama III (Nangklao) (Jessadabodindra) (d. 1824) on Mar. 31 in Bangkok; son of Rama II (1767-1824) and Chao Chom Riem; brother of Rama IV (1804-68); known for keeping his money in big red bags beside his bed. German Nazarene painter Franz Pforr (d. 1812) on Apr. 5 in Frankfurt am Main. French-German painter Baron Charles (Carl) Auguste Guillaume de Steuben (d. 1856) on Apr. 18 in Bauerbach, Thuringia; teacher of Gustave Courbet. French mathematician-physicist Augustin Jean Fresnel (d. 1827) on May 10; inventor of Fresnel mirrors. Am. Gadsden Purchase diplomat-soldier James Gadsden (d. 1858) on May 15 in Charleston, S.C.; grandson of Am. Founding Father Christopher Gadsden (1724-1805). Scottish explorer Bain Hugh Clapperton (d. 1827) on May 18 in Annan, Dumfriesshire. Am. Quaker abolitionist James Mott (d. 1868) on June 20 in North Hempstead, Long Island, N.Y.; husband of Lucretia Mott (1793-1880). French projective geometry mathematician Jean-Victor Poncelet (d. 1867) on July 1 in Metz; educated at Ecole Polytechnique. Swiss Nazarene painter Georg Ludwig Vogel (d. 1879) on July 10 in Zurich. English ornithologist Prideaux John Selby (d. 1867) on July 23 in Alnwick, Northumberland; educated at Univ. College, Oxford U. English historian (Jewish) Sir Francis Palgrave (Francis Ephraim Cohen) (d. 1861) in July in London; son of Jewish stockbroker Meyer Cohen; in 1823 marries Elizabeth Turner, daughter of banker Dawson Turner (1775-1858) and converts to Anglicanism, adopting his wife's mother's maiden name; father of Francis Turner Palgrave (1824-97), William Gifford Palgrave (1826-88), Sir Inglis Palgrave (1827-1919), and Sir Reginald Palgrave (1828-1904); knighted in 1832. Italian cardinal Luigi Ciacchi (d. 1865) on Aug. 16 in Pesaro. Am. clergyman (Disciples of Christ co-founder) Alexander Campbell (d. 1866) (AKA Clarinda) on Sept. 12 in Ballymena, County Antrim, Ireland; son of Thomas Campbell (1763-1854); educated at the U. of Glasgow; founder of Bethany College (1840); emigrates to the U.S. in Aug. 1809. U.S. First Lady (1849-50) Margaret Mackall Smith "Peggy" Taylor (d. 1852) on Sept. 21 in Calvert County, Md.; wife (1810-) of Pres. Zachary Taylor. English "Peregrine Bunce" novelist-humorist Theodore Edward Hook (d. 1841) on Sept. 22 in London; son of James Hook (1746-1827); educated at Harrow School and Oxford U. British gen. (Crimean War CIC) Fitzroy James Henry Somerset, 1st Baron Raglan (d. 1855) on Sept. 30 in Badminton; educated at Westminster School; created baron in 1852; known for his no-seams-at-the-shoulder raglan coat. Scottish theologian Thomas Erskine (d. 1870) on Oct. 13 in Linlathen; educated at the U. of Edinburgh. Scottish "The Constitution of Man" phrenology leader George Combe (d. 1858) on Oct. 21 in Edinburgh; educated at the U. of Edinburgh. Am. "Mary Had a Little Lamb" writer Sarah Josepha Hale (d. 1879) on Oct. 24 in Newport, N.H.; ed. of "Godey's Lady's Book" (1837-77). Venezuelan gen. Rafael Jose Urdaneta y Faria (d. 1845) on Oct. 24 in Maracaibo; husband (1822-) of Dolores Vargas Paris (1800-78). Russian Adm. Mikhail Petrovich Lazarev (d. 1851) on Nov. 3 in Vladivostok. El Salvadorian pres. (1829-30, 1830-2) Jose Maria Cornejo Merino y Guevara (d. 1864) on Nov. 10 in San Vicente. Am. patent leather inventor Seth Boyden (d. 1870) on Nov. 17 in Foxboro, Mass.; moves to Newark, N.J. in 1815; "One of America's greatest inventors" (Thomas Edison); too bad, he doesn't believe in patents, and dies broke? English "Ingoldsby Legends" humorist novelist-poet clergyman Richard Harris Barham (AKA Thomas Ingoldsby) (d. 1845) on Dec. 6 in Canterbury; canon at St. Paul's Cathedral; educated at Brasenose College, Oxford U. Am. Pres. Lincoln's stepmother Sarah Bush lincoln (d. 1869) on Dec. 13 in Elizabethtown, Ky.; 2nd wife (1819-) of Thomas Lincoln. English sanitary reformer-physician Thomas Southwood Smith (d. 1861) on Dec. 21 in Martock, Somersetshire; grandfather of Octavia Hill (1838-1912). Spanish Basque Carlist Gen. Tomas de Zumalacarregui e Imaz (Tomás de Zumalacárregui e Imaz) (Tomas Zumalakarregi Imatz) (d. 1835) on Dec. 29 in Ormaiztegi, Gipuzkoa. Am. Lemhi Shoshone interpreter-guide Sacagawea (Sacajawea) (Sakakawea) (Hidatsa "tsagaaga" + "mia"= bird + woman) (d. 1812) in the Lemhi River Valley near modern-day Salmon, Idaho; sister of Shoshone Chief Cameahwait. French pirate Louis-Michel Aury (d. 1821) in Paris. English landscape painter William Collins (d. 1847); father of Wilkie Collins (1824-89); student of George Morland. Am. white supremacist writer Josiah Priest (d. 1861) in Unadilla, N.Y. Scottish brewer (maltster) Patrick Stead (d. 1868) in Leith Walk, Edinburgh; educated at Perth Academy. English inventor ("Father of Diving") Augustus Siebe (d. 1872) in Saxony, Germany; emigrates to the U.S. in 1815; inventor of the closed diving suit (1830). Am. abolitionist Lewis Tappan (d. 1873) in Northampton, Mass.; brother of Benjamin Tappan (1773-1857) and Arthur Tappan (1786-1865). Deaths: French marshal Louis Francois Armand de Vignerot du Plessis, duc de Richelieu (b. 1696) on Aug. 8. French painter Maurice Quentin de Latour (b. 1704) on Feb. 17 in Saint-Quentin; had a nervous breakdown in 1773. French scientist George-Louis LeClerc, Comte de Buffon (b. 1707) on Apr. 16. English hymn writer Charles Wesley (b. 1707) on Mar. 29. German harpsichordist C.P.E. Bach (b. 1714). English surgeon Percivall Pott (b. 1714) on Dec. 22. Spanish Bourbon king #3 (1759-88) Charles III (b. 1716) on Dec. 14 in Madrid. French chemist Francois de Lassone (b. 1717) on Dec. 10. Irish actor-lexicographer Thomas Sheridan (b. 1719). English "Young Pretender" Bonnie Prince Charlie (b. 1720) on Jan. 31 in Rome. English bigamist courtesan Elizabeth Chudleigh (b. 1720) on Aug. 26 in Paris. French adm. Francois de Grasse (b. 1722) on Jan. 14. German astronomer Johann Georg Palitzsch (b. 1723) on Feb. 21 in Prohlis. English "Blue Boy" painter Thomas Gainsborough (b. 1727) on Aug. 2 (cancer). German composer-organist Johann Gottfried Muthel (b. 1728) on July 14 in Bienenhof. British colonial gov. William Tryon (b. 1729). Swiss painter-poet Salomon Gessner (b. 1730) on Mar. 2 in Zurich. Scottish poet William Julius Mickle (b. 1734) on Oct. 28 in Forest Hill. English adm. Samuel Greig (b. 1735) on Oct. 26. Spanish (Mexican) explorer Juan Bautista de Anza (b. 1736) on Dec. 19 in Sonora. French explorer Jean Francois de la Perouse (b. 1741) in the Solomons. Am. statesman (DOI signer) John Penn (b. 1741) on Sept. 14. Am. surveyor John Filson (b. 1747) on Oct. 1 near the Great Miami River in Ohio (captured by the Shawnees).





















































1789 Paris experiences a critical food shortage this year and next, which is blamed on people having too many dogs; for years loose dogs feed on blood from the guillotines, and corpses, going vicious and sometimes requiring military intervention. On Jan. 10 the First U.S. Pres. Election (begun Dec. 15) is held for electors who will choose you know who it's a done deal. On Jan. 9 the U.S. negotiates a treaty with the Six Nations, and another with the Wyandot. Whether or not you go for the theory that the Illuminati founded the U.S., the Jesuits and Roman Catholics don't take long to move into Washington, D.C. in force? On Jan. 23 after the Vatican approaches U.S. pres. George Washington about naming a new bishop in the U.S., which Washington consents to, although the distrust of the U.S. govt. is so great that it doesn't establish full diplomatic relations with the Vatican for almost two cents. (1984), Georgetown U. (originally Georgetown College) is founded in the Georgetown neighborhood of modern-day Washington, D.C. by John Carroll (1735-1815), who becomes Roman Catholic bishop of Baltimore, Md. on Nov. 6 (until Dec. 3, 1815), becoming the oldest Roman Catholic and Jesuit-affiliated univ. in the U.S.; after the U.S. Civil War they adopt blue and gray as school colors; by 1920 their athletic teams are nicknamed the Hoyas (Gr. "hoya" = what, such); Carroll, a Jesuit who returned to the U.S. in 1774 after their suppression in Europe, who was appointed in 1784 by Pope Pius VI as prefect apostolic of the U.S. at the recommendation of Benjamin Franklin becomes the first Roman Catholic bishop in the U.S., followed by archbishop in 1808; all the church groups in the U.S. are getting federal fever and seeking to nationalize their orgs. now.?; Georgetown U. incl. U.S. Pres. William Clinton, U.S. Supreme Court Justice Antonin Scalia, CIA dir. George Tenet, King Felipe of Spain, and 1K U.S. Foreign Service diplomats. In Jan. after George III reads Shakespeare's King Lear and suffers another bout of madness last Nov., the 1789 Regency Crisis sees PM William Pitt demand and receive a regency for Prince George from Parliament. In Jan. after the rock-u-like-a-hurricane Tay Son Rebellion sees a Chinese (Qing) army capture Thang Long (Hanoi), the Tay Son army, led by Gen. Nguyen Hue leaves Hue City and scores a V in a surprise attack during the Tet New Year Festival at the Battle of Dong Da Hill in SW Hanoi, uniting N and S Vietnam, after which Hue crowns himself emperor Quang Trung (1753-93) (until 1793), ending the Later Le Dynasty (founded 1428), and founding the romantic Tay Son Dynasty (ends 1802), making 6-tone Vietnamese the official language instead of 5-tone Chinese, distributing land to poor peasants, melting coins to make cannons, and other romantic stuff; too bad, resilient Nguyen leader Phuc Anh's French volunteers arrive in S Vietnam in July, establishing a beachhead and consolidating the area - I love being a Ninja Turtle? On Feb. 4 the 1789 U.S. Pres. Election by the electoral college elects Gen. George Washington (1732-99) as U.S. pres. #1 with 69 votes (unanimous) (69? get it?), but the sealed ballots are sent to New York City to be officially counted by Congress, and although the new U.S. govt. is supposed to go into effect on Mar. 4, a quorum does not assemble to hold the first session of the U.S. House of Representatives at Federal Hall in New York until Apr. 1, so the lawmakers adjourn; Washington is a Freemason, the first of 15 by the time of U.S. pres. #43 George W. Bush (a Freemason). On Feb. 17 Count Frederik Axel von Fersen the Elder (1719-91) and 20 other nobles are arrested, ending opposition to king Gustav III. On Feb. 26 chestnut foal thoroughbred horse Eclipse (1764-89), descended from the Darley Arabian, born on the estate of the Duke of Cumberland during a solar eclipse, who won 26 consecutive races (incl. 11 King's Plates at Newmarket), and went on to sire three English Derby winners dies; his heart weighs 14 lbs.; one of his hooves is set in gold and made into a drinking goblet, where it is placed in the Jockey Club of Newmarket. On Mar. 4 the U.S. Senate meets for the first time, with 8 of 22 members attending; on Apr. 1 the U.S. House of Reps. holds its first full meeting in New York City with 65 reps.; the first law passed is regarding oaths of office; at first the min. size for a Congressional district is 30K, and the number of House seats increases every decade until 1912, when it levels off at 435, with 210K avg. residents per district; by 2009 the avg. district has 650K, with the largest district being Nevada (960K) and the smallest Wyoming (493K). On Mar. 10 (maybe because of that haunting feeling of a new King George being crowned on the other side of the pond?) mad King George III apparently recovers, causing the biggest fireworks celebrations ever seen in London, and he magnanimously pardons many convicts convicted under the Bloody Laws (death for petty offenses), giving them transportation to Australia instead, esp. a number of women, helping complete the required 225 fertile convict women needed as cargo for the Lady Juliana, which departs from England on July 29, with a special surgeon and an expensive contract for good food paid for by the govt. in the hope that the women would populate Australia with pure white wabbits. In Washington Adam was jeopardized by a mad monster. Adam and Jack ran to the bureau, but in their hurry they broke a tile and poked a tailor. They filmed more buildings, pierced by a cannon which was linked by John's son to granite. The haze over garden and field sheltered Arthur, who cleaved his way in a hurry. He cleaved mockingly as he cried "A rose taffeta dress will hardlybe the right thing in a college, but whoever desires rose veils may truly wear them"? On Apr. 6 the electoral ballots are opened and counted, and George Washington, AKA "the Father of His Country", "the Sword of the Revolution", "the Surveyor", "the American Fabius", "the American Cincinnatus", "the Old Fox" (Lord Cornwallis' name for him), "the Sage of Mount Vernon", "the Farmer President", "His Excellency", "Town Destroyer" (Iroquois name for him) is elected as the first U.S. pres. (until Mar. 4, 1797), with John Adams receiving 34 electoral votes to become the first U.S. vice-pres. (N.Y. Gov. George Clinton receives 3 electoral votes, and 32 more votes are scattered among various Federalists and Antifederalists); the first of 12 U.S. presidents who own slaves (last is #18 Ulysses S. Grant); on Apr. 21 John Adams (1735-1826) is sworn in as the 1st U.S. vice-pres. (until Mar. 4, 1797); on Apr. 30 the 1st U.S. Pres. Inauguration under the new constitution is held in Federal (City) Hall in New York City (outdoors) (near the future site of the Twin Towers in Manhattan?), where Washington begins a tradition by kissing the Bible, and adds the words "So help me God" to the 35-word oath of office in the Constitution (first pres. precedent), then goes to the Anglican St. Paul's Chapel (near the later site of the World Trade Center, which is miraculously untouched after 9/11?), sits through a 2-hour service and takes communion, then gives Washington's First Inaugural Speech, beginning "Fellow citizens of the Senate and the House of Representatives", and mentioning "an indissoluble union" and "that Almighty Being who rules over the Universe, who presides in the Councils of Nations, and whose providential aids can supply every human defect", and on Oct. 3 declares Nov. 26 (Thur.) a Nat. Day of Prayer and Thanksgiving with a Thanksgiving Proclamation, starting out "Whereas it is the duty of all nations to acknowledge the providence of Almighty God, to obey His will, to be grateful for His benefits, and humbly to implore His protection and favor"; the inaugural buttons have a neat eagle and sunburst motif; Federal Hall at 26 Wall St., site of the 1735 Peter Zenger trial is the first capitol of the U.S. (until 1790), and is torn down in 1812 and replaced by the U.S. Customs House, then made into a U.S. nat. memorial in 1955; Washington's annual salary as pres. is $25K; he had offered to work for expenses, like during the war, but since he racked up a $400K bill for 1775-83, his salary becomes "the country's first economy wave" (Marvin Kitman); he refuses to shake hands, considering it demeaning to the presidency (wait till he sees Pres. Obama bow to kings?); on Apr. 23 Pres. Washington and first First Lady (she likes to be called "Lady Washington") Martha Washington (1731-1802) move into the first U.S. pres. mansion at 1 Cherry St. ("George Washington Slept Here") (cherry? get it?); next Mar. 22 Thomas Jefferson becomes the first U.S. secy. of state (until Dec. 31, 1793), John Adams becomes the first pres. of the Senate, and on Apr. 1 Frederick Muhlenberg (1750-1801) becomes the first speaker (dean) of the U.S. House of Reps. (until Mar. 4, 1797); new U.S. Sen. from Conn. (1789-96) Oliver Ellsworth (1745-1807) (coiner of the term "United States") becomes Washington's personal spokesman, and chmn. of a committee organizing the U.S. federal court system; Washington issues the first executive order; at first Adams thinks he will actively direct the Senate, leading debate like a schoolmaster, but when he proposes that the president should be addressed as "His Excellency" instead of "Mister President", the members begin to distrust him and limit him to silently watching the proceedings, forever setting a precedent that makes the vice-pres. job pretty much useless? - cheese it? On Apr. 7 sultan (since 1774) Abdul Hamid I (b. 1725) dies 4 mo. after the disaster at Ochakov, and is succeeded by his nephew (son of Mustafa III) Selim III (1761-1808) as Ottoman sultan #28 (until May 29, 1807), becoming known as a good music composer and performer and poet - did he tell his physician if his immune system wasn't normal from advanced HIV? On Apr. 28 (a.m.) near Tofoa Island 1.3K mi. W of Tahiti near Tonga, just as the Washingtons are settling into their new homey home home home, the famous Mutiny on the Bounty on the British ship HMS Bounty (launched in 1784) begins in the Friendly Islands (Tonga) in the South Pacific 3.1K mi. E of Australia after it had been sent in 1787 to transport Tahitian breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis) to the West Indies and was returning from Tahiti, and some coconuts are stolen from the ship's store, fed by beautiful bare-breasted friendly Polynesian poontang and led by 23-y.-o. everhard master's mate acting lt. Fletcher Christian (1764-93), who was so pussy-whipped by Maimiti he decided he'd rather live a married landlubber than die a horny captain?; cruel whip-cracker Capt. William Bligh (1754-1817) and 18 loyal members of his crew are set adrift, and land on the South Pacific island of Timor near Java on June 14 after traveling 3618 mi. in 45 days in the Bounty's longboat with scanty provisions, then set the British authorities on the mutineers to make them dance from the ends of ropes; after trying to settle on Tubuai and being chased off by natives, and returning to Tahiti so that Christian could marry Maimiti (daughter of a chief) and drop off 16 crewmen incl. four Bligh loyalists, a total of nine mutineers, six Tahitian men, and eleven Tahitian women settle on one of the four volcanic Pitcairn Islands, which grows to a whopping pop. of 49 by 2006) (annexed by Britain in 1838); mutineer Matthew Quintal sets the Bounty on fire; too bad, the mistreatment of the Tahitian men combined with the sexual imbalance later leads to insurrection and the deaths of most of the men; the last mutineer John Adams (1767-1829) alias Alexander Smith is discovered in 1808 by Capt. Mayhew Folger of the ship Topaz along with nine Tahitian women, who had all converted to Christianity, and Adams is later granted amnesty; the main settlement is named Adamstown; the more famous U.S. pres. John Adams lives in 1735-1826. France says Me Too? On May 5 Louis XVI calls the first meeting of the Estates-General since 1614, with the third estate (middle class) getting double representation: nobles 300, clergy 300, commons 600. On May 7 the First U.S. Inaugural Ball is held in New York City in honor of Pres. Washington and his wife Martha. On June 3 Scottish-born North West Co. fur trader Sir Alexander Mackenzie (1764-1820), using charts provided by trailblazer (Conn. Yankee) Peter Pond (1740-1807) sets off from Ft. Chipewyan near Lake Athabasca in Alberta, Canada with 13 companions in three canoes, arriving at the Arctic Ocean, and discovering the Mackenzie River system; after traveling with French-Canadian voyageurs up the Mackenzie River, exploring W Canada to the Arctic, he had hoped the northerly river would turn W and end up in the Pacific Ocean, so he goes back to the drawing boards and plans another trip. Just a little bit, just a little bit, sock it to me sock it to me? On June 17 after the king's financial adviser Jacques Necker (1732-1804) (wrong name for this country?) rigs the voting by rank to nullify the third estate's advantage, Abbe Emmanuel Joseph Sieyes (Sieyčs) (1748-1836), author of of the hit CD What Is the Third Estate? makes a motion, causing it to bolt and meet to form a new constitution, declaring itself the beat-me-heat-me-come-on-eat-me Nat. Assembly, and inviting the other estates to join, which causes king (since May 10, 1774) Louis XVI (1754-93) on June 20 to lock them out and suspend meetings for three days, which doesn't phase them, because they got cat scratch fever and meet in an indoor tennis court, swearing the Tennis Court Oath to stay in session until they create a new constitution; on June 23 the king continues to try to stop them, ordering each estate to meet separately, and Honore (Honoré) Gabriel Riqueti, Comte de Mirabeau (1749-91) (elected for both Marseille and Aix) steps forward and answers royal messenger Henri Evrard, Marquis de Dreux-Breze (Dreux-Brézé) (1762-1829) with the truly breezy immortal Mr. Saturday Night Special soundbyte: "If you have orders to remove us from this hall, you must also get authority to use force, for we shall yield to nothing but to bayonets"; a Great Fear descends, causing the aristocracy to fear a terror by "brigands", which don't actually exist, but their fear causes the peasants to organize armed bands; the 10-year 7-mo. 11-day French Rev. (ends 1799) begins as 24M French citizens kept down by 400K aristocrats upend the entire social structure, infecting the world with incurable dreams of equality that overtake the milder Am. Rev.; on June 27 after the three estates unite, Louis XVI orders the rumps of the first two estates to join them, and Comte de Mirabeau emerges as leader; although Louis XVI is waffling, his wife Marie Antoinette makes him take the hard line, talking him into sending troops from Versailles to surround Paris in an obvious plan to you know what; the aristocratic favorite drink tea becomes unpopular for the next 50 years. In June Mass. passes An Act to Encourage the Manufacture and Consumption of Strong Beer, Ale, and Other Malt Liquor, ordering brewhouses to make at least 100 barrels of beer per year, exempting them from taxes for five years; "The wholesome qualities of malt liquors greatly recommend them to general use", especially "preventing the pernicious effects of spirituous liquors"; George Washington announces his "Buy American" policy, announcing that he will only drink porter made in America- rinse out your mouth with the medication, spit it out? On July 2 dirty bastard Marquis de Sade (1740-1814), who is imprisoned in the Bastille yells to the crowds outside "They are killing the prisoners here!", causing a riot, after which on July 4 he is transferred to the Charenton insane asylum near Paris, missing out on the July 14 storming of the Bastille, although his estate in Lacoste is sacked by a mob later this year; he is finally released in 1790 after the assembly abolishes the instrument of lettre de cachet that had been used to imprison him sans charges, divorces his wife and hooks up with actress Marie-Constance Quesnet, with whom he spends the rest of his life, growing extremely obese and calling himself "Citizen Sade", getting elected to the Nat. Convention representing the far left despite his aristocratic background. Catastrophe theorists here's your butterfly flapping its wings and causing a hurricane? On July 12 reformer French minister Jacques Necker is suddenly fired by the king, and failed French lawyer Camille Desmoulins (1760-94) has his 15 min. of fame when he loses his usual stammer and jumps up on a table on a cafe outside the Palais Royal and utters the immortal soundbyte: "This dismissal is the tocsin of the St. Bartholomew of the patriots!", after which he draws two pistols and declares that if the pigs are going to take him they will have to take some bullets first, triggering riots in Paris, which on July 13 leads to a partisan militia, later becoming the Nat. Guard being formed; Desmoulins is now a celeb, and becomes a writer-journalist, going on to pub. Discours de la Lanterne aux Parisiens, which quotes John 3:20 ("He that does evil hates the light"), causing him to become known as the "Lanterne Prosecutor", going on to pub. the pro-violence Histoire des Revolutions de France et de Brabant (until July 1791), making him rich and famous; meanwhile on July 12 wax heads of Jacques Necker and the Duc d'Orleans made by Dr. Philippe Curtius (1741-94), mentor of Madame Tussaud are carried in a protest march. Prison break! Prison break! Those pipes are the way out? On July 14 (Tues.) (Bastille Day) after the prisoners cry to be released, the 14th cent. crenelated Bastille fortress prison in Paris falls after the soldiers refuse to fire on Parisian citizens and they storm it and release all seven prisoners inside (they leave a copy of Nostradamus' "Centuries" open to the Preface on a table for 10 days to allow people to file past and read how their rev. has been predicted?); aided by French Royal Guard deserters they capture and kill Bastille gov. (since 1776) Bernard-Rene (Bernard-René) Jourdan, Marquis de Launay (b. 1740), then shoot and murder Jacques de Flesselles (b. 1721) at the Hotel de Ville, who becomes the last provost of the merchants (mayor) of Paris (since 1785); the king is awakened in the middle of the night by his chamberlain to tell him the potty news, and now that he has lost the support of his army he knows he's kaput, and writes in his diary "Nothing", meaning he didn't go hunting?; on July 15 the electors of Paris abolish the French feudal system and set up a Commune after Louis backs down and orders his troops out of Paris; Marquis de Lafayette becomes cmdr. of the Nat. Guard (originally proposed by Comte de Mirabeau), and bookish painter-tragedian-scientist (expert on the history of Science) Jean-Sylvain Bailly (1736-93) is elected mayor of Paris (until Nov. 1791 1791); on July 17 amid a gen. panic about a "famine plot" by the aristocrats (10%) to starve or burn-out the rest of the pop., causing peasants and townfolk to unite and mobilize, the king recalls Necker; the French Tricolor Flag is adopted, white for France, blue and red for Paris; on July 20 peasants arise throughout France, beginning the Grande Peur (Fr. "great fear"), which ends on the night of Aug. 4 with the nobles and clergy surrendering their feudal rights and privileges, ending feudalism in France and kicking the manorial lords out of Dauphine, Provence, Burgundy, et al.; Burgundy, a province since 1678 is split up into the depts. of Ain, Cote d'Or, Saone-et-Loire and Yonne; the smarter French nobles begin skedaddling from France in the Emigration of the Nobles - it's time to get outside and grow something? On July 21 the Battle of Fokshani is a V for the Russians and Austrians under Russian gen. Alexander Suvorov, followed on Sept. 11 by the decisive Battle of the Rimnik River, where the 100K-man Turkish army is outmaneuvered by 18K Austrians under Prince Coburg and 7K Russians under Suvorov, with Turkish losses of 15K-20K, making Suvorov a big hero (one of the top three gens. of all time, along with Alexander the Great and Napoleon?), receiving the title of Count Rimnikski from Russia and count of the HRE by Austrian HRE Joseph II. On July 21 5K blacks who fought for Britain leave Savannah, Ga. for Jamaica or St. Augustine, Fla., but as property of Loyalists they never gain their freedom, causing 300 smart ones to refuse evacuation. On July 26 the naval Battle of Oland (Öland) sees 18 ships under Russian adm. Vasili Yakovlevich Chichagov (1726-1809) defeat (draw?) 30 ships under Swedish king Charles XIII (Prince Karl, Duke of Sodermanland) after his 2nd in command adm. Per Liljehorn fails to reach the fight in time, causing a Swedish retreat to Karlskrona, after which Liljehorn is convicted of misconduct and barely escapes execution. On July 27 Congress creates the U.S. Dept. of Foreign Affairs, which is changed to the Dept. of State on Sept. 15; Jefferson and Hamilton form the core of Pres. Washington's first cabinet; their constant disagreements form the basis of the U.S. 2-Party System. On July 31 the U.S. Customs Service is formed to hassle people at the borders. On Aug. 4 the reps. of the nobility in the French Nat. Assembly surrender their feudal rights, but fudge it by making it a gradual process with compensation for the owners (never paid); noble titles are abolished, the sale of offices prohibited, and guilds are dissolved. On Aug. 7 Congress creates the U.S. Dept. of War (until Sept. 18, 1947), with retired Gen. Henry Knox as secy. of war #1 (#3 in rank), and a number of subdivisions, each under a chief of staff, incl. the HQ of the Army, through which the orders of the U.S. pres. are issued. On Aug. 26 the Nat. Assembly in Versailles adopts the Declaration of the Rights of Man, written by the Marquis de Lafayette, based on his English and Am. studies, guaranteeing citizens the rights of liberty, equality, security, and property, and stating that the aim of society is public happiness, but limiting it all to males only. On Sept. 2 the death-and-taxes U.S. Treasury Dept. is established; on Sept. 11 after Robert Morris declines, Alexander Hamilton is named treasury secy. #1, going on to single-handedly work out the U.S. financial system and end up on the back of the U.S. $10 bill (until ?) - snack happy? On Sept. 15 the U.S. Dept. of Foreign Affairs is renamed the Dept. of State. On Sept. 24 the First U.S. Congress (1st session) passes the U.S. Judiciary Act of 1789 according to Article III Section 1 of the U.S. Constitution, creating a U.S. atty. gen. and a U.S. court system, consisting of the U.S. Supreme Court (SCOTUS) with six justices, district courts for each of 13 judicial districts (one for each state except two for Mass. and Va.) (N.C. and R.I. haven't ratified the Constitution yet), and three circuit courts; on Sept. 26 Edmund Jennings Randolph (1753-1813) becomes the first U.S. atty. gen. (until Jan. 26, 1794); on Sept. 26 New York City-born John Jay (1745-1829) becomes U.S. Supreme Court chief justice #1 (until June 29, 1795); on Sept. 26 John Rutledge (1739-1800) of S.C. (brother of DOI signer Edward Rutledge) becomes the 2nd (associate) justice (until Mar. 4, 1791); on Sept. 27 William Cushing (1732-1810) becomes #3 (until Sept. 13, 1810); on Sept. 29 Scottish-born DOI signer James Wilson (1742-98) of N.C. (most erudite of the Founding Fathers) becomes #4 (until Aug. 21, 1798); on Sept. 30 John Blair Jr. (1732-1800) of Va. (2nd most erudite?) becomes #5 (until Oct. 25, 1795); Robert Hanson Harrison (1745-90) of Md. (George Washington's 2nd private secy. in 1775 after Joseph Reed) is selected as #6 to fill out the first U.S. Supreme Court, but declines for health reasons; the All Writs Act, attached to the Judiciary Act gives U.S. courts the power to "issue all writs necessary or appropriate in aid of their respective jurisdictions and agreeable to the usages and principles of law". On Sept. 25 a force of Russian and Zaporozhian Cossack troops under Gen. Count Ivan Vasilyevich Gudovich (1741-1820) capture the Turkish citadel of Khadjibey in Ukraine, which is renamed Odessa (modern-day pop. 1M); the Jews begin to settle there. On Sept. 25 Congress proposes 12 amendments to the U.S. Constitution, incl. the 10-article Bill of Rights, which is sent by Pres. Washington to the states for approval in Oct.; aborted amendment #1 would have required one U.S. rep. for every 30K pop.; Pres. Washington becomes the first U.S. pres. to name a majority of justices to the U.S. Supreme Court, followed by Abraham Lincoln, Andrew Jackson, William Taft, Franklin Delano Roosevelt, and Dwight David Eisenhower. On Oct. 3 Pres. George Washington issues a Thanksgiving Day Proclamation, setting Nov. 26 as the day for it; "It is the duty of all nations to acknowledge the providence of Almighty God, to obey His will, to be grateful for His benefits, and humbly to implore His protection and favor." On Oct. 5 a mob of angry women from Paris stages a Women's March to Versailles 10 mi. away, and demonstrates in front of the gates demanding bread and the queen's head (thigh, entrails, etc.), then kills two bodyguards, enters the queen's bedchamber and trashes it, thrusting pikes through her bed, while the queen escapes to the king's bedchamber through a secret passage; after being rescued by Lafayette and the Nat. Guard, the royal family is forced to leave and is put under house arrest in the Tuileries, complete with servants - and plenty of cake? On Oct. 10 Nat. Assembly deputy Dr. Joseph Ignace Guillotin (1738-1814) proposes a new, more humane method of execution to the new Legislative Assembly, using an oblique-edged vertical iron blade, two upright grooved posts, and a rope, which promises a swift and easy death, and the debate begins - based on his work with pesky pigeons? All hail cold turkey, gum, and the patch, so why not test it on the king? On Oct. 17 Juan Vicente de Guemes (Güemes), 2nd Count of Revillagigedo (1738-99) becomes viceroy of New Spain (until July 11, 1794), becoming known as a great reformer, the last able viceroy of New Spain. On Nov. 21 after being satisfied with the Bill of Rights, "Tar Heel State" North Carolina (N.C.) is admitted as the 12th U.S. (slave) state after a ratification vote of 194-77. On Dec. 11 the U. of N.C. at Chapel Hill is chartered, becoming the first state univ. in the U.S.; also Penn. State U. is founded from Philadelphia Academy (founded 1749). On Dec. 13 the French Nat. Guard is created, and Lafayette joins it. Liberté, Egalité, Fraternité is fine, but who's gonna pay for it all? On Dec. 19 the Nat. Assembly passes a decree creating an issue of 400M paper assignats, using wealth confiscated from the Catholic clergy as security; the Jews are granted full rights for the first time in any European nation; the salt tax is repealed; its members are forbidden from accepting any office under Louis XVI. On Dec. 22 the Nat. Assembly changes the ancient regional districts of France into departments. Gustavus III (1746-92) Sweden passes his Act of Union and Security without the consent of his nobles, fomenting a mutiny. Austria takes Belgrade; the Austrian Netherlands declares independence as Belgium. The 1789 Georgia Constitution is ratified. The Austrian Netherlands declare independence and become Belgium. The Third Anglo-Mysore War in S India between the Kingdom of Mysure and the East India Co. allied with the Maratha Empire and the Nizam of Hyderabad begins (ends 1792). The Xhosa cross the Fish River in the Eastern Cape, coming into conflict with Afrikaner trekboers and starting a 20+-year war that pushes them E - we planned that vacation for months and wouldn't you know it, a migraine hit? King (since 1774) Kpengla dies, and his eldest son Agonglo (1766-97) becomes king #8 of Dahomey in W Africa (until 1797), becoming the first king of Dahomey to marry a white woman, a Dutch babe named Sophie. Pierre Samuel du Pont de Nemours elects him to the French Estates Gen. from the district of Nemours, and he works his way up to the constituent assembly and twice becomes pres. The Spanish attempt to colonize the Pacific coast region N of Calif., and build a fort in Nootka Sound. The U.S. govt. votes pensions to disabled veterans of the Am. Rev. War. The Ainu lose the Battle of Kunasiri-Menasi to the Japanese, falling completely under their control. Repub. lawyer James Kent attends the first session of the U.S. House of Reps. in New York City, and calls it "the consummation of our wishes... which might in some future age, much more truly than the Roman Senate, be regarded as the refuge of nations", then goes on to see his Repubs. defect to the Federalists on various votes, calling Edward Livingston "an unprincipled and malicious incendiary" - glad he didn't say refuse of nations? Italian grifter Count Alessandro di Cagliostro (1743-95) (real name Giuseppe Balsamo) returns to Italy after years of traveling through Europe with his beautiful wife peddling his "elixir of immortal youth" to the nobility and others, always a step ahead of the cops, and begins peddling his own form of Egyptian Freemasonry, ending up condemned to death as a heretic by the Roman Inquisition; luckily his sentence is commuted to life in prison. After the pesky Iroquois are herded into the Buffalo Creek Rez to the W, the city of Buffalo, N.Y. (named after a Seneca Indian who lived there) (modern-day pop. 260K/1.2M) near Buffalo Creek on the E shore of Lake Erie at the head of the Niagara River 17 mi. SSE of Niagara Falls is settled by Dutch trader Cornelius Winney from Albany and ex-slave Joseph "Black Joe" Hodges, followed by Iroquois interpreter Capt. William Johnston; it is officially founded in 1801; in 1802 the first road from the Conn. Western Reserve in Ohio to Penn. is built through it; in 1804 a spoke-diagonal street plan mimicking Washington, D.C. is designed by D.C. surveyor Joseph Ellicott (1760-1826) (brother of Mason-Dixon Line surveyor Andrew Ellicott) for the 400 pop.; it is incorporated as a city in 1832 after the completion of the Erie Canal in 1825 causes pop. to zoom, attracting Roman Catholic Irish and German immigrants along with fugitive black slaves; Buffalo goes on to become known as "the City of Light" for its early embrace of electric power, and the 2nd largest city in N.Y. The city of Hammerfest, Norway (Norse "hamran" = steep mountainside), the northernmost town in Europe (modern-day pop. 10.5K) is founded; it is incorporated on Jan. 1, 1838. The first Gen. Assembly of the Presbyterian Church in the U.S. is held in Philadelphia. The First Gen. Convention of the Protestant Episcopal Church in the U.S. is held under Bishop Samuel Seabury of Conn., uniting in a federal union and issuing the U.S. Book of Common Prayer. The U. of N.C. in Chapel Hill, N.C. is chartered, becoming the first state univ. in the U.S. Penn. State U. is founded from Philadelphia Academy (founded 1749). Ater breeders begin shipping cattle from France there first to avoid import duties, damaging their rep, Jersey Island bans imports of foreign cattle, allowing only Jersey cows (known for their high butterfat milk and low maintenance costs) (until 2008). Benjamin Franklin writes the immortal soundbyte in a letter to Jean-Baptiste Leroy: "Our new Constitution is now established, and has an appearance that promises permanency; but in this world nothing can be said to be certain, except death and taxes." Mr. Wootton installs the weathercock on the tower of St. Peter's Church in Nottingham, England. After the French Rev. makes it un-PC for the rich to maintain cooking-catering staffs, Maison Chevet is founded by Marie Antoinette's former rose gardener Hilaire-Germain Chevet to supply food and chefs for major functions in Paris and throughout Europe, dominating the French catering business; "Chevet was not simply the supplier [of food] to French high society, but also to the high priests of European finance. An array of cooks, respected, respectful, and well-disciplined, would execute magnificent work" (Joseph Favre); in 1820 they sell-out to Potel & Chabot, who expand, setting up a chain of tea salons and boutiques, which they sell after WWII, continuing in the catering business, doing 1K parties a year, incl. Aga Khan and the Shah of Iran. Under hypnotism by Morey Bernstein, Mrs. Ruth Simmons of 19th cent. Colo. claims that she had lived her previous life as Bridey Murphy in this year. Mail coaches are introduced in Britain and Ireland. The Hope Diamond disappears for 25 years (until 1813). The terms "lapel", "aristocrat" and "working class" first appear in print this year - the working class don't have lapels like aristocrats do? The 16th cent. French court dance called the gavotte becomes poison. The Tammany Inst. (Hall) in New York City is founded; its logo is a tiger; the leading officials are called sachems, like Algonquian Indian chiefs. Chrysanthemums are introduced to Britain from the Far East. Journal des Debats is founded in Paris. Jacques Pierre Brissot returns to France, takes part in the July 14 Bastille attack, and becomes ed. of the repub. journal Patriote Francais (until 1793). Science: Sports: Famous English racehorse Eclipse dies unbeaten - uneclipsed? Inventions: The first steam-powered textile (cotton) factories are opened in Manchester. Oliver Evans of the U.S. patents a steam-carriage design, but financial difficulties cause him to take over a decade to built one. William Jessup of England designs the flanged wheel for wagons that ride on tracks. Science: William Herschel builds the world's largest telescope for the next 50 years, with a 48-in. aperture; on Aug. 28 he discovers Saturn's 6th moon Enceladus (the 100-armed giant?), and on Sept. 17 its 7th moon Mimas (named after a son of Gaia), marked by the giant Herschel Crater. German chemist Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1743-1817) makes the first chemical analysis of Pitchblende, and discovers Uranium (U) (#92), which initially is used in ceramics and textiles; he also discovers the metallic element Zirconium (Zr) (#40) in the sands of the rivers of Sri Lanka (Srilankium?); uranium is later used to make fuel elements for atomic reactors, zirconium in containers for fuel elements since it doesn't absorb neutrons. After moving from Berlin to Paris last year, Italian mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange (Giuseppe Luigi Lagrangia or Lagrancia) (1736-1813) introduces Lagrangian Mechanics, which uses the Calculus of Variations. After Carl Wilhelm Scheele proves in 1778 that molybdenite (molybdenum sulfide), graphite (black lead or plumbago), and galena (lead II sulfide) are three different minerals, German Prussian geologist Abraham Gottlob Werner (1749-1817) names black lead Graphite, from the Greek "graphein" = "to draw or write". Nonfiction: Jean Joseph Marie Amiot (1718-93), French-Chinese Dictionary; introduces the Manchu and Tartar languages to Europe. Jeremy Bentham (1748-1832), Introduction to the Principles of Morals and Legislation; how an action is moral to the degree that it is useful, meaning its capacity for giving pleasure or preventing pain, ergo the purpose of all conduct and legislation should be "the greatest happiness of the greatest number" (borrowed from Joseph Priestley and Francis Hutcheson), founding the theory of Utilitarianism - now that America is lost, it's time for Brits to begin moralizing? Charles Burney (1726-1814), History of Music (1773-89). General Catalog of the Qing Library (92 vols.); lists 10K+ works. Olaudah Equiano (1745-97), The Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano, or Gustavus Vassa, the African (autobio); his maltreatment as a slave in 1756-68 before he buys his freedom, whipping up anti-slavery sentiment in England. Edward Gibbon (1737-94), Memoirs of My Life and Writings. Antoine-Laurent de Jussieu, Genera Plantarum Secundum Ordines Naturales Disposita juxta Methodum in Horto Regio Parisiensi Exaratam; modern classification of plants. Bernard Germain de Lacepede (1756-1825), Histoire Naturelle des Reptiles. Antoine Lavoisier (1743-94), Traite Elementaire de Chimie; the first modern chemical textbook; defines an element as a single substance that can't be broken down by chemical analysis and from which all chemical compounds are formed; announces that fermentation produces carbon dioxide (carbonic gas) and spirit of wine, saying that it is "more appropriately called by the Arabic word alcohol since it is formed from cider or fermented sugar as well as wine", and pub. the first chemical equation "grape must = carbonic acid + alcohol", calling it "one of the most extraordinary in chemistry", adding: "In these experiments, we have to assume that there is a true balance or equation between the elements of the compounds with which we start and those obtained at the end of the reaction." Daniel Mendoza (1764-1836), The Art of Boxing; an English Jew founds scientific boxing. Antoine-Augustin Parmentier (1737-1813), Treatise on the Culture and Use of the Potato, Sweet Potato, and Jerusalem Artichoke (Traité sur la culture et les usages des Pommes de terre, de la Patate, et du Topinambour); "printed by order of the king". David Ramsay (1749-1815), History of the American Revolution (2 vols.). Antonio Scarpa (1752-1832), Anatomicae Disquisitiones de Auditu et Olfacu (Anatomy of the Hearing and Olfactory Systems). E.J. Sieyes, Qu'est-ce que le Tiers Etat? Music: Jean Dauberval (pupil of Jean Noverre), La Fille Mal Gardee (The Ill-Guarded Girl) (comic ballet). Andre Gretry (1741-1813), Raoul Barbe-Bleue (opera) (Paris). Vicente Martin y Soler (1754-1806), The Unfortunate Hero Kosmetovich (opera) (St. Petersburg); libretto party written by Catherine the Great. Giovanni Paisiello (1740-1816), Nina (opera) (Naples); I Zingari in Fiera (opera) (Naples). Art: Jean-Jacques-Francois Le Barbier, Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen; depicts the red Phyrigian cap, and the Eye of Providence. Robert Barker of Bath, England paints and names the first Panorama (of Edinburgh, Scotland), coining the term. Francois Gerard (1770-1837), Joseph and His Brothers. Jean-Antoine Houdon (1741-1828), Thomas Jefferson (sculpture). Thomas Lawrence (1769-1830), Portrait of Miss Farren; makes him an instant star, the fashionable portraitist of England. Plays: Marie-Joseph Blaise de Chenier (1764-1811), Charles IX, ou L'Ecole des Rois (Nov. 4) (Paris); stars Francois Joseph Talma; produced after being held back by censors for two years, becoming a big hit, with the audience coming away "drunk with the vengeance and torment of an evening of blood" (Marquise de Ferrire), after which Camille Desmoulins says that it does more for the French Rev. than the Days of Oct. William Dunlap (1766-1839), The Father, or American Shandyism (Sept. 7) (John St. Theatre, London); his first successful play, followed by 60 more, making him the Father of Am. Drama? Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749-1832), Iphigenie auf Tauris (iambic verse). August von Kotzebue (1761-1819), Menschenhass und Reue. Poetry: William Blake (1757-1827), Tiriel (unpub.); The Book of Thel; Songs of Innocence and of Experience (Showing the Two Contrary States of the Human Soul); (1789, 1794); incl. The Little Black Boy, which disses slavery, equating blackness with sunburn, but observing "Look on the rising sun: there God does live"; The Tyger; "Tyger, Tyger, burning bright/ In the forests of the night,/ What Immortal hand & eye/ Dare frame thy fearful symmetry?" William Lisle Bowles (1762-1850), Fourteen Sonnets; influences Coleridge, Southey, and Wordsworth. Erasmus Darwin (1731-1802), Botanic Garden (1789-92); "When Love Divine, with brooding wings unfurl'd,/ Call'd from the rude abyss the living world". Kalidasa, Sakuntala (Sacontala), or the Fatal Ring (tr. Sir William Jones). Novels: Richard Cumberland (1732-1811), Arundel. Aagje Deken (1741-1804) and Betje Wolff (1738-1804), Wandelingen door Bourgogne (Walks in Burgundy). John Moore (1729-1802), Zeluco: Various Views of Human Nature, Taken from Life and Manners, Foreign and Domestic; an evil Italian nobleman; used by Lord Byron as the basis of Childe Harold. Ann Radcliffe (1764-1823), The Castles of Athlin and Dunbayne (first novel) - not in my house? Births: British historian and undersecy. of state for the colonies (1836-47) (abolitionist) Sir James Stephen (d. 1859) on Jan. 3 in Lambeth; 3rd son of James Stephen (1758-1832); brother of George Stephen (1794-1879); father of Sir James Fitzjames Stephen (1829-94) and Sir Leslie Stephen (1832-1904); educated at Trinity Hall, Cambridge U. Am. fur trading magnate (founder of Pierre, S.D.) Pierre (Cadet) Chouteau Jr. (Pierre Cadet Chouteau) (d. 1865) on Jan. 19 in St. Louis, Mo.; son of Jean Pierre Chouteau (1758-1849). Canadian statesman William Machin Stairs (d. 1865) on Jan. 21 in Halifax, N.S. Scottish utilitarian economist John Ramsay McCulloch (d. 1864) on Mar. 1 in Whithorn, Wigtownshire; successor to David Ricardo. French sculptor Pierre-Jean David d'Angers (Pierre Jean David) (d. 1856) on Mar. 12 in Angers. German Ohm's Law mathematician-physicist Georg Simon Ohm (d. 1854) on Mar. 16 in Erlangen, Brandenburg-Bayreuth. Am. historian (pres. of Harvard U., 1849-53) Jared Sparks (d. 1866) on May 10 in Willington, Conn.; educated at Phillips Exeter Academy, and Harvard U. Am. real-life "Uncle Tom" escaped slave (black) Rev. Josiah Henson (d. 1883) on June 15 near Port Tobacco, Charles County, Md.; escapes with his wife and four children on Oct. 28, 1830 to Dresden, Ontario, Canada, and establishes the British-American Inst., the first vocational school for fugitive slaves; his story is used by Harriet Beecher Stowe in "Uncle Tom's Cabin". German "Die Lorelei", "Alle Jahre Wieder", "Ich Hatt Einen Kameraden" song composer Phillipp Friedrich Silcher (d. 1860) on June 27 in Schnait (Weinstadt). German Nazarene painter Johann Friedrich Overbeck (d. 1869) on July 3 in Lubeck; son of Christian Adolph Overbeck (1755-1821). British soldier-historian James Grant Duff (Cuninghame) (d. 1858) on July 8 in Banff, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; grows up in Aberdeen; educated at Marischal College. Ottoman sultan #30 (1808-39) Mahmud II (d. 1839) on July 20 in Topkapi Palace, Constantinople; posth. son of Abdulhamid I (1725-89). German political economist (inventor of the National System of Innovation) Georg Friedrich List (d. 1846) on Aug. 6 in Reutlingen, Wurttemberg. Am. politician (leading member of Andrew Jackson's Kitchen Cabinet) Amos Kendall (d. 1859) on Aug. 16 in Dunstable, Mass.; educated at Dartmouth U.; co-founder of Gallaudet U. French mathematician Baron Augustin-Louis Cauchy (d. 1857) on Aug. 21 in Paris. Persian Qajar prince Abbas Mirza (d. 1833) on Aug. 26; younger son of Fath Ali Shah (1771-1834); father of Mohammad Shah Qajar (1810-48). German Nazarene painter Friedrich Wilhelm Schadow (d. 1862) on Sept. 7 in Berlin; 2nd son of Johann Gottfried Schadow (1764-1850). Am. astronomer (dir. 31 of Harvard College Observatory) William Cranch Bond (d. 1859) on Sept. 9 in Falmouth (Portland), Maine; father of astronomer George Phillips Bond (1825-65), who discovers 11 comets; inventor of the electrochronograph; discoverer of the Great Comet of 1811; co-discoverer (with his son) of satellites of Neptune and Saturn. Am. writer ("America's first major novelist") James Fenimore Cooper (d. 1851) on Sept. 15 in Burlington, N.J.; 12th of 13 children. English painter-caricaturist Isaac Robert Cruikshank (d. 1865) on Sept. 27 in London; son of caricaturist Isaac Cruikshank (1756-1811); brother of caricaturist George Cruikshank (1792-1878) - is there something to the theory of names as destinies? French ecclesiastical historian Rene Francois Rohrbacher (d. 1856) on Sept. 27 in Langatte, Metz. English Bright's Disease physician ("the Father of Nephrology") Richard Bright (d. 1858) on Sept. 28 in Bristol, Gloucestershire; educated at the U. of Edinburgh. Am. Texas rev. leader Lorenzo de Zavala (d. 1836) on Oct. 3. German sunspot astronomer Samuel Heinrich Schwabe (d. 1875) on Oct. 25 in Dessau. Am. Protestant missionary (to Hawaii) Hiram Bingham (I) (d. 1869) on Oct. 30 in Bennington, Vt.; educated at Middlebury College, and Andover Theological Seminary; father of Hiram Bingham II (1831-1908); grandfather of Hiram Bingham III (1875-1956); great-grandfather of Hiram Bingham IV (1903-88) and Jonathan Brewster Bingham (1914-86). Dutch scholar and lit. critic Jacob Geel (d. 1862) on Nov. 12 in Amsterdam. Am. missionary (to Ceylon) Rev. Miron Winslow (d. 1864) on Dec. 11 in Williston, Vt.; educated at Middlebury College, and Andover Theological Seminary. English abolitionist and industrial reformer ("the Factory King") Richard Oastler (d. 1861) on Dec. 20 in Leeds, West Yorkshire. U.S. Sen. (DR-Mich.) (1837-41) John Norvell (d. 1850) on Dec. 21 in Danville, Ky. (Va.); descendant of Capt. Hugh Norvell (1666-1719); father of Mary Novell, wife of James Walker, father of William Walker (1824-60). U.S. Supreme Court justice #29 (1845-51) Levi Woodbury (d. 1851) on Dec. 22 in Francestown, N.H.; educated at Dartmouth U.; first SCOTUS justice to attend law school; father-in-law of Montgomery Blair (1813-83); great-great-grandfather of Montgomery Clift (1920-66). U.S. Whig-Repub. treasury secy. #14 (1841) and interior secy. #1 (1849-50) Thomas Ewing Sr. (d. 1871) on Dec. 28 in West Liberty, W. Va.; father of Ellen Ewing Sherman (1824-88) (wife of William Tecumseh Sherman), Hugh Boyle Ewing (1826-1905), Thomas Ewing Jr. (1829-96), and Charles Ewing (1835-93). South African 4'10" world's largest ass woman ("the Hottentot Venus")(black) Sara(h) "Saartje" Baartman (d. 1815) in Hankey, Eastern Cape; of Khoikhoi descent. Egyptian gen. (Sunni Muslim) Ibrahim Pasha (d. 1848) in Kavala, Greece; adopted son of Mehmet Ali; father of Khedive Ishmael (1830-95). Am. railroad builder Gridley Bryant (d. 1867); father of Gridley James Fox Bryant (1816-99). Deaths: Swiss artist Jean-Etienne Liotard (b. 1702) on June 12 in Geneva. English fiction author John Cleland (b. 1709) on Jan. 23. Czech composer Frantisek Xaver Richter (b. 1709) on Sept. 12 in Strasbourg, France; leaves 28 masses, 69 symphonies et al. French painter Claude-Joseph Vernet (b. 1714) on Dec. 4. French economist Victor de Riqueti, marquis de Mirabeau (b. 1715) on July 13 in Argenteuil. Dutch anatomist Petrus Camper (b. 1722) on Apr. 7 in The Hague. German painter Johann Heinrich Tischbein the Elder (b. 1722) on Aug. 22 in Kassel. German-French philosopher Baron P.H.D. d'Holbach (b. 1723). Turkish sultan (1774-89) Abdul Hamid I (b. 1725) on Apr. 7 in Constantinople; buried in his own tomb called Bahcekapi. Dutch physicist Anton Brugmans (b. 1732). Irish-born British col. Barry St. Leger (b. 1733) in Quebec, Canada. Am. physician John Morgan (b. 1735) on Oct. 15. Am. diplomat Silas Deane (b. 1737) on Sept. 23 (poisoned?). Am. Rev. War hero Ethan Allen (b. 1738) on Feb. 12 in Burlington, Vt. Am. Rev. War Gen. Thomas Nelson Jr. (b. 1738) on Jan. 4 in Hanover County, Va. French Bastille gov. (1776-89) Bernard-Rene Jourdan de Launay (b. 1740) on July 14 in Paris (murdered by a mob). English pro-Am. Rev. writer Thomas Day (b. 1748) on Sept. 28 in Barehill, Berkshire; thrown from a horse while trying to break it using kindness.